How does the implantation process occur?
The embryo transfer procedure during IVF is painless, lasts on average 5 minutes, and does not require anesthesia. The endometrium of the uterus must be completely ready for embryo transfer for implantation to be successful. For this purpose, the woman is provided with hormonal support before and after embryo transfer.
The endometriotic layer of the uterus changes depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. Its receptivity and readiness for embryo attachment is called the “implantation window” and lasts only 2-3 days - approximately 5-7 days after ovulation. By this time, the endometrium should become thicker (at least 7 mm) and filled with new blood vessels. If implantation is successful, the endometrium will provide nutrition to the embryo during the first period of gestation.
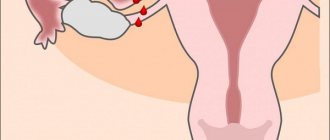
The embryo comes into contact with the endometrium through the outer layer of trophoblast. Trophoblast cells “cling” to the epithelium, penetrating deeper and deeper. At the site where the embryo is attached, a defect is formed in the endometrium, which is closed with a clot of fibrinogen (protein) after complete implantation occurs - after about 12 days. The defect disappears, and the embryo, completely immersed in the endometrium, forms a bulging tissue at the site of attachment.
Sizes of fertilized egg by week
The size of the embryo determines the gestational age with an accuracy of 2-3 days. Up to one and a half months, the date of birth is determined by the DPP - the diameter of the fertilized egg. The diameter is measured at the widest part in three different planes. There is a special table to calculate the due date.
A criterion such as SVD - average internal diameter - does not determine the date of birth very accurately. After 6 weeks, when an embryo appears on ultrasound, the period is determined by CTP - coccygeal-parietal size. The embryo image is measured longitudinally. Sizes 6 to 8 weeks:
- 6 weeks - 3.5-7 mm;
- 7 weeks - 7.9-13.2 mm;
- 8 weeks - 14.2-21 mm.
When performing an ultrasound, a specialist assesses the condition of the fetus and determines developmental defects. Down syndrome can only be determined at 11-12 weeks. After passing this milestone, the embryo develops rapidly, all internal organs and limbs are formed.
The normal result of an ultrasound is an embryo with membranes corresponding in size to the gestational age. One egg or several may be found in the uterus.
In the video you can see the fertilized egg in the uterus:
Timing of implantation of the fertilized egg
When sex gametes are combined in vitro during IVF, a cell containing a chromosome set (diploid) is formed. The cell begins to divide, forming a blastomere (6–8 cells), then a morula appears (16–64 cells), then a blastocyst, which is implanted into the uterus.
Implantation of embryos occurs in one of three periods, which differ from each other in days after fertilization:
- Early - on the 6th day.
- Medium - on days 7–8, five-day implantation is carried out during IVF, which ends in success in 90% of cases.
- Late - on the 10th day.
The average time for implantation of embryos into the endometrium is 7–8 days after fertilization.
When the fertilized egg attaches later
During IVF, blastomeres are cultivated for 3–5 days, after which the highest quality embryo is transplanted into the uterus. The entire process from fertilization, cultivation, embryo selection to replantation takes 5–8 days. Therefore, late implantation is more typical for IVF . In addition, with artificial insemination, the embryo needs more time to adapt. For successful late embryo implantation
Sufficient production of progesterone by the female body is necessary. The success of the embryo transfer process can be judged by the increase in hCG produced by chorionic tissue one day after successful attachment. An ultrasound visualizes a small (2 mm) fertilized egg.
Late embryo implantation is no different from early or middle implantation in terms of possible negative impact on the course of pregnancy, on the development and health of the fetus.
To avoid rejection during late implantation, a woman is recommended to:
- avoid intimacy at first;
- do not take baths, do not visit saunas, steam baths, avoid any thermal procedures, including exposure to the sun (if the procedure takes place in the summer);
- do not lift heavy objects;
- do not engage in sports or active activities;
- do not overcool;
- avoid psycho-emotional overloads, to which sex and gonadotropic hormones that support pregnancy are highly sensitive.
(For more information about what to do after embryo transfer, read this material - note altravita-ivf.ru).
Description of the fertilized egg
The fertilized egg is the protective membrane surrounding the embryo. They attach to the wall of the uterus, forming a vascular connection with it. Through the vessels, the growing embryo receives nutrition from the mother's blood. On ultrasound, the fertilized egg looks like a rounded dark gray formation.
It becomes visible when it reaches a size of 5 mm. This corresponds to 4 weeks of pregnancy. The embryo inside the egg is not yet visible. It can be seen after the 35th day; it looks like a dark stripe. Parts of his body can be seen at 12 weeks of pregnancy - at this time the first examination is usually carried out.
Signs
When resorting to IVF, every woman expects that the attempt will be successful and she will become pregnant. During the implantation process, many patients listen too much to their well-being, and those who are especially sensitive may exaggerate their sensations. Of course, this does not mean that symptoms are completely absent; some people really don’t have them, while others have them to varying degrees. Women describe their feelings during late implantation
subjective, but you need to try to evaluate the change in your well-being objectively. This is important for the doctor for further actions in case of failure, in order to draw the right conclusions, as well as in case of a favorable outcome, in order to competently manage the pregnancy.
Symptoms of late embryo implantation:
- Bleeding when the embryo penetrates the uterine layer, when small endometrial vessels rupture. With minor bleeding, a woman may decide that she has started menstruation, and implantation has failed. An hCG test will help you draw the right conclusions in the absence of heavy bleeding.
- A common sign of late implantation is nagging pain around the lower back and lower abdomen. They can be intense or weak.
- Low-grade fever may persist throughout the first trimester.
- Nausea.
- Weakness, fatigue, dizziness, drowsiness.
- Taste of metal in the mouth.
- Psychological instability, from depressive states to strong emotional upsurges.
If the discharge is significant, continues for a long time, and the temperature rises above 38 degrees, severe pain in the abdomen is noted, this should be reported to the doctor immediately. Heavy bleeding should be especially alarming. Symptoms are not typical for late implantation; each woman may have some other manifestations. Also, the absence of symptoms does not mean that pregnancy has not occurred; an hCG test will allow you to assess the situation. The doctor will explain what the patient may experience during implantation, whether it happened on time or later, so you need to be prepared for any development of events, but set yourself up only for a positive result. Anxiety can negatively affect the outcome of the procedure.
Reasons for non-attachment of the fertilized egg
Each patient has an individual response to IVF procedures, so late implantation may not take place.
The most common reasons for rejection:
- embryo with genetic abnormalities;
- poor quality material;
- unhealthy endometrium;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies of a woman during an IVF program;
- the patient's age is 35 years or more;
- unexpected disorders of the reproductive system.
If late implantation fails, an examination is carried out, the doctor analyzes the situation, draws conclusions about the reasons for the failure, draws up a diagnostic and IVF program taking into account the information received.
Read more about cryotransfer after unsuccessful IVF in this material - note. altravita-ivf.ru.
Results of in vitro fertilization
Has the embryo been implanted
, checked by analyzing human chorionic gonadotropin - hCG. Testing is carried out approximately 2 weeks after the transfer. It is not advisable to do an analysis earlier, since hCG has not yet risen to a level where it can be accurately determined, so as not to make a mistake with the onset or non-occurrence of pregnancy.
| Embryo age | Day after transfer of a 3-day-old embryo | Day after transfer of a 5-day embryo | Minimum hCG value, honey/ml | Average hCG value, honey/ml | Maximum hCG value, honey/ml |
| 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 10 |
| 8 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 17 |
| 9 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 10 | 18 |
| 10 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 17 | 25 |
| 11 | 8 | 6 | 11 | 26 | 46 |
| 12 | 9 | 7 | 17 | 47 | 68 |
| 13 | 10 | 8 | 20 | 75 | 105 |
| 14 | 11 | 9 | 30 | 105 | 171 |
| 15 | 12 | 10 | 38 | 160 | 280 |
| 16 | 13 | 11 | 70 | 260 | 400 |
| 17 | 14 | 12 | 120 | 400 | 580 |
| 18 | 15 | 13 | 210 | 660 | 850 |
| 19 | 16 | 14 | 380 | 970 | 1300 |
| 20 | 17 | 15 | 510 | 1370 | 2000 |
Even after 2 weeks, some women may still have low hCG in their urine, so the test will show a negative result. At this time, you should not stop taking prescribed hormonal medications and other medications. A more accurate result will be obtained by laboratory testing of blood serum for hCG using the enzyme immunoassay method. Venous blood is taken on an empty stomach in the morning. The evening before, they have dinner no later than 19:00. You can conduct a rapid test for hCG, the results of which will be available in 1.5–2 hours. A typical hCG test will take 1-2 days. Gestation after IVF is confirmed using ultrasonography performed 3 weeks after embryo transfer, when the fertilized egg and its location are clearly visible. If late implantation does not take place and menstruation begins, then hCG is also tested after 1–2 days.
How does a miscarriage happen?
According to research, 15 to 20% of diagnosed pregnancies end in miscarriage.
Sometimes, at the time of spontaneous abortion, a woman may not even be aware of her pregnancy. This is possible if the bleeding was preceded by a slight delay, which can be explained by physiological reasons or hormonal imbalance, or when the period came on time. In this case, what is happening will be perceived as normal menstruation. Perhaps a little more painful and with a heavier discharge.
A failed pregnancy can be judged by the signs of an early miscarriage - one or several large clots, but it is not always possible to control all the discharge during the bleeding period. At a period of 6 to 12 weeks, their size can be up to 5 cm. The fertilized egg can be rejected entirely or in parts. From the 6th week, a miscarriage may be accompanied by cramping pain of moderate intensity. The whole process takes from several hours to several days and on average does not exceed menstruation.
What might a fertilized egg look like if expelled during an early miscarriage? Photos give a general idea:
6 weeks Photo source: desprecopii.com
The fact that pregnancy has occurred will be confirmed by an elevated hCG if you take a blood or urine test after a suspected miscarriage. For some time it will be higher than normal for non-pregnant women. You can also use a pregnancy test strip, in most cases it is also informative.
If a woman knew that conception had occurred, the clinical picture does not change, but what is happening is perceived completely differently, especially if she knows how a miscarriage occurs. Spotting or bloody vaginal discharge is a serious sign of a threatened miscarriage and a reason to urgently consult a doctor. If bleeding occurs, you must call an ambulance or see a specialist yourself as soon as possible. If there is a threat of miscarriage, hospitalization is indicated. Perhaps the pregnancy can be saved with timely and competent medication support.