It is believed that the gestation period for a baby is 40 weeks. However, often a baby is born before the due date, but doctors do not consider him premature. Sometimes obstetricians even try to speed up labor due to the fact that the baby has spent too much time in the mother’s womb. When is a fetus considered fully ready for birth?
Intrauterine development: at what stage is the fetus ready for life outside the mother’s body?
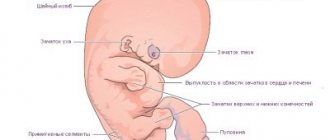
Throughout the entire period of gestation, the child is constantly developing. The first few weeks after fertilization, it bears little resemblance to a newborn. Throughout the first trimester, the baby develops internal organs and systems. By the 14th week, all the main organs have already been formed, but they are not able to function outside the mother’s body.
Physiological development continues in the second trimester. During this period, the nervous system and brain improve, the baby begins to hear and respond to loud sounds. After the 21st week, the process of formation of subcutaneous fat is activated. However, according to WHO, the minimum chance of survival in case of premature birth appears only after the 22nd week.
Despite the formation of the main organs and systems, during this period the child is still underdeveloped:
- the ability to breathe and digest food;
- swallowing and sucking reflexes;
- thermoregulation;
- brain activity.
Children born after 7 months of pregnancy are considered more viable. Provided that preliminary stimulation of lung maturation was carried out, with proper care such infants can be saved in 50% of cases. The baby is more prepared for life outside the womb after the 32nd week of gestation. During this period, those substances that contribute to the opening of the lungs are formed in the lung tissues. However, their level is still insufficient for full breathing.
Babies born at the end of the 36th obstetric week are also considered premature. Their development is sufficient to live outside the mother's womb. However, they require special care and are very vulnerable to the negative effects of the external environment. After 37 weeks, the fetus's respiratory and nervous systems fully mature. If born at this stage, the baby does not require increased attention from medical staff.
Degrees of prematurity and indicators
Medical assistance to ensure life support for premature birth is provided from the 22nd week of pregnancy, provided that the baby weighs at least 500 g and its body length is 25 cm or more. The statistics include babies born viable who have reached 1 kg and 35 cm in height from the 28th week. From 22 to 27, medical care is provided and the necessary care measures are taken. If such a child has lived for more than a week, he is registered alive.
The main criteria for recording in the medical history by week of pregnancy:
- 22-27 - 4th degree of prematurity, weight from 0.5 to 0.999 kg;
- 28-31 – 3rd degree of prematurity, - 1 kg–1.5 kg;
- 32-35 - 2nd degree of prematurity, - 1,501 kg–2.0 kg;
- 36 (sometimes 36-37) week - 1 degree of prematurity, - 2.001-2.5 kg;
- 37-40 - considered full-term;
- 41-42 – postponed.
According to WHO recommendations, births occurring between 22 and 37 weeks are considered premature. A baby born at 37 weeks is already considered born at the minimum time for physiological birth; if the baby was born a week earlier, he is still not full-term to the lower limit of normal.
Signs of a full-term newborn
The condition of the newborn is assessed by a neonatologist in the delivery room. Depending on this, the baby is given an Apgar score. According to the assessment system, a healthy full-term baby should receive at least 8 points.
When deciding how many Apgar scores to give a newborn, they consider such characteristics as the intensity of the cry, skin color, muscle tone, heart rate, and the presence and severity of reflexes.
Body mass
Body weight is one of the main signs by which the viability of a newborn is assessed. After weighing, the baby’s weight is compared with the standards established by WHO for children of different sexes. If the baby is under or overweight, he is additionally examined to exclude possible developmental pathologies. The table shows the standard weight indicators for full-term infants:
| Floor | Lower limit of normal, kg | Norm, kg | Upper limit of normal, kg |
| Boy | 2,9 | 3,3 | 3,9 |
| Girl | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,7 |
When comparing body weight indicators, the hereditary characteristics of the newborn and his height are also taken into account. Tall parents have a dense build and the child is born large. The average height of girls ranges from 47–51 cm, boys – 48–52 cm.
Motor activity and muscle tone
Immediately after birth, doctors note how active the baby is. A full-term baby has good motor activity. His movements are chaotic, he moves his arms and legs a lot. A healthy child reflexively bends his arms and legs, crosses them, and while lying on his stomach tries to push off from the support.
In the first weeks of a baby's life, muscle tone is slightly increased. This is expressed in the fact that the limbs are in a semi-bent state.
Breathing and heartbeat, first cry
The baby's first cry is important for both the mother and doctors. The mother understands that the child is alive, and doctors receive a signal to begin independent breathing. A healthy baby screams loudly, but quickly calms down.
The breathing of a newborn is different from that of an adult. His breathing movements are rapid and intermittent, but he does them effortlessly. Normally, a full-term baby takes 40–60 breaths per minute. In the first moments of life, the pace is slightly higher than after 5 minutes.
Heartbeat is one of the most important indicators of a newborn’s condition according to the Apgar system. If the baby's heart beats at a rate of more than 100 beats per minute, the child receives the highest score for this criterion. Normally, the heart rate in newborns is 100–140 beats/min.
Unconditioned reflexes
Unconditioned reflexes help a newly born baby adapt to the outside world. The following reflexes are distinguished that a fully formed newborn should have:
- Sucking. If you run your finger along the baby's cheek and then insert it into the baby's mouth, he will begin to make sucking movements.
- Protective. When lying on his stomach, the baby will try to turn his head to the side.
- Swallowing. When food gets into the mouth, the child must swallow it.
- Proboscis. Tapping the lips forces the baby to extend them forward.
- Search. If you touch the corner of a newborn's mouth, he will turn his head towards the irritating factor.
- Palmo-oral. When pressing on the pads of the palms, the baby opens his mouth.
- Prehensile. The baby tightly squeezes the fingers placed in his palms.
- Babinsky. The child bends his foot and spreads his toes when a hard object is passed along the sole of his foot.
During the first days of life, the baby also develops other unconditioned reflexes. After a few months, some of them gradually fade away.
Skin color
The color of the skin is assessed in the first seconds after birth and after 5 minutes. A normal full-term baby's skin should be pink. Some newborns have a bluish tint to their skin at birth. However, normally the skin returns to its normal color after a few minutes. When crying a lot, the color of the skin around the mouth turns purple, which is also normal.
Presence of lubrication, gun on the body
The vernix lubrication covers the baby's entire body after birth. In the womb, it protects his skin from the effects of amniotic fluid, and during childbirth, it facilitates the passage of the child through the birth canal. In the first minutes of a newborn's life, the lubricant resembles white mucus.
The fluff appears on the fetal body after 12 weeks of pregnancy. It is called lanugo and is the result of the first hair follicles. By 28 weeks, the fluff covers the baby’s entire body, but gradually disappears by the end of gestation. In a full-term baby, lanugo remains only on the upper back, shoulders and forehead.
At what stage of pregnancy is the baby full term?
When assessing the full-term pregnancy, one cannot fail to take into account the degree of maturity, and therefore the full-term, of the child himself. It is the development of the baby that determines its readiness to come into the world and support life outside the womb of a woman. If the baby is not full term, it requires special care until the body gets stronger.
The signs of maturity were based on parameters at 38-40 weeks of pregnancy with a full-term baby:
- The weight of the baby is 3000 - 3500 g (normal variations range from 2800 g to 4000 g).
- The baby’s body length, the most significant factor in assessing the baby’s full term, ranges from 45 to 55 cm.
- The head circumference is 1-2 cm greater than the baby's chest circumference. These values do not exceed 34-35 cm.
Important diagnostic criteria are:
- The first cry, which should be loud and quite intense.
- Color and condition of the skin. Full-term babies have smooth, elastic, pink skin covered with a specific white lubricant.
- The presence of a small and large open fontanelle.
- Increased muscle tone, causing the child's limbs to be slightly bent.
- Heart rate - 120 - 150 beats per minute.
Each parameter is assessed on a scale from 0 to 2 (Apgar scale) in the first minute and 5 minutes after the birth of the baby. This is why the Apgar score includes 2 numerical values, written separated by a slash (for example, 9/10, 7/8). A variant of the norm is an indicator of 8 points or higher. The interval 4 - 7 points indicates the average severity of the newborn’s condition. If the indicators are in the range from 1 to 3 points, the child’s condition is extremely serious.
When assessing the full-term birth of a child, both the gestational age at which the birth occurred and the maturity of the baby are taken into account. So the baby can be born at 37-38 weeks, but have signs of immaturity. In this case, the pregnancy will be full-term, but the child will not.
When is the baby considered full-term and can you give birth?
At what week is a baby considered full term? When setting the expected date of birth, doctors rely on a gestational age of 40 weeks. However, according to statistics, only about 10% of women give birth exactly at this time. The birth of a baby is considered optimal at 38–40 obstetric weeks. By this time, the fetus is completely ready for life outside the mother’s womb and has all the necessary reflexes.
Some women suggest that the longer the baby is in the womb, the better. However, this assumption is wrong. Starting from the 42nd week, the placenta loses its ability to fully support the life of the fetus. The baby may lack oxygen and nutrients. The process of ossification also begins, which increases the risk of birth injuries and complicates delivery.
After 42 weeks the pregnancy is called post-term. If labor has not begun before this date, doctors take actions to stimulate labor. Based on the above, you can give birth after a full 37 obstetric weeks (we recommend reading: 37 weeks of pregnancy - how many months is that?). It is advisable that the baby is born before the end of the 41st week of pregnancy.
Minimum and physiological term of labor
The birth of a baby is considered optimal at 40 weeks, but only every tenth pregnant woman survives. This is the ideal time to give birth, and in life rarely anything is ideal. At 40 weeks, nature provided the necessary conditions for the birth of a healthy baby, and the birth process passed without complications.
The development of the fetus in the mother's womb must be complete. Clinical studies have shown that small deviations from the pediatric norm do not have a significant effect on the condition of the newborn.
At what age can you give birth to a viable baby? For a long time in modern pediatrics, births between 37 and 42 weeks have been considered full-term. The first obstetric week is counted from the 1st day of the last menstruation and is verified according to ultrasound data in each trimester.
A full-term baby can be delivered from 37 to 40 weeks inclusive. At 36 it is still considered full term, at 41 and 42 – post-term. In the last week, the issue of auxiliary measures to stimulate the labor process or early delivery via cesarean section is decided.
In the WHO recommendations, adopted as a basis in the regulatory documents of the Russian Federation, the main determining criterion for the physiology of the birth of a child at a time determined by nature, and its viability, was the gestational age, and not the weight and height of the newborn, although indicators are also taken into account. A woman gives birth to a full-term baby only at 37, 38, 39 and 40 weeks. From 22 to 36 it is considered premature, at 41 and 42 – post-term.