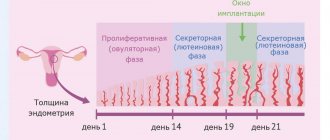
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy in the early stages
Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy is a pathology in which a fertilized egg attaches and develops outside the uterus.
About one in 80 pregnancies is ectopic. The causes of ectopic pregnancy are not always known. Risk factors include:
- previous ectopic pregnancy;
- previous inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs;
- fallopian tube surgery;
- surgical interventions on the abdominal organs;
- endometriosis.
A higher risk of ectopic pregnancy exists in women over 35 years of age.
Frozen pregnancy at different stages
The cessation of fetal development before 28 weeks is called miscarriage, and beyond 28 weeks is called fetal death. The cause of the pathology is infections, including STIs, exposure to medications, climate change, air travel, stress, but most often it is a natural process of discarding an embryo with genetic disorders.
According to WHO, 70% of all pregnancy arrests occur before 2 weeks, so the woman does not even suspect that something has happened to her. In this case, the fertilized egg comes out on its own, causing slightly more intense bleeding than usual, which the woman perceives as her menstruation due.
In 25% of cases, pathology occurs before the 10th week. At such a stage, a frozen pregnancy often does not lead to a miscarriage; the fetus remains in the uterus and decomposes, poisoning the woman’s body, so the help of a gynecologist is required.
Does the test show an ectopic pregnancy?
There may be no symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages. Often its symptoms are mistaken for another pathology - for example, indigestion, irritable bowel syndrome or appendicitis.
Symptoms of VB:
- vaginal bleeding that differs from menstrual bleeding in color;
- pain during ectopic pregnancy is concentrated in the abdominal area (usually only on one side);
- diarrhea, vomiting;
- pain during bowel movements;
- dizziness, weakness.
Does the test indicate an ectopic pregnancy? Yes, it does. Therefore, if, in the presence of “two stripes,” a woman has a stomach ache or blood is released from the vagina, she should immediately consult a doctor. There are no periods during an ectopic pregnancy, but spotting may be observed.
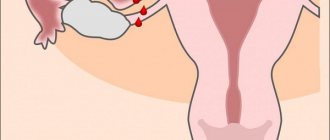
An ectopic pregnancy is most often tubal, when the fertilized egg does not reach the uterine cavity, but attaches to the wall of the fallopian tube. In rare cases, pregnancy develops in another “wrong” place: the ovaries, the abdominal cavity.
Signs and symptoms of frozen pregnancy
1. In the early stages. In the first trimester.
This diagnosis comes as a shock to many because a frozen pregnancy in the early stages causes virtually no symptoms. Nevertheless, women who are attentive to their condition, based on some subjective sensations, themselves record symptoms that can suggest that the pregnancy is fading.
These signs are:
- a decrease in basal temperature to 36.8° within two days and then continues to fall to 36.5°. This sign may work earlier than others if the woman continues to monitor her temperature. In a normal pregnancy it should be 37°.
- disappearance of symptoms of early toxicosis. Nausea begins from the moment the fertilized egg attaches to the walls of the uterus and the production of the hormone hCG. The disappearance of toxicosis may be a sign of trouble in the development of pregnancy.
- the absence of engorgement of the mammary glands is purely subjective.
- There may be spotting vaginal discharge with blood streaks. As a rule, they do not appear immediately. At least two weeks pass. Blood streaks are associated with detachment of the fertilized egg from the walls of the uterus
- At the same time, nagging pain occurs in the lower abdomen
- a general uncomfortable state with elevated temperature. This sign of a frozen pregnancy occurs already when the body is intoxicated by a decomposed fertilized egg. Typically, this situation occurs when the dead fetus is in utero for 3 weeks.
The listed signs of a frozen pregnancy are subjective and ambiguous. Similar symptoms occur when there is a threat of miscarriage. In any case, this situation requires urgent medical attention.
How to determine a frozen pregnancy? Diagnostics.
Objective evidence of embryo death in the first trimester is:
- lack of heartbeat. In a normal pregnancy, it is visualized already from the 5th week.
- the size of the embryo recorded on ultrasound does not correspond to the actual gestational age. The size of the fertilized egg determines the period at which the pregnancy froze.
- a decrease in the level of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin, hCG, the pregnancy hormone, which is produced first by the corpus luteum, and then, when it is formed, by the placenta. During normal pregnancy, it doubles daily.
2. In the second and third trimesters
Usually the intrauterine presence of the fetus is felt, its movement is felt, therefore the main signs of a frozen pregnancy in the later stages are: - sudden cessation of fetal activity - leakage of amniotic fluid. Spontaneous miscarriage often occurs at this time.
What to do next if you see signs of a frozen pregnancy and they are confirmed by a doctor?
There is only one answer: 1. Remove it in a hospital setting under intravenous anesthesia in clinics that have a license to operate. (Medservice Clinic) 2. Be examined for the reasons that caused the missed abortion 3. Plan the next pregnancy under the guidance of a doctor
Call online Make an appointment
HCG for ectopic pregnancy
How to determine an ectopic pregnancy? Its diagnosis includes:
- study of anamnesis;
- ultrasound scanning. Signs of ectopic pregnancy on ultrasound – absence of fertilized egg in the uterine cavity (for a period of 4.5-5 weeks);
- pregnancy test (urine or blood test);
- laparoscopy.
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the blood is determined over time. The information content of hCG testing for ectopic pregnancy is 97%. With this pathology, the hCG titer increases slowly and does not correspond to the duration of pregnancy. It is important to know that the analysis does not always reliably distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from a complicated intrauterine pregnancy.
If an ectopic pregnancy is detected at an early stage, methotrexate injections are sometimes used to terminate it. After the injection, the hCG level is continued to be monitored, and if it remains high, the drug is reintroduced.
Signs of an incipient miscarriage
In the initial stage of spontaneous abortion, aching, sometimes cramping pain in the lower abdomen or lumbar region is observed. When the placenta separates from the wall of the uterus, bloody discharge appears from the genital tract. As the detachment process progresses, the bleeding intensifies. Often, heavy bleeding may occur, leading to severe anemia. Together with the blood, the fertilized egg comes out of the uterus. After this, the uterus begins to contract and the bleeding stops. If parts of the membranes and placenta remain in the uterus, it will not contract and bleeding will continue. Heavy uterine discharge can become life-threatening. The cervix remains slightly open, which favors the development of inflammatory diseases due to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms there.
Sometimes the elements of the fertilized egg retained in the uterus are very small, and bleeding may stop, but subsequently polyps are formed from these elements, preventing the healing of the surface of the uterus. They can lead to prolonged bleeding from the genital tract.
Determining whether the fetus is developing in the womb or not can be determined by determining the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) over time. An increase in the amount of this hormone in two days indicates a normal pregnancy. If the level of human chorionic gonadotropin remains the same or decreases, it means that the development of the fetus has stopped.
Consequences of ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy can result in a tubal abortion - a termination of pregnancy in which the fertilized egg is released into the abdominal cavity. A tubal abortion can last for several days. The woman is worried about cramping pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the ribs, shoulder, and rectum. During an attack the following symptoms are observed: dizziness, nausea, weakness, vomiting, diarrhea. Bloody discharge from the genital tract appears later. Treatment for tubal abortion is surgical.
The consequences of an ectopic pregnancy can be more severe. A rupture of the fallopian tube usually occurs acutely and is accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture: severe pain, a drop in blood pressure, and fainting. Some patients with a ruptured fallopian tube experience hemorrhagic shock due to excessive blood loss.
Surgery for ectopic pregnancy can be organ-preserving - salpingotomy, when the fertilized egg is removed while preserving the fallopian tube, and radical - salpingectomy, when the fallopian tube is removed. With early diagnosis of a developing tubal pregnancy, organ-preserving surgery is performed, which helps prevent rupture of the fallopian tube. Read more about the methods of performing operations for ectopic pregnancy on our website Dobrobut.com.
After laparoscopic surgery, the patient is discharged after 1-2 days, after laparotomy - usually after 5-10. It is important to monitor the hCG level weekly after surgery to ensure that the fragments of the fertilized egg are completely removed.
Women who have undergone surgery due to an ectopic pregnancy are prescribed combined oral contraceptives (to stabilize the menstrual cycle and prevent pregnancy in the first 6 months after surgery).
What are the symptoms of anembryonic pregnancy?
There are no specific symptoms of anembryonic pregnancy. However, with anembryonia, more often than with a normally developing pregnancy, symptoms of threatened miscarriage occur in the form of bloody discharge and pain in the lower abdomen. When testing blood for hCG, this indicator may not correspond to the expected gestational age. And only by ultrasound can you see the absence of an embryo. With anembryonia, pregnancy cannot develop indefinitely and always ends in spontaneous miscarriage in the 1st trimester (up to 12 weeks).
Pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy
The chances of a normal pregnancy remain even after salpingectomy, because the fallopian tubes are a paired organ. About two thirds of women are able to become pregnant again. The chance of another ectopic pregnancy ranges from 7 to 15 percent. It all depends on the results of the treatment and the condition of the remaining fallopian tube.
A normal pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby depend on the history of the ectopic pregnancy. A randomized trial conducted in 2013 found that the rate of normal pregnancies 2 years after treatment for ectopic pregnancy was approximately 64% for women who had radical surgery and 70% for those who had breast-conserving surgery.
Related services: Ultrasound examination Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist during pregnancy
What to do for different types of frozen pregnancies
The course of the process depends on the classification of the failed miscarriage and the type of frozen pregnancy, which happens:
- With anembryonia type 1.
In this case, the embryo located in the fertilized egg is not visualized on ultrasound. The size of the uterus corresponds to the 6th week of development. With this pathology, both the fertilized egg and the embryo stop developing. For up to 6 weeks, the patient is prescribed drugs that stimulate uterine contractility - causing a miscarriage. After 1-2 days, the contents of the uterus come out on their own. - With anembryonia type 2
. The fertilized egg continues to develop, it corresponds to the required development period, but the embryo has already died and is not growing. The woman undergoes a cleaning to remove any remaining fertilized egg. - All types of fetal death after 7 weeks.
After 7 weeks of pregnancy, the patient is prescribed a cleaning for any type of pregnancy loss. A course of antibiotics is also prescribed to prevent the development of endometritis - inflammation of the endometrial layer in the uterus.
Oksana Igorevna
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
Abortion and contraception clinic in St. Petersburg - department of the medical gynecological association "Diana"
Make an appointment, tests or ultrasound via the contact form or by calling +8 (812) 62-962-77. We work seven days a week from 09:00 to 21:00.
We are located in the Krasnogvardeisky district, next to the Novocherkasskaya, Ploshchad Alexander Nevsky and Ladozhskaya metro stations.
The minimum cost of a medical abortion in our clinic is 4,500 rubles. The price includes all pills, an examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound to determine the timing of pregnancy.
What happens if a frozen pregnancy is not removed? How long can you walk with her?
It is impossible to revive a frozen fetus, so you need to eliminate the consequences as quickly as possible. If this is not done, the fertilized egg will begin to decompose, releasing carcinogenic substances.
If measures are not taken at this stage, inflammation and sepsis will develop - blood poisoning, which is life-threatening. In an extremely advanced situation, the patient’s uterus is removed, but doctors are determined to preserve the organ, so they cleanse the uterus of embryonic remains. Then the woman undergoes long-term rehabilitation therapy; she will be allowed to become pregnant no earlier than after 3 years.