What it is
In a healthy child, the tongue has a uniform pink color without spots or plaque. But in the presence of any pathology, spots of various colors and sizes may appear, which represent:
- An uneven accumulation of plaque on the surface of the tongue, which consists of exfoliated epithelium, tiny food particles, and microorganisms.
- Excessive proliferation of epithelium in certain areas of the mucous membranes.
- Limited inflammation.
- Benign or malignant neoplasms.
Let's look at the main reasons for the appearance of various spots and methods of treating them.
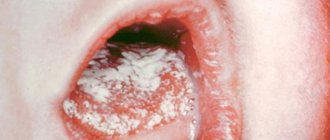
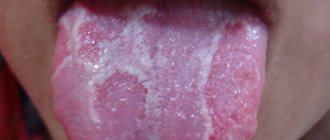
White
In a baby, the appearance of white spots on the tongue most often indicates thrush - a fungal infection of the mucous membranes due to a decrease in immune defense in the body or when taking antibiotics. Such spots are located asymmetrically, can have a variety of sizes, and are often covered with a cheesy coating.
If a child shows signs of thrush on his tongue, then it is necessary to visit a pediatrician who will find out the reasons for its appearance. Delay in treatment can cause progression of the disease and inflammation of the mucous membrane, which will cause pain and discomfort in the child. You cannot try to remove the plaque on your own; this can lead to additional trauma. To eliminate such white spots, it is most often recommended to treat the child’s oral cavity with a weak solution of baking soda or ordinary brilliant green. In more severe cases and with relapse of the disease, it may be necessary to take antifungal drugs.
Treatment of white plaque on a child’s tongue
Before starting treatment, you need to show the child to the pediatrician. Depending on the clinical picture, especially if there is bad breath, he may refer you to a gastroenterologist, dentist, internist, dermatologist, infectious disease specialist or toxicologist. In order to treat correctly, a diagnosis is made, and then a therapeutic program is developed.
- Most often, at 2 months and up to a year, children suffer from thrush. To combat this disease, antifungal drugs are prescribed, which are used to treat pathological areas.
- In one-year-old children and 2-year-olds, infections and viruses are a common problem. In such a situation, antibiotics and immunoglobulins are usually prescribed. For herpes stomatitis, the dentist prescribes solutions with an analgesic and wound-healing effect.
- Preschoolers and school-age children are most often diagnosed with aphthous and allergic stomatitis. The range of medications for older children is wider than for infants. Antiseptic therapy is carried out.
Parents must remember that only timely treatment and strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions will eliminate the problem and prevent the development of serious complications.
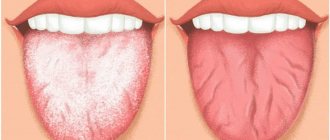
Geographical
If red spots and a white coating along their edges appear on the tongue, then this is a sign of a geographic tongue - desquamative glossitis. The disease is not inflammatory in nature and may indicate some hormonal disorders, worms and problems in the digestive system. Such spots do not have smooth outlines, they quickly change their location and do not bother the child in any way. They can be oval, round or have fancy shapes.
This disease lasts a long time and often goes away on its own after some time, even without specific therapy. Sometimes antiseptics, vitamins and drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration processes are used to treat geographic tongue. But most experts (for example, Dr. Komarovsky) believe that there is no need to treat geographic spots.
Spots on the tongue
General information
The tongue is an important organ that influences the process of speech formation, and consequently, communicative functions and digestion.
However, in addition to this, the tongue is also a kind of “mirror” of the internal organs. Based on the condition of the tongue, a specialist can determine the presence of many diseases. Tongue stains are a common problem that people do not pay enough attention to. They can be of different shapes and colors, which makes it possible to suspect one or another disease that provokes their occurrence. The spots are white, red and blue. In addition, there are such concepts as “geographic tongue” - inflammation of the tongue, accompanied by peeling of the surface layer, and “bald tongue” - the formation of spots on the tongue that are areas of dying papillae.
It should be understood that each of these pathologies is not a cosmetic problem, but a symptom of a disease, and in some cases quite serious and dangerous.
Causes
White spots on the tongue in most cases are a sign of the following diseases:
- candidiasis or thrush (can be localized not only in the vagina, as many believe, but also on the mucous membrane of the mouth. Quite often, a white coating on the tongue is the result of a fungal infection. When you try to clean off such plaque, you can find bleeding ulcers underneath);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (a whitish coating on the tongue is a clear sign of problems in the gastrointestinal tract. In most cases, its appearance indicates the presence of chronic diseases of the stomach and duodenum).
Red spots on the tongue can form due to the following pathologies:
- tongue injury (a cut or biting the tongue can leave behind a red spot, slightly painful when pressed, which goes away on its own after some time);
- exudative erythema (the presence of this disease is indicated by the appearance of red spots on the tongue, surrounded by bubbles with a yellowish liquid. Over time, the bubbles can turn into ulcers);
- herpes virus (although most often red spots with herpes appear on the face and lips, the tongue is also no exception. The appearance of such spots indicates a significant decrease in immunity);
- other viral infections (red dotted spots - petechiae - on the tongue indicate the presence of a viral infection and reduced local immunity).
Dark spots on the tongue (brown or almost black) are a sign of serious pathologies. Their reasons are:
- tongue cancer;
- necrosis.
The appearance of blue spots on the tongue can be caused by the following factors:
- hemangioma (benign tumor);
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system (especially in chronic heart failure).
Also, the appearance of spots on the tongue can be a consequence of dental problems (stomatitis, gingivitis).
The appearance of “bald” areas on the tongue is a consequence of a severe burn or large-scale trauma to the tongue, since the areas of the tongue damaged in this way are overgrown with connective tissue that does not have papillae.
“Geographical language” is a rather rare phenomenon. The reasons for its occurrence are not reliably known, but in most cases this symptom occurs with pathologies of the digestive system, childhood diathesis and blood diseases.
Reds
The appearance of red spots on a child’s tongue is a sure sign of an infectious or inflammatory process in the oral cavity:
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- bacterial dermatosis;
- herpetic infection.
Also, red spots may be due to an allergic reaction or consumption of foods that are bright red in color.
Very often, such formations are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms: pain in the tongue, a feeling of discomfort, increased salivation. Due to pain, children may be capricious and refuse to eat or drink. The general condition may also suffer - body temperature rises.
Only a doctor should treat red spots. After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the following may be prescribed:
- treatment of lesions with antiseptic agents;
- taking antibiotics or antivirals;
- use of anti-inflammatory medications.
How to get rid of white spots on your baby's tongue
Until a diagnosis is made, no manipulations should be carried out with the white spots on the child’s tongue. Self-medication (including folk remedies) in this case is unacceptable, since it is unknown how the delicate mucous membrane will react to this or that remedy.
In most cases, doctors recommend:
- Treat the affected areas (for stomatitis and thrush) with a soda solution, which allows you to create an alkaline environment in the oral cavity that is harmful to the fungus. For this purpose, one or two teaspoons of soda are dissolved in a glass of warm water. Having thoroughly washed his hands, an adult wraps a sterile bandage (gauze) around his finger, dips it into the solution and slowly, delicately, avoiding strong pressure, wipes the areas with white spots, repeating the procedure about six times a day.
- Lubricate white spots with a solution of methylene blue, a two percent solution of boric acid (for stomatitis).
- Use (if the child’s age allows) special antifungal drugs in the form of a gel, cream, solution, tablets or suspensions.
- Eliminate sour fruits, carbonated drinks, hard, hard, hot and cold foods, pickles, spices, and sweets from the child’s diet.
- If the temperature rises, take antipyretic drugs and drink a sufficient amount of fluid (preferably clean, still water).
To relieve inflammation and soothe the mucous membrane, you can use sea buckthorn oil or herbal decoctions: chamomile, sage, calendula. But this should only be done with the permission of a doctor.
If your baby refuses to eat, you should not force feed him. It is better to offer soft foods (mashed potatoes, liquid porridge, broth) in small portions, but often.
Dark
Dark spots on the tongue often occur when eating food that contains dark pigments that color the plaque on the surface of the mucous membranes. Such spots do not pose any danger to the child and disappear after hygiene procedures. But there are a number of conditions that manifest as dark spots in the mouth and which can have very serious consequences.
Black
Black spots on the tongue in children most often appear during a long course of antibiotic therapy as a result of the active proliferation of microorganisms and fungi. Blackening of the tongue develops gradually and can last up to 2-3 weeks. The main treatment for this condition is to restore normal microflora in the child’s intestines and oral cavity. For this purpose, eubiotic drugs are prescribed (for example, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin).
It is extremely rare that black spots on the tongue appear as a result of deep degenerative processes accompanied by necrosis of areas of the mucous membrane. This condition is very dangerous and requires emergency medical attention. The treatment of such spots is often surgical.
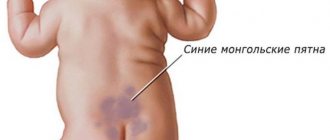
Blue
Blue spots in a child's mouth are a rare occurrence. They may appear in the following situations:
- The presence of severe heart failure due to heart disease and defects. Spots on the tongue appear due to stagnation of blood in the venous bed and are accompanied by blue discoloration of the lips and limbs. Their treatment consists of eliminating cardiac pathology and normalizing blood microcirculation in the vessels.
- With the growth of a benign vascular tumor - hemangiomas. This blue spot is most often single. Treatment is only possible through surgery.
What tests will help determine the cause of red spots on a child’s tongue?
In order to diagnose the cause of the red spots on the baby’s tongue, the doctor may prescribe:
- general blood analysis;
- bacteriological analysis. It is prescribed for the purpose of examining scrapings from the surface of the tongue in order to identify microorganisms and determine how sensitive they are to medications;
- immunofluorescence analysis (to detect streptococcal antigens in scarlet fever, intracellular accumulations of the herpes simplex virus in scraping smears, etc.);
- serological analysis (to determine the content of anti-O-streptolysin in scarlet fever);
- skin tests;
- provocative tests, etc.
Bald
Normally, the lingual surface is covered with a large number of small taste buds, which give it a velvety appearance. If such papillae die or atrophy for any reason, “bald” spots appear. They are pink in color, irregular in shape and do not spread to the mucous membranes of the cheeks, lips or gums.
Reasons that can cause the appearance of such pink “bald” spots:
- Inflammatory diseases (glossitis, stomatitis).
- Tongue injuries.
- Burns from heat or chemicals.
“Bald” spots do not cause any inconvenience to children, but may slightly change the taste sensations. It is impossible to cure such formations, since the taste buds cannot be restored.
If you find that your one-year-old or older child’s tongue has become spotted, you should not panic and try to treat it yourself. Also, the appearance of spots on the tongue should not be ignored, as they may indicate the presence of serious diseases. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will find out the exact cause of such changes and, if necessary, select appropriate treatment for the child.