Babies stick out their tongues for many reasons, and sometimes for no apparent reason at all. A child who sticks out his tongue may be hungry, full, or does not want a certain food.
Babies may also stick out their tongues to imitate or get a response from their parents. Studying your child's habits will help determine why he is sticking out his tongue.
A child's habits, awareness and ability to copy the behavior of adults change with age. Babies younger than 6 months may stick out their tongue instinctively, while babies older than this age may do it intentionally.
A baby under 6 months sticks out his tongue - reasons
For babies under 6 months of age, the most common causes of tongue protrusion are natural reflexes, hunger, and genetic differences.
Tongue thrust reflex
Tongue thrust reflex is a condition in which a child automatically sticks out his tongue in response to touching his lips. This reflex makes it easier for small babies to feed when the mother offers the breast or bottle.
The tongue thrust reflex usually lasts up to 4-6 months. Parents should not offer their baby solid foods until this reflex disappears. However, most babies do not need solid foods until they are 6 months old.
Hunger
Young children often stick out their tongues when they are hungry. The child may turn his head to one side, open his mouth, and then do the same while looking in the other direction.
Genetic condition
Congenital diseases are conditions that are present from birth. Some congenital conditions can cause a baby to have a larger-than-normal tongue. This may cause the tongue to protrude from the mouth. This is different from when a child deliberately sticks out his tongue. Children with conditions such as Down syndrome
and
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
, may stick out the tongue most of the time, along with other signs and symptoms.
Genetic diseases are the least likely reason why babies stick out their tongues. In most cases, a protruding tongue is not a sign that the child has any genetic differences.
Why do newborns stick out their tongues?
Children grow quickly, and mom and dad try to catch every movement of their baby and have time to notice all the subtleties of his development.
One day, parents may see their child sticking out his tongue every now and then. And this can become a habit repeated daily. What does it mean? Should you rejoice at such an event as a new achievement or worry? Let's look at what could be the reasons why a newborn sticks out his tongue.
Why is language needed?
For communication, of course! And also to participate in meals. As the baby grows up, he learns to control his body, trying to understand why this or that part of it is needed. And language is a very interesting object for research. Judge for yourself: he moves, helps “speak”, feels how delicious his mother’s milk is, etc.
Isn't it time to refresh yourself?
Watch your child. Maybe he was just hungry. Then, with the help of the tongue, the usual sucking reflex appears, signaling to the mother that it is time to refresh herself. This is especially true for breastfed children.
I can do the same
A 2-month-old baby is already able to master communication skills, as he has learned to coo. Perhaps, with the help of the tongue, he is trying to make a new sound. Or maybe he is simply repeating the actions that he observed in adults. And if an older brother can stick his tongue out at a baby, then why not do the same?
Often the baby copies the facial expressions of adults
First teeth
The baby can feel new reliefs in his mouth when teeth begin to emerge. Often, the gums swell, itch a little, and hurt, causing discomfort to the baby.
Elements of gymnastics
You can see how a one-month-old baby moves everything that moves: waves its arms and legs. Older children try to roll over and crawl. And the tongue is the same muscle that needs training. So the baby is training.
Big tongue for a small mouth
There are cases when a child's tongue is slightly larger than the standard size. It does not fit in the mouth, which may be an anatomical feature. As a rule, this problem goes away on its own with age. But it’s still worth going to the pediatrician, since tongue prolapse may indicate serious genetic diseases.
If the child is gaining weight normally, his sucking reflex is well developed, and his tongue does not stick out all the time, but occasionally, there is no reason for concern.
When to worry
If an infant sticks out his tongue constantly or regularly after feedings, the baby is capricious and nervous, this may indicate the pathological development of one of the diseases.
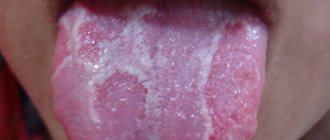
A disease in which the oral mucosa is damaged by fungi of the genus Candida. Every fifth baby under one year of age experiences symptoms of candidiasis. Thrush is identified by a white coating on the tongue, cheeks and palate. By sticking out his tongue, the baby tries to relieve the discomfort.
Hypothyroidism
It occurs due to a lack of thyroid hormones and has serious consequences in the form of mental and physical retardation. Often the diagnosis of hypothyroidism is made in the maternity hospital. However, it can manifest itself at a later date, in the first year of life.
In breastfed babies, signs of hypothyroidism appear later, since the baby receives hormones in small doses through mother's milk for some time.
A protruding tongue may indicate a serious illness
A large, swollen tongue that does not fit in the mouth is one of the signs that requires immediate contact with an endocrinologist.
Intracranial pressure
Along with a prolapsed tongue, a characteristic sign of the disease is a head thrown back. This condition requires close monitoring of the baby by the parents, as well as treatment by a neurologist.
After a thorough examination, drug therapy and therapeutic massages are prescribed. Treatment should begin as early as possible, since pathological processes lead to mental retardation and vision problems.
Be discerning when caring for your child. Don’t invent something that doesn’t actually exist, but don’t ignore the situation if there are warning signs.
A baby older than 6 months sticks out his tongue - reasons
At around 6 months, babies develop some communication skills, meaning they can intentionally stick out their tongue. A child may stick out his tongue to imitate an older child or adult, to get a reaction from a parent, or to signal hunger.
Imitation
Most children begin to imitate adult behavior when they are about 8 months old. However, premature babies and children with developmental delays may imitate a little later.
Getting a reaction
Children crave attention and are constantly learning about relationships with the people they encounter. A child may stick out his tongue to test the response he is getting from a particular person. If an adult laughs in response to a child sticking out his tongue, the child will do it more often. However, some children may continue to stick their tongues out even if an adult does not approve because they are curious about adults' behavior.
Hunger
Some children learn that sticking out their tongue gives them food. They can do this even when they can signal hunger in other ways.
Sticking out tongue after feeding
There are several reasons why a baby might stick out his tongue after feeding.
Satiety signal
After eating, the child may turn his head away from food or refuse to eat. Some children try to push food out of their mouth by sticking out their tongue.
Hunger alarm
There are times when a child is still hungry even if he has just eaten. This can happen during breastfeeding if the mother's milk supply is low, or if the baby has not received enough food.
Babies of different ages may show a range of signs that they are hungry.
Children under 6 months:
- open their mouth
- smack lips
- clench their fists
- crying
Children over 6 months:
- reaching for food
- get excited by the sight of food
- crying
- use hand movements to indicate hunger
Food Dislike Alarm
Some children stick out their tongues when they don't like a new food. This is normal for children who refuse new foods.
Parents should never force their child to eat. Instead, you need to continue to introduce a wide range of healthy foods. Many children have to be given food several times before they like it.
Why does a 3-5 year old child stick out his tongue when doing something?
The nervous system in children 3-5 years old is not yet particularly developed, so many children, when doing something exciting, may unconsciously stick out their tongue
When they concentrate their attention on any object (assembling a puzzle, constructor, drawing, etc.), the brain cannot yet keep track of all the processes, but this moment is the norm at this age. Over time, the baby will learn to control his body perfectly, and such situations will no longer occur.
Typically, children 3-5 years old stick out their tongue when:
Doing something diligently
If the baby is serious about doing something (draw a picture, build a house from parts, etc.), then concentrating his attention on monotonous, painstaking work, he can stick out his tongue. They can't do anything. If a child fails to do something the first time (color a picture, read a syllable, a letter), due to this overstrain the brain does not follow all the processes. Have problems with speech
In this case, when talking to the baby, you can see how he sticks out his tongue, trying to tell something. A speech therapist deals with this problem. They are capricious or show character. In this case, you need to stop the child and not allow him to make such gestures, even if they come involuntarily.
If there are no pathologies or diseases, then the problem of a protruding tongue “dissolves” by itself over time as the baby grows up.
It is advisable to combine facial muscle massage with elements of facial gymnastics. So, when massaging the forehead, the child is asked to raise his eyebrows (to give his face an expression of surprise) and with his fingers they help activate the forehead muscles to correctly perform the pose in full. In order to develop facial muscles, it is necessary to form the child’s ability to voluntarily perform differentiated facial movements and exercise control over them. To do this, in front of a mirror, children are taught to open and close their eyes, wink alternately, puff out their cheeks by moving air from one half of the mouth to the other, “draw” air under the upper lip, under the lower, etc. In this case, you can use the games “Monkeys”, “Mirror”. The most differentiated movements of the facial muscles and their full volume can be achieved when performing symbolic poses (facial expressions of “surprise”, “joy”, “sadness”, etc.). When performing these poses, children are of great emotional interest using not only illustrated children's facial expressions, but also the correlation of the proposed plots with the poetic form. This helps children correctly comprehend this type of movement, relate it to a specific situation and remember it.
To prepare the lips and tongue for static-dynamic movements, you can include elements of self-massage of the lips and tongue: suction of the corners of the mouth, alternately stroking the lips with the lips and teeth (like the “Comb” exercise). Self-massage of the tongue is carried out using the lips and teeth in 4 steps: interlabial stroking, interlabial tapping (or smacking), interdental stroking, interdental tapping. During self-massage, control should be exercised over the protrusion of the tongue along the midline.
The mobility of the lower jaw and the full range of its movements are important for the correct formation of the sound-pronunciation aspect of speech.
Considering the limited range of movements and spasticity of the muscles of the lower jaw in children with cerebral palsy, special attention in the work on the formation of articulatory praxis should be paid to the activation of the lower jaw. Work on activating the muscles of the lower jaw is best done sequentially
At the initial stage, game moments are widely used with the use of toys (dummies) “The little pebble wants to eat”, “The little bird is singing”. Then the child is asked to perform counting exercises. Holding a pose while counting helps the child not only more accurately sense and feel this position, but also remember it kinesthetically and realize it. We open, close and hold the lower jaw with the following instructions: “We know how to open our mouths: once - open your mouth wide and hold it for a count of 5.” During the exercise, the child's attention is activated to the position of the tip of the tongue at the lower incisors.
The child has his mouth open and his tongue sticking out
When to see a doctor?
A protruding tongue does not usually indicate that anything is wrong. However, some children may stick out their tongue in situations where other children would not.
You should take your child to the pediatrician if he or she frequently sticks out his tongue for no apparent reason or exhibits other developmental differences.
Any change in a child's behavior may also be a warning sign of a problem. For example, a baby who consistently shows signs of hunger immediately after breastfeeding may not be getting enough breast milk or formula. In addition, the child may have problems digesting food.
Behavioral changes that occur after a blow to the head or other trauma may signal an emergency. A child who has had an injury of any kind should receive immediate medical attention.
During the first year of the child's life, parents regularly visit the pediatrician. Parents should discuss changes in behavior and ask about signs of normal child development.
Always call a doctor if your child exhibits the following symptoms:
- constant signs of hunger, especially if the baby is breastfed
- tongue sticking out in addition to problems swallowing or
a change in behavior that has no clear cause
- signs of physical discomfort
You should go to the emergency room if your child's behavior changes significantly during or after an injury, fever, or illness.