Many new mothers begin to panic if, when pumping, they discover that their breast milk is clear. The thought immediately arises of the need to supplement the baby's feeding, since he most likely will not get enough of such a liquid suspension. Such actions lead to the end of breastfeeding, because the less the baby suckles, the weaker the milk is produced.
Features of breast milk
Each woman's milk differs in composition and organoleptic properties. It is adapted specifically for your baby. This means that if one mother’s milk is clear, and another’s milk is yellowish, then this is not yet a reason to doubt the low nutritional value of the lighter breast product.
The uniqueness and usefulness of breast milk lies not only in its nutritional value, but also in its ability to change throughout lactation. This happens under the influence of external factors, as well as with changes in the baby’s age, when his needs begin to change.
If we consider the periods during which breast milk will change in composition, color, consistency and this is considered normal, then the following stages are distinguished:
- The first stage of lactation is the appearance of colostrum. In the last months of pregnancy or a couple of hours after the birth of the baby, the most valuable suspension for the newborn appears. Colostrum is thick, has a creamy, yellowish tint, and has a viscous structure. There is little water in it, there is a high concentration of nutrients.
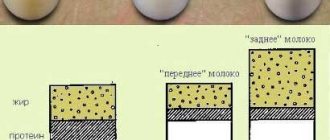
- Established lactation. It occurs within 1.5-2 weeks, with proper attachment to the breast. A peculiarity of feeding is that at first the baby eats “foremilk”; it mainly consists of water and is light in color. It is when she sees it while expressing that a woman may be concerned that her breast milk has become transparent. The most nutritious milk, most enriched with vitamins, proteins, fats and other elements important for the development of the baby, is hind milk. Now it is already thick and yellowish. The baby gets to it later, having drunk a portion of the front one, which is slightly less valuable in nutrition.
- Long-term breastfeeding, more than a year. When a child’s diet changes and new foods appear, the need for breast milk decreases, but at the same time changes appear in the structure of the breast fluid. The mother’s body adapts to the needs of the growing child and now breast milk is largely not food, but a source of immunity, vitamins, and minerals.
For each stage, changes in hue, clarity and composition are normal and should not be a cause for concern, except for sudden, painful changes during feeding.
Composition and type of breast milk
The chemical composition, appearance, and nutritional value of breast milk may vary depending on a number of factors. It should be understood that every woman’s body is individual. He responds to the needs of her child. Therefore, her breast milk is ideal for feeding her baby. And there is no need to worry about the fact that it is like water.
Breast milk changes its color and chemical composition throughout the entire period of breastfeeding and even during one feeding.
- Colostrum. This is the name of the milk that is formed in the last days of pregnancy and released in the first days after the birth of the baby. Externally it is a yellowish, thick and viscous liquid. It has great energy and nutritional value. But it contains little water. This is important to prevent overloading the child's kidneys. Colostrum also has laxative properties, thereby helping the baby get rid of meconium. Studies have confirmed its effectiveness against pathogenic bacteria. In a word, colostrum completely satisfies all the baby’s needs in the first days of life.
- When lactation is established, the milk becomes mature and its quantity increases. In the first 5-15 minutes of feeding, the baby receives foremilk. It is indeed almost transparent, like water, and is intended to quench thirst. It is this milk that often leaks from a woman and she expresses it. That’s why he often thinks that such clear milk is not beneficial for the baby. But in reality this is not so. 15-20 minutes after the start of feeding, hind milk begins to arrive. And now it is thicker, fattier and more nutritious. This is, directly, baby food. Its calorie content is 70-80 kcal per 100 ml, the amount of carbohydrates is milk - 8%, fat - 4%, proteins, vitamins, minerals - 1-3%. Feeding only breast milk is preferable for a child under 6 months. And even up to 1 year old, the baby can only eat it. This is a guarantee of its proper development, the formation of all organs and systems, protection from viruses, microbes and bacteria. As the child ages, the composition of breast milk also changes, but it always meets his needs at the moment.
- The color of breast milk can also be affected by the food a woman eats. For example, when consumed in excess, carotene becomes yellow or even orange.
From the above, we can conclude that there is no need to worry about why breast milk is like water. This is a normal process, thought out to the smallest detail by nature itself. Feed your baby on demand and for as long as he needs it. This way he will receive both drink and food.
What affects the color and fat content of milk
The shade of the breast suspension varies depending on the type of food consumed by the mother, but these differences are not fundamental. For example, after drinking carrot juice, after some time during feeding you may notice a yellowish tint. Until six months, pediatricians do not recommend that young mothers experiment with coloring products; there is a risk that the baby will develop allergies.
A woman’s nutrition is reflected in the fat content and nutritional value of milk, but a proven fact is the body’s ability to “take away” the missing nutrients from the mother’s tissues. This means that although at first glance milk is like water, it contains a complex of necessary elements. Therefore, the better the mother eats, the easier it is for her to recover after childbirth and lactation, and the baby during breastfeeding will take everything he needs from the milk himself.
The psychological state of the woman is also important, on which the quality of feeding also depends. If, due to a stressful situation, changes have occurred in the quantity and quality of milk, then you need to balance your emotional state, continue to offer your baby the breast, and the previous lactation will be restored.
What not to do
If there are doubts that the child is not getting enough to eat, precisely because the milk has become translucent, there is no need to immediately start supplementing him with formula. You can analyze your baby’s satiety by his behavior, frequency of bowel movements, urination, and weight gain. To do this, you can contact a guardian consultant or an observing pediatrician. Stopping lactation is not difficult, but it will not benefit the baby.
Having discovered clear milk, it is not recommended to take such measures as:
- Pumping before feeding in order to free the breast from the front milk so that the baby eats the back milk, which is thicker. Each layer of breast fluid has its own value for the baby’s body. Depriving him of foremilk can provoke a feeling of thirst in the baby and deprive him of a portion of water-soluble vitamins and carbohydrates.
- A radical change in diet. A lot of fatty and nutritious food will not help to instantly adjust the composition and color of milk. If there is a need for this, then you can test the value and fat content of milk, and only then take measures to create a menu.
- Taking medications that increase lactation. An artificial increase in the amount of milk can negatively affect its composition and provoke lactostasis.
Problems with milk are often far-fetched and in some cases it is simply impractical to take measures to increase thickness or change color.
Is it necessary to increase the fat content of breast milk?
Traditionally it is believed that the fattier the food, the more satisfying and nutritious it is. However, this does not apply to breast milk. In addition, milk that is too fatty causes stool problems and dysbacteriosis. If the baby is active and cheerful and gains weight normally, there is no need to worry about the quality and fat content of the milk.
If a child does not get enough milk, does not gain weight, often cries and asks for the breast, you can check the fat level. To measure indicators at home, take a regular sterile test tube. Express milk into a container after 15-20 minutes of feeding. Leave the liquid for 5-6 hours. During this time, it will be divided into two parts, the top of which will be the fattest. We measure this layer using a ruler, where one millimeter corresponds to one percent.
The average fat content is 4.5%. However, sometimes it can vary between 3.5-5%. These indicators are considered normal. Only when the fat content is below three percent should you think about increasing the nutritional value of the product. Let's find out how to do this.
When to worry
There are situations when you need not to be puzzled as to why breast milk has become clear, but to immediately take measures to preserve the mother’s health and, if possible, continue lactation.
Dangerous conditions include the following phenomena:
- Appearance of blood. The appearance of blood from the thoracic ducts requires special attention. Abrasions and injuries to the nipple can be easily treated with special means and proper application, and bleeding from the inside is a dangerous sign.
- Unpleasant odor, white and greenish clots. This is a symptom of suppuration, which is often found with mastitis. With such structural changes in milk, feeding continues; additional pumping may be required, as it is important to prevent fluid stagnation.
Women should understand that if the milk was yellowish one day and then became translucent, this is not a cause for concern, provided the baby’s behavior is normal.
The problem of changes in the nutritional value of breast fluid should not be excluded, since in some cases women may undergo various changes in the body. They may not appear visually, that is, the milk does not necessarily become transparent. The main signs of infant malnutrition and changes in the composition of milk are:
- significant underweight of the child;
- baby's restless sleep, tearfulness;
- frequent loose stools, increased gas formation.
It is correct to obtain more accurate information with the help of a pediatrician, who will help identify possible problems with guards.
Is translucent milk nutritious enough for a baby?
There is no need to think that if milk is clear, then it is low in nutrition, and therefore try to eat more fatty foods.
This unique product is precisely tailored to your child's needs. All a nursing mother needs to do is eat a balanced diet. Eliminate unhealthy foods (smoked meats, marinades, carbonated drinks, lots of sweets, chips).
Important! Breast milk changes, strictly adapting to the baby. You just need to eat right, rest regularly, and avoid stress.
Is there a normal breast milk rate?
There is no point in focusing on a certain color or consistency of breast milk for a young mother, since each woman has her own characteristics and is produced by the body specifically for her baby.
The normal color of milk is white, yellowish, with a bluish tint, creamy. Even if the milk is translucent or like water, it is rich in valuable and beneficial compounds for the baby. According to breastfeeding experts, breast milk should vary throughout the feeding period. This confirms that a woman’s body is adapting to the new requirements of a growing baby.
- Related Posts
- How to freeze breast milk and how to store it
- Why is breast milk different in color?
- How is breast milk renewed: after how many hours?
« Previous entry
What does human milk look like normally?
The transparency of milk varies from clear (almost like water), such as “foremilk”, to opaque (contains a large amount of protein, fat and has a deep white or even cream color), like hind milk.
Sometimes when storing expressed breast milk in the refrigerator, you may notice that it is clearer than before. This phenomenon can be explained quite simply. The balls of milk fat stuck together, and since fat is lighter than water, they accumulated in a single layer on top. To obtain a homogeneous white product, shake the bottle with its contents well, and the liquid will again become white and opaque.