Sweet or bitter?
The composition and consistency change over time, and this affects the taste. Colostrum is the baby's first milk, produced by the breasts before birth and for several days after. It has a high content of proteins, sodium, immunoglobulins and low content of lactose, fats and glucose.
Colostrum is saltier. It tastes similar to breast milk, which is produced during mastitis. Or when the baby begins to be weaned.
Mature milk contains lactose, the main form of sugar in this product; lactose and gives it a sweetness that babies love.
Breastfeeding then and now: obvious advantages of the modern approach
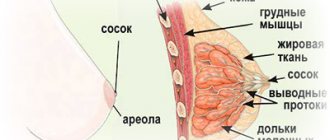
Composition and taste of milk
Mother's milk is a unique substance. Its composition is not constant and depends on:
- Child's age. At each period of a baby’s life, the nutritional composition meets the needs and developmental goals.
- Immune status. The mother supplies the child with food with bacteria and specific nutrition for them, so that the intestines are populated with beneficial microorganisms and form his immunity. When a child is sick, the mother, in constant contact with him, strokes and inhales pathogens - attacking microorganisms. Her immune system responds by producing specific defense cells that both protect her from disease and are released into her milk. In this way, the mother's body provides the child with the best possible protection.
- Stage of each feeding. At the beginning of the feeding process, the so-called foremilk is more liquid, contains more water with lactose and less fat with proteins. This is a drink because it is important to first restore fluid balance and gain energy. Then the baby reaches hindmilk - food.
- Time of day. At night, an increased amount of certain types of amino acids (proteins) is recorded in milk. They are believed to have a hypnotic effect, among other functions.
This unique food contains many substances that are beneficial for children:
- Squirrels. Required as a building material.
- Fats. Suppliers of substances for the construction of nervous, eye tissue, brain, etc.
- Carbohydrates. The high lactose content provides the child with energy, and oligosaccharides (there are tens of times more of them in human milk than in any other mammals) feed the beneficial bacterial flora of the intestines.
- Vitamins and minerals. For the full development of all organs and systems.
- Growth factors. Special substances that control the normal growth and development of internal organs.
- Hormones. Due to the immaturity of the child’s body, the normal functioning and growth of organs and systems is stimulated.
- Enzymes. Promotes digestion of food and better absorption of nutrients.
- Bacteria, etc.
The taste of breast milk is usually sweetish; there may be various deviations towards greater or less sweetness, saltiness, or even manifestations of bitter taste. The last two characteristics are considered a deviation from the norm.
Salty or bitter milk can cause the baby to turn away, drop the breast, and become capricious.
Sweet
Due to the high content (about 7% on average) of lactose, milk should be sweet. This compound is also present in animal milk: the familiar light sweetness of cow's milk is its influence. Lactose in the intestines breaks down into glucose and galactose, which supply energy to cells, especially the rapidly growing brain.
The level of lactose in a woman's milk is not particularly dependent on her diet and is relatively constant. Therefore, mothers should not indulge in sweets during the feeding period, especially if it is important to lose excess weight.
The sweet taste is also supported by oligosaccharides - substances that are not digested by the child’s body, but they are needed to feed beneficial microflora. This bacterial component of the intestine helps digest food, builds immunity, and produces additional substances beneficial to the body. For example, some B vitamins.
Salty
The taste of human milk can be affected not only by food, but also by medications and breast diseases. In particular, breast congestion and mastitis can make the child's only food salty. There are other reasons why breast milk tastes salty. The best person to deal with this is the baby himself. It is capable of dissolving lumps: it is important to apply it specifically to the problematic lobes of the breast during feeding.
Milk may become salty during the period when lactation ends naturally due to the increasingly slow renewal of the contents of the mammary glands. Nature has provided such a mechanism to easily complete the breastfeeding process for both mother and child.
Bitterish
Sometimes mothers notice that breast milk has become bitter. Radishes, radishes, garlic, teas containing natural bitterness, seasonings with a strong taste and other food products can cause it to acquire a bitter taste. Also, we must not forget about drugs that penetrate into milk along with their inherent bitterness. In any case, this is a temporary cause that can be easily eliminated by adjusting the diet or consulting a doctor if we are talking about medications.
Why does milk become sour?
Milk has a completely different taste if it is fresh, “from the tap.” For some mothers, it quickly sours and becomes like spoiled cow's milk.
There are several reasons why your milk smells bad. Most often, they are associated with the breast pump and storage conditions.
It is extremely important to thoroughly clean the parts of your breast pump. Improper cleaning of the pump can result in milk contamination and altered taste. It is recommended to store your baby's food in polypropylene or Pyrex containers rather than in plastic bags. This way you minimize the loss of any nutritional components.
Source: Freepik
What foods should be included in a nursing woman's diet?
The daily calorie intake for a young mother is 3000-3200 calories. This is enough for both mother and baby - the energy expenditure for one breastfeeding is 500-800 calories , the rest will serve as energy for the mother herself. But exceeding the norm can provoke hypogalactia - a decrease in the amount of breast milk until it disappears.
To ensure that the baby and mother feel good, pediatricians recommend that nursing women adhere to the 1-1-4 rule - this is the ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and consume healthy foods in quantities sufficient for two.
Healthy foods in the diet of a nursing woman:
- Lean fish (protein, vitamin D).
- Dairy and fermented milk products (protein, calcium).
- Liver (folic acid).
- Cereals (millet, oatmeal, buckwheat – vitamin B1).
- Cottage cheese, cheeses (vitamin B2).
- Butter, eggs, pork, beef liver (vitamin A).
- Carrots, greens (beta-carotene).
- Red bell pepper, currants, sea buckthorn (vitamin C).
- Walnuts (increase the fat content of milk, making it more nutritious).
Pediatricians strongly recommend including foods rich in iron in the mother’s diet (liver, meat, eggs, figs, blueberries, black currants, buckwheat).
You should also not forget about the rules for taking fluids: the daily fluid intake for a nursing woman is no more than 2 liters. Excess fluid impairs the properties of breast milk, making it watery and diluted.
My child doesn't like the taste of milk
Another cause of sour taste is the enzyme lipase. It can also make your milk “soapy” or give it a fishy taste. Because of this, children often refuse to feed.
But don't worry. The enzyme is completely safe for the child and, moreover, you can neutralize it by simply scalding the milk.
How to do it:
- Pour your breast milk into a saucepan (immediately after pumping) and heat gently until tiny bubbles form around the edges. If you have a way to measure the temperature, preheat to 72°C.
Note: Do not bring the milk to the boiling point as this will damage important immunological factors. Do not put milk in the microwave.
- Immediately pour the milk into a container with ice and cold water and place it in the refrigerator. Use within 2 days.
Your baby won't feel the difference.
Well-fed and happy: 9 funny photos of babies after feeding
Harm of smoking while breastfeeding
19.02.2021
6231
0
Not all nursing mothers think about the dangers of smoking while breastfeeding. However, this mother’s addiction causes enormous harm to the child’s health.
If during pregnancy most women who smoke try to give up the bad habit, then after childbirth many mothers remove this restriction. But after the birth of a child, his connection with his mother does not stop. Harmful substances consumed by a woman reach the baby through his natural food - mother's milk. In addition, the child is not protected from inhaling cigarette smoke if the mother smokes in the same room where the baby is. Not everyone thinks about the dangers of smoking while breastfeeding. However, this mother’s addiction causes enormous harm to the child’s health.
Are temporary pleasures really higher than the health of the baby? There is a fairly widespread belief that smoking is compatible with breastfeeding. The following fallacious arguments are usually given in favor of this:
- Milk has the ability to neutralize harmful components. This is far from true. The value of milk is undeniable, but all the substances entering it are passed on to the baby, including nicotine.
- Nicotine is broken down in the body of a nursing woman and does not enter milk. Research shows that the amount of nicotine found in breast milk is 2.9 times greater than that found in mother's blood plasma. In addition to nicotine, cigarettes contain harmful compounds and tars that negatively affect the baby’s body.
Smoking reduces lactation by 25%. Both taste and smell change, as with the consumption of alcoholic beverages, garlic, and spicy foods. If a woman is unable to quit smoking, the number of cigarettes smoked per day should be reduced to a minimum. At the same time, experts do not recommend giving up breastfeeding and switching the baby to artificial feeding. In any case, breast milk is healthier for the baby than ready-made milk formulas.
Smoking has a direct negative effect on the functioning of the mammary glands. Nicotine disrupts a woman's hormonal balance, which changes after childbirth. It reduces the formation of prolactin and oxytocin, hormones that stimulate lactation. If a mother smokes from the first days after childbirth, the likelihood of stopping the secretion of the mammary glands increases, and the amount of valuable components in the milk itself decreases. Addiction to nicotine also negatively affects a woman’s psychological state. A smoking mother should be prepared to breastfeed her baby for no more than six months.
The relationship between smoking, demographic variables and breastfeeding status at 8 weeks postpartum was examined in 510 women. 400 of them gave birth to full-term babies, and 110 gave birth to low birth weight babies.
Even if the mother smokes in an isolated room, the baby is not protected from the effects of nicotine. Harmful substances are absorbed into a woman’s blood and then enter the milk.
Thus, the body is completely freed from nicotine after 4 hours. This period increases if the woman has kidney problems. But the unpleasant taste of milk remains, even if there is no nicotine in it.
A woman is not recommended to be near her child wearing clothes in which she smoked. Those mothers who smoke frequently constantly give the baby nicotine along with their milk. This has an extremely negative effect on the baby. Possible consequences of smoking:
Impaired proper functioning of the heart. Nicotine leads to vascular spasms. As a result, the normal rhythm of the child’s heart is disrupted, and an acceleration of the heartbeat is observed. Subsequently, the child may develop heart failure.
Increased likelihood of sudden death of a child , sleep apnea: 5 times - if both parents smoke, 3 times - if the mother smokes.
Negative effects on the gastrointestinal tract. A child of a smoking mother is susceptible to frequent intestinal colic. In children whose mothers lead a healthy lifestyle, colic is rare. The baby's liver is not able to cope with the nicotine load. Intoxication may develop, accompanied by vomiting, nausea, and loss of appetite.
Decreased appetite causes problems with weight gain. Three factors play a role in this: the unpleasant taste and smell of milk, poor liver function, and decreased lactation. The underdeveloped microflora of children's intestines is even more inhibited under the influence of nicotine. This manifests itself in the inability of the intestines to fully absorb the nutrients of milk. It takes a very long time for nicotine to be eliminated from the body: the excretory system of a newborn is not yet fully formed.
Nicotine also affects the child’s respiratory system . The protective functions of the respiratory epithelium are reduced, and respiratory tract diseases often occur.
Moms, remember that the health of your future children lies in a healthy lifestyle!
Does taste depend on what you eat?
If you express breast milk and feel that it tastes or smells sour, the food you are consuming may be the cause.
You can control the quality of your breast milk by avoiding certain foods.
Some of them:
- Garlic
- Anchovies
- Certain nuts (Brazil nuts are known to rot easily)
- Expired vegetable oils
- Fish fat
- Flaxseed supplements.
Truths and fictions about breast milk
We hasten to reassure young mothers: your milk, no matter what you think about it, is the most suitable for your baby! To satisfy the research interest of doubting mothers, we will try to understand the most common questions and misconceptions about breast milk.
Three ages of breast milk
“I have no milk! — I complain to my mother on the second day after giving birth. “What should I feed the baby?”
Everything goes according to the laws of Nature. In the first 2-4 days after birth, the mother's body secretes colostrum. Then colostrum is replaced by transitional milk, and from 8-14 days mature milk is finally produced. Having looked at the plate about the components of breast milk, we will get answers to many questions.
Notice how concentrated (which is why it appears yellower) colostrum is: it has several times more protein than mature milk. Accordingly, colostrum is higher in calories. This explains the fact that a newborn baby needs a very small amount of colostrum, only 1-2 spoons a day, if, of course, you measure it by spoons. That's how much of it stands out. And mothers think that it should flow like a river!
Transitional milk is like an intermediate stage both in terms of arrival time and calorie content.
“My milk is kind of watery! — say mothers of 1.5 month old children — “It used to be thick, almost orange!”
There is no need to compare mature milk and transitional milk. The protein content in mature milk is small - only about 1g per 100 grams of milk. Moreover, the proteins in human milk are on a downward trend: the older the child, the lower the protein content.
Why? In nature, everything is for a reason. Let’s think about it for ourselves: the growth rate of a child is decreasing all the time, which means that less and less protein is needed to build body cells.
For color lovers
The presence of a blue or milky tint in mother's milk is explained by the fact that during one feeding the milk is not uniform. At the beginning of feeding, when the mother feels a “tide” and there is a quick return, the baby receives the so-called “foremilk”. Towards the end of feeding, when many mothers feel that the baby is already sucking on an “empty” breast, “hind” milk is released at a much slower pace. Sometimes the terminology is slightly different - “early” and “late” milk, but the essence does not change.
Foremilk contains more water (that's why it appears almost clear!), milk sugar (lactose), while hind milk contains more fat (that's why it's white) and enzymes that help digest the milk. This fact is worth taking into account.
Because this is why: • It is recommended to change breasts after about 2-2.5 hours so that the baby gets to the hindmilk. • There is no need to express after feeding (unless, of course, there are special indications), because in this case the fatty hind milk does not reach the baby, but is poured out. • Fatty hind milk acts as a satiety regulator, which is why the baby falls asleep so sweetly, snoring at the breast, and the mother sometimes thinks that the baby is mocking her and using the breast as a pacifier.
Shelf-life Unlimited
“Stop feeding! - mothers of 11-12 month old children hear more and more often. “There’s nothing in your milk anymore, just water.”
So nothing? Milk contains more than 400 components - this is not a reason to think that there is “nothing” there.
According to the World Health Organization, breast milk continues to be a source of all necessary substances for the child after a year, in addition, it supplies enzymes that help the child digest foreign food. Few people know that mother’s milk is very valuable for a growing baby from the point of view of immunological prevention. Milk is a kind of vaccination, against all diseases at once, and also has no contraindications.
The fact that expressed milk does not spoil for at least 12 hours at room temperature indicates that the milk contains a high content of “good” bacteria that suppress the growth of pathogenic ones. Isn’t this useful for a baby who puts everything in his mouth, barely learning to walk?
Unfortunately, very, very few mothers feed their babies before the so-called “involution of lactation.” This period begins after 3 years (or a little earlier). The baby is rarely put to the breast, the volume of milk is small, but the composition of the milk is close to colostrum in its high content of immunoglobulins, which means that such milk protects both the baby and the mammary gland itself for a long time.
Mother's temperature does not spoil milk
Many people have heard that you cannot feed a child if the temperature is more than 38.5 degrees. Therefore, when Olesya came down with a cold and fever, the child was switched to formula. True, it was too tiring for her to get up and administer this mixture, and even in her chest there was stagnation of milk from overflow.
Olesya’s fears were completely unfounded. Milk could not harm the child. During a mother’s illness, antibodies to her illness appear in the milk, so the baby receives protection through the milk. Even if the child does get sick, the mother’s body helps him cope with the disease faster. Contrary to misconceptions, milk from a mother with a fever does not sour, burn out or spoil. If this were so, then humanity would have died out long ago, because mothers sometimes get sick, and in nature there is no bottle of formula that replaces breast milk.
Milk always tastes good if it’s your mother’s!
“My baby doesn’t like my milk,” some mothers complain
One of the greatest advantages of breast milk is the ability to provide your baby with a palette of different tastes: the more varied your menu is, the more taste sensations your baby gets. Some products, such as garlic, onions, melon, herring and others, add some piquancy to the taste of milk. Eat them in small quantities and it most likely won't bother your baby.
Often mothers complain that babies refuse to breastfeed after engorgement or lactostasis. Indeed, milk may slightly change its taste: it becomes saltier due to a temporary increase in the concentration of sodium salts. There is nothing dangerous for the baby; the mother should be persistent and put the baby to the breast.
Milk cannot cause allergies
It’s a pity that mothers needlessly blame themselves because their milk is not suitable for their babies. An allergy is a peculiar reaction of the body to a foreign protein. And mother's milk contains the same cells from which the baby's body was formed - it is suitable for the child, like a key to a lock. In the vast majority of cases, allergens penetrate into milk from products that the mother consumes, for example, cow's milk, chocolate.
By the way, you shouldn’t completely give up such foods: by consuming them a little at a time, you gently prepare your baby for complementary feeding and for the transition to the common table.
What else affects the taste of breast milk?
Sometimes these are medications, such as antibiotics. This does not mean that breastfeeding mothers have to “pump” if they are taking medications. Your doctor will help you determine whether your medications are affecting your milk.
Exercise can cause you to sweat, which can give your skin a salty taste. After intense exercise, lactic acid can also accumulate in breast milk; it also affects the taste. There is no evidence that this acid is harmful to infants.
Aroma is another reason why the taste of milk may change. The use of perfumes, creams or body lotions is not always pleasant for babies.
Source: Freepik
What does taste depend on?
Many foods and bad habits can affect the taste of breast milk, and your baby may not like it. During pregnancy, the baby gets used to the foods that the mother consumes daily, so you shouldn’t suddenly change your eating habits.
Products that change the taste of mother's milk:
- Onions and garlic increase the baby's appetite.
- Sugar makes milk sweet, and not all children like it.
- Vanilla affects the smell of milk. Mothers really like this, but children are neutral about it.
- Cinnamon also adds flavor.
- Pepper adds a bit of bitterness and is often perceived negatively.
- Cumin, curry, basil may not be to your taste.
- Mint in large quantities adds bitterness.
- Radishes and radishes will also make the milk bitter.
- Pumpkin gives a sweet taste and your child will really like it.
- Zucchini, potatoes, cabbage make milk more bland.
Habits and conditions that change the taste of mother's milk:
- Sport. We must try not to do heavy loads during the lactation period. This will affect both the taste and quantity of milk.
- Medicines. They can change the taste for the worse. But this does not mean that the baby will refuse breastfeeding.
- Alcohol and smoking. These two habits should be abandoned during pregnancy and lactation. Alcohol and nicotine not only affect the taste and smell of milk, but also have a negative effect on the child’s health.
- Freezing breast milk. In rare cases, the baby may refuse it due to the “soapy” taste.
- Mastitis and lactostasis. Gives a salty taste. In these cases, it is better to contact your doctor.
- Cosmetic preparations. Before feeding, you should try not to apply creams and gels to the breast area. It also changes the taste for the worse.
New foods are introduced into the mother’s diet gradually, while carefully monitoring all the child’s reactions.
Human milk is an indispensable product for newborns, especially in the first weeks of feeding.
There is not a single complementary food that can also adapt to the child and fully transfer all the vitamins to the baby. And he will definitely like the taste, unless his culinary preferences change dramatically.
What does milk taste like during pregnancy?
Interestingly, a pregnant mother begins to produce colostrum at around 16 weeks. This first milk is all your baby needs immediately after birth. It is high in sodium, antibodies and protein, making it less sweet than the ripe variety.
Breast milk from mothers who gave birth prematurely has slightly different properties. This helps protect premature babies as they are much more vulnerable, especially if they are NOT breastfed.
Surprisingly, if you become pregnant while breastfeeding your older baby, your breast milk will become similar to colostrum later in pregnancy. It will turn from sweet to salty. Some children will not object, others will refuse to eat. But those who remain breastfed will be able to receive additional immune protection.
What's in the plate: myths and truths about diets for nursing mothers
What does breast milk taste like?
Normally, the nutritional liquid should be slightly sweet. This is due to the high sugar content in it. Many women compare the taste of their milk with the taste of diluted condensed milk (if you dissolve 1 teaspoon of the product in 1 glass of clean water). Sometimes the liquid resembles a sweet protein shake that athletes use to build muscle mass.
If there are no sharp deviations in the mother's diet, milk does not have strong flavors. It leaves a pleasant aftertaste. The predominance of creamy taste indicates a high fat content.
Many women report a salty taste to their milk. This may be due to the increased content of table salt in it. In some cases, it begins to taste bitter, causing anxiety in both mother and child. If the milk has acquired a bitter taste, this does not mean that breastfeeding should be stopped. It is better to try to find out the reason for the change and eliminate it.
Is it good for adults?
Those who have read this far understand the undeniable benefits of breastfeeding for babies. Milk has amazing properties such as stem and immune cells, and is a complete nutrition that changes as the child grows. Your breast milk is so amazing that it can detect pathogens in your baby's saliva and produce antibodies to fight disease and infection.
However, for adults, breast milk has no benefits that they could not get from a normal, healthy diet. In fact, if it is used in place of a well-balanced adult diet, it can become harmful.
It has become fashionable for bodybuilders to buy breast milk on the black market for consumption. However, purchasing from an unknown source carries a huge risk of viruses, bacteria and contamination. It seems best to reserve breast milk for feeding babies.
When else does taste change?
Mom's diet is not the only factor influencing the taste of milk.
- Hormonal status. All changes that occur in a woman’s body affect the taste of milk. These include periods of menstruation, new pregnancy.
- Sports activities. If a woman engages in intense sports during breastfeeding, lactic acid begins to accumulate in her body. In addition, sweating increases, which affects the smell and taste of milk in a negative way. Therefore, during the feeding period it is recommended to avoid increased exercise.
- Taking medications. Some medications can also worsen the taste of milk. If a woman notices that the baby has stopped eagerly suckling at the breast, and the duration of feeding has decreased, then you should pay attention to what medications the woman takes during this period.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages. The alcohol contained in alcohol passes into breast milk, making it extremely unpleasant for the baby. Therefore, after drinking even a glass of wine, you should not immediately put your baby to your breast. It should take at least two hours.
- Smoking. A special study was conducted which showed that a smoking nursing mother will have a specific taste of milk. Therefore, the baby may refuse such food. If a woman cannot quit smoking, then it is better to do this only after feeding.
- Use of certain cosmetics. If a nursing mother, during the period of breastfeeding, intensively lubricates her mammary glands with lotions, various creams and oils, and uses eau de toilette liberally, then all this can affect the taste of the milk. It is recommended to wash off applied cosmetics from the surface of the skin before each feeding.