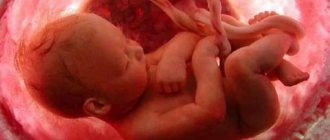
The growth and development of a baby in the mother’s womb occurs without the conscious participation of a person, and it is almost impossible to influence this process. Nature has provided everything that the baby needs - he is warm, protected from external influences, receives nutrition and grows together with his “house”. One of the baby’s key needs is oxygen saturation of the blood. In order for the fetus to be provided with life-giving gas, its mother’s body has a whole respiratory system.
Mother-placenta-fetus system
To understand how a baby breathes in the womb, it is important to know that the baby’s respiratory system matures before the seventh month of intrauterine development. Up to 12 weeks, the embryo feeds on the reserves of the yolk sac, and from 13–14 weeks, until the moment of birth, the developing fetus feeds and breathes through the placenta. This organ performs many tasks, one of which is to prevent the blood of mother and child from mixing.
The placenta consists of dense villi, deeply rooted in the wall of the uterus. The villi constantly communicate with the uterine vessels, receiving nutrition through them. The baby extracts oxygen from the outside through the hemodynamic (i.e., caused by the movement of blood through the vessels) “mother-placenta-fetus” system. In this case, metabolic products and carbon dioxide molecules are transferred in the opposite direction. This means that in the placenta there are simultaneously two interconnected blood flows - mother and child.
Placenta
The placenta is the whole world for a little person, because it not only allows him to breathe, but also provides him with nutrients. It also performs the functions of removing carbon dioxide and other waste products.
If we consider the process of breathing through the placenta, it looks like this. The placenta and umbilical cord contain a large number of vessels, veins and 2 arteries. It is through them that blood enriched with oxygen is supplied, and through the veins there is an outflow of carbon dioxide.
In order for a sufficient amount of oxygen to reach the baby, a woman should walk more in the fresh air . Parks are best suited for such walks.
You should also avoid places where the air is particularly polluted with harmful substances. After all, when they enter the body of a pregnant woman, they also penetrate to the child. This could worsen his health.
If there is a lack of oxygen, the baby may develop chronic hypoxia. This is a very serious condition in which oxygen starvation occurs. With such a long-term condition, the formation of important organs in the fetus may be disrupted, and some systems may begin to function incorrectly. However, a growing child in the womb is able to accumulate the necessary amount of such an important component not only for breathing within a couple of minutes.
Structure of the placenta
In other words, he stores it for future use. But, nevertheless, this does not mean that the development of such a condition can be allowed. The main danger is that if some systems malfunction, the baby seems to go into energy-saving mode. At the same time, the formation and growth of all organs slows down, and in this case they are not able to survive.
The placenta is a special organ. It can compensate for the lack of useful and necessary components even when there is a deficiency in the mother’s body. This occurs due to the accumulative function.
Around the 35th week, a substance called surfactant begins to be produced. It allows you to open up your lungs at birth and take your first independent breath.
Why does the fetus need oxygen in the womb and how does it get it?
All living organisms on our planet need oxygen to function. This chemical element is transported to every cell through blood circulation. Oxygen plays a key role in the process of biochemical reactions - it oxidizes nutrients supplied by the blood and synthesizes ATP (adenosine triphosphoric acid). ATP is the main supplier of energy in the human body, and without it the life of any creature is impossible.
We get oxygen from the air and in the process of breathing we saturate our blood with it. The fetus, while in the mother's belly, also breathes. In this case, the vital chemical element reaches him through the placenta through the main artery of the umbilical cord. In this way, gas exchange occurs between the body of a woman and her child. At this time, the baby’s respiratory system is forming, the lungs are just getting ready to perform their main function.
What is the baby doing in the mother's belly? 15 interesting things
Nine months locked up - now this may seem like real hell to some. But the future baby spends this time very excitingly.
He is busy with important work: growing, forming body systems, learning to hear, control his body, mastering skills that will be useful to him immediately after birth, for example, sucking. The baby sleeps, eats, moves, and even has fun. We have collected all the most interesting things about what a baby does in the womb.
Learns to listen
As strange as it may sound, the womb is the baby's first learning environment. In utero, a little person learns to hear and distinguish sounds and voices. The baby recognizes his mother's voice immediately after birth. And if his dad sang songs to him and read fairy tales, then he did too. There are studies that say children are able to differentiate between languages; the one that mom speaks is distinguished from others.
Playing
What can you play in such a limited space, and even alone? Yes, whatever. The baby can play with the umbilical cord, with his own arms and legs, and fingers. Sometimes the mother even feels it - like a child tugging at the umbilical cord. And if there is more than one in your stomach, then there are even more creative ideas for games.
hiccups
Doctors still don’t know why this happens. But it’s a fact: children hiccup, and sometimes so intensely that the mother feels it too. Sometimes intrauterine hiccups can be an alarming symptom, in which case you need to consult a doctor.
Breathes
How do children breathe in their mother's belly? Of course, through the umbilical cord - it supplies them with oxygen. But at the same time, the baby trains his still immature respiratory system: he imitates inhalations and exhalations, drawing amniotic fluid into his nose. Therefore, after birth, fluid may come out of the baby's nose.
Sniffs
A child's sense of smell develops long before birth. Scientists say that he is able to distinguish the taste of the food his mother eats. If she loves onions, then the baby will also love them with a high degree of probability. The baby may even smell smoke if someone smokes near the pregnant woman. Therefore, you should stay away from people with bad habits.
Yawns
This was captured on an ultrasound - yes, the baby is not only sleeping and awake, but also yawning, just like a big man. Moreover, this does not mean that the child wants to sleep at this time. Scientists tend to believe that yawning is associated with the development of the infant's nervous system. The closer the due date, the less the baby yawns.
Makes faces
The development of facial muscles is a delicate matter. By the third trimester, the baby will have already mastered 19 facial movements. There is only one way to learn how to control your facial muscles - try. This is what the child does - he makes faces while no one sees him. Except for the ultrasound specialist.
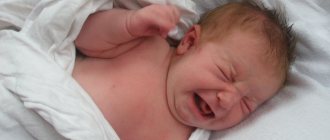
Crying
This whining expression on a tiny face cannot be confused with anything - yes, the baby is crying, albeit without tears. In addition, scientists managed to capture the sounds that the baby makes. And yes, these are sobs muffled by amniotic fluid. But researchers have not yet found out the reasons for intrauterine crying.
Thumb sucking
If you manage to catch this moment on an ultrasound, it will immediately become clear whether the baby will be left-handed or right-handed. In most cases, it starts in utero. And by sucking a finger, babies calm themselves down, then the finger will replace the nipple.
Feels the taste
Taste buds on the baby's tongue are formed already in the ninth week of pregnancy. So it’s in vain for mothers to think that for the first time he tastes food when she offers the child vegetable puree. Swallowing amniotic fluid, the baby tastes what his mother is eating. That's when his favorite dishes appear.
Dreams
It would seem, well, what can a child dream about when he has not yet seen anything - literally. He wasn't even born yet! However, studies claim that babies do dream: they go through the REM sleep phase, as evidenced by their eye movements. But what these dreams are about is unknown.
Dancing
As the future baby learns to control his movements, he learns to move to the rhythm of the music. Yes, of course he hears her. A child's musical taste is formed based on what songs he hears most often while in the womb. Babies are generally musical by nature.
Responds to strokes
If you pat your belly, your baby will knock back. This won't happen every time, but still. This ability of the child is the basis of haptonomy - a method of teaching mathematics even before birth: knocking on the stomach several times, and then counting how many times the baby will do the same, but from the inside.
Feeling themselves
This is the only way for a baby to become aware of his body. So he finds out that he has arms, legs, he touches his face and, in general, everything he can reach. This is necessary to study yourself.
Feels stressed
First of all, the one that mom feels. Scientists have even discovered a pattern: the more often a child touches his face with his left hand, the greater the stress that both mother and baby experience. But this can affect the growth and development of the child, even his tendency to depression in adulthood.
What happens to a child when there is a lack of oxygen?
If the baby in the womb experiences a lack of oxygen, this can cause disturbances in the process of its growth. The main danger is the development of hypoxia - a condition when organs and tissues do not receive enough oxygen. Hypoxia can be chronic, and at first it is compensated by the child’s body’s own resources, then a number of pathologies begin to develop. Among the most severe are disorders of the central nervous system and brain functions. An acute lack of oxygen can cause asphyxia, cause suffocation, and lead to death.
Prevention of intrauterine oxygen starvation
To ensure that your baby does not experience a lack of oxygen, it is important to follow the recommendations of the gynecologist. Basic rules that a pregnant woman must follow:
- Spend at least two hours a day outdoors. Hiking in the forest, park, and near natural reservoirs is good.
- You should not spend a lot of time immobile (unless specifically recommended by your doctor). During movement, the blood is more efficiently saturated with oxygen, and the mother gives the baby the right amount of life-giving gas, the fetus breathes fully.
- It is important to periodically ventilate the room, especially before going to bed.
- Quit smoking completely and do not be near a smoker.
- Regularly visit an obstetrician-gynecologist, take tests, undergo an ultrasound. Timely detection of circulatory disorders or placental abruption and competently prescribed therapy guarantee the absence of negative consequences for the child.
Umbilical cord
The umbilical cord is a kind of transport channel that transfers all the necessary nutrients and oxygen to the baby.
It also removes all waste products in the opposite direction.
The placenta and umbilical cord work as one unit, thanks to which the fetus is supplied with all the substances it needs.
With an incorrect (unhealthy) lifestyle of the expectant mother, the placenta and umbilical cord begin to age prematurely.
In this case, they begin to function defectively, and nutrients begin to flow to the fetus in a smaller volume.
What can trigger premature aging of the placenta:
- smoking (active and passive);
- severe, prolonged stress;
- some medications if taken incorrectly.
To prevent such an unpleasant and detrimental phenomenon for the fetus, you should avoid people who smoke, give up this habit personally, walk more in the fresh air, try not to be nervous and not experience stressful conditions. You should also eat properly, fully and take the necessary vitamin complexes. As a rule, they are prescribed by a gynecologist taking into account the needs of the body of the woman carrying the baby. It is also necessary when taking any medications to take them only with the permission of a doctor and strictly follow the instructions for use.
The umbilical cord is a full-fledged link between mother and child. Through it, oxygen and nutrients are exchanged, and it also removes carbon dioxide and other metabolic breakdown products during fetal development.
When does the baby begin to breathe through the lungs and how does this happen?
Until the moment of birth, the fetal respiratory organs are only preparing to perform their functions. It is known that the baby inside the fertilized egg makes movements that simulate inhalation and exhalation. At the same time, he draws in amniotic fluid with his nose, which does not reach further than the nasopharynx. This process is clearly visible in the video, and it may seem to the mother that the baby is hiccupping.
According to various estimates, the baby’s lungs are finally formed at 34–37 weeks of intrauterine life. By this time, the placenta is aging, its resources are depleted, and by the end of the period it can no longer fully function. The respiratory organs of the fetus are filled with a special substance - surfactant, which is necessary for breathing. The baby will take its first breath only after birth, which can occur at 38–42 weeks of gestation.
How do babies born prematurely breathe?
There are situations when labor begins ahead of time, some time before the planned date.
The baby is not ready, but due to certain circumstances he is forced to leave his mother’s warm and cozy tummy. But he has not yet “ripened”; his respiratory system is not ready to work independently. What do you do in such cases? The baby's lungs are ready to take their first breath at about 34-36 weeks, not earlier, the lung tissue is fully formed, the lungs have surfactant - a substance that helps them open and function in the future.
Babies born prematurely are forced to be placed in a special box, providing conditions close to intrauterine conditions, and connected to an artificial respiration apparatus, introducing medicinal stimulants for the maturation of surfactant and lung tissue.