A child is allergic to cereal: what is the reason?
Until the age of six months, a child usually has enough breast milk. However, as the baby grows up, it becomes insufficient, therefore, starting from 4-6 months, it is customary to supplement the breastfeeding menu with the introduction of complementary foods. Usually, as additional food, infants receive complementary foods in the form of vegetable and fruit purees, as well as porridge.
The transition from mother's milk to more “adult” food is often accompanied by unpleasant moments. Allergy to cereals in infants is a fairly common phenomenon.
One of the reasons for the appearance of such an allergy is the use of whole cow's or goat's milk when preparing porridge. Hypersensitivity and allergies to milk protein are particularly common, particularly in formula-fed babies.
Due to the risk of developing allergic reactions, most pediatricians recommend avoiding early complementary feeding using dairy products. Doctors advise cooking porridge not with milk because of the risk of allergies, but with water.
Another prerequisite for the development of allergies is intolerance or hypersensitivity to gluten and gliadin, contained in many cereals. If you are intolerant, gluten has a special effect on the intestinal villi, which can result in flatulence, abdominal pain, lethargy and apathy, headaches, increased skin sensitivity, itching, sore throat, and rashes.
In the intestines, plant protein is broken down into amino acids. But since the baby’s gastrointestinal tract is not yet fully formed, an insufficient amount of enzymes necessary for the high-quality digestion of gluten and gliadin is produced. This is why complementary feeding should start with gluten-free cereals. These include corn, buckwheat, and rice.
Cereals contain a large amount of fiber. Coarse plant fibers normalize and stimulate intestinal function, but in some cases (for example, in childhood) they can cause digestive problems. It is for this reason that children should not be given whole grain cereals, coarse oatmeal, or barley.
Dried fruits and candied fruits are often added to children's dry cereals, which can also cause allergies. Therefore, it is advisable to start complementary feeding with cereals without fruit additives - this is especially true for citrus fruits, apples, strawberries, raspberries and exotic fruits.
Despite the fact that sugar is a carbohydrate and not a protein, its content in baby cereal can also be a prerequisite for the development of allergies. The presence of sugar in foods leads to increased fermentation and putrefaction processes in children's intestines. Because of this, it is recommended to take cereals marked “sugar-free” for complementary feeding.
What causes this reaction
An allergy is an inadequate immune response to naturally safe molecules.
The body’s defense system becomes overly cautious and evaluates every new substance entering the body with particular predilection.
Proteins are the most suspicious because their molecules are larger than the others. An error in the immune system in identifying a harmful substance can have various consequences - from mild illness to hospitalization. It all depends on the intensity of the reaction.
Allergic pathology is not characteristic of every person. For a disease to appear, several factors must come together. If the body is stable, it will take a lot of external stimuli to shake it. If he is not distinguished by endurance, just one external reason is enough.
Key factors causing allergies:
- heredity;
- weakened immunity due to past illnesses;
- abnormal consumption of an allergen product;
- serious psychological and physical stress;
- hormonal changes;
- physiological impairment due to age or chronic changes;
- unstable environmental situation.
Allergy to porridge: symptoms
Depending on the general state of health, the level of immunity, living in an environmentally favorable or unfavorable region, as well as heredity, signs of allergies may have varying degrees of manifestation. For some people, the atypical reaction may be limited to mild redness of the skin, while for others the problem takes on more serious forms.
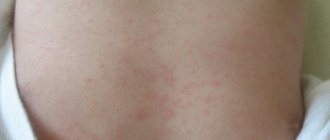
Symptoms of a porridge allergy include the following:
- small rashes on the skin, which eventually combine into larger spots;
- in some cases, weeping erosions may appear at the site of the rash;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- itching and skin irritation;
- dryness and flaking of the epidermis;
- swelling of the skin (sometimes angioedema);
- stomach ache;
- bloating;
- problems with bowel movements;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- the appearance of allergic rhinitis;
- sneezing;
- cough.
Diagnostics
For treatment of a disease to be effective, its cause must be established.
To do this, you should contact an allergist and undergo a thorough diagnosis.
To identify an allergic reaction to buckwheat, the doctor prescribes laboratory and instrumental tests.
Most often, allergological and provocative tests help identify the allergen.
Skin testing may also be used. An elimination diet is also an informative method.
If there is a suspicion of the development of a true allergy, allergy tests should be performed and an immunogram should be done.
If the doctor believes that the patient suffers from pseudo-allergy, an examination of the internal organs and an assessment of metabolic processes are indicated.
Rashes need to be differentiated from various diseases - atopic or cutaneous dermatitis, neurodermatitis, eczema.
The main method of treating this disease is to completely avoid contact with the allergen. If you are allergic to buckwheat, the main principle of treatment and prevention of the disease is to avoid consuming it.
If the manifestations of the pathology are not too pronounced, then the use of medications is not required.
For allergic rhinitis and severe skin rashes, antihistamines should be used:
- Tavegil. This remedy is used in tablet form. Adults can take 1 tablet maximum 4 times a day. It is recommended to do this before meals, washing down the drug with water. Patients 6-12 years old should take half a tablet twice a day. Children 1-6 years old are prescribed medicine in the form of syrup. Dosage – 1 teaspoon twice a day.
The drug is contraindicated for children under one year of age. Also, women should not drink it during pregnancy and lactation.
- Suprastin. This drug should be taken at a dosage of 25 mg after meals. Adults are prescribed 1 tablet 3 times a day, and children under 14 years of age need to take half a tablet, after crushing it into powder.
- Zyrtec. For adults and children over 6 years of age, the doctor prescribes tablets. Daily dose – 1 tablet. It should be washed down with water. For children from six months to 6 years old, Zyrtec is prescribed in the form of drops.
Babies 6-12 months old should be given 5 drops of the drug once a day, children 1-2 years old should be given 5 drops twice a day. Children 2-6 years old can take 5 drops twice a day. Patients of this age can also be given 10 drops of syrup once a day.
- Diazolin. This drug is taken after meals. Adults and children over 12 years of age can drink 0.05-0.2 g of medication twice a day. Children under 12 years of age need to drink 0.025-0.05 1 to 3 times a day - it all depends on the severity of the disease.
The use of such drugs is indicated until acute manifestations of allergies are eliminated.
It is worth considering that each antihistamine provokes the appearance of unpleasant symptoms in the form of increased drowsiness and a feeling of dry mouth.
Many people complain of dizziness, lethargy, and increased dryness of the nasopharynx.
Sometimes vomiting, nausea, and pain in the stomach occur.
Various ointments can be used to treat skin rashes. These include:
Zinc ointment or desitin is also prescribed.
In particularly difficult cases, the use of hormonal drugs is required.
To speed up the process of removing allergens from the body, sorbents are used.
But most often, antihistamines are sufficient.
Allergy to buckwheat porridge
Buckwheat is considered one of the healthiest and rarely causes allergies. It contains a number of valuable microelements, B vitamins, soluble fats and salts. At the same time, buckwheat does not contain gluten, is easily digestible, and does not cause constipation, so it is recommended to use it as the main porridge during the period of introducing complementary foods.
However, despite its relative safety, buckwheat can cause allergies. It is believed that the prerequisite for this are proteins such as albumins, prolamins and globulins that are part of it.
The following signs of an allergy to buckwheat porridge are usually mentioned: swelling of the tongue and lips, tingling sensation in the mouth, coughing and sneezing, the appearance of a rash accompanied by itching, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, pain in the sinuses.
Allergy to wheat porridge
Unlike the cereals described above, wheat contains gliadin, a plant protein that requires special enzymes to process. If they are produced in insufficient quantities, a person develops an allergic reaction. Therefore, people who are allergic to gliadin or gluten will have to exclude wheat porridge from their diet.
Signs of an allergy to wheat cereals include the skin problems described above, as well as irregular heart rhythms, difficulty breathing, and elevated body temperature.
Prevention
Preventative measures to help prevent allergies include limiting the consumption of buckwheat and pre-soaking it. If an allergic reaction occurs in an adult, it is necessary to completely exclude cereals from the diet for 2–3 months. You should also avoid products that provoke cross-reactions with cereals. The list includes nuts, milk, beef, kiwi and members of the cruciferous family (radish, horseradish, mustard, radishes). After this period, doctors recommend introducing buckwheat into the menu with caution. If an infant has allergies, cereal-based complementary feeding should be postponed until 2–3 years.
Some doctors claim that soaking buckwheat allows you to break down complex proteins into simpler ones and improve their digestibility. Therefore, before eating, it is recommended to soak the cereal in water for 4–5 hours.
If a child or adult is allergic to buckwheat, there is no need to panic. Timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment will help quickly get rid of the disease. Strengthen your immune system and stick to proper nutrition - this will help you avoid allergic reactions in the future.
Rate this article 5 5 (2 ratings)
Diagnosis and treatment of porridge allergy
Therapy should begin with consultation with a specialist. If you notice signs of an unusual reaction to a particular cereal in yourself, your loved ones or your child, you need to make an appointment with an allergist or dermatologist.
To find out which cereals that cause allergies caused the development of an abnormal response of the immune system, the doctor will conduct skin tests and prescribe a blood test for IgE. It is these studies that help to accurately identify the allergen. To carry them out, the doctor applies potential allergens to the skin of the forearm and observes the body's reaction.
Once the allergen has been identified, the doctor will prescribe appropriate therapy. Usually it consists of using enterosorbents, taking antihistamines, treating skin rashes with antipruritic ointments and creams, and using anti-inflammatory drugs. If rhinitis occurs, hormonal drops may be prescribed.
In addition, it is important to follow an anti-allergy diet. This means that the following should be excluded from the diet of the patient (or the nursing mother, if we are talking about a baby):
- seafood;
- nuts;
- milk;
- eggs;
- honey;
- chocolate;
- bakery products;
- sausages;
- sausages;
- cheese;
- ketchup;
- mayonnaise;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- sugar;
- alcohol;
- chips and other snacks;
- red vegetables, berries and fruits;
- fried and smoked dishes.
Are there ways to combat the disease?
Allergies do not accept negligent treatment of themselves, and self-medication is a manifestation of irresponsibility. The first thing to start therapy if you suspect a buckwheat allergy is to create a hypoallergenic diet that does not include this grain.
Important! Buckwheat allergy overlaps with other food allergies. It is necessary to limit the menu and exclude, at least for the duration of an exacerbation, meat, nuts, milk and its derivatives, all cruciferous vegetables.
It is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own. The cause of the disease after a series of tests, studies and examinations is announced by the allergist.
The doctor also determines a further treatment plan for the patient, taking into account age and general health. Without some means, successful treatment is impossible:
- Histamine blockers. The purpose of these medications is to normalize the level of histamine in the blood to reduce swelling and inflammation. Antihistamines have side effects on the nervous system and are not prescribed without a doctor.
- Glucocorticosteroids are complex, fast-acting hormonal drugs. Easily eliminate asthma attacks. Again, you can’t take it without a doctor because of possible negative consequences.
- Sedatives to relieve general stress in the patient.
- Adsorbents for absorption and removal of antigens.
- External lotions, ointments and sprays to relieve inflammation and disinfect mucous membranes and skin.
Medicines, of course, are effective, but conservative therapy can be supplemented with folk therapy. It will not get rid of allergies, but will help you survive it with less severe symptoms.
Examples of anti-allergy recipes:
- herbal baths for eczema with nettle or string;
- ointment based on string and chamomile (cosmetic Vaseline is mixed with a decoction of herbs);
- ingestion of diluted dandelion juice and infusion of sage, chamomile and green tea;
- inhalations with eucalyptus, mint, fir.
Attention! Traditional medicine, instead of benefit, will cause harm if used to treat a particularly sensitive person with a wide range of allergens, so preliminary consultation with a specialist is necessary.
How to speed up recovery if you are allergic to porridge?
For therapy to be as effective as possible, it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. You can also additionally use auxiliary products - for example, La-Cri intensive and restorative creams.
When choosing a suitable remedy, you need to start from the symptoms of the allergy. If there is increased dryness and rashes, it is advisable to use an intensive cream, and if there is itching without pronounced dryness, it is better to use the La-Cri restorative cream.
Clinical researches
Conducted clinical studies prove the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of the products. The cream for sensitive skin is suitable for daily care of adult and children's skin with mild to moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
The products are recommended by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
Sources:
- Smirnova G.I. Atopic dermatitis and skin infections in children, Russian pediatric journal, 2014
- N.L. Rybkina, Modern approaches to newborn skin care: pediatrician tactics, journal Bulletin of Modern Clinical Medicine, 2014
- I.I. Ryumina, V.V. Zubkov, Newborn skin care, Healthy Child magazine, 2017