Laryngitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the larynx and is accompanied by a barking cough. In children, treatment of the disease takes several days or can be lengthy if the inflammation becomes chronic. The nature of the disease can be either infectious or allergic. In older children, the cause of inflammation is often pressure in the vocal cords.
In pediatrics, laryngitis is diagnosed especially often in children under 2 years of age with acute respiratory diseases. As a result of the disease, obstruction of the upper respiratory tract may develop, which requires emergency medical attention.
Types of laryngitis in children
Laryngitis in a child can take various forms:
- Spicy. An independent disease that arose under the influence of certain factors and causes. The most common form in childhood.
- Chronic. A consequence of regular relapse of acute laryngitis and its improper treatment. More common in adults.
The most common types of laryngitis in children are catarrhal, hypertrophic and atrophic. Each of them is characterized by certain manifestations:
- Catarrhal (the simplest type of disease). Accompanied by pain and other unpleasant sensations in the throat, hoarseness, and a rare dry cough.
- Hypertrophic laryngitis affects the larynx and trachea, up to the appearance of nodules on the vocal cords (sometimes their removal is required).
- Atrophic laryngitis is accompanied by thinning of the mucous membrane of the larynx and the posterior wall of the pharynx (not always). It develops extremely rarely in children. The main reason is the consumption of foods and drinks that irritate the mucous membrane.
Diet
Diet for influenza, ARVI, colds
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 4-7 days
- Terms: 5-12 days
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles per week
To reduce irritation of the pharyngeal mucosa, it is recommended to exclude from the diet those foods that can irritate it chemically, thermally and mechanically. Avoid eating too hot or cold foods. It is advisable to consume vegetables in the form of puree.
During the treatment period the following foods should be excluded from the diet:
Very fatty foods - cream, fatty fish, lamb, pork, pastries with cream.
- Drinks with caffeine - Coca-Cola, coffee, strong tea.
- Products with pepper and other spices, mustard, horseradish, garlic, onions.
- Soda.
- Alcohol.
- Seeds, nuts.
The following foods and dishes will be useful during the treatment period:
- Chicken bouillon.
- Vegetable oils.
- Puree of fruits and vegetables.
- Kiseli.
- Porridge.
- Lean fish and meat.
Causes of the disease
Among the factors determining the acute course of laryngitis are viruses and bacteria. The leading place is occupied by the parainfluenza virus, streptococci and staphylococci.
The following provoking factors of laryngitis in children are identified:
- physical fatigue;
- infection in the oral cavity (caries, stomatitis, etc.);
- inhaling cold, dry or dusty air through the mouth;
- inclusion of excessively hot or cold drinks in the diet;
- overstrain of the vocal cords (choral singing, screaming, etc.);
- contact with various allergens (house dust, plant pollen, animal hair, etc.);
- lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis (weakness of the upper respiratory tract);
- psycho-emotional factors that led to laryngeal spasm (shocks or strong experiences).
Chronic laryngitis occurs as a result of prolonged exposure to irritants on the mucous membrane of the larynx. This form of the disease is more severe and has serious consequences.
Chronic laryngitis can be caused by prolonged or frequent exposure to harmful chemicals or allergens. The cause may be acid reflux, frequent infections in the sinuses, and passive smoking. A chronic form of laryngitis can develop due to yeast infections caused by frequent use of an asthma inhaler.
Classification
Depending on the causes of the disease, there are several types of laryngitis in children.
- Catarrhal - the disease develops as a result of hypothermia or irritation of the mucous membranes by toxic components. With this disease, itching and hoarseness are initially noted. Later, these symptoms are replaced by a wet cough, and the temperature rises. Sometimes swelling of the larynx , and purulent crusts accumulate.
- Stenosing laryngitis mainly develops in children. Stenosing (subglottic) laryngitis (false croup) is a dangerous condition in which the lumen of the larynx narrows and breathing becomes difficult, which can even lead to death. The main signs of this condition are barking cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, blue discoloration of mucous membranes and nails due to lack of oxygen. With this form of the disease, the child develops attacks lasting up to half an hour. During attacks, false croup in children can cause a state of suffocation - it becomes difficult for the child to breathe. After this, the patient sweats, his condition returns to normal. The attacks may recur.
- Hypertrophic (nodular) - with this condition, severe hoarseness of the voice, dry cough, and sore throat are noted. Due to the appearance of nodular formations on the ligaments, the timbre of the voice may change.
- Atrophic - with this form of the disease, the internal mucous membrane of the larynx becomes thinner, dry mouth, dry cough, and hoarseness are noted. If a person coughs very hard, purulent crusts streaked with blood may come out. In children, this form of the disease is very rare.
- Professional – its development is associated with the need to constantly strain the vocal cords. This form of the disease is typical for singers, lecturers, teachers, etc.
- Phlegmonous - this form is characterized by a severe course. Extensive purulent infiltration develops, which affects not only the mucous membranes, but also muscle tissue, and sometimes cartilage. This is a rare form that is sometimes diagnosed in older children.
- Allergic – develops against the background of allergies. Swelling of the larynx is characteristic, and there is a risk of suffocation.
- Hemorrhagic - this form of laryngitis is provoked by diseases of the hematopoietic organs, heart, blood vessels, as well as a toxic form of influenza. As the disease develops, hemorrhages form in the laryngeal mucosa.
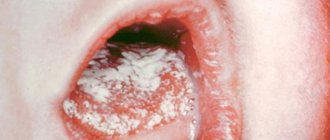
- Fungal (candidiasis) - develops due to damage to the laryngeal mucosa by the Candida fungus. A distinctive symptom is the appearance of a white, cheesy coating on the laryngeal mucosa. May develop during treatment with antibiotics.
According to the form of the course, acute and chronic laryngitis are distinguished.
- Acute laryngitis can be either an independent or concomitant form of the disease. It often develops against the background of respiratory infections and manifests itself with severe symptoms. The acute type of the disease usually responds well to treatment.
- Chronic laryngitis may be a consequence of improper or incomplete treatment of inflammatory processes in the larynx or the influence of other provoking factors.
Symptoms of laryngitis
Symptoms of laryngitis in children may differ from those in adults. This condition is often characterized by a hoarse, barking cough and fever, and may also present as false croup.
Symptoms of laryngitis in children, for which it is recommended to consult a doctor:
- temperature from 37.5 to 38°C and above;
- hyperemia and redness of the throat;
- excessive salivation;
- feeling of dryness in the throat;
- difficulty swallowing;
- whistling sounds when inhaling.
In principle, the symptoms of laryngitis are very similar to the development of other diseases of an infectious nature. Distinctive signs include voice problems and a barking cough.
Older children may complain of throat discomfort and other manifestations of the disease. Newborns and children of the first two years of life cannot express their feelings in words. Parents should be wary of excessive moodiness, anxiety and general lethargy in the child. An absolute indicator that the baby is sick is wheezing and difficulty breathing, cough and runny nose.
In children, as well as in adults, it occurs for the same reasons. However, due to a weak immune system, children get sick much more often. All parents should be familiar with the symptoms of laryngitis and know how to properly treat it.
Symptoms and treatment of laryngitis in a child
How to identify symptoms of laryngitis in a child? In most cases, laryngitis is diagnosed in children only with the onset of changes in the voice. It is necessary to ensure that the child does not become hypothermic and does not scream in the cold while playing. The doctor should examine the child's ligaments, as well as the throat and larynx for inflammation. The latest technology allows you to examine your sore throat in detail using a tube with a camera that is inserted into your mouth or nose. A child's complaints of a sore throat and difficulty breathing are the first symptoms of laryngitis. Children of preschool age get sick more often, since the cartilage of the larynx is still weak and cannot withstand deep breaths. In infants, laryngitis manifests itself through a cough with an increase in body temperature above 38.0 C.
Acute laryngitis can begin suddenly with an upper respiratory tract infection. The most common viruses that cause laryngitis in children are Haemophilus influenzae and Branchhamella catarrhal. It is these viruses that cause pain during speech.
Laryngitis in children - treatment
How do you start treating laryngitis in children? First, you need to determine the cause. If laryngitis occurs against the background of a viral infection, then doctors recommend drinking plenty of fluids and resting the vocal cords. Of course, during this period, parents will have to force the child to be silent for some time.
Other treatment is resorted to if laryngitis is caused by improper functioning of the alimentary sphincter. In such situations, you should follow a certain diet that will exclude from the child’s diet some foods that cause increased acidity.
During the period of treatment of the child, the correct drinking regime should be observed. The liquid is needed to wet the larynx. Plain water can be replaced with herbal teas or nutritious juices. Hot tea with milk and honey is useful in case of laryngitis. Warm drinks soothe the throat, and honey works as an antiseptic, preventing the growth of bacteria. To achieve the fastest results, doctors recommend a traditional remedy - steam inhalation.
Remember that timely contact with specialists will help your child get rid of illness and discomfort faster. Our clinic offers the services of experienced specialists with extensive experience.
Laryngitis in a child: symptoms and features of the course of the disease
Laryngitis is commonly understood as inflammation of the larynx, which is the narrowest point of the respiratory tract. During the acute respiratory infections season, many children suffer from this disease. Unfortunately, very often it gives complications in the form of breathing problems. Let's figure out how you can help your child.
Signs of laryngitis
The characteristic symptoms of laryngitis are directly related to the place of its localization, because the ligaments actually suffer, as a result of which the voice changes. Signs of the disease are:
- hoarseness or hoarseness of voice;
- a short, rough, hacking cough, which is also called “barking.”
Laryngitis can be viral, bacterial or allergic in nature. In order to identify the cause of the disease, its other symptoms should be analyzed.
For example, with allergic laryngitis there is no increase in body temperature and lethargy, and a coughing attack is preceded by contact with an irritating substance.
Viral laryngitis is most often accompanied by a runny nose, sneezing, hyperthermia and other usual signs of ARVI. By the way, sometimes this disease occurs with measles, rubella, chickenpox and other non-respiratory infections.
Bacterial laryngitis is considered the most dangerous for a child. Often it is a companion to diphtheria.
It is worth noting that very rarely inflammation of only the larynx occurs; in most cases, the trachea also suffers, that is, laryngotracheitis is diagnosed.
Croup
Quite often, inflammation of the larynx leads to the fact that air cannot pass through it freely, that is, stenosis occurs. Breathing becomes noisy, heavy, very difficult, and a whistling sound is heard when inhaling. This condition, combined with hoarseness, barking cough and symptoms of an infectious disease, is called croup (from the English word “croak”).
There are true croup, which occurs with diphtheria, and false croup, which develops against the background of ARVI. Today, true croup is rare, unlike false croup.
As a rule, children from six months to five years old suffer from viral croup, and boys experience it twice as often as girls. Many children grow up not knowing what croup is, while others get it several times a year. Medical science cannot explain why this happens. It all depends on the structure of the larynx and the immunity of each individual child.
Prevention of croup and first aid for a child
In most cases, viral laryngitis begins with a runny nose, fever, hoarseness and a barking cough. Breathing problems most often occur at night: the child coughs and cannot breathe air. Therefore, the first symptoms of laryngitis are a reason to call a doctor.
In addition, it is advisable to give a baby who has contracted ARVI plenty of water and feed according to his appetite. It is very important to put him to sleep in a cool room with high humidity. If an attack of croup occurs, you should call the emergency room or take the child to the hospital.
While waiting for medical help, it is recommended:
- do not panic and calm the baby;
- dress him warmly and give him the opportunity to breathe outside (cool) air;
- turn on the hot water in the bathroom and bring the child there so that he can breathe the steam.
Direct treatment of laryngitis depends on its nature and is prescribed by a doctor. It is worth noting that only bacterial infections require antibiotics.
Laryngitis in a child requires special vigilance from parents, because it can result in croup, characterized by difficulty breathing. This disease requires mandatory consultation with a doctor and strict adherence to the principles of treatment of acute respiratory viral infections: drinking plenty of fluids and proper air conditions in the children's room.
Possible complications
In young children, acute laryngitis can provoke false croup, in which there is a strong narrowing of the passage in the larynx due to swelling of the mucous membrane. This is accompanied by a strong barking cough and bluish discoloration of the nasolabial triangle. Most often, false croup occurs at night. The child may suffocate. Urgent hospitalization is required. This condition is not typical for adolescents and adults.
A serious complication of laryngitis is phlegmonous processes, which are characterized by the involvement of the muscular layer of the organ in the process. Pus begins to accumulate in it. Purulent abscesses are dangerous because they can cause infection of the blood, neighboring organs and structures.
Consequences and complications
In the absence of adequate treatment, acute laryngitis can become chronic and provoke complications associated with dysfunction of the respiratory system. The following complications are possible:
- Bronchitis develops when the pathological process gradually spreads to the bronchi.
- Vocal aphonia – the voice loses its usual sonority.
- False croup - narrowing of the larynx with false croup can lead to attacks of suffocation and be life-threatening.
- Airway obstruction - develops as a result of narrowing of the lumen of the larynx and the accumulation of large amounts of mucus in the pharynx.
- Mediastinitis is an inflammatory process affecting the mediastinum (the space between the mediastinal sections of the right and left pleura). This condition can be life-threatening.
- Laryngeal paresis - with this condition, the motor activity of the laryngeal muscles decreases, which can lead to respiratory dysfunction.
- Cellulitis of the neck is a purulent inflammation that resolves acutely.
Diagnosis of laryngitis in children
If symptoms of laryngitis appear, you should contact an ENT specialist. Comprehensive clinical diagnostics includes:
- collection of medical history and patient complaints;
- conducting a general examination (assessment of lymph nodes, oral cavity, etc.);
- visual examination of the larynx using an endoscope (detecting narrowing of the lumen, the presence of swelling and redness).
To determine the causative agent of laryngitis, a smear is taken from the mucous membrane of the larynx. A detailed blood test allows you to determine the nature of the disease (bacterial or viral).
Based on the results obtained, the pediatrician makes a diagnosis, prescribes treatment and, if necessary, refers the patient to an ENT specialist.
The child needs hospital treatment if there are pathologies of the respiratory tract and narrowing of the larynx. The need for constant medical supervision arises with an allergic predisposition, diseases of the central nervous system (CNS), as well as with the development of complications.
Tests and diagnostics
The doctor initially conducts a survey of the patient or his parents. This helps to determine the causes of the disease and its characteristic symptoms.
A specialist must conduct an examination of the oral cavity. A classic visual examination of the pharynx can be performed, as well as examination using a laryngoscope. If necessary, during such an examination, biomaterial is collected for laboratory testing in the future.
In addition, general clinical blood and urine tests are carried out, the results of which make it possible to determine the presence of an inflammatory process.
Treatment of laryngitis
Therapy of laryngitis in a child requires the organization of therapeutic and protective measures. The patient must observe drinking and bed rest, and also limit vocal activity. It is necessary to ensure daily wet cleaning and ventilation of the room in which the patient is located. You should also ensure that the room has a sufficient level of air humidity - at least 70%.
Of great importance is the diet, which should be gentle - excluding cold, hot, irritating foods, as well as avoiding carbonated drinks. A warm alkaline drink gives a good healing effect.
Treatment of laryngitis in children has the following directions:
- Drug therapy. Medicines are prescribed by a pediatrician or ENT doctor. It is recommended to approach drug therapy in a comprehensive manner: antihistamines, antibacterial lozenges for resorption. Antibiotics are rarely prescribed - in the case of a bacterial nature of the disease. Antipyretic drugs are used to reduce temperatures above 38.5 degrees.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. In some situations, inhalations with local hormonal drugs are used.
Treatment of laryngitis in children at home should be carried out under the supervision of an experienced specialist. It is unacceptable to use folk remedies that can dull the symptoms without eliminating the cause of the disease, which can lead to chronicity of the process and the occurrence of complications.
If false croup develops, measures must be taken to eliminate swelling and spasm of the larynx in order to restore normal breathing. In this case, the child needs hospitalization.
Symptoms of acute and chronic laryngitis
The main signs of acute laryngitis:
- cough;
- sore throat, but upon examination the pharynx shows no signs of inflammation;
- hoarseness of voice;
- slight increase in body temperature.
In severe purulent forms, high fever and severe intoxication (headache, malaise, pain in muscles and joints) are possible.
The main symptom of chronic laryngitis is a change and hoarseness of the voice, it becomes lower, similar to a whisper. With increased stress on the ligaments, a sore throat may occur.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures for laryngitis in children are aimed at preventing the disease:
- increasing the protective functions of the body;
- timely treatment of inflammation of the ENT organs;
- vaccination against major childhood infectious diseases;
- avoiding contact with allergens that are potentially dangerous;
- maintaining a rational voice mode.
To prevent the development of laryngitis in children, follow preventive recommendations. You should not ignore the primary signs of the disease, which will eliminate the inflammatory process at the initial stage of progression.
Prevention of laryngitis
Prevention will help reduce the risk of developing the disease and its relapse. To do this, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Temper yourself.
- Monitor oral hygiene and treat all dental diseases in a timely manner.
- Eat right and lead an active lifestyle.
- Avoid putting excessive strain on the vocal apparatus.
- Strengthen immunity.
- Undergo preventive examinations and promptly treat inflammatory processes in the ENT organs.
- Ventilate the room more often and walk in the fresh air.
- During periods when the risk of contracting viral infections is increased, avoid crowded places.
Advantages of treating laryngitis at the RebenOK clinic
What to do if a child has laryngitis? If primary symptoms of the disease appear, contact the RebenOK clinic. The medical center is equipped with modern diagnostic equipment adapted for children. The clinic employs highly qualified certified specialists with extensive practical experience.
Competent otolaryngologists conduct a full examination and prescribe treatment for laryngitis in children based on symptoms, research results and in full accordance with established protocols. If necessary, you can call an ENT specialist to your home. It is also provided, during which an experienced doctor will tell you how and how to cure laryngitis in a child in order to avoid complications.
List of sources
- Volosovets A.P., Krivopustov S.P. Modern approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of acute stenosing laryngotracheitis in children // Health of Ukraine. – 2007. – No. 18/1. – pp. 26-27.
- Daynyak L. B. Special forms of acute and chronic laryngitis / Bulletin of Otorhinolaryngology. 1997. - No. 5. — P.45.
- Zaplatnikov A.L., Girina A.A., Maykova I.D., Koroid N.V., Mozzhukhina M.V., Ivakhnenko Yu.I., Melnikova N.I., Ologina E.S. Acute obstructive laryngitis in children: emergency treatment at the prehospital stage (in tables and diagrams). Medical advice. 2018;(2):110-113.
- Romanenko S.G. Acute and chronic laryngitis. Otorhinolaryngology. National leadership. Brief edition ed. V.T. Palchuna. M.:GEOTAR-Media, 2012, p. 541-547.