Causes of ABCM in children
There are more than 120 food products known to which the baby’s body can react negatively. Cow's milk proteins are the most common allergen in children under one year of age. The product contains 3 types of proteins - lactalbumin, casein and lactoglobulin. An allergy can develop to any of them (either one or all of them).
Why is this happening?
The immune system protects the body from infections, pathogenic bacteria and viruses. However, for some reason, she may perceive components of products as harmful. In our case, cow's milk proteins. Then the baby’s immune system begins to fight them - and this fight manifests itself in characteristic symptoms, which we call allergies.
As a rule, the cause of a reaction to protein in a newborn is the early introduction of milk into the infant’s diet - in formulas, porridges.
More about allergies
Fermented milk products contain protein. This protein is different from the protein found in milk.
Some believe that the body's reaction to fermented milk products is a consequence of lactose intolerance or related diseases, but this is not the case. At any age, the body can experience reactions to fermented milk products. At a very early age, the answer occurs due to the fact that complementary foods are not introduced into the child’s menu in a timely manner.
- Allergies in very young children are a normal response as their digestive systems are just beginning to develop. Allergies can arise from any food, even the healthiest one.
How to determine milk allergy in a baby
Children's bodies react differently to proteins. Therefore, the symptoms may differ.
The most common include:
- Digestive problems: vomiting, colic, reflux, diarrhea or constipation;
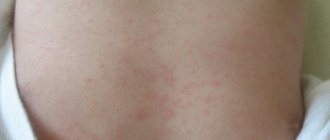
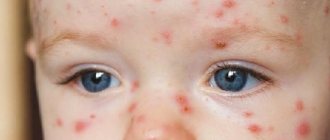
- Skin rashes: redness, rash, eczema, urticaria, itching, papules;
- Respiratory symptoms: noisy or hoarse breathing, cough, runny nose, sore and itchy throat, swelling of the laryngeal mucosa;
- Psycho-emotional state: anxious sleep or insomnia, fatigue, moodiness, crying, restless behavior while eating, poor weight gain, refusal to eat.
The severity of symptoms is different for each child: some will have only one and not much, while others will have several pronounced symptoms even after consuming a small amount of dairy products.
An allergic reaction can appear either 2 hours after eating or within 2 days.
Atopic dermatitis is a common symptom
Another symptom that often occurs in infants. Parents may confuse the dermatitis with seborrheic dermatitis or miliaria.
But there are signs by which you can suspect that your baby has atopic dermatitis.
Dermatitis affects the skin on the cheeks, elbows and popliteal folds, around the mouth, on the genitals, buttocks, and a little less often on the back, arms and legs.
At first, the skin becomes very dry, peels, and then begins to get wet, and crusts form.
The symptoms do not disappear, but get worse. Against the background of this condition, the child’s general well-being deteriorates, and his nervous system suffers.
Symptoms of milk allergy in adults
The immune system's reaction to milk protein is quite standard and manifests itself in the form of redness of the skin, small rashes and itching. Flatulence, pain in the stomach, diarrhea and constipation are symptoms of allergies in the gastrointestinal tract. Swelling of the nasopharynx, runny nose, sore throat and sneezing after eating dairy products also indicate an allergy. To confirm (exclude) this type of food allergy, experts recommend testing for lactose intolerance.
Diagnosis of protein allergy
At the first suspicion of an allergic reaction to protein, consult a doctor - a pediatrician or an allergist.
First, the doctor will examine the newborn and collect anamnesis. Assess your general health and check whether your parents or grandparents suffer from allergies. After all, a predisposition to a reaction can be inherited.
Then he will order an examination. Early diagnosis and treatment will allow you to take control of the disease and improve the condition of the baby.
Diagnosing dairy allergy is not an easy task. The problem is that the symptoms that accompany it are also characteristic of other diseases.
Here are the diagnostic methods used:
- Allergy tests. They will show whether there are antibodies to proteins in the newborn’s blood. But even they do not always give an objective picture;
- Elimination method. For some time, any dairy products are excluded from the child’s diet. If he reacts to them, then the symptoms should decrease and soon go away on their own. If there are doubts, after a while the baby is given dairy products again and the reaction is observed. With allergies, symptoms will not take long to appear;
- Provocative test. They resort to it if there are still doubts after other methods. It is carried out only in a doctor's office under his supervision;
- Coprogram. This is a stool analysis to determine the degree of digestion of food and the presence of an inflammatory process in the intestines.
Formula-fed babies under the age of six months undergo a component diagnosis of allergies to all three proteins.
If all tests show negative results, a test for lactase deficiency and celiac disease is prescribed.
Diagnostics
There are several methods to determine milk protein allergy. It is better to use them in combination:
- Feces for scatology. The analysis reveals which foods or their components have not been digested by the child’s stomach. This is how intolerance is determined. If you have an allergy, protein will not be fully absorbed.
- Test for the level of immunoglobulins E. Donate blood from a finger or vein.
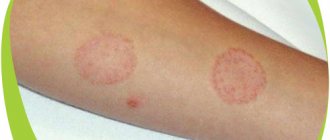
- Allergy tests. Scarification is prescribed for children from 3 years of age. The doctor makes small scratches on the child's wrist and shoulder. Allergens are applied to them in low concentrations. Each scratch has a number. The result is assessed in a few minutes. A red or swollen wound indicates an allergy to the substance.
- Anamnesis collection.
Heredity, congenital pathologies, past infections, and artificial feeding of a newborn provoke the development of immune disease and intolerance. The collected data helps the doctor find out where the child’s predisposition to lactose intolerance comes from. You need to check whether there may be a hereditary form of the disease by interviewing close relatives. - Keeping a food diary. Parents will have to try. You need to write down all menu items daily, noting any manifestations of a negative reaction.
Important! You can take blood and stool tests all year round, but it is better to do prick tests in the winter.
Allergy treatment methods
When treating infants, simple and effective methods are used.
Firstly, diet. Dairy products are completely excluded from the diet.
Secondly, skin care. To restore the skin, gels, emulsions, and ointments are prescribed. These are so-called emollients - they perfectly moisturize the skin and restore its functions.
Dear parents, pharmacies offer a wide selection of emollients. These are not simple cosmetic products, but medicinal lines for the care of atopic skin. Therefore, let the doctor select them for your child.
Diet of bottle-fed children
It is necessary to choose an adapted hypoallergenic formula for your baby. The choice depends on the degree of allergy.
For light and medium - mixtures based on highly hydrolyzed proteins. But keep in mind that these mixtures have a bitter taste and a specific smell, so not all children agree to eat them.
For severe allergies, mixtures based on amino acids are suitable. They are universal - they can be given for any degree of allergic reaction. These mixtures are neutral in taste and children eat them more readily.
Adapted mixtures as part of correctional therapy are prescribed for a period of six months to a year. After this, the baby is transferred to the regular formula. If he reacts negatively again, the adapted mixture is given for another six months.
The mixture should be changed gradually and under the supervision of a pediatrician.
Diet of breastfed children
Here we are talking about the mother’s diet, because what she eats, her baby will also receive in milk. Therefore, mom excludes any dairy products from the diet. Moreover, this group includes not only kefir, cottage cheese and fermented baked milk, but also baked goods and desserts - they also contain milk. Mom will have to study the composition of products before eating them.
If the baby already eats porridge, then you can give only dairy-free, and better yet, gluten-free ones - they are the most hypoallergenic.
Features of allergies in infants
Children on breastfeeding suffer from an allergy to milk protein, which enters the body along with mother's milk. Women need to go on a dairy-free diet: exclude all products with cow protein from their diet. This:
- cream;
- dry, baked, condensed milk;
- bakery;
- ice cream;
- chocolate;
- buns
If an allergy to milk protein appears infrequently during breastfeeding and is mild, you can include fermented milk products and drinks in your mother’s menu: kefir, fermented baked milk, sour cream, cottage cheese.
Lactose intolerance is more often diagnosed in artificially raised children. Mothers of such babies need to worry about selecting a special formula - dairy-free (hydrolysis), fermented milk or goat's milk based.
Watch the video about the features of milk allergy in newborns. Dr. Komarovsky gives clear and simple recommendations on how to identify intolerance and what parents should do in this situation.
Allergy danger
- Please note that if an allergic reaction occurs in infants, the allergy may disappear by the age of two or three years. It is very rare for allergies to fermented milk products to persist for life.
Sometimes, during the manifestation of allergic reactions, complications can arise that threaten the health and life of the baby.
Most often this happens due to experiments with the amount of food consumed or attempts to accustom children to fermented milk products.
The most common complications are:
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Improper functioning of some organs of the child, leading to other complications and pain throughout the body.
- Development of asthma.
- Edema of varying severity.
- A rarer, but more unpleasant case: the occurrence of anaphylactic shock.
Treatment with diet
In this case, it is better to consult a doctor to create the right diet for your baby.
For example, if you are allergic to fermented milk products, you can sometimes consume a little milk. The drinking diet is a special nutrition system that consists of consuming only liquid food. Solid foods are not used during the diet. The use of a liquid diet does not exclude replenishment of the water balance with a daily norm of 1.5 liters. In the article we will talk about how to properly follow such a diet, for how many days, and show photos of the results and reviews of those losing weight. Any drinking diet, be it a weight loss method using kefir, broths, green tea, juices or even plain water, is based on fluid intake. In this case, all tests must be carried out so that you can be sure that the child will not have allergies.
- When treating symptoms, it is necessary to exclude all fermented milk products from the menu.
In general, it is best to feed your baby the following foods:
- Pasta products. You cannot add butter.
- Broth based on vegetables and meat.
- Various meats.
- Egg dishes.
- You can feed porridge with water, without butter and milk.
- Vegetables and fruits, if they are not allergens.
- Juices.
- Light tea.