Classification
According to the nature of its course, mastitis can be acute or chronic:
There are several types of mastitis:
Lactational
It develops mainly in lactating women in the 1st month after childbirth or in the last weeks of pregnancy, provoked by stagnation of milk and the penetration of bacteria into the gland tissue through defects in the skin and milk ducts when personal hygiene rules are violated. It turns into purulent mastitis after 3-4 days if left untreated.
Non-lactational
Occurs in women against the background of: breast injury; purulent processes in the skin and subcutaneous fat of the mammary gland (boils, carbuncles, atheromas); foreign body (piercing); the presence of mastopathy (mainly cystic, with cysts more than 1.5 cm in diameter).
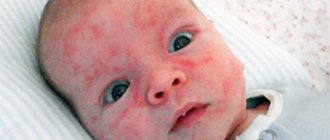
Neonatal mastitis
Develops after physiological mastopathy of newborns due to improper care of the baby, most often towards the end of the 1st month of life.
The most common type is lactation mastitis, it affects up to 85% of all women who apply. This is always an acute process that requires immediate medical attention.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a mammologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Vishnevsky ointment during pregnancy
As mentioned above, Vishnevsky ointment is often and effectively used for inflammation of the pelvic organs and appendages in women. But it is worth noting that this area of application of the drug must be strictly carried out as prescribed by the attending physician and exclusively under his supervision. Self-medication in this case can only aggravate the problem or cause serious complications.
Women who have problems with the pelvic organs are prescribed tampons with Vishnevsky ointment.
During pregnancy, the ointment has no contraindications for external use. In hospital departments today, Vishnevsky’s ointment is not very popular, since more powerful drugs have already been created, but for self-treatment of external problems this remedy is very good.
An important point for successful treatment is treating the area where the ointment is applied with alcohol after removing the compress.
During pregnancy, a common problem in women is varicose veins in the legs. In this case, to relieve pain and improve blood flow, you can wrap with gauze and Vishnevsky ointment until the ointment dries completely.
Causes of mastitis
Each type of mastitis has its own causes.
Lactation mastitis develops in pregnant women, starting from the 35th week of pregnancy and during breastfeeding. As a result of improper latching of the baby to the breast or inept expression of milk, the gland is not completely emptied, and lactostasis or milk stagnation occurs. This is a breeding ground for the proliferation of bacteria that enter the milk ducts through cracks in the nipple, or are carried through the bloodstream from other sites of chronic infections. Pathological flora enters the ducts due to poor personal hygiene; wearing tight and rough underwear, which compresses the gland, also contributes to stagnation of milk.
Mastitis of newborns. Physiological mastopathy of newborns develops in 70% of cases, both in girls and boys, in the first days after birth. This is one of the mechanisms of adaptation to extrauterine life; it begins on the second day of life and goes away within 2-4 weeks. The process can be one-way or two-way. All changes in the mammary glands (swelling of tissue, discharge from the nipple) during this period are reversible and do not require visiting a doctor or drug treatment. If you care for your baby improperly: insufficient or excessive hygiene, using compresses, heating, ointments, trying to massage or expressing discharge from the nipple, you can injure the delicate skin and nipple, cracks in which become entry points for bacterial flora. Microbes, getting inside, provoke a severe septic condition - mastitis of newborns. Symptoms increase, the child’s condition deteriorates sharply. If left untreated, an abscess forms at the base of the mammary gland, which requires immediate surgical treatment. If left untreated, the purulent process turns into a generalized form - sepsis.
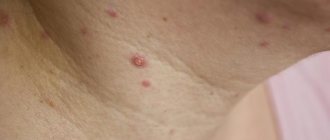
Non-lactation mastitis occurs in nulliparous women more often against the background of trauma to the mammary gland, purulent processes in the skin and subcutaneous fat of the mammary gland (boils, carbuncles, inflamed atheromas), the presence of mastopathy (mainly cystic, with cysts more than 1.5 cm in diameter), thermal effects on gland tissue (hypothermia, overheating). Chronic recurrent mastitis is extremely rare, which periodically manifests itself in the patient against the background of complete well-being. Requires immediate contact with a specialist, further examination and treatment.
In recent years, the cause of acute purulent mastitis is often a piercing or puncture into which jewelry is inserted. This body modification, even when performed correctly, is not always harmless, since it affects the areola of the nipple, where the sebaceous and sweat glands are located, as well as the Montgomery glands, designed to moisturize the nipple during lactation. In the depths of the areolas there are lacteal sinuses, designed to store milk. If the rules of asepsis are violated or low-quality jewelry is used, the piercing becomes an entry point for infection.
Symptoms of mastitis
The manifestations and symptoms of mastitis at the onset of the disease are the same for all types. This:
- fever that appears suddenly and quickly reaches high numbers - up to 39 C and above;
- signs of intoxication – chills, fever, headache, lack of appetite;
- sharp pain in the mammary gland, which intensifies when palpating or attempting to feed (pus or blood may be found in the milk);
- the mammary gland becomes dense, swollen, hot to the touch, skin color changes (redness);
- as inflammation increases, regional lymph nodes enlarge.
In its development, acute mastitis can go through several stages:
- serous;
- infiltrative;
- purulent, which is divided into abscess (limited abscess) and phlegmon (spread suppuration);
- gangrenous, when the gland tissues completely die after purulent melting.
In turn, chronic mastitis is often limited to the infiltrative stage.
In the chronic course of mastitis, a capsule of fibrous tissue is formed around the inflammatory focus, delimiting the area of inflammation from healthy tissue. In this case, fever and other manifestations of intoxication may be mild, and the encysted focus of inflammation can be felt as a dense, fused to the skin and inactive formation.
The sooner a woman sees a doctor, the more likely it is to stop inflammation at the initial stage.
Causes and symptoms of mastitis
In medicine, there are two main forms of the disease - lactation and non-lactation mastitis. In the first case, the causes of the development of pathology may be:
- producing too much breast milk;
- abnormal nipple structure and associated feeding difficulties;
- violation of the child's feeding technique.
Mastitis in a nursing mother (lactation) does not always develop even in the presence of the indicated causes - provoking factors should also “work”:
- nipple injuries (cracks);
- already diagnosed breast tumors of benign or malignant origin;
- carriage of Staphylococcus aureus;
- postpartum depression;
- exacerbation of any chronic diseases;
- hormonal disorders.
Non-lactation mastitis can develop at any age and not only in women, but also in men and girls. The causes of this form of the disease are considered to be persistently disrupted hormonal levels and breast injuries. Non-lactation mastitis is diagnosed only in 5% of all cases; its development is not acute, but in almost every case it becomes chronic.
The symptoms of mastitis will be the same, regardless of its form:
- pain, feeling of fullness in the chest;
- swelling of the mammary gland on one or both sides (unilateral/bilateral mastitis);
- severe pain when palpating the source of inflammation;
- pronounced redness of the skin over the pathological area;
- enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes, their pain when palpated.
There is also general weakness, increased body temperature (sometimes to critical levels), nausea and vomiting, and dizziness.
If purulent mastitis begins (usually on the 5th day of development of the disease in the absence of treatment), then all of the above symptoms become more intense, a pronounced vascular network appears on the chest, and the focus of pathology on palpation is defined as softened, with iridescent liquid inside. In this case, urgent medical care is needed, therapy is not even implied, the patient is immediately sent to a surgeon - the abscess is opened, the pus is removed, the cavity is washed.
Diagnosis of mastitis
In a typical case, diagnosing mastitis does not cause difficulties. Upon examination, the mammologist detects a focus of compaction that is hot to the touch, changes in the color of the skin above it, and also possibly enlarged axillary lymph nodes on the affected side. If an abscess has already formed, then fluctuation (oscillatory movement of liquid pus) may be felt at its location.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound of the mammary glands, which will reveal a typical picture: smoothing of the echo response, dilation of the ducts, thickening of the tissue and skin. Ultrasound clearly shows inflammatory infiltrates, abscesses, and necrosis. This is the most informative technique that allows you to establish an accurate picture of the disease.
In a chronic process, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) or core biopsy may be required, which is performed with thin needles of different diameters under ultrasound guidance. After local anesthesia, the needle is inserted into the center of the lesion, from where biomaterial is taken for cytological or histological examination. Studying the cellular composition of a suspicious lesion provides answers to all questions.
To clarify the spectrum of bacterial flora and prescribe effective treatment, it is possible to culture purulent discharge from the lesion with further determination of sensitivity to antibacterial agents.
Treatment of mastitis
Treatment of mastitis depends on the type and stage of inflammation. In the stage of serous inflammation, the best result is obtained by regular, frequent and complete emptying of the gland, which is performed manually or mechanically. Elimination of lactostasis at an early stage allows you to maintain full breastfeeding.
In later stages of inflammation, treatment is incompatible with breastfeeding. Medicines that a sick woman needs pass into breast milk and can disrupt the baby’s natural digestive processes. After the woman recovers, breastfeeding can be continued.
If an abscess has formed, it must be sanitized surgically. The abscess is opened, the pathological contents are removed, drainage is installed if necessary, the amount of treatment directly depends on how quickly after the onset of the first symptoms the patient sought treatment.
Treatment of more complex types of non-lactation mastitis requires a full clinical examination and identification of the causes that led to the disease, followed by treatment and observation by a specialist.
Mastopathy during menopause
27.08.2020
How does mastopathy manifest itself during menopause?
A woman is a beautiful flower, which with age opens all the petals of its rich bud. And it is very important that every representative of the fair sex monitors not only her appearance, but also her health, especially women’s.
Menopause and mastopathy are not a death sentence
Such a phenomenon as mastopathy most often causes concern among women, since there is a risk of the formation of malignant tumors, but one should not panic prematurely. Since the structure of the milk ducts can change and the proportions of stroma and parenchyma can fluctuate with any changes in hormonal levels, in particular during menopause .
Mastopathy during menopause occurs quite often, because hormonal changes affect not only the reproductive system, but also many others. Therefore, there is no need to worry in advance; you need to undergo a comprehensive examination.
Menopause is translated from Greek as “step,” meaning a period in the life of every woman when the body begins to function differently, as if having stepped onto a new stage of development.
Each woman menopause at a different age, the time range ranges from 45 to 60 years. Features of menopause can manifest themselves with varying degrees of intensity. During menopause , you may experience:
- hot flashes;
- profuse sweating ;
- chest pain ;
- mood changes;
- increased fatigue;
- motor disorders.
And during such a period of life, a woman may feel dissatisfied with herself and feel the approach of inevitable old age.
During the climacteric period of a woman’s life, it is very important to minimize all adverse manifestations and its possible consequences. All changes in the female body are directly related to hormonal imbalance.
The endocrine system, which is responsible for the production of hormones , begins to work in a different mode, which causes malfunctions in the functioning of various systems. Consequently, with the onset of menopause , the likelihood of the appearance of various diseases increases, among which mastopathy occupies a special place.
What kind of disease is mastopathy during menopause?
Mastopathy during menopause is a fairly common disease that involves abnormal growth of connective tissue in the chest , which is accompanied by pain.
These formations are benign, but in some cases there is a possibility of oncology .
Mastopathy during menopause - symptoms
Symptoms of mastopathy during menopause appear in a much more intense form than in other periods of women’s lives. But often these symptoms are hidden under menopausal symptoms and in the initial stages it is difficult to track the first symptoms.
When you conduct an examination or self-examination, you can notice obvious changes in the structure of the female breast .
Symptoms of mastopathy include:
- increase in the volume of the mammary glands , feeling of heaviness;
- lumps in the chest ;
- painful pressure on certain areas of the mammary glands ;
- nipple discharge ;
- headaches and insomnia ;
- elevated temperature;
- nausea and vomiting.
At the moment, over 50 forms of mastopathy are known. In clinical practice, fibrocystic mastopathy during menopause occurs both nodular and diffuse.
Treatment of the disease
It is quite difficult to independently diagnose the disease in the early stages, which means that every woman needs to regularly visit a mammologist . At the initial appointment, the specialist will find out the possible preconditions for the occurrence, find out if there are any complaints, and determine whether the patient is at risk.
of the mammary glands , armpits and nodes located above the collarbones is mandatory If necessary, the mammologist prescribes:
- mammography;
- puncture biopsy;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands ;
- blood chemistry ;
- analysis of hormone ;
- MRI is additionally prescribed.
If mastopathy is detected, then drug therapy Treatment can be: hormonal, non-hormonal and in special cases surgical . It is selected individually for the patient.
Results
Every woman should monitor the condition of her breasts , in particular during a special period of life, because menopause and mastopathy can turn into identical concepts.
Published in Gynecology, Mammology Premium Clinic
Our services in mammology
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| Needle biopsy (without the cost of histological examination) | 2 500 |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands | 3 000 |
| Minor operations under local anesthesia | 15 000 — 40 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions