A little theory
The main causative agent of this infectious pathology is tetanus bacillus or a gram-positive flagellated bacterium, which is capable of growing, developing and multiplying in oxygen-free conditions.
In fact, the bacterium itself does not pose any danger to the human body, but the exotoxin it produces can be very unsafe and lead to death. Once in the body, this substance enters the medulla oblongata and spinal cord through the motor fibers of the peripheral nerves. When this stick is active, a person may notice severe cramps in the arms and legs, and difficulty breathing.
The composition contains horse blood immunoglobulins, which are pre-vaccinated with tetanus toxin and toxoid. During the manufacturing process, this whey goes through many stages of purification, and in the end it is intensively concentrated using salt fractionation. Visually, it does not look like blood at all, since the serum has a clear or slightly yellowish tint, without any sediment, and is available in the form of a liquid for injection in clear glass ampoules.
Why is tetanus dangerous?
Once tetanus toxin binds to nerve endings, it cannot be removed. To fully recover from a tetanus infection, new nerve endings must develop, which may take several months.
Consequences of tetanus infection:
· Fractures. The severity of muscle spasms can lead to fractures of the spine and other bones.
· Development of pulmonary embolism. A displaced clot may block the main artery of the lung or some of its branches.
· Death. Severe muscle spasms caused by tetanus can cause respiratory failure, which is the most common cause of death.
To prevent a sad outcome, it is recommended to vaccinate your child against tetanus on time.
How is the vaccination done?
Tetanus vaccination is given at regular intervals. They are done more often in children than in adults. The fact is that immunity in children develops over a long period of time, so the risk of infection with various diseases increases significantly.
To ensure that the baby can easily endure this procedure, the doctor must conduct an examination. If signs of colds and other pathologies are observed, then medical advice is given. If there are no health abnormalities, parents receive recommendations for caring for their child after vaccination and are sent to the vaccination office.
Vaccination rules and vaccination schedule
The first tetanus vaccine is prescribed to a child at 3 months. Then it is repeated twice (after 45 days), namely at 4, 5 and 6 months. Usually, the DPT vaccine is used so as not to give the baby several injections separately (see also: how are the second and third DTP tolerated?).
READ ALSO: What are the side effects of DTP vaccination in infants?
This frequency is necessary for the proper formation of immunity to infection. It should be understood that no vaccination will protect a child from possible infection 100%, but it will help to survive the disease in a mild form and without complications.
READ ALSO: What can be the complications after vaccination with measles, rubella, mumps?
Revaccination is carried out three times:
- 1.5 years;
- 6–7 years;
- 14–15 years old.
Revaccination is mandatory before entering school, then in adolescence and at 18 years of age, after which it is repeated every 10 years. There are also a number of emergency cases when a tetanus vaccination is given as soon as possible:
- animal bites;
- open wounds due to injuries and frostbite;
- gangrene, ulcers that do not go away for a long time;
- before performing surgical operations (if there is no information about the availability of tetanus vaccinations).
To exclude the development of side effects after vaccination, parents are advised to start giving their child antihistamines in advance (2-3 days). A runny nose, cough and other signs of illness are a reason to postpone the vaccination until complete recovery.
Where is the vaccine given?
The tetanus shot is always given into a muscle, in places where there is no large amount of subcutaneous fatty tissue and the skin is quite thin.
For a child under 3 years of age, toxoid is injected into the lateral thigh, for adolescents and adults - into the shoulder or subscapular region.
Before the procedure, you should check the ampoule - it should have the appropriate markings. The presence of sediment and flakes at the bottom is not allowed.
How to behave after vaccination and is it possible to wet the injection site?
After vaccination, a person can lead a normal life, but babies sometimes experience undesirable effects. To prevent this, you must adhere to certain recommendations.
When your baby is given the injection, make sure that the body reacts normally to the toxoid. It is better to stay in the clinic for an hour - if allergies or other complications arise, doctors will promptly help you.
Is it possible to get a tetanus shot wet? The answer is yes. The child is allowed to wash; the injection site can be wetted, but not rubbed with a sponge or hand. It is also prohibited to swim in open water, as there is a risk of contracting an infection.
You cannot visit the bathhouse/sauna; you should refrain from walking in the fresh air and in places with large crowds of people for 2-3 days. Active physical activity is also undesirable.
Doctors advise immediately upon returning home to give the baby an antipyretic and continue taking antihistamines. All medications are prescribed for preventive purposes; medications should be dosed according to age. It is also recommended to drink plenty of fluids for 1-2 days.
How long does it last?
The tetanus vaccine does not have a permanent effect, so it must be repeated periodically to be effective. It is better to consult a doctor for how long its effect lasts. He will look at the timing of the toxoid administration and tell you the expected date of the next vaccination. The vaccine is given to adults for 10 years, but it is less effective in children.
READ IN DETAIL: What vaccination is given once every 10 years?
What to do after vaccination
You don't need to do anything special after getting a tetanus shot. It is advisable not to wet, rub or scratch the injection site for 24 hours. Adults are not allowed to bathe; small children are not given a bath on the day of vaccination. But walking is not prohibited, and if the weather is good, parents can easily spend time with their baby in the fresh air. You also need to remember that vaccination in general is a mini-disease, so for good health you should drink more fluids and not communicate with people with colds, flu and other respiratory diseases.
Polio vaccine 10
553
As for nutrition after a tetanus vaccination, you can eat everything as usual. The exception is small children, for whom it is better to briefly exclude so-called obligate allergens (foods that often cause food allergies) - do not eat chocolate, citrus fruits, honey and nuts, as well as fish - another of the few restrictions that cannot be done after vaccination.
Emergency vaccination scheme
There are situations when urgent, unscheduled administration of a vaccine is necessary. Before the injection, the person being vaccinated must sanitize the wound.
Emergency indications include:
- injuries;
- frostbite;
- burns 2-4 degrees;
- preoperative period, if there is no data on previous tetanus vaccinations;
- animal bites;
- long-term non-healing wounds (cuts) or ulcers;
- out-of-hospital births, abortions.
In these cases, the immunization schedule depends on whether the patient has been vaccinated previously. If the procedure has already been carried out, immunoglobulin (human) is used, since it carries a minimum of post-injection complications. Antitetanus serum can also be used.
If a person has not been vaccinated before, he is injected intramuscularly with toxoid (in one part of the body), and then (after half an hour) in another place with anti-tetanus serum.
The effectiveness of emergency vaccination lies in its urgency. It should take place as soon as possible - no later than 20 days from the moment of injury.
Pathogen, mode of transmission and clinical manifestations of tetanus
The “indestructibility” of tetanus is explained by the special properties of its bacteria. The pathogen is normally present in the intestines of a sick person or animal, and then, along with excrement, ends up in water and soil. This increases the risk of infection when scraped or bruised skin comes into contact with the ground. A gram-positive rod, when exposed to unusual, extreme conditions for it, is transformed into spores that perfectly adapt to sub-zero temperatures and retain their properties even after many hours of boiling. Sticks can live in soil without losing their viability for 100 years.
Tetanus is transmitted by contact, for example, when soil gets into the wound. A splinter may penetrate your leg, or it may be injured by something sharp. The reasons may be frostbite of the extremities with a violation of the integrity of the skin. The disease can develop during illegal abortions, or when childbirth occurs without observing sanitation standards.
Infection occurs when dirt or dirty water comes into contact with injured skin or mucous membranes. Conditions in a deep wound promote the transformation of infected spores into active bacteria. Risk groups for tetanus include:
- young children (under 9 years old) who are often injured;
- newborn babies (violation of asepsis when cutting off the umbilical cord);
- representatives of professions associated with excavation work and increased injury rates: builders, loaders, diggers, railway workers;
- athletes;
- military.
You can become infected with tetanus very easily if there are cuts, wounds, or abrasions on your body. If dirt gets into the wound, after 1-2 weeks (sometimes the incubation period of the disease lasts up to 1 month), characteristic symptoms may appear, on the basis of which doctors make a diagnosis.
- The wound, even when healed, aches when it shouldn’t hurt anymore.
- Trismus – the patient has noticeable contraction of the facial muscles. It's hard to open your mouth.
- A “sardonic smile” occurs due to the distortion of facial features.
- Dysphagia develops, and it hurts the person to swallow.
- Tension of the muscles of the back of the head appears - rigidity.
- Headache, sweating, irritability.
These symptoms of tetanus do not always appear. There are often cases when the wound has completely healed, but symptoms still appear (muscle tension at the site of the wound).
In the presence of such clinical manifestations, doctors conclude that the patient has a tetanus infection; the described specific signs do not require confirmation by tests. There are several options for localizing the infectious process.
- Local tetanus. One or more muscle groups in the area of skin trauma are paralyzed. Characteristic of those who have been vaccinated against tetanus.
- Generalized tetanus. All muscle groups are susceptible to cramps. In such patients, the severity of the disease is divided into degrees:
- light;
- moderate severity;
- heavy;
- extremely difficult.
According to the type of entrance gate, the forms of the disease are:
- traumatic – after injuries, wounds, frostbite;
- inflammatory-necrotic – occurs in the presence of bedsores and where there is a disintegrating tumor;
- cryptogenic - forms at a healed wound site (a person may not even remember this), the gates of infection are not identified, the incubation period is extended to several months.
Prevention of tetanus
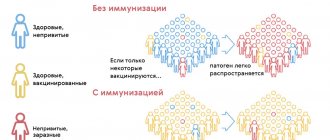
Prevention of tetanus is, first of all, vaccination, which is carried out at certain periods (according to the vaccination calendar). Vaccination significantly reduces the likelihood of contracting tetanus, and even if the pathogen enters the body, there is a possibility that the disease will be local in nature or occur in a mild, harmless form.
Tetanus vaccine and how it works
The tetanus vaccine is a drug containing toxoid - a neutralized substance that is secreted by bacteria that enter the body, and which causes damage to the nervous system.
It is important to understand that a person who has had tetanus does not receive immunity against this disease, since the toxin produced during the reproduction of the tetanus bacillus is not enough to produce antibodies. Therefore, for vaccination, an toxoid is used, free of negative effects on the body, but in a dose sufficient to form immunity
Tetanus shot: when is it done?
Prevention of tetanus begins in childhood, when at three months the child receives the first dose of tetanus toxoid. It is usually included in the DTP, but a tetanus shot can also be given with another drug - it all depends on which tetanus shot is recommended by the medical institution. After the first vaccination, the second dose is administered 45 days later, and the third after another 45 days. Revaccination after the third dose should be carried out one year after the tetanus shot.
Instead of DPT, today they offer complex vaccines, which in many cases are easier to tolerate by children (Infantrix Hexa or Pentaxim). But vaccinations using these vaccines are usually paid for. Unlike DPT, which is given free of charge in the children's clinic to which the child belongs.
Before vaccination, it is necessary to take a urine and blood test to make sure that the child does not have hidden inflammation or other health problems. You should also visit your pediatrician to get approval for the vaccine. If the child has been sick, the vaccine can be given no earlier than two weeks after complete recovery.In order to maintain immunity against tetanus, according to the vaccination schedule, the child will need to be revaccinated at 7 years and at 14 years. In adulthood, a tetanus vaccine containing tetanus toxoid is given every 10 years.
In recent years, the opinion has gained some popularity that a child does not need to be vaccinated, since the likelihood of contracting many diseases is negligible
It is important to understand that the likelihood of becoming infected has become low precisely because the vast majority of people in our country and in many civilized countries have been vaccinated. In addition, tetanus is a disease that a person, and especially a child, can encounter at any time. After all, the causative agent of tetanus is able to maintain its viability while in the soil for 100 years
After all, the causative agent of tetanus is able to maintain its viability while in the soil for 100 years.
Adverse reactions after tetanus vaccination
Although the tetanus vaccine contains a neutralized toxin, some adverse reaction is inevitable when it enters the body. Moreover, a tetanus shot is one of the vaccinations that most often causes adverse reactions. It is possible to distinguish between “normal” and severe side effects after a tetanus vaccination.
“Normal” manifestations are considered local redness at the site of the tetanus injection, accompanied by swelling and pain. After a tetanus vaccination, many vaccinated people experience an increase in body temperature and changes in the reactions of the nervous system (some patients note a feeling of lethargy, others, on the contrary, are more excitable than usual). Gastrointestinal reactions are also common after a tetanus injection: vomiting, diarrhea, refusal to eat.
If a person who has received a dose of tetanus vaccine has a severe headache or excessive swelling at the site of the tetanus shot, they may have a severe reaction. Neurological manifestations in the form of seizures and short-term impairment of consciousness are also possible, but these cases after tetanus vaccination are extremely rare. Severe reactions are a recommendation to discontinue the course of tetanus vaccine.
Tetanus is a rather dangerous disease, which cannot be excluded even in those who have undergone vaccination courses
Therefore, in case of any injury, it is necessary to observe precautions and rules for treating wounds, and if you suspect that bacteria have entered the body, immediately seek help from a medical facility
Contraindications to vaccination
Contraindications for nursing mothers
Like any drug, tetanus vaccine has a number of contraindications. Conventionally, they can be divided into absolute and relative.
In the first case, vaccination is completely prohibited, since it can cause irreparable harm to a person. These include a severe allergic reaction to the components of the drug, as well as immunodeficiency.
The list of relative contraindications is much wider:
- Any acute diseases, as well as exacerbations of chronic ones. Vaccinations should not be done at elevated temperatures.
- Low weight in babies. For children born prematurely, vaccinations are postponed until their condition returns to normal.
- The recovery period after serious illnesses, as well as chemotherapy, radiation, and immunosuppressive therapy.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
In such cases, doctors often give medical withdrawal for a while.
If the child’s last vaccination caused severe, long-term pain or other acute adverse reactions, the more aggressive DPT vaccine can be replaced with DPT, which is better tolerated, or other lighter vaccines.
One of the problems that many parents face is frequent medical withdrawals where there is no real need for them. Many neuralgic conditions and allergic reactions in infants do not actually increase the risk of developing complications, but because of them, the child may be left without protection from these dangerous diseases, so it is not worth delaying vaccination for too long.
We hope that we have answered your question about why the tetanus shot hurts and how long this condition can last, as well as how to avoid complications.
Touch Sensitivity
As Aspergers themselves state, their world is much louder than that of the average person. This is due to increased sensitivity to any stimuli, be it smells, touches, sounds, or visual images. It has been established that a similar phenomenon occurs in approximately 40% of people with AS. A hypersensitivity reaction can be triggered by anything: air temperature, bright light, food, clothing such as scratchy wool or labels on the underside, the touch of other people or large accumulations of them.
For example, when riding on public transport (subway, train, bus), Aspies sometimes use earplugs or headphones that play their favorite music. The mass of people, stuffiness and noise irritate them, unbalance them and lead to stressful conditions. Music helps to distract and calm down. When the situation becomes extremely tense, they have to leave it, go off the route to stand alone and enjoy the silence, and then continue on foot.
There are special types of therapy to cope with sensory problems. One of them is sensory integration therapy. Its essence lies in deliberate contact with unpleasant stimuli, occurring gradually and in doses. Thus, a person begins to get used to such collisions, no longer feeling irritability and panic.
It is very important for Aspergers to identify a method or strategy for neutralizing unpleasant impulses. For some, this solution is a small dose of alcohol.
According to Aspies, it muffles all obsessive sensations and helps reduce stress levels. Someone needs to retire for a while, wander through empty streets, someone swings on a swing.
Features of the tetanus vaccine: how long does the vaccination last?
Health > Be healthy > Features of the tetanus vaccine: how long does the vaccination last?
Tetanus is an infectious disease in which there are signs of toxicosis and convulsions that occur as a result of damage to cells of the nervous system by toxins.
The causative agent of the disease is considered to be Escherichia coli. Typically, the route of infection is the entry of a pathogenic microorganism into the mucous membranes or through damage to the skin.
Tetanus is a dangerous pathological condition that leads to the development of severe complications, often fatal.
Vaccination is considered a measure to prevent the disease. The features of such vaccination are discussed in this article.
Briefly about vaccination
Most often, tetanus occurs in children between three and seven years of age.
Tetanus bacillus usually enters the body through contaminated puncture and laceration wounds. The main cause of infection in children is considered to be leg injuries, when bare feet are injured, due to injury from prickly and sharp objects.
In infants, tetanus can develop as a result of infection of the umbilical cord when antiseptic rules are violated.
Tetanus is dangerous due to various complications, it often leads to death, therefore routine vaccination against the disease in children has been developed. To increase immune strength against this disease, children starting from three months are given tetanus toxoid.
Features of tetanus vaccination
Tetanus toxoid is contained in the following vaccines:
- Pentaxim
- DTP
- Tetraxim
- Infanrix
- Tetrakok
- Triaceluvax DPT
The vaccine is given three times, maintaining an interval of one and a half months. After this, revaccination is performed one year after the last vaccination. Thus, revaccination is done when the child is one year and six months old.
Vaccination is the key to your child’s health
According to the vaccination calendar, the next revaccination is carried out at seven and fourteen years. After this, vaccination must be done once every ten years.
Typically, the drug ADS-M is used for this.
Thus, the tetanus vaccine is valid for ten years.
The peculiarity of vaccination against this infection is the fact that it can be done unscheduled. Such emergency cases include injury, in which the integrity of the mucous membranes and skin is violated, with burns and frostbite, starting from the second degree.
In addition, tetanus prophylaxis is required after out-of-hospital births and abortions.
Indications for the use of the vaccine are animal bites, necrosis, gangrene, prolonged carbuncles and abscesses.
Usually 0.5 milliliters of vaccine is administered. If unvaccinated people or children are vaccinated, the injection is given in a volume of 1 milliliter.
The vaccination is done under the shoulder blade, inserting a needle deep into the skin. It is recommended to administer injections this way to adults and adolescents. For children, it is done intramuscularly in the anterior outer area of the thigh.
Recommendations from pediatricians
Usually, vaccination against the disease is tolerated well. However, experts say that in some situations, the tetanus vaccine can cause side effects such as fever and general weakness. A local reaction is possible - for example, hyperemia of the skin and pain in the injection area.
Ten years is the period of validity of a tetanus vaccination.
In addition, an allergic reaction in the form of anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, and rashes may occur. Seizures may also occur.
In such cases, it is recommended to take antipyretic medications and antihistamines. If more severe side effects occur, you should consult a specialist.
It is also important to remember that you must undergo a medical examination before vaccination. Weakened immunity can affect the development of adverse reactions, so vaccination should be carried out in completely healthy people
Before vaccination, you should consult with a specialist about possible such phenomena.
Pediatricians advise that after vaccination and revaccination, avoid contact with infected patients and not visit crowded places.
Another important rule in preparing for vaccination is the exclusion of introducing new foods into the child’s diet.
The vaccine is not allowed to be given during pregnancy, if you are allergic to substances included in the injection, or if there is an exacerbation of chronic diseases.
About tetanus - in detail in the video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=UcTsaVcPAtw
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Composition and mechanism of action of tetanus vaccines
The composition of tetanus vaccinations depends on the manufacturer and type of drug.
For example, there are many combination vaccines that protect against tetanus and a number of other diseases. Polyvalent vaccinations have approximately the following composition:
- tetanus toxoid;
- aluminum hydroxide as an adsorbent;
- merthiolate (preservative).
The mechanism of action of tetanus vaccines is based on the fact that after penetration into the body, the antigenic material stimulates the production of antibodies, which for a long time can fight the causative agent of a dangerous infectious pathology.
When and where to get a tetanus shot: schedule
For infants, three-time vaccination is used. The injection is given intramuscularly into the thigh
The baby does not yet understand the importance of immunization, so he just needs to be distracted, and then encouraged and praised
For preschool children and adolescents, the injection is given into the shoulder or under the shoulder blade. Parents are informed in advance about revaccination and receive written permission from one of them.
After adulthood, revaccination is necessary every 10 years.
If more than 5 years have passed since the last administration of the toxoid and severe contamination of the damaged skin has occurred, then an unscheduled anti-tetanus injection is necessary. Carrying out such a procedure also applies to planned pregnancy, or upcoming participation in hostilities.
This preventive precaution is carried out due to the fact that in many people the properties of toxoid disappear after 5 years
Vaccination calendar in Russia for children of the first year of life
Article on the topic: Herbal preparations for menopause
How quickly do tetanus spores spread throughout the body of an adult and a child?
The causative agent of tetanus is the tetanus bacillus.
It is one of the opportunistic microorganisms, since it is constantly present on the body of each of us or in the intestines, without causing disease. The bacteria's exotoxin, which it begins to produce when exposed to a favorable environment, is dangerous to humans. As a rule, tetanus bacteria are in an inactive state in the environment, taking on the form of spores. In this form, they easily tolerate temperature changes and persist for a long time in soil, dirt, and manure. Tetanus bacillus is a classic anaerobe that turns into a vegetative form at a temperature of at least -40 C and the absence of oxygen.
The ideal environment for the growth and reproduction of the microorganism is wound surfaces, especially deep puncture or incised wounds, crushed tissue, and burns. Tetanus can enter the body with unsterile instruments during surgical operations under aseptic conditions, criminal abortions, and poor-quality dental procedures.
Once in the body, tetanus spores transform into a vegetative form and begin to produce an exotoxin - tetanospasmin. The period of time from infection to the development of the first symptoms of the disease is called incubation and can last from three days to a month for different people.
The length of the incubation period depends on many factors:
- the amount and activity of tetanus bacillus, which entered the body through the wound surface;
- the presence of vaccine immunity in the patient and his condition;
- supporting forces of the body;
- age characteristics;
- concomitant diseases.
In children, the exotoxin begins to act much faster than in older patients, since less of it is needed to develop seizures. As a rule, it takes 8 to 14 days for the first signs of the disease to appear.
This time is quite enough for, if a potentially infected patient does not have a tetanus vaccination, to begin administering antitetanus serum, which will protect him from the likely progression of the pathological process.
Normal reaction to a vaccine
Mothers often wonder whether it is possible to wet a tetanus shot. Experts say that it is worth protecting the vaccine injection site from water for at least 2 days to avoid the risk of skin irritation. The body most often reacts normally to this vaccination, although minor reactions may occur that do not require additional action or medication, namely:
- local inflammation: redness, swelling of the skin, slight compaction at the injection site;
- slight pain at the injection site;
- increase in body temperature within 37.5 C;
- general weakness, fatigue, lethargy.
These symptoms indicate that the immune system is reacting to the irritant and disappear after a few days.
When do you get a tetanus shot?
What is the tetanus vaccination schedule? This is a mandatory vaccination included in the national calendar, which is given to all babies a few months after birth. At what age do children get a tetanus vaccine? The first meeting of the child in the case of routine vaccination against tetanus occurs at the age of 3 months. This is not the only protection during this period of a child’s life, since the vaccine in most cases is complex and also includes antigens against whooping cough and diphtheria (DTP). The event is planned in advance, so the mother and child are invited by a nurse to the clinic, where the doctor examines the baby and then sends her to the prevention room.
In order for the immune system to work better when encountering an infection, the vaccine must be administered at least three times. Therefore, according to the vaccination schedule, the next vaccination is given 1.5 months after the first, and then another one at 6 months.
How often do you get a tetanus shot? At 18 months, to consolidate the effect, a revaccination is carried out, the second at 6 years, then at 16 (sometimes the third revaccination takes place at 14 or 17 years, it depends on the vaccination schedule, it has changed a little over the past decades). After the third revaccination, a tetanus vaccine is given every 10 years. There are no age restrictions for her. Bacteria are found on almost all objects around us and in the soil; you can encounter an infection at any age, and after 50 complications there are many more due to the weakness of the body.
In addition to planned cases, there are also emergency tetanus vaccinations. When are they made?
- Before carrying out operations. When referring for surgical treatment, one of the mandatory points in the referral is the presence of vaccinations. If vaccination data is lost, the patient must be vaccinated additionally.
- Emergency vaccination is carried out for frostbite, burns and all types of wounds. It is done regardless of whether a routine tetanus vaccination has been carried out or not.
- An emergency tetanus shot is given when a dog is bitten. Wounds with deep penetration are dangerous due to numerous complications, the development of tetanus is one of them. To prevent an infectious disease, tetanus toxoid is urgently administered.
- Long-healing ulcers, ulcerative lesions of the extremities, gangrene of the fingers are an indication for additional vaccination.
- In what other cases should you get a tetanus vaccination? Women are vaccinated after home births and illegal abortions.
Vaccination scheme
Tetanus vaccination is carried out according to routine immunization. Vaccinations begin from infancy. The schedule largely depends on the drug used.
The routine ADS vaccination schedule for children is given below:
- first vaccination – at 3 months;
- the second - at 4-5 months;
- third - in six months;
- fourth - at 1.5 years;
- fifth - at 7 years old;
- sixth - at 14 years old.
Further revaccination is carried out every 10 years. A single dose for children and adults is 0.5 ml.
It is important to get vaccinated on time to minimize the chance of infection with Clostridium tetani bacteria.