Persuading a child to go to the dentist is not an easy task, especially when dental treatment is required. Sometimes it takes 2-3 days to persuade, and sometimes a whole week. But if caries at the initial stage can still be tolerated, then an abscess on the gum requires urgent medical intervention.
Yes, sometimes a purulent formation can go away on its own. But, as a rule, inflammation returns, especially in autumn or winter, when the child’s immune system is weakened. It is not uncommon for a lump to form during colds. But an abscess can lead to tooth loss or infection of other teeth. Don't wait for the lump to disappear on its own or appear again, contact your pediatric dentist!
Treatment
Depending on whether a permanent or baby tooth caused a lump on the child’s gums , the doctor carries out appropriate treatment. If a permanent tooth is damaged, seek help immediately while there is a chance to save the child’s tooth. The doctor will have to remove the nerve and fill the canals. In this case, adult dental treatment is a necessity, because if high-quality treatment and appropriate treatment are not carried out, the child may lose a tooth.
Milk teeth are removed immediately - their root system has not yet had time to form, and it is impossible to properly fill the canals. In addition, if the diseased tooth is left, the molar may grow back with defects.
The specialists of the Medexpert Center for Family Dentistry will help you
cure or remove a child’s tooth All procedures in the clinic are performed under medical sedation. While the baby is sleeping peacefully and does not feel pain or discomfort, the doctor can carry out all the necessary procedures. The ability to treat teeth in a dream is a real salvation for parents and children. In addition, sedation is safe for the child’s body and even helps to cope with dental phobia.
Teething cyst
Bumps on the gums that appear during the eruption of milk or permanent teeth (usually at 5-6 years old or much less often at 7-8 years old) have a major difference from abscesses - they are not inflammatory in nature and are only a reaction of soft tissues to the advancement of the dental crown .
Signs of an eruption cyst
Such formations form quite rarely and can appear both on the upper gum and in the area of the lower teeth. Non-inflammatory bumps do not cause any discomfort to the child and are detected only during examination of the oral cavity. Only sometimes infants may experience excessive salivation.
2-3 weeks before the tooth appears, a transparent or blue lump forms on the mucous membrane of the gum, which has a soft consistency and does not hurt when pressed. If the developing cyst affects a small blood vessel, then hemorrhage into its cavity is possible. She turns black. At the moment of eruption of the dental crown, such a lump is imperceptibly opened or gradually dissolves without a trace. The general condition of the children does not change in any way.
Treatment
This type of dental cyst does not require treatment. Sometimes, if such a lump appears in the area of the front teeth and causes cosmetic discomfort to the child, then it is possible to open it in the sterile conditions of a dental office.
Memo to parents
Even though baby eruption cysts are not dangerous and do not cause any complications, there are some things you should be aware of:
- It is strictly forbidden to open the cones yourself, since non-sterile objects can introduce infection into the gum tissue and cause the development of inflammatory reactions.
- It is extremely rare, but eruption cysts can fester. If, against the background of complete well-being, the baby begins to complain of pain in the gums, fever, and the lump itself becomes red and swollen, then you should immediately seek the advice of a dentist.
Purulent bumps and cysts during teething are not a sign of pathology in the development of the dental system. In both cases, it is important to maintain proper oral hygiene, periodically examine the mucous membranes and, if necessary, visit the dentist.
Prevention
- oral hygiene (make sure your baby brushes his teeth properly);
- balanced diet;
- rinsing your mouth every meal;
- preventive procedures (remineralization, fluoridation; fissure sealing);
- timely dental treatment;
- preventive examinations at the dentist 2 times a year.
Timely dental treatment for children and proper oral hygiene are the main weapons in the fight against caries and other diseases. Teach your child to take care of the health of their teeth and beautiful children's smiles will delight you every day!
Reasons for the formation of cones
The causes of a lump in a child’s mouth depend on the child’s age and the development of the maxillofacial system. The etiology of a dental problem is divided into:
- bacterial or fungal infection;
- age-related changes in the oral cavity;
- damage from external factors.
Teething
Each person teethes twice in his life: 5 months after birth and at the age of 6 years. Temporary (baby) teeth form bumps on the gums when they erupt. Such growths hurt and itch, thereby disturbing the child.
The permanent dentition replaces the lost baby teeth. Front teeth erupt at age 6 or 7, first molars and canines at age 8, and second molars at age 9.
It is important to remember that the timing of teething in children is strictly individual and depends on the degree of development of the child’s body. But, despite this, the signs of tooth growth are always the same: the appearance of bumps in the mouth, pain and itching in the gums, deterioration in general condition, an increase in body temperature to 37 degrees.
Purulent lump
The growth of a lump with pus in a child’s mouth is possible for 2 reasons:
- Caries of one or more teeth in an advanced stage.
- Severe inflammation of the gums, accompanied by deep periodontal pockets, bacterial plaque and tartar.
Pathogenic microflora and the toxins it produces accumulate in the soft tissues of the gums, thereby forming a purulent ball.
When examining the mouth, all signs of an inflammatory process are observed: the presence of gingival growth, redness of the gums, a large amount of plaque on the teeth, halitosis and the release of pus when pressed.
To prevent infection of nearby tissues and organs, it is recommended to begin treatment immediately after detecting signs of the disease.
Gum injury
In most cases, gum injury occurs in one-year-old children. This is explained by high activity in games and excessive curiosity about the world around us. At this age, children are very vulnerable and difficult to control by their parents. Damage to the gums also occurs at older ages, but such cases account for only 40% of childhood dental injuries.
After a bruise, a blood clot accumulates in the soft tissues, turning the gums scarlet or bluish. The child complains of throbbing pain that increases with palpation. To prevent the lump from increasing in size and the blood clot to begin to dissolve faster, it is recommended to apply dry cold to the damaged area.
In the photo you can see examples of gum injuries sustained in childhood.
Flux or periostitis
A soft lump on the gum may indicate purulent inflammation in the mouth. After a child’s gums become inflamed, the alveolar process begins to swell and thereby enlarge the cheek. The facial configuration changes, and this is one of the patient's main complaints. Since the nerve in the tooth dies due to the activity of pathogenic bacteria, gumboil is not always accompanied by pain.
To avoid phlegmon, sepsis and other dangerous complications, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible to remove the source of infection.
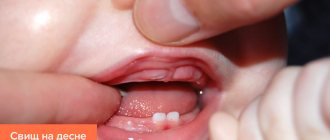
How to treat an abscess on the gum?
If an abscess or fistula appears, then you should not expect that the situation will resolve on its own: you need to make an appointment with a dentist. Treatment of an abscess on a baby tooth and a molar one will be different.
The appearance of an abscess on a baby tooth indicates periodontal inflammation. Such teeth must be removed, since the inflammatory process in the upper part of the root, accompanied by the formation of pus, may well spoil the molar, which will soon erupt in place of the milk tooth. This happens because the roots of temporary teeth are located next to the rudiments of molars. Bad bacteria and infection can also enter the lymph nodes under the jaw, causing them to become inflamed. The occurrence of a fistula means that pus will constantly seep into the mouth, which can cause the development of tonsillitis, since the tonsils will become infected. Various colds in a child are a direct consequence of an abscess on a tooth. Also, do not forget that toxins formed in the area of inflammation will definitely enter the bloodstream: this can result in allergic reactions, asthma and other serious general somatic diseases.
If we are talking about an abscess on a molar, then ordinary treatment is required for adults (provided that the tooth is not fundamentally damaged and can still be saved from removal).
Having discovered an abscess in a child, you should not try to cure it on your own. You can easily find a lot of advice on the Internet on how to relieve inflammation, but no amount of rinsing or even taking powerful antibiotics can eliminate the inflammatory focus located at the root of the tooth. Moreover, it is useless to hope that the tooth ache will stop. A bursting lump (this often happens) indicates only a short respite, during which, meanwhile, bacteria will still continue to enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. This situation can turn into a serious problem if the child has diseases of the respiratory system, heart and other internal organs.
Often, dentists suggest leaving teeth near which the inflammatory process is occurring, persuading the parents of a young patient to carry out the silvering procedure. The arguments for refusing removal can be very compelling: possible problems with diction and pain during the removal operation. However, such dentists neglect the information contained in every textbook on dentistry, which clearly states that a baby tooth with a purulent focus must be removed. Silvering will only complicate the situation, and an unresolved inflammatory process can lead to asthma, tonsillitis and even diabetes: in comparison with these diseases, temporary problems with diction will seem like sheer nonsense.
But the formation of an abscess can be prevented, and this is not difficult to do - just teach the child to maintain oral hygiene. At an early age, a child cannot be adequately responsible for his actions, including those related to the care of the oral cavity, teeth and gums, so responsibility for the procedure lies entirely with his parents, who must control how and when the child brushes his gums and teeth . It is the parents who should buy the most effective baby toothpaste that guarantees maximum protection against caries.
How to treat a fistula?
You should absolutely not self-medicate your child, but there are a number of folk remedies that can, in case of severe pain from a fistula, reduce it and even eliminate it altogether in order to wait for a trip to the dentist:
- Take 10 grams of calendula and strawberry leaves and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Moisten a cotton swab with liquid and apply to the painful area. Change the tampon every hour until the pain subsides.
- Pour 10 grams of St. John's wort into 100 ml of water, boil and rinse your mouth with the resulting infusion every 2 hours. To soften the unpleasant bitter taste of the medicine, because of which the child may even refuse it, add 10 grams of natural honey.
- Take 15 grams of medicinal chamomile flowers, 10 grams of oak bark and 10 grams of sage herb, pour 200 ml of boiling water and leave in a warm place for an hour. You need to rinse your mouth with this infusion 6-7 times a day.
- Pour 50 grams of medicinal chamomile flowers into 200 ml of boiling water and place in a dark place for an hour. You need to rinse before and after meals.
- Take 20 grams of calendula flowers, 10 grams of yarrow flowers, 10 grams of dandelion roots and 10 grams of tansy herb. Grind the mixture in a coffee grinder, add 20 grams of ichthyol ointment and 10 grams of honey. After mixing well, lubricate the affected gums. This is an effective remedy for the treatment of fistula.
Having relieved discomfort with these remedies, you should not delay your trip to the doctor. He will take an x-ray, make a diagnosis and make a decision: is it worth starting treatment of the tooth or is it better to remove it. A small fistula can be treated when the tooth root has minimal damage. If the fistula is serious enough, it is more advisable to remove the tooth in order to avoid possible complications and harmful effects on the child’s fragile body.
For a child’s health, the development of a fistula is dangerous because the baby swallows the pus released from the fistula, and it enters the stomach, causing damage to the child’s immune system. The consequence can be various diseases, including the most dangerous blood poisoning.
Inflammation of the tooth root can lead to a dangerous aggravation at any time. A severe toothache will cause unnecessary stress for a child. The pus released from the fistula can have a negative effect on the tissues located around the teeth. This may become an ongoing problem in the future. A fistula that appears on a child’s gum is not a cause for severe anxiety, but if additional symptoms occur—redness of the gums, swelling, pain—it is imperative to consult a specialist. The baby tooth that caused the fistula will most likely need to be removed.
How to treat at home
If it is not possible to immediately take the child to the dentist when an abscess appears, at home parents can provide the following first aid to the toddler:
- Give an antipyretic drug approved for the child's age at elevated temperatures.
- Suggest rinsing the mouth with a warm decoction of chamomile or sage if the child already knows how to rinse and the abscess has not opened.
- Do not give your child hard or hot food.
- To reduce pain, apply something cold to your cheek.
- Do not allow the child to touch the abscess.
- Give your baby more fluids.
- Call an ambulance if the baby's condition worsens.
If an abscess is detected in a child, it is strictly prohibited:
- Try to open the formation with your own hands. This threatens infection in the blood.
- Warm the area of inflammation using hot compresses or rinsing with hot water.
- Giving your child an antibiotic without a doctor's prescription.
- Rinse your mouth if the abscess opens.
Treatment of neoplasms in the oral cavity
A lump under the jaw or on the gum can be detected upon examination. For an accurate diagnosis, a biopsy or x-ray is prescribed. Treatment is selected taking into account the cause of the formation of a bubble in the oral cavity. It will be necessary to stop the further spread of infection and eliminate discomfort.
The doctor will determine how to remove the lump after a complete diagnosis, but the main measures include:
- fistula - pus is removed by rinsing with a disinfectant solution;
- epulis - surgical intervention (removal using diathermocoagulation, cryodestruction or a scalpel);
- periodontitis - removing fillings, cleaning canals, removing pus, rinsing with herbal decoctions and soda solution;
- periostitis - placement of special drugs under a temporary filling (if there is no result, the tooth will have to be removed);
- gingivitis - cleaning of periodontal tubules, antiseptic and antibacterial therapy, removal of lumps.
When a formation appears on the gum, you can rinse your mouth with vodka, diluted alcohol or juice from fresh Kalanchoe leaves.
Timely diagnosis allows you to prevent further spread of infection and save teeth. Only an experienced dentist will help you get rid of a lump in your mouth, minimizing the risk of developing serious complications. At the first signs of pathology, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Preventive measures to prevent the formation of lumps on the gums
To reduce the likelihood of an abscess to a minimum, a child from childhood should be taught to carefully observe oral hygiene.
The list of the most effective measures includes:
- Brushing your child's teeth twice a day. First, parents should brush their child’s teeth themselves, showing how to do it correctly, gradually giving the child more independence in this matter;
- rinsing your mouth after every meal;
- minimizing sweets in the diet - it is important to ensure that the child keeps caramel and candies in his mouth as little as possible;
- Do not introduce your child to chewing gum (the product is especially harmful if it contains sugar).