Human immunity is directly related to the intestinal microflora, respiratory system and genital area. Tests for dysbacteriosis are a reliable and affordable way to clarify the origin of ailments and erect a reliable barrier to pathogenic strains. An imbalance, the disappearance of beneficial microorganisms, is often the root cause of many chronic diseases. Leads to the accumulation of toxins, atrophy of the gastrointestinal mucosa, poor absorption of vitamins and microelements, and activates the action of viruses.
Features of the analysis for dysbacteriosis
Feces are the end product of human life. They carry information about the quality and speed of absorption of nutrients, the condition of the organs involved in digestion. The main task of the analysis for dysbiosis is to provide information about the ratio of beneficial, harmful and opportunistic bacteria in the body. When the colony of beneficial species decreases, harmful bacteria begin to dominate the intestines unhindered, causing bloating, problems with stool, skin, abdominal pain, and general malaise.
The ambiguity of the reasons for the disruption of interaction between species significantly complicates the diagnosis of diseases. Therefore, in many cases, when clarifying the diagnosis and choosing tactics for successful treatment, key indicators in the analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis play a decisive role:
- Color, smell, consistency.
- Presence of undigested food particles.
- Presence of blood, mucus.
- Leukocyte count.
The obtained result of the study allows the doctor to notice in a timely manner
- presence of problems with the stomach, pancreas;
- the beginning of the inflammatory process;
- helminth infection;
- lack of beneficial microflora.
In order to monitor the dynamics of treatment, an extended analysis for dysbacteriosis can be prescribed to the patient repeatedly. In some cases, when a more in-depth examination is required, the patient must undergo additional tests for worms and enterobiasis, pathogenic bacteria.
By contacting the Euromedperstizh multidisciplinary clinic in Moscow, you will be confident in the quality of any tests. The bacteriological laboratory, equipped according to European standards, is our pride. Modern equipment and knowledge of advanced techniques allow us to perform traditional and unique clinical diagnostic studies. High accuracy of the results of stool analysis for dysbacteriosis, immunological study of urine, bile, blood and cerebrospinal fluid is guaranteed.
Analyzes are performed in 2 ways: traditional and inexpensive bacteriological and advanced biochemical, providing an answer within 1 day.
When a doctor prescribes a test for the presence/absence of dysbiosis:
- if a person has undergone a long course of therapy with antibiotics, immunosuppressants, glucocorticosteroids, or a course of chemotherapy;
- if a person uncontrollably took antibacterial drugs or laxatives without a doctor’s prescription;
- if antibacterial therapy does not bring the expected result;
- if a person suffers from chronic alcoholism, chronic pancreatitis and other conditions characterized by malabsorption - lack of nutrients as a result of their insufficient absorption in the small intestine;
- with frequently recurring or regular diarrhea;
- for allergic diseases that are not amenable or poorly amenable to therapy;
- if a person has been exposed to radiation, chemicals;
- after surgical interventions;
- after acute intestinal infections.
Indications for testing for dysbacteriosis
Living in an urbanized world of haste, constant stress, physical overload and poor nutrition leads to the destruction of beneficial intestinal microflora and, as a result, to a decrease in immunity. Actually, this is the essence of dysbiosis: there are a lot of bacteria, but there are few of them necessary for the human body. Frequent constipation, heartburn, nausea, belching, bad breath and even “snudges” in the corners of the lips are already a good reason to get tested for dysbacteriosis. In addition, the prerequisites for prescribing a bacteriological examination of stool are:
- flatulence, feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the stomach;
- persistent diarrhea, constipation, foul-smelling stool;
- noticeable loss of appetite, lethargy, drowsiness, black or gray stools;
- rejection of certain foods;
- previous treatment with hormonal drugs and antibiotics;
- severe forms of allergies that are difficult to treat conservatively;
- sudden weight loss, bloating, cheesy coating on the tongue;
- personal request of the patient.
The sudden appearance of a skin rash, unstable stool, mucus and blood in the excrement should also alert you. Only a specialist can determine the need for a stool test for dysbacteriosis: a therapist, an infectious disease specialist or a gastroenterologist. You can contact him with your complaints and symptoms that occur after consuming fatty heavy foods or alcohol. If the doctor considers the analysis necessary and useful for you, he will give a referral, and after receiving the result, he will provide a transcript for free. Prescribing a study on your own simply does not make sense.
Normally, the gastrointestinal microbiota has the following composition:
- in the stomach there is the lowest density of microorganisms with a predominance of lactobacilli, streptococci, and sarcina;
- the small intestine is populated predominantly by lactobacilli and streptococci in an amount of 103-108 CFU/ml;
- The large intestine is especially densely populated - up to 1012 CFU/ml; bacteroides, clostridia, fusobacteria, and bifidobacteria predominate.
On average, the intestines are populated by about 50 trillion (!) microorganisms of approximately 500 different species, including yeast, the role of which is not yet completely clear.
Until some time, microbiota were considered exclusively commensal organisms, i.e., coexisting harmlessly with humans. However, it turned out that the relationship between the “host” and microorganisms is more complex and based on mutual benefit.
Microbiota maintains our immunity in good shape, prevents the growth of harmful types of microorganisms, exhibits antagonism to pathogenic bacteria, produces enzymes, and produces bacteriostatic and bactericidal substances. The microbiota plays a great role in modulating physiological processes: motility and secretion of the gastrointestinal tract, maintaining the integrity of the epithelial barrier.
Go to analyzes
Preparation and rules for collecting material
Strict adherence to the rules for preparing and taking samples of biomaterial is the key to the reliability of the result. To carry out the procedure, you must prepare the necessary container in advance - a pot or a duck. Wash thoroughly without using chemical detergents. Treat with medical alcohol and rinse with boiling water. Before defecation, perform hygiene of the anal area.
- For analysis of dysbacteriosis, stool obtained naturally without the use of laxatives and enemas is selected. Taking carrier medications and using medicinal suppositories should be stopped 3-4 days before submitting the material for research.
- 72 hours before the procedure, avoid drinking alcohol, meat, fish, and foods that color feces, change the smell and consistency. For example, beets, kiwi, blueberries, strong coffee.
- For 2-3 days, do not take medications that affect intestinal motility and accelerate the removal of food from the stomach.
- Women are not recommended to take a stool test for dysbiosis during menstruation.
- Collect the biomaterial in a sterile pharmaceutical container, tightly closed with a lid. Deliver to the laboratory within 4-8 hours. Do not freeze!
A sample taken earlier than 4 days after intestinal endoscopy or stomach radiography using contrast enhancers is considered unsuitable for research.
The most popular question, how to take 10-15 g of feces into a container, can be solved very simply. In order not to struggle with cotton swabs, matches and toothpicks, the easiest way is to use a plastic teaspoon.
How to collect stool for analysis
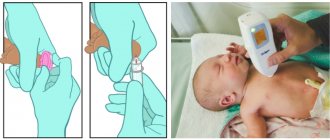
So, the doctor ordered a test for dysbiosis in the baby. How to collect material for analysis?
Experts do not recommend using a diaper to collect feces. If the toilet is performed at a certain time in the morning, it is necessary to place the child on a clean oilcloth, and then carefully collect what happened from it.
If you have problems with bowel movements, you can help your baby by bending his legs towards the navel or laying him on his tummy. You can also use a rubber gas tube for stimulation, lubricating the tip with Vaseline. It needs to be inserted into the anus - shallowly - and rotated slightly. A few minutes after this procedure everything will happen. Feces need to be collected with a spoon, which comes with the container for testing.
You can also help your baby by giving him a tummy massage. Place your palm on the belly near the navel and gently massage your baby's tummy in a clockwise direction. Periodically press the baby's bent knees toward his stomach to speed up the process.
On the container with the received material, it is necessary to indicate the surname, first name and age of the child, as well as the time of stool collection.
Features of therapy
Treatment largely depends on which microorganisms have deviated from the norm, whether there is mucus, blood and other particles in the stool that should not be there. The doctor, studying the results, makes a diagnosis no earlier than he analyzes all the indicators.
If the transcript shows a decrease in the amount of E. coli, this may indicate the presence of worms in the intestines. Sometimes the cause may be a decrease in enzymatic activity, which is why this bacterium does not bring any benefit (although it does not harm). Despite all the benefits of E. coli, its number should not exceed the norm. If this happens, it means that dysbiosis is developing in the body.
As for hemolytic E. coli, in young children they should be completely absent. These pathogens produce toxins that negatively affect the nervous system and intestines, and can also cause various intestinal diseases and allergies.
Deficiency of bifidobacteria and bacteroides leads to long-term intestinal disorders in both children and adults. These bacteria appear in the baby on the tenth day of life. At the same time, children born through cesarean section have significantly fewer of them than babies born naturally.
Lactose-negative enterobacteria in children and adults should not exceed the norm. If the analysis shows their increased proliferation, this can explain the baby’s heartburn, regurgitation, belching, and increased gas formation. Enterococci normally do not harm the body and are even beneficial. But if their number is higher than normal, they will cause the development of infectious diseases of the pelvic organs and urinary tract.
While non-pathogenic staphylococci do not particularly harm the body (within normal limits), the presence of Staphylococcus aureus is dangerous for children. It causes diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, high fever in the baby, mucus and blood are present in the stool. Therefore, Staphylococcus aureus should be absent in the feces of infants . If Staphylococcus aureus is present in the body, then its effect depends on beneficial bacteria . If their number is normal, the body is not afraid of Staphylococcus aureus and the baby does not need treatment. In severe cases, hospitalization is required.
When the doctor prescribes treatment, his instructions must be followed. To destroy fungus, clostridia, Klebsiella, lactose-negative enterobacteria, Staphylococcus aureus, normalize the digestive system, and get rid of mucus in the feces, special medications designed for small children are needed.
During treatment, special attention should be paid to the nutrition of children, since in many cases it is an incorrectly selected diet that causes the growth of clostridia, enterobacteria, Klebsiella and other pathogens. The diet must be agreed with your doctor. If the baby is breastfed, the mother must follow the diet.
When testing for dysbacteriosis in a child’s body, a tendency is immediately revealed that confirms the immaturity of the organs of the digestive system. At the same time, this type of analysis confirms the existing imbalance in the intestinal microflora. Most often, with dysbacteriosis in infants or newborns, there is a risk of having any diseases, as a result of which a malfunction occurred in the body. In most cases, dysbiosis does not have pronounced symptoms and is usually similar to any other disease of the digestive tract. In this regard, it becomes quite difficult to determine and identify dysbiosis in the child’s body. Therefore, submitting stool for analysis is one of the reliable and accurate laboratory methods that can confirm this diagnosis.
Degrees of dysbacteriosis
| Microorganisms | Indicators for children under one year old, CFU/g | Indicators for children after one year, CFU/g |
| I degree of dysbacteriosis | ||
| Reduction of bifidobacteria | 10*9-10*8 | 10*8-10*7 |
| Reduction of lactobacilli | 10*5-10*4 | 10*6-10*5 |
| Reduction of typical Escherichia | 10*6-10*5 | |
| Growth of typical Escherichia (possibly) | 10*9-10*10 | |
| II degree of dysbacteriosis | ||
| Reduction of bifidobacteria | from 10*8 and below | from 10*7 and below |
| Reduction of lactobacilli | from 10*4 and below | from 10*5 and below |
| Growth of opportunistic bacteria, mainly hemolytic Escherichia | 10*5-10*7 | |
| Detection of groups of opportunistic bacteria | 10*4-10*5 | |
| III degree of dysbacteriosis | ||
| Reduction of bifidobacteria | from 10*8 and below | from 10*7 and below |
| Reduction of lactobacilli | from 10*4 and below | from 10*5 and below |
| Presence of groups of opportunistic bacteria | 10*6-10*7 | 10*8-10*7 |
**Literature: Dysbiotic intestinal disorders in children, principles of correction. Fayzullina R. A., Pikuza O. I., Zakirova A. M., Shoshina N. K. – Methodological manual. – Kazan, KSMU, 2015.
Dysbacteriosis occurs in 90% of infants. Most often, an imbalance of intestinal microflora is diagnosed in babies who are bottle-fed, born prematurely and with low weight. Dysbacteriosis is treated with the help of probiotic preparations - Linex, Bifidumbacterin, etc. These drugs stimulate the reproduction of beneficial microflora. Often, when dysbiosis is detected, a doctor advises sticking to a diet and switching to a different mixture.