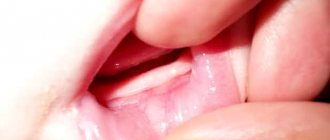
What does a fistula on a child’s gum look like?
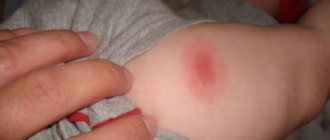
It's just a purulent tubercle with a hole. Symptoms of the formation of a fistula on the gums of a child are fever, acute pain, bad breath, difficulty breathing. These signs should be a reason for parents to urgently consult a dentist.
Where does this misfortune come from? The age of the baby sometimes helps to understand the cause of the disease.
- ✔
At two years old, a fistula on the gums of a child most likely indicates congenital pathologies of the dentition.
✔
Up to three years of age, a fistula on the gum in a child can be caused by osteomyelitis.
✔
At the age of 4, a child’s fistula on the gum usually occurs due to inflammation of the maxillary sinuses.
✔
In a 5-6 year old child, a fistula on the gum may appear after an injury and indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
Possible causes of the problem
The cause of a fistula is usually a pathological process. To understand why a child has a tubercle above a tooth, you should pay attention to the accompanying symptoms, which may indicate the following conditions:
- granulating periodontitis: one of the most common causes of fistula in childhood. This disease often becomes a complication of advanced caries. Inflammatory processes in the periodontium - the tissues surrounding the tooth root - are accompanied by the proliferation of granulation connective tissue. Most often, this form occurs in children. The catalyst becomes one of the external factors: hypothermia, severe fatigue and viral diseases,
The photo shows periodontitis in a child - osteomyelitis: inflammatory processes in the jaw bone are infectious in nature and usually occur against the background of certain dental diseases. A child's fragile immune system allows the disease to spread quite quickly. The child develops a fever, and in some cases it is necessary to resort to hospital treatment,
- cyst: a kind of capsule with liquid that occurs as a result of certain disturbances in the development of teeth or due to untimely treatment of dental diseases. If appropriate measures are not taken in time, the cyst will develop into a fistula,
- sinusitis: inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is accompanied not only by the formation of fistulas, but also by nasal congestion, headaches and general weakness of the body,
- tooth retention: difficulties in teething can also provoke the appearance of a purulent tubercle on the gum. A phenomenon such as retention may be associated with abnormalities in the structure of the gums or too early loss of baby teeth. In such situations, a cyst with an infected membrane is formed, which gradually develops into a fistula,
Formation of a tubercle on the gum during teething - trauma to the tissues of the oral cavity: damage to the mucous membrane and teeth from sharp objects and too hard foods, injury due to a blow or fall,
- medical errors: incompletely sealed canals leave room for the rapid proliferation of bacteria. In addition, a fistula can appear due to an incorrectly installed filling or careless injury to soft tissues during a dental procedure.
Fistula in a child as a consequence of periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the tissues surrounding the root of the tooth.
As a rule, in children it is asymptomatic and with minimal pain. A common form of periodontitis in primary teeth is chronic granulating, and a fistula on the gum is a common addition to this disease. This is due to the anatomical features of the bone structure in children and the physiological changes that constantly occur in it. For example, on the gum of a baby tooth, a fistula in a child often appears due to improper eruption. In the granulating form of periodontitis, an odontogenic fistula can form on the gums, skin, and submandibular region. The disease is preceded by excessive growth of granulations (tissue with a granular surface that develops during the healing of wounds and foci of inflammation). During the course of the disease, a shallow carious cavity forms, the mucous membrane around the tooth turns red, it becomes mobile, and the inflammatory process provokes the appearance of a fistula in the child. If left untreated, the infection spreads to other organs.
Causes
A fistula is a signal that there is a pathogenic microflora in the mouth. There are several common causes of the disease.
- Thin and weak children's enamel. Baby teeth quickly decay. In the carious cavities, inflammation begins, leading to suppuration and hardening of the gums.
- Untreated caries that promotes the growth of granulosa tissue. Because of this, periodontitis develops, stimulating the accumulation of pus at the root.
- Osteomyelitis. Infectious lesion of the skeletal system, provoked by bacteria and weakened immunity.
- Injuries that compromise the integrity of the gums. They become a trigger for inflammation.
During the examination, the dentist must take into account the age of the child. A fistula in children under 2 years of age may indicate congenital abnormalities of the jaw or improper teething. Children 7-10 years old are susceptible to the disease during the period of replacement of milk teeth with molars.
In the vast majority of cases, fistula is a consequence of untreated caries
The formation of a fistula canal is facilitated by a passion for sweets, superficial oral hygiene, sudden hypothermia, and improper filling of teeth. In preschoolers, the cause is the habit of sucking fingers and putting toys in their mouth.
Purulent fistula on the gum of a child
Odontogenic osteomyelitis, like periodontitis, is characterized by the presence of purulent inflammation and the formation of fistulas on the gums in children. The source of infection is caries: in 80–87% of cases this is true for primary molars and the first permanent chewing tooth on the upper or lower jaws. Among the prerequisites for the disease are age-related imperfections of the immune system, which, in turn, is associated with the immaturity of the nervous, endocrine and lymphatic systems. Physical fatigue, hypothermia and previous infectious diseases contribute to the development of osteomyelitis. Timely treatment of a purulent fistula on the gums of a child will help avoid abscess, inflammation of the molar and infection of internal organs.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis will require a visual examination and x-rays.
If a fistula appears in the gum area, the child must be taken to see a dentist. It is possible to see and find out the real source of a purulent formation only with a standard examination and examination.
A fistula is a tubercle on the surface of the gum mucosa, which is very clearly visible upon visual inspection. It is often located near the root teeth and differs in color from the gums.
For a complete diagnosis, the dentist prescribes an x-ray of the jaw. This is the most effective and informative examination method. It allows you to determine the degree of damage and the type of pathological condition. Thanks to an X-ray image and a detailed visual examination of the gums, the dentist will differentiate the diagnosis and prescribe a competent course of treatment.
Cause of primary fistula
Sinusitis is one of the causes of primary fistula. After removing a diseased tooth in the upper jaw, there is a risk of the formation of a fistula tract (ostium) between the maxillary sinus and the oral cavity through the tooth socket. Bacteria penetrate through it from the oral cavity, which provokes inflammation of the sinuses. Usually the hole lasts from 7 to 10 days, then it epithelializes and takes the form of a fistula tract. This is the so-called primary fistula. A secondary fistula forms after an unsuccessful operation.
Children's fistula is the result of a tooth that has not fully erupted
A tooth that has not fully erupted can also cause the formation of a childhood fistula. The space between the sac covering the crown of the growing tooth and the enamel increases and fills with liquid. As a result, a follicular cyst is formed - a thin capsule lined with stratified squamous epithelium. If its membrane becomes infected from the oral cavity, then suppuration occurs. Such chronic inflammation provokes the formation of fistulas on the gum of a child’s baby tooth.
Also, fistulas form on the mucous membrane of the palate, depending on the position of the crown of the impacted tooth. The cause may be caries or a chewing abscess. Sometimes there is also the formation of a fistula on the child’s face. It also occurs in advanced cases - when an abscess spontaneously opens or after the integrity of the source of inflammation is violated by an external incision.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a fistula at the beginning of the disease do not manifest themselves in any way. Then, depending on the degree of development of the disease, characteristic signs appear:
- At an early stage, pain develops in the area of the tooth, which intensifies when touching the formation on the gum or when eating food.
- At a later stage - redness of the gums, swelling of the mucous membrane, discharge of purulent contents from the fistula opening, causing loose teeth and the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
- In a complicated course against a background of weakened immunity, osteomyelitis may develop in infants. With the progressive form of the fistula, hyperthermia, enlarged lymph nodes, and facial asymmetry due to swelling of the upper lip and neck are noted.
- There is difficulty breathing due to inflammatory manifestations and an increase in the amount of pus, leading to blockage of the nasal passage.
- Swelling of the eyelids and corners of the eyes is possible.
- Symptoms of a fistula , the predecessor of which was the chronic form of single-genus sinusitis. They are different and depend on the age of the child. Infants and young children experience redness of the upper jaw and signs identical to those of osteomyelitis. In adolescents, inflammation spreads to many facial sinuses.
The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- Heat.
- Migraine.
- Respiratory dysfunction.
- Swelling of facial muscle tissue.
- Acute pain in the trigeminal nerve area.
- Painful palpation of the fang pit and gums.
- The skin and mucous membrane of the nostrils and upper lip have changes in color.
Attention! If you notice one or another symptom in a child that is characteristic of a fistula on the gum, you should contact a dental clinic and receive qualified medical care.
Treatment of a fistula on the gums of a child
What to do if a child has a fistula? To begin with, the main thing is not to panic, exclude solid foods from food and rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions to relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. However, these are only basic measures to alleviate the condition a little. How to cure a fistula on the gum of a child? It is necessary to consult a dentist for qualified help. Depending on the stage of development of the disease, treatment of a fistula on the gums in a child involves various options.
Drug treatment
At the early stage of infection, it is enough to use antibacterial drugs to relieve swelling and prevent the spread of infection.
Therapeutic method
For more complex forms of the disease, a specialist will clean the tooth canals, remove plaque and purulent deposits. Then he will do a professional cleaning and fill the diseased tooth.
Surgical intervention
If the affected area is too large and the tooth can no longer be saved, all that remains is to remove it and treat the surrounding tissue.
To prevent the occurrence of a fistula on the gum and other dental diseases, parents should promptly familiarize the child with the rules of oral hygiene and subsequently monitor their compliance. Brushing your teeth twice a day and getting regular dental checkups are healthy habits that should be instilled in children from an early age.
What can you do at home?
Many parents are concerned about whether it is possible to cure a fistula on their own and what to do if a suspicious lump appears on the child’s gum. It should be understood that any traditional medicine methods can only be used with the permission of a professional specialist. They usually act as additional measures to reduce inflammation, but the main treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Important! If a child develops any neoplasm on the soft tissues of the oral cavity, you should immediately consult a dentist. Only a doctor can advise what to rinse your mouth with and what medicinal decoctions and infusions can be used in this case.
Chamomile decoction for treatment
Among the most popular remedies that can be prepared at home are decoctions of St. John's wort, calendula flowers and strawberry leaves. Infusions of chamomile, oak bark and sage have proven themselves to be quite good. You can also prepare an ointment from crushed medicinal herbs and sea buckthorn oil. All this really helps relieve inflammation, but the use of such drugs must be agreed upon with a doctor.