Sticking out tongue is the cause of the disease
Why should you worry? It happens that the reason that a newborn cannot keep his tongue in his mouth for a long time is a disease. Parents may notice their baby sticking out his tongue regularly throughout the day, and even at night while sleeping. In this case, if all non-medical reasons are rejected, you should immediately consult a doctor. After all, if the cause of such behavior in the baby is a disease, diagnosing it at an early stage will significantly facilitate treatment and avoid complications. Unusual behavior may be a symptom of the following diseases:
- Increased ICP – intracranial pressure can cause tongue sticking out. At the same time, the child tilts his head back. This disease can lead to a number of complications and delays in the development of the baby, both physical and mental. In this case, treatment is prescribed by a neurologist.
- Oral disease, most often thrush. The mother needs to carefully examine the child’s throat and mouth. Thrush will be indicated by a light-colored coating on the mucous membranes. It causes pain and discomfort, and the baby will constantly move his tongue in and out. For treatment, you should contact your pediatrician.
Is there a problem if a child sticks out his tongue: in what cases should you be concerned?
The fact is that the baby does not yet know how to talk, so if he wants or needs something, he tries to express the request using gestures and facial expressions. Language becomes, in a way, a tool of communication. Seeing that the baby has stuck out its tongue, one can assume that it is hungry or wants to be paid attention to. Another reason is that the baby is sick and his health leaves much to be desired.
Parents should be wary if the baby sticks out his tongue not only when playing, but continuously, even during sleep, without retracting it back. Here it is advisable to sound the alarm and pay a visit to the pediatrician. Having examined the little one, he may send the parents with him for consultation with other medical specialists.
Tongue sticking out
The reasons for such a constant reflex as the baby demonstrating his tongue can be neurological, endocrine or infectious in nature. The presence of some alarming symptoms will be an indicator of one or another disease, which we will present below.
Hypothyroidism
Occurs due to problems with the thyroid gland. The main reason is iodine deficiency in the body, the level of which is determined by a blood test. The test is carried out in the maternity hospital, a blood sample is taken from the baby’s heel.
In addition to the protruding tongue, the baby has a number of other signs such as:
- Yellowish or pale skin tone.
- Dry, flaky surface of the epidermis.
- Slow mental and physical development.
- Severe swelling in the mouth, due to which the tongue does not fit, sticking out.
- Blueness of the area near the nose and lips.
- No weight gain.
- Development of stable constipation.
This case involves hormone therapy as treatment and examination prescribed by a doctor.
Facial muscle atrophy
Damage to the trigeminal nerve is associated with malfunction of the thyroid gland. Reasons: previous acute respiratory infections or any injuries to the face.
Additional symptoms include:
- Lack of movement of the facial muscles, changes in facial expressions (the baby stops crying, smiling, and no longer develops facial folds).
- Lips swell noticeably.
- The face becomes asymmetrical.
- There is drooping of the eyelids.
- Shifting the chin to the side.
May be due to atrophy
The baby is being treated with medications and vitamins by a neurologist. In addition, the child undergoes MRI and ultrasound. Treatment is mainly medicinal. Additional treatments include massages and physiotherapy.
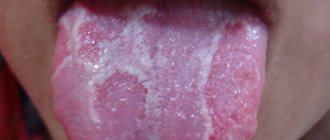
Candidiasis
An infection that affects the mucous membranes of the mouth. The reasons may be: reduced immunity and regurgitation more often than usual.
The child sticks out his tongue, in addition to this it is noticeable:
- The appearance of a whitish, cottage cheese-like plaque in the mouth.
- Redness and inflammation of the gums, uvula, palate.
- The appearance of a grayish-yellow plaque in the absence of proper treatment.
This case requires consultation with an infectious disease specialist, as well as a dermatologist, who will prescribe the necessary ointment and solution for topical use, as well as a complex of vitamins and medications to improve the condition of the immune system.
The main condition that a nursing mother must fulfill is to follow a special diet.
Stomatitis
It appears when viruses or bacteria enter the baby’s body. Noticeable symptoms include:
- Inflammation, redness and swelling of the mouth.
- The appearance of ulcers on the tongue, in the area of the palate and gums.
- Increased body temperature.
- The baby becomes capricious and refuses to eat.
- Sleeps restlessly.
Due to stomatitis
Parents can get help from: a dentist, an immunologist, an infectious disease specialist, who will prescribe a complex of vitamins, immune modulator drugs, as well as the necessary ointment, medicinal solution, and antiviral/antibacterial medications.
Increased intracranial pressure associated with central nervous system pathologies
Causes: damage received during childbirth or infection, such as inflammation of the brain.
Symptoms that require a visit to the doctor:
- If the girth of the child’s head is greater than age norms
- The baby's head is always thrown back
- Swollen fontanel
- The muscles are clearly tense
- The child's eyes are squinted
- Hands and chin are shaking
- The toddler doesn't sleep well
- His eyeballs roll down
An urgent consultation with doctors is recommended: a neurologist and an ophthalmologist, who will prescribe a CT scan of the brain, as well as neurosonography, with which you can study the condition of the fundus. During the treatment, circulatory functions improve. In addition, special gymnastics, a massage procedure and vitamin intake are prescribed.
Weakness of the tongue muscles
A disease caused by birth trauma, abnormalities in the endocrine system, and premature birth. The transfer of infections has the same effect.
If the following are added to tongue protrusion:
- the baby is lethargic and inactive
- sleeps for a long time
- does not gain weight
- eats poorly
- lags behind in terms of physical development
You should contact a neurologist. Treatment: taking medications, taking a course of massages, doing gymnastics.
Due to weak tongue muscles
When parents see that a child is sticking out his tongue, they first need to carefully examine the surface of his skin and examine the condition of the mucous membranes. Having discovered alarming signs, it is worth visiting a pediatrician, who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Diseases in which the baby constantly sticks out his tongue
In some cases, this behavior indicates a problem, either minor or quite serious. It’s better not to specifically look for alarming symptoms in your baby, but you need to know about them in order to prevent more dangerous pathologies:
- Hypothyroidism. This disease is caused by problems with the thyroid gland. Occurs if the mother experienced iodine deficiency during pregnancy. Its main signs are pale, marbled or yellow skin of the baby, developmental delay, and bluish discoloration of the nasolabial folds. The tongue swells and does not fit in the mouth. The diagnosis will be made by an endocrinologist after conducting appropriate examinations, followed by long-term treatment.
- Hypotonicity of the tongue. If the child is drowsy, inactive and slowly gaining weight, this may be due to a head hematoma, birth injury, endocrine or infectious disease. The problem often occurs in premature babies. A sign of pathology is a flaccid, “loose”, sedentary tongue with decreased muscle tone.
- High intracranial pressure. Occurs as a result of difficult childbirth, disorders of the central nervous system, or previous meningitis. The child's behavior becomes restless, he throws his head back, sleeps little. He has an increased head size compared to his peers, the fontanel is slowly tightening, hand tremors, strabismus, and increased muscle tone are observed. If suspicion arises, it is necessary to consult a neurologist, ophthalmologist, and undergo diagnostics.
- Atrophy of the facial muscles. This problem affects mainly girls and manifests itself in the absence of facial expressions. The baby is unable to smile; when he grimaces, there are no folds on the forehead; his face seems petrified. The reason is associated with a violation of the ternary nerve, endocrine glands and the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. It is a complication after infectious diseases and injuries.
- Thrush. The disease is caused by the fungus Candida, which affects the mucous membrane. A white coating appears in the mouth, the gums become inflamed and red. The baby sticks out his tongue to relieve any irritation. In this case, you should immediately show it to your pediatrician, who will identify the pathogen and prescribe ointments and mouth rinses. Good hygiene and a low-carbohydrate diet will help you avoid this problem.
- Stomatitis. A fungal disease leads to the appearance of ulcers and redness on the tongue and palate, accompanied by an increase in temperature. The child's sleep is disturbed, his appetite worsens, and he often cries. The disease is caused by bacteria, herpes virus, and fungi.
All these diseases are dangerous for the baby’s health, and a protruding tongue is just one of the manifestations. It is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will analyze the symptoms and choose the appropriate treatment taking into account the characteristics of the baby’s body.
Whatever the reason, it is impossible to ignore the baby’s abnormal behavior, but most often it is not necessary to rush straight to the hospital. If there are no acute attacks that cause pain, you should observe the child for some time, make sure that the symptom is repeated more than once, and tell the pediatrician about it at the next examination. It is dangerous to delay treatment for serious illnesses, but it is no less harmful to treat a baby for no reason. It is better to double-check the diagnosis and conduct additional examinations.
What is the problem behind?
The baby cannot speak. He expresses all his desires and needs with the help of gestures and facial expressions. The tongue is one of the tools of communication. If a baby sticks out his tongue, it means he wants to eat or is simply seeking attention. Or he reports that he is sick and does not feel well.
You should be alarmed when the tongue sticks out not only during play, but constantly, even in sleep. In this case, you should definitely visit a pediatrician. After examining the child, he can refer him for consultation to other specialists.
If a child shows his tongue, this may be the cause of neurological, endocrine or infectious diseases. There will definitely be other warning signs.
Disease of the endocrine system – hypothyroidism
The problems are related to the thyroid gland. The main reason is the lack of a trace element such as iodine in the body. To determine its level, blood is examined. Blood is collected from infants from the heel in the maternity hospital.
In addition to the fact that the child sticks out his tongue, other symptoms are present:
- skin color becomes yellow or pale;
- the surface of the skin is dry and flaky;
- there is a delay in mental and physical development;
- the tongue protrudes outward because it does not fit in the mouth due to large swelling;
- the area around the nose and lips becomes blue;
- no weight gain;
- persistent constipation develops.
In this case, treatment (the basis of therapy is hormones) and additional examination (ultrasound, blood tests) are prescribed by an endocrinologist.
Neurological disorders - atrophy of facial muscles
The trigeminal nerve is most often affected. This may occur due to malfunctioning of the thyroid gland. The problem becomes a consequence of previous respiratory diseases or various facial injuries.
Additional symptoms appear:
- the face becomes immobilized, facial expressions change (the child does not cry, does not smile, there are no facial folds);
- swelling of the lips is observed;
- facial asymmetry is observed;
- eyelids droop;
- the chin moves to the side.
The treatment is carried out by a neurologist. The results of MRI and ultrasound examinations may be needed. Treatment is mainly medicinal. Additionally, vitamins, massage, and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Infectious disease - thrush
The mucous surface of the oral cavity is affected. The reasons for its occurrence may be a decrease in immunity, frequent regurgitation.
The child sticks out his tongue, and other symptoms appear:
- a white, cheesy coating appears in the mouth;
- gums, tongue, palate become inflamed and red;
- If treatment is not started, the plaque becomes gray or yellow.
Consultation with an infectious disease specialist and dermatologist is necessary. Ointments and solutions, vitamins, and drugs that help improve immunity are prescribed locally.
The main condition is compliance with a special diet for a nursing mother.
Stomatitis
The reason that the baby constantly shows his tongue may be stomatitis. This disease occurs when viruses and bacteria enter the body. The symptoms are easy to notice:
- the oral cavity is inflamed, swollen, red;
- ulcers are clearly visible, which can appear anywhere: on the tongue, on the palate, on the gums;
- body temperature rises;
- the child is capricious and refuses to eat;
- sleep becomes restless.
A dentist, immunologist, and infectious disease specialist can help. Vitamin complexes, immunomodulators, ointments and medicinal solutions, antiviral or antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Increased intracranial pressure
It is caused by serious disorders of the central nervous system. This can happen due to a birth injury or a serious infectious disease such as meningitis.
Symptoms that are a reason to consult a doctor:
- the diameter of the child’s head exceeds the age norm;
- constant throwing of the head back;
- swelling of the fontanelle;
- severe muscle tension;
- the child squints his eyes;
- trembling of hands and chin;
- poor sleep;
- rolling the eyeballs downwards.
Consultation with many doctors is necessary, including a neurologist and an ophthalmologist. A prerequisite is to undergo brain tomography, neurosonography, and the fundus of the eye is studied. Treatment is aimed at improving circulatory functions. Additionally, therapeutic exercises, massage and vitamins are prescribed.
Tongue hypotonia (muscle weakness)
This disease is caused by birth trauma, disruption of the endocrine system, and premature birth. Past infectious diseases also have an impact.
Signs that accompany tongue protrusion are:
- lethargy, low mobility of the child;
- he sleeps for a long time;
- lack of weight gain;
- poor appetite;
- retardation in physical development.
A neurologist will help solve the problem. Drug treatment, massage, and gymnastics are recommended.
If parents often notice their baby’s tongue sticking out, it is necessary to carefully examine his skin and mucous membranes. If warning signs are detected, you should immediately visit your pediatrician. Only he can give recommendations on further treatment tactics.
Hypothyroidism
The cause of this disease is problems associated with the thyroid gland. Children whose mothers received insufficient iodine during their waiting period are especially likely to get sick. Tests to detect the disease are taken from newborns while still in the maternity hospital. The site for blood collection is the baby's heel. If after the examination, mommy was not invited to receive medical recommendations, then there is no need to worry. This means that the child is not sticking out his tongue because of hypothyroidism.
The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the skin becomes marbled or yellow in color;
- the baby is constantly with his tongue hanging out;
- the skin loses moisture and becomes drier;
- the baby has a developmental delay;
- swelling of the tongue, in which it swells and does not fit in the baby’s mouth;
- the outlines of the face become denser;
- cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle appears;
- it is difficult to gain weight;
- The baby suffers from constipation.
Treatment of the disease begins only after a thorough examination, which includes an analysis of the content of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the baby’s blood and an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. Only after this the doctor prescribes drug treatment with drugs containing thyroid hormones.
How to see danger?
Parents should carefully monitor their child. First of all, attention should be paid to his well-being, as well as the quality of his sleep. In particular, against the background of which the tongue sticks out: the baby may grimace, gurgle or throw his head back. Often, it is the mother who can accurately determine whether the baby’s actions are intentional or involuntary.
If your baby sticks out his tongue at 3 months, he needs to be closely monitored. After all, this does not always mean that the baby is just playing around and playing. Often, such an action can be a signal of disruption of the nervous or endocrine system.
In the case where a child rarely shows his tongue, especially if this happens only during play, there is no reason to worry. After all, the baby is just playing around and that’s normal. In the case when a newborn constantly sticks out his tongue and cannot hold it, including in his sleep, you need to consult a pediatrician about this. After all, thanks to early diagnosis, you can deal with the problem quickly and as painlessly as possible.
Associated symptoms
Many symptoms of various diseases can accompany tongue chewing. As mentioned above, these are endocrine disorders, infectious diseases, often teething or pathologies of the bite and development of the jaw bones.
In addition to all of the above, this habit can be accompanied by many inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity:
- glossitis - inflammation of the tongue,
- stomatitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane,
- gingivitis – inflammation of the gums.
These pathologies always cause discomfort in babies in the form of itching and pain, so they begin to drown it out by chewing their tongue. A vicious circle is created here - the child bites the tongue, thereby injuring it, which further aggravates the inflammatory process. That is why chewing the tongue itself contributes to the development of diseases.
Causes of your child sticking out his tongue that you shouldn’t be afraid of
Baby sticks out tongue a month
It is at this age that most infants begin to do this. Although they were recently born, they have already mastered this “exercise.” Why this happens:
- The child may simply want to eat, because he grabs the nipple or nipple on the bottle with the help of a tongue. Therefore, if the baby repeats the same actions with his tongue as when eating, then perhaps it is time to feed him. He may also begin to suck his tongue and even bite lightly.
- At this very young age, the child is already becoming interested in everything and with the help of his tongue he can explore his mouth and lips. He can get carried away by something, he can stare at his dad or mom, at some toy and involuntarily stick out his tongue, this is normal.
- If it is summer and the temperature is too high, then the baby could simply overheat a little, he is hot. That is why the child sticks out the tip of the tongue or completely.
- In very rare cases, it happens that the baby is born with a very large tongue. It doesn’t really want to fit in his mouth and the baby sticks it out. There is nothing terrible here and there is no need to sound the alarm. After some time, the dimensions will fall into place.
The child sticks out his tongue at 2, 3 months
Added to all the above reasons is the fact that the baby’s first teeth are already beginning to bother him. Yes, at such a very young age, his gums may already begin to itch. In this regard, the baby begins to worry and scratch his gums with his tongue and even massage them. From the outside it will look as if he has his tongue out of his mouth and moving it back and forth.
Take a close look at your child's gums. If they are swollen or red, then that’s exactly how it is, your baby will soon have his first teeth.
Also, at 2 months, the child is already playing a little more actively with his parents and may well begin to stick out his tongue in the process. This phenomenon may begin to occur a little more often, because the baby is already more interested in something than in the first month.
Baby sticks out tongue at 4, 5, 6 months
At this age, sticking out the tongue, plus spitting in different directions, becomes a habit for the child. He finds it very funny. If he likes it, he will begin to constantly stick out his tongue until he gets tired of this idea and finds other adventures for himself. If you start playing with him at this time and laugh off him or with him, then consider that sticking out your tongue will become your baby’s favorite pastime and can last for a year or a year and a half. Therefore, you don’t need to respond by repeating all the child’s actions or pretending that you really like everything he does.
In addition, a child at this age is already beginning to try to crawl. In this case, the tongue will stick out if the baby is experiencing difficulties, strains, tries to crawl to the goal, etc.
If a child sticks out his tongue at 1 year or 2 years or older, it may be because he is playing. If at this age the tongue sticks out frequently and you cannot find out the reason, then it is best to consult a doctor about this issue.
Possible diseases
In addition to the reasons described above, constant tongue protruding can be caused by a dangerous disease. Let's look at the most common of them.
Hypothyroidism
. This pathology is associated with the thyroid gland. Hypothyroidism can appear in a child from three months old if the mother did not have enough iodine during pregnancy. In addition to a protruding tongue, the disease is indicated by dry skin, a pale yellow complexion, late teeth, slow development of the baby, the formation of coarse facial features (thick lips, wide nose, short neck), a swollen tongue that not only protrudes, but literally falls out mouth If you suspect hypothyroidism, you should immediately show the child to an endocrinologist and do all the necessary tests.
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP).
In addition to frequent tongue protruding, a sign of this phenomenon may be throwing your head back in your sleep. To diagnose ICP, it is necessary to show the baby to a neurologist and undergo an ultrasound examination. Treatment usually includes physical exercise, medication, and massage courses.
Thrush.
If your baby constantly sticks out his tongue, carefully examine his oral cavity. If you find a white coating on your tongue, palate, or the inside of your cheeks, this most likely indicates the presence of thrush (a fungal disease). It causes discomfort in the child and that is why he sticks out his tongue. To cure thrush in a baby, you need to consult a pediatrician.
Stomatitis
. With this disease, damage occurs to the oral mucosa. Quite painful ulcers appear in the mouth, sometimes they form under the tongue, which the child sticks out to relieve the pain. out of 5 (5 votes)
Does your newborn baby stick out his tongue often? Surely this habit worries you. But should we panic? Why does he do this? Let's look for answers to these questions together.
The fact that a child shows his tongue can be either a harmless action or a symptom of a serious illness. When you see your baby doing this, just watch him. It is worth assessing the general condition of the baby: is he capricious, is he sleeping well, etc. It is usually quite easy to determine when a baby involuntarily sticks out his tongue and when he is in play. If the baby rarely shows his tongue, that is, only when playing with his parents, then there is no need to worry. In this way he expresses his emotions, which he still cannot control. You need to be wary if the baby constantly sticks out his tongue, as if he cannot keep it in his mouth, or shows his tongue while sleeping. In this case, you need to consult a doctor. Such a seemingly harmless action may be a symptom of diseases of the nervous system or indicate problems with the thyroid gland. If a baby sticks out its tongue when sleeping and at the same time throws its head back, this indicates high intracranial pressure. In this case, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Why does a small child stick out his tongue? Often the baby uses his tongue to play with others, play around, and express emotions. He can repeat the "gesture" seen in adults. Often the tongue sticking out is accompanied by an attempt to make a new sound. When you see that your newborn baby is sticking out his tongue during vigorous activity (crawling, waving his legs, trying to “speak”), then you should not worry.
A protruding tongue may indicate that your baby is teething. The baby is interested in exploring new reliefs in his mouth, which he does with the help of his tongue. But since he does not know how to fully control his body, it turns out that he sticks out his tongue.
Many pediatricians believe that a protruding tongue in newborns indicates that the baby lacks tactile contact with the mother. This “gesture” can be observed in babies who are breastfed: when left “alone”, they stick out their tongue and even chew it. This behavior is considered quite normal: this is how the baby demonstrates that he misses his mother.
If your baby often sticks out his tongue, but you understand that this is not a game, and you do not observe other alarming symptoms, then be sure to examine your baby’s oral cavity. A protruding tongue may indicate stomatitis or thrush. With stomatitis, ulcers form in the mouth, and with thrush - a white coating. All this causes discomfort to the baby, causing him to stick out his tongue. Be sure to consult your pediatrician about the treatment of stomatitis or thrush.
Nuances that should alert you
Most diseases accompanied by tongue protrusion in infants respond well to treatment, especially if they are identified and treated at an early stage. A protruding tongue rarely acts as the only symptom of the disease (the exception is when the baby constantly shows only the tip of the tongue from the mouth).
Sometimes this phenomenon is perceived as one of the symptoms of dementia, but debility in babies under one year old can only be congenital and is accompanied by specific symptoms that are difficult to confuse with anything. In addition to the fact that the child’s mouth is open and his tongue is sticking out, parents should be alerted to the appearance of one of the following nuances:
- swelling of the tongue,
- dry skin,
- the baby does not pull out his tongue, but sticks it out, cannot keep it in his mouth,
- pale yellow skin
- the child is constantly worried, cries, sleeps poorly,
- baby spits up frequently
- the baby constantly sticks out only the tip of his tongue,
- pulsating and bulging fontanel,
- in a dream the head tilts back,
- there is a white coating on the tongue and in the oral cavity,
- the child’s inability to control his facial expressions.
Tongue keeps falling out of mouth
Why does a child's mouth remain open and his tongue keep falling out? This may indicate that he is suffering from hypothyroidism. The disease develops in children whose mothers experienced iodine deficiency during pregnancy. In modern perinatal centers, tests for hypothyroidism are taken from a child almost immediately after birth.
Why does a baby chew and suck its tongue?
You should not panic if you notice this, but you should figure out the reasons and eliminate the “bad habit” in your child yourself or seek the help of a doctor. There are many factors in the development of this phenomenon, and in this article we will try to identify possible sources of the problem and find ways to solve them.
Possible diseases
Sometimes the cause of chewing and tongue sucking can be various pathologies:
The so-called thrush (an infectious fungal disease that affects the baby’s oral mucosa) is a common problem that parents face. Due to the whitish coating on the cheeks, gums, and especially the tongue, the child can stick it out, chew and suck. In addition to dense deposits, the child may feel pain and discomfort. To identify and treat the disease, you need to consult a pediatrician. If a child chews his tongue, endocrine diseases may be the cause. Hypothyroidism - insufficient production of thyroid hormones - can also manifest itself in the muscular organ. It swells and becomes larger than normal. The child tries to “remove” it from his mouth, that is, he walks with his tongue sticking out. It is clear that discomfort can also result from chewing the tongue. Endocrinologists identify this pathology and prescribe treatment. Pathologies of the jaw bones and malocclusion are phenomena that cause children several months old to chew and suck their tongue
Due to an excessively small lower jaw and irregularly shaped dental arch, children can feel the “size” of the tongue and, as a result, pay attention to it and chew it. This may also apply to children during teething – when the gums become inflamed, itchy and painful.
To reduce discomfort, the child tries to compensate for the pain by chewing his tongue. During teething, you need to visit a pediatric dentist, and for children with existing teeth and pathology of the bite or jaws, an orthodontist. The reason for chewing and sticking out the tongue during sleep is increased intracranial pressure. Children with such problems should be urgently shown to a pediatrician.
READ ALSO: Why does a baby sometimes stick out his tongue?
If a child adheres to this habit for a long time, and there are no other symptoms, then he should consult a neurologist. He will help you find the problem and fix it.
Causes not related to pathologies
The most common cause of tongue chewing in infants is the child's transition to feeding adult food. Before the baby begins to eat food containing solid elements, it develops increased salivation.
This process appears at 3-4 months and older. The mechanism of the phenomenon is simple - for the normal absorption of such food, saliva mechanically helps its passage from the oral cavity further along the gastrointestinal tract. It performs an important function - it breaks down carbohydrates using the enzymes it contains. In this regard, excessive salivation often forces the baby to move his tongue in the mouth, chew and suck it.
READ IN DETAIL: increased salivation in infants: causes and solutions
The reason could also be simple hunger. When feeding time comes, the baby begins to chew his tongue if he does not get food. However, over time, when the child learns to express his need for food and immediately receive it, the bad habit will stop.
During the developmental period of the baby, while he is weaned from the pacifier, he may chew and suck his tongue due to habit. Accustomed to constantly having a pacifier in the mouth, the child, in its absence, feels that something is wrong, and automatically makes chewing movements coupled with sucking - only now these actions extend directly to the tongue.
When the baby is busy with an interesting game, watching cartoons or communicating with people and pets, he may chew and suck his tongue or even stick it out. There is nothing wrong with this and, most likely, he is simply busy with an interesting activity, and, as you know, even adults who are carried away by any process can perform uncontrolled actions.
As a bad habit, tongue chewing can develop in children older than 12 months. This is one of the common habits (along with thumb sucking and nail biting) that children develop when they are bored. Without proper attention from adults, the baby begins to amuse himself, and this will lead to such actions as systematic chewing and tongue sucking.
When to see a doctor?
A protruding tongue does not usually indicate that anything is wrong. However, some children may stick out their tongue in situations where other children would not.
You should take your child to the pediatrician if he or she frequently sticks out his tongue for no apparent reason or exhibits other developmental differences.
Any change in a child's behavior may also be a warning sign of a problem. For example, a baby who consistently shows signs of hunger immediately after breastfeeding may not be getting enough breast milk or formula. In addition, the child may have problems digesting food.
Behavioral changes that occur after a blow to the head or other trauma may signal an emergency. A child who has had an injury of any kind should receive immediate medical attention.
During the first year of the child's life, parents regularly visit the pediatrician. Parents should discuss changes in behavior and ask about signs of normal child development.
Always call a doctor if your child exhibits the following symptoms:
- constant signs of hunger, especially if the baby is breastfed
- tongue sticking out in addition to problems swallowing or
a change in behavior that has no clear cause
- signs of physical discomfort
You should go to the emergency room if your child's behavior changes significantly during or after an injury, fever, or illness.
Causes of tongue protrusion
Most babies can use their tongues to indicate the presence of some discomfort or simply try to communicate with their interlocutor in this way. Typically, a protruding tongue in a newborn may indicate the following:
- Teeth are being cut. When the baby's first teeth appear, the gums begin to swell greatly, which is accompanied by pain. To dull the pain, the child reflexively begins to move his tongue;
- Want to eat. If the newborn is hungry, he can stick out his tongue and suck on it, which will be a signal to the mother to feed him;
- The tongue is tight. Some babies have a tongue that is slightly larger than the standard size and does not fit well in the mouth. That's why he often ends up sticking out. In this case, there is no need to sound the alarm, because... over time (when the child grows up a little) everything will return to normal;
- The kid is exercising. For some reason, when a newborn waves his little legs or arms, this is considered normal, but when a child begins to stick out his tongue, his parents immediately become wary. The tongue is a muscle that performs important functions in the human body, therefore, like any other organ, it needs development and training;
- Pampering. An infant's tongue sticking out may be a copy of a similar movement by its parents. The child may also stick out his tongue when trying to produce a new sound. These actions occur quite rarely, so there is no reason to worry;
- The baby is hot. If a child becomes hot, then by sticking out his tongue he increases the surface on which moisture evaporates, which leads to cooling of the body. It may also indicate that the newborn is thirsty;
- Stomatitis. This disease affects the oral mucosa. As stomatitis develops, very painful ulcers begin to form in the baby’s mouth. Sometimes such ulcers appear under the tongue, which the baby sticks out to reduce pain;
- Hypothyroidism. This disease is characterized by decreased thyroid function. Hypothyroidism is a very dangerous disease that can lead a child to serious developmental delays. You should know that early diagnosis of this disease contributes to the development of fewer consequences for the baby. With hypothyroidism, the baby's tongue falls out of the mouth, simply not fitting into it. Also, this disease may be accompanied by jaundice or severe weight gain in the child, therefore, at the first suspicion of hypothyroidism, you must immediately contact an endocrinologist, after which you must pass all the necessary tests;
- Thrush. This is a fungal disease that affects the baby's mouth. The development of thrush in a child can be indicated by the formation of a white coating on the baby’s tongue, his cheeks and palate, which causes serious discomfort to the baby, forcing him to stick out his tongue;
- Increased intracranial pressure. In addition to frequent tongue protruding, a symptom of this phenomenon may be the child throwing his head back during sleep. To confirm (or refute) the diagnosis, it will be necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination, as well as an examination by a neurologist. Treatment, as a rule, includes the use of medications, physical exercise, and various massages;
Causes for concern
If mom and dad notice that the baby is constantly opening his mouth, sticking out his tongue, you need to visit a specialist. Let's talk about the most common ailments that accompany the “bad habit.”
Frenum defects
About a third of all newborns have a short frenulum. This pathology is called ankyloglossia. It occurs much more often in boys than in girls. A mucous membrane connects the tongue to the floor of the mouth. It is either not attached correctly (starting from the middle) or is less than 8 mm in size. Causes of pathology:
If the pediatrician diagnoses ankyloglossia, a minor cosmetic surgery is performed and the frenulum is trimmed. The newborn does not feel pain, the process is not accompanied by anesthesia. Timely intervention will help avoid problems with breastfeeding, speech defects, and discomfort for the baby.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract
Most often these include gastritis, constipation, and high acidity. Thus, a reaction to early introduced complementary foods may occur. There is no need to panic, but if you notice that colic and bloating are accompanied by mouth opening, see your pediatrician.
Diseases of the ENT organs
With otitis media, sinusitis, and rhinitis, the nasal sinuses are clogged with mucus. The baby is forced to breathe through his mouth. This is especially noticeable during sleep. If you observe that, in addition to opening the mouth, the baby:
Most likely, the child involuntarily pulls his hands towards the sore spot (nose, ear). Don't hesitate to see a doctor. Inflammatory processes not only cause pain and discomfort to the baby, but can also lead to irreversible loss of smell and hearing. Contact an ENT specialist, he will quickly make a diagnosis based on an external examination and analysis of mucosal secretions.
Muscle weakness
If a newborn periodically opens his mouth in his sleep in the absence of other symptoms, there is no need to sound the alarm until the child is six months old. The phenomenon is not a serious pathology; as a rule, it goes away on its own. The habit should not be left unattended. This may lead to increased salivation in the future. The disease is treated with massage courses, sometimes with injections of drugs for tone.
Hypothyroidism
Thyroid dysfunction. In addition to prolapse of the uvula, jaundice, an increase in body weight and head circumference are added. Appetite may be reduced. Drowsiness and constipation are noted. The child cries hoarsely. It is necessary to show the baby to an endocrinologist. He will take the necessary tests (blood for the hormones TSH, T4, biochemical urine), perform an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, and palpate it. If the diagnosis is not made in time, disturbances in mental development, coordination of movements, and the appearance of strabismus are possible. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. The specialist prescribes the necessary medications containing thyroid hormones.
Facial muscle atrophy
With pathology, the child experiences the so-called “flaccid child syndrome.” Normal muscle tension, including facial muscles, decreases, as a result of which the tongue falls out during sleep. The baby's face resembles a mask. He does not smile or grimace, like most healthy children of this age. The skin is dry, with spider veins. The screams are sluggish, weak, muffled. Strabismus may develop. Additionally observed:
Consultation with a pediatrician is required. He conducts an external examination, palpation, collects the mother’s pregnancy history, takes the necessary blood tests, and examines the lists of medications that were given to the baby. MRI and CT are used as additional diagnostics. The disease is treated with medication. Massage is often prescribed.
Candidiasis
A whitish coating on the gums, the surface of the tongue, and on the mucous membrane of the cheeks indicates a possible thrush. The Candida parasite provokes unpleasant sensations and causes discomfort. To make this clear to the parents, the child opens his mouth every now and then. Associated symptoms include loss of appetite, sleep disturbance, and frequent crying. Causes:
Diseases can be provoked by frequent regurgitation, mechanical injuries to the mucous membrane, and treatment with hormones. This is an inflammatory process that requires immediate treatment. The pediatrician takes a swab from the oral cavity, identifies the growth of fungal flora, and prescribes antibiotics and antifungal drugs. It is recommended to increase the humidity in your child's bedroom using a humidifier.
Safe reasons for your baby to stick out his tongue
Carefully observe your baby's behavior. However, don't panic every time your baby sticks out the tip of his tongue. Remember, even adults sometimes have a desire to make faces, but it would never even occur to anyone to show any concern about the state of their health. So babies often make faces and move their tongues back and forth for very understandable reasons.
The baby is playing
The reasons for sticking out the tongue may be related to the child’s good mood and his desire to play at the moment. It is by sticking out his tongue that he shows others his playful attitude.
Kid shows off his skills
At two months, the baby is ready to learn new communication skills, because he already coos so well. Why does the baby stick out his tongue at the same time? Maybe this is how he is trying to learn to make new sounds or copying the behavior of adults.
Baby doing gymnastics
Many parents notice that their baby actively moves his arms and legs. As he gets a little older, he tries to roll over or crawl on his own. But the tongue is also a muscle that needs to be exercised regularly. That is why the baby sticks out its tongue, performing the necessary gymnastics.
Is it time to eat?
A sticking out tongue can signal that the baby is hungry and is asking the mother for food. This is how the baby tells his mother with his tongue and saliva that it is time to feed. This is especially true for children who are breastfed.
Teeth cutting
If a baby sticks out his tongue at 2 months, then the mother should carefully examine his mouth. Most likely, this is due to teething and with the help of the tongue the baby is exploring new reliefs in the mouth. This process is usually accompanied by swelling of the gums and itching. The same symptoms can be observed in children at 3 and 4 months.
Baby has a big tongue
In a newborn, the tongue can constantly be in a protruding state due to its anatomical features. The tongue does not fit in the newborn’s mouth, which means that he has to keep his mouth open all the time. As a rule, this problem resolves on its own as the child grows older.
The room is too hot
Very often, due to the temperature in the room being too high, the baby becomes thirsty. This can be signaled by the child sticking out his tongue.
Short sublingual membrane
The tongue and lower jaw are connected to each other by a frenulum, which is too short and can cause discomfort. In addition, the baby's sucking reflex is disrupted and he refuses to take the breast. Usually doctors notice such a defect already in the maternity hospital and cut the baby’s membrane. This procedure is painless, so it does not require anesthesia.
But not only the above factors can be the reason why a newborn sticks out his tongue. Each child has his own reasons for sticking out his tongue. For example, in order to better study the objects around him, the baby licks them with his tongue. Sometimes, if a child sticks out his tongue, you can guess that he is shy about someone. To better understand a newborn, it is necessary to carefully observe how the baby reacts to this or that circumstance. This will help protect parents from groundless worries.
Mothers should definitely learn to distinguish the symptoms of diseases from the behavioral characteristics of their baby.
Natural causes
Young mothers worry about their babies sticking out their tongues. If there are no other symptoms, then this phenomenon has natural causes:
The baby takes an example from those around him. If one of the adults sticks out his tongue, the child will repeat this grimace. The baby learns the world in this way; he tries to restore all the actions that he noticed in his parents or older brothers and sisters. Sometimes the baby tries to make some sound, but instead his tongue comes out of his mouth. Don't worry about your child sticking out his tongue or trying to chew it during active play.
The appearance of the first teeth can also cause the tongue to protrude. During this process, the gums swell and swell, so the child tries to explore the oral cavity with the organ. Up to six months, the baby eliminates the itching caused by teething with his tongue. During physical development, the baby actively moves his limbs, head and tries to make sounds. It is not surprising that during this period he trains the only muscle in his mouth and constantly moves it.
A child may stick out his tongue due to attention deficit and hunger. This action is a signal to the mother that it is time to feed the baby. And also in this way he requires increased attention, shows his desire to get into the arms of a loved one. In newborns, during the first feeding, pathologies of the connective tissue between the tongue and lower jaw are detected. If its length is not sufficient for normal tongue movement, the child experiences discomfort and sticks it out.
In medicine, there are many cases where a baby showed his tongue due to its enlarged size. In the first months of life, the organ does not fit in the mouth due to the small lower jaw. At seven to nine months, the proportions of the body change, so the problem will go away on its own. High room temperature has a negative effect on the condition of the child's body. The baby sticks its tongue out to speed up the evaporation of moisture and cool the body from the inside.
You should not consult a doctor after your child sticks out his tongue for the first time. This usually occurs due to natural reasons, but in some cases the effect occurs due to certain viral and infectious diseases. Parents should observe the baby’s behavior and check his mucous membranes. If your baby constantly sticks out his tongue and other symptoms appear, then contact your pediatrician for help.
Source
Baby sticks out tongue
Sometimes caring parents notice that their newborn child begins to stick out his tongue frequently. What is this: pampering or a sign of some disease? We will hasten to reassure you - everything is probably fine with your baby. It’s just that the child recently arrived in our world and began to actively explore it, including his body, and in particular his tongue. If the baby is constantly sticking out his tongue, concerned parents should watch his behavior. Surely many have heard that this may turn out to be far from innocent fun, but a rather serious symptom of a disease of the endocrine or nervous system.
Why does a newborn stick out his tongue?
Many young, inexperienced parents often look for explanations for the simple and harmless behavior of their baby. But, most often, the reasons that a baby sticks out its tongue are quite prosaic:
- the baby may simply show his tongue because he once saw this “gesture” in adults;
- perhaps he is trying to make some new sound, but with all his attempts he can only stick out his tongue
- most often you can notice that an infant sticks out the tip of his tongue during some “turbulent” activity;
- If your baby is over three months old, this may be a sign that he is teething. In this case, the child experiences quite unpleasant sensations and has a desire to “scratch” his gums;
- As for babies who are breastfed, the reason for the protruding tongue may be the lack of tactile contact with the mother. In other words, the baby simply missed his mother’s breast.
Baby sticks out tongue - possible diseases
- A fairly common reason for a child sticking out his tongue is thrush. Because with this disease, the baby develops a white coating on the cheeks, palate and tongue, which sometimes causes very unpleasant and sometimes even painful sensations. To treat thrush, you need to consult a pediatrician.
- It is worth worrying if a prolapsed tongue in a newborn is accompanied by throwing the head back during sleep. This may indicate increased intracranial pressure. It is imperative to consult a specialist and undergo the necessary examination.
- Sometimes, due to the individual structure of the lower jaw, the child simply cannot completely fit the tongue behind the teeth. Most likely this is not a disease, but you should consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examination. Because in some cases, an increased size of the tongue may indicate the presence of some congenital disease.
- If the newborn's tongue seems to fall out of the mouth and at the same time looks quite large and swollen, immediate assistance from a specialist is necessary. This may be a sign of thyroid disease - hypothyroidism. However, it is worth noting that children with hypothyroidism differ from healthy children not only by constantly sticking out their tongues. Typically, with this disease, the child's voice becomes low and hoarse.
As you can see, the reasons that a newborn baby sticks out his tongue can be quite varied and do not always indicate the presence of serious diseases. But in any case, if you are concerned about this phenomenon, consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examinations. Every caring parent knows when to “sound the alarm”, the main thing is not to overdo it!
Why does a 2-3 month old baby stick out his tongue?
If an adult's tongue sticks out or falls out, this may indicate excessive enthusiasm for the current activity or the development of a disease such as segmental dystonia. What will cause a child to stick out his tongue?
A baby at the age of 2-3 months sticks out his tongue in order to eat, play, or because he is developing a disease. This may be a sign that the baby is hungry. In this way he tells his mother that it is time to feed him. While eating, the baby opens his mouth and sticks his tongue out to make sucking movements, so when he wants to eat, he makes similar movements reflexively. You need to offer your baby a breast or a bottle - perhaps, after eating, he will hide his tongue. Experts identify a number of reasons (besides hunger) that can lead to a baby sticking out his tongue.
| Category | Causes | Note |
| Natural | A game | Feel the gums, touch the lips, lick the rattle - this is how the baby plays and learns about the world. |
| Copy | If one of the parents entertains the child by making faces and sticking out his tongue, soon the baby will begin to do the same. | |
| Tongue size | At the age of 1-3 months, the tongue is too large, long and simply does not fit into the mouth. This problem resolves itself within six months. | |
| The room is hot | Sticking out his tongue, he tries to cool himself down a little. | |
| Sign of teething | Most babies experience the first signs of teething at 4-5 months of age, but for some, painful sensations in the gums appear a little earlier, sometimes in two-month-old babies. Sticking out his tongue, he moves it along the gums - this is how the baby tries to massage and moisten them a little. | |
| Pathological | Lack of iodine in the body | The symptom may indicate the development of hypothyroidism. |
| Irregularly formed facial muscles/distorted jaw | You must consult a doctor immediately. | |
| Intracranial pressure | In most cases, this diagnosis is made already in the maternity hospital, and the necessary therapy is prescribed there. |
Causes of a child's tongue sticking out
Good day to you, dear friends! Today we will look at another issue that concerns the health of your baby. We're talking about sticking out the tongue. Surely this phenomenon has not passed by any young family and, I am sure, it causes concern among parents. “What if this is a very serious illness?” - This is exactly what most mothers think.
Looking ahead a little, I would like to say right away that sticking out the tongue is a completely normal phenomenon for infants. Almost any small child will sooner or later start doing this. He will also spit and drool, there is no escape from this.
It is also worth distinguishing between two concepts: whether the baby sticks his tongue out on his own or whether it constantly falls out and does not hold on. If you have the second option, then here you urgently need to sound the alarm and run to the pediatrician.
I will help you figure out the reasons for the tongue sticking out. It is also worth noting that they may differ depending on the age of the baby.
Harmless reasons
The little ones surprise mom and dad with something new every day. Many people are frightened by their child’s “strange” habits, but it is difficult to understand their cause, because the baby cannot speak. First, we’ll tell you why recently born babies show their tongues or open their mouths. Before you run to the pediatrician, watch your child. He can stick out his tongue for a variety of non-threatening reasons.
a child can sleep with his mouth open during the period of teething