In some cases, a nursing mother may face a situation where she cannot continue breastfeeding her baby. This could be treatment with drugs that are incompatible with breastfeeding, carrying another child, or forced separation.
Most often, a long break becomes the reason for the cessation of milk production, or its production in insufficient volume. The baby, who has already become accustomed to the new circumstances, begins to refuse to breastfeed. Many young mothers are interested in the question: “If milk is lost, how to resume lactation?” Let's take a closer look at how to return milk to a nursing mother.
Relactation - what is it?
Relactation is a technique for resuming lactation. It includes complex actions, the purpose of which is to organize breastfeeding after a forced pause.
Often, the reason for refusing to breastfeed a baby lies in the mother’s treatment with drugs that are prohibited during lactation.
In addition, the source of the problem may be pathologies of the mammary glands, which require immediate treatment, sometimes in a hospital setting, or other diseases that require the mother to stay in the hospital for a certain time.
Products to improve mother's milk lactation
For proper lactation, proper and balanced nutrition is extremely important. Every breastfeeding woman should take time to worry about establishing breastfeeding.
Nutrition during lactation must meet the following criteria:
- balance and the mandatory presence of useful components, vitamins;
- optimal calorie content;
- exclusion of allergenic products;
- regular inclusion of fresh vegetables and fruits, meat, cereals, and dairy products in the diet;
- optimal fluid intake.
New mothers should sometimes include foods in their diet that help increase breast milk production. Focusing only on proper nutrition does not always bring the desired results.
Squirrels
Proteins are very important for every child, as they contribute to the strengthening and proper development of the child’s body. A young mother should take care of her baby’s health by including protein foods in her diet on a regular basis.
The following foods should be consumed daily:
- meat;
- chicken;
- cheeses;
- fermented baked milk or kefir;
- cottage cheese.
With the right combination of protein products with vegetables or fruits, whole grain bread, you can guarantee that the baby is provided with all useful microelements with a guaranteed improvement in lactation.
Nuts
Nuts contribute to the successful establishment of breast milk production. This can be used by many women during lactation. It is important to remember that nuts often contain a high level of fat, so the product cannot be fully absorbed by the child’s body.
To improve breastfeeding, it is enough to eat 2-3 walnuts per day. A small amount of product will allow you to count on the optimal supply of potassium and magnesium.
Almonds are recommended during lactation, because they contain a lower level of fat. Despite this, it is best to limit yourself to 4 – 5 cores. Otherwise, the baby may suffer from bloating and increased gas production.
You can find out if a nursing mother can eat hazelnuts in our article. Is it possible to eat pine nuts while breastfeeding? Read here.
Can a nursing mother eat pistachios, read the link
Pine nuts are ideal for making nutritional smoothies. To do this, pour a tablespoon of kernels with 250 milliliters of water and leave overnight. In the morning, the drink is boiled and cooled to room temperature, after which it is drunk. It is recommended to sweeten the cocktail with natural honey.
Nuts are an allergenic product, so you should carefully monitor your baby's condition. If necessary, nuts should be completely abandoned.
Honey
Honey is a strong allergen. Despite this, a nursing mother should not refuse this product. A teaspoon of honey can be beneficial. What is its benefit anyway?
Honey contributes to overall support of good health:
- complete formation of blood cells;
- prevention of constipation and normalization of intestinal function;
- improving emotional state and preventing stress;
- activation of lactation.
It is recommended to take honey only if the mother and her baby do not have allergies. The main task is to limit yourself to a small portion of honey.
Dairy products
To improve lactation, it is advisable to drink a glass of kefir or fermented baked milk every day. Whole milk cannot be a help, as it leads to bloating in the baby and serious gastrointestinal disorders.
Beverages
Refusal of fluid leads to deterioration of lactation. For full milk production, it is recommended to drink 2 – 2.5 liters of liquid per day. It is advisable to give preference to tea, herbal infusions, and juices. Warm tea with the addition of a small amount of milk or natural honey helps normalize lactation. The greatest benefit comes from a drink drunk 20 minutes before feeding the baby.
Other healthy drinks traditionally include:
- compotes made from dried fruits;
- dill tea;
- decoction of anise or caraway seeds;
- milkshake with the addition of crushed dill seeds, nutmeg, and a pinch of salt;
- lemon balm, ginger root or mint tea;
- freshly prepared juices from carrots or currants, diluted with boiled water;
- barley decoction or ready-made barley drink (the decoction has the greatest benefits);
- dandelion decoction (to prepare the drink you need to use a teaspoon of the root or leaves of the plant and a glass of boiled water);
- juice based on dandelion leaves and with the addition of salt, honey or sugar, lemon juice.
Proper drinking regimen, the inclusion of special drinks, and healthy meals help not only strengthen the immune system, provide comprehensive support to the mother’s body, but also improve lactation. However, nutrition does not play the only important role. A young woman should take care of proper rest, since any overwork or physical, emotional overload leads to serious consequences.
Night feedings always become the basis for improving lactation. In this case, the duration of the break does not play any role.
How to resume lactation after a forced pause due to illness of the mother or baby
Young parents have to face various problems regarding the upbringing and development of their child. During the first year of a baby’s life, the main question remains breastfeeding – whether he receives enough mother’s milk to fully develop.
But in life all sorts of unforeseen circumstances can arise. Sometimes, at the insistence of doctors, you have to give up breastfeeding due to the health of the young mother or the baby itself.
Lactation experts advise not to panic in such a situation. When a woman wants to continue breastfeeding after some time, certain measures are required to help maintain lactation.
Reasons for the decline of lactation
Only two women out of a hundred experience the sudden and irrevocable loss of breast milk (true hypolactia). In such a situation, mothers have to switch the baby to a bottle and look for a suitable formula for him. Women always face difficulties when choosing an alternative to breast milk.
One mixture causes allergies in the baby, another has a bad effect on the gastrointestinal tract, and the third may simply not be to your liking. Understand the reasons for the decline of lactation. In most cases, it is possible to cope with them and restore blood pressure.
Main reasons:
- incorrect application;
- feeding by the hour;
- introduction of supplementary feeding due to an artificial lack of milk;
- use of pacifiers, bottles, pads and other accessories;
- overwork, lack of sleep and nerves;
- spasmodic development and growth of the baby;
- a break in breastfeeding due to travel, illness or other reasons.
Feeding according to the schedule
In the 20th century, it was believed that a newborn should be fed by the hour. Grandmothers developed this stereotype due to the fact that previously they had to go to work three months after giving birth. In such conditions, it is impossible to feed the baby on demand. But times change, as do views on GW.
If a woman loses her milk, the most common reason is feeding by the hour. The longer the break between feedings, the less baby food the mother produces.
In the first days of a newborn baby, it is necessary to apply it frequently. This is necessary for the formation of lactation.
Milk is produced only if it is in demand. When a baby nurses once every 3-5 hours, food production gradually decreases. Sooner or later, this will lead to the fact that the baby will stop eating, he will gain weight poorly and become capricious.
Supplementary feeding
One of the biggest mistakes nursing mothers make is switching their baby to mixed feeding. Often women feel that the child is not getting enough nutrition. Such thoughts come to mind if the baby hangs on the chest, freaks out, is capricious, or simply refuses to suckle. Most often, this behavior has nothing to do with the amount of breast milk.
If a woman decides to introduce supplementary feeding, then she takes the first step towards curtailing lactation. It is easier to get formula from a bottle than to get milk from your mother's breast. Therefore, over time, the child consumes more artificial nutrition and asks for the breast less. In such a situation, milk will inevitably begin to disappear, and the baby will completely switch to IV.
Mom substitutes
Breastfeeding consultants strongly advise against giving newborns a bottle or pacifier. In the first months, a child learns to receive nutrition from his mother’s breast. Proper attachment is important for successful lactation. But the principle of sucking a pacifier is different from sucking a breast. Therefore, most children who are familiar with mother substitutes from birth cannot grasp the areola correctly. Unclaimed milk may “burn out.”
Incorrect attachment leads to problems with lactation. The baby cannot suck out milk and has digestive problems due to swallowing air. If the areola is not captured correctly, the mother develops mother-in-law nipples and it is painful for her to feed. This situation often ends with a complete refusal of breastfeeding and transferring the child to formula. Therefore, for successful lactation it is important not to use nipples and pacifiers from the first days of life.
Break from breastfeeding
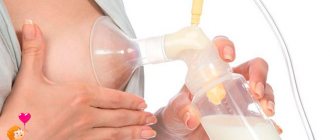
A break also leads to a decrease in milk supply. Baby food is produced on demand. The more the baby sucks, the more comes to the next feeding. If mom is forced to leave, she will have to pump regularly. A breast pump or manual expression supports breast function and allows you to restore lactation after a break.
If you do not express your breasts while you are apart from your baby, milk production will gradually stop. Just a few days are enough for the amount of food to decrease. Maintaining lactation during separation is much easier than trying to restore it later.
Overwork and stress
Due to stress, the volume of baby food in the mother's breast decreases. The fact is that the hormones prolactin and oxytocin are responsible for lactation. One promotes production, and the other is responsible for the evacuation of nutrition from the gland. When a newborn appears in the house, a large burden is placed on the mother. Overwork, lack of sleep, and household responsibilities lead to stress. A woman’s body produces stress hormones – cortisol and adrenaline. They suppress prolactin synthesis and negatively affect lactation.
For successful breastfeeding, a nursing mother needs emotional calm, proper rest and help with household chores.
Lactostasis
- Feel. Secretion stagnation appears in one or more lobes. Lumps form, in the area of which the skin may turn red. Sometimes feverish symptoms develop and the temperature rises. The mother tries to frequently place the baby on the affected breast, but the lump may disappear and come back again, or not go away at all. Some try to express milk “to the last drop” and actively knead the “lumps”, despite the pain of these manipulations. It happens that the baby is unable to properly latch onto an overfilled and tense breast. A woman may temporarily stop feeding or reduce the number of feedings. And after lactostasis, she notices that she has less milk.
- Reality. Frequent applications do not help remove the secretion from the stagnant lobes. The baby eats what comes easily from the breast. And the problem share remains overcrowded. Under such conditions, milk will not be wasted, because the body receives enough signals to produce it. But if a mother reduces or temporarily stops breastfeeding, the concentration of prolactin drops. When a woman resorts to traumatic pumping, she can damage the ducts. This disrupts the outflow of fluid and leads to new stagnation. Some of the lobes remain overcrowded for a long time, so the formation of milk in them is reduced.
- Actions. If the mother notices that after lactostasis the milk seems to have disappeared or there is less milk, it is important to ensure frequent stimulation and effective emptying of the breast. You can combine your usual feeding regimen with additional pumping. This will speed up the return of previous milk volumes.
We recommend reading: Herpes during breastfeeding in a mother
Lactation crisis
Women think about the fact that milk has disappeared during a lactation crisis. In fact, nutrition production does not decrease during this period. The baby just begins to consume more. However, the mammary gland is not able to switch to a new regime immediately. Therefore, it takes several days for the amount of food to increase.
During a lactation crisis, many women begin to feed supplements, which provokes a transition to IV. It is better to wait a few days and make efforts to increase the amount of breast milk. After 1-3 days, the breasts will adapt to the baby’s requirements.
High load on the body
During the feeding period, an acceptable climate should be created for a woman in the family. Quite often, milk disappears after stress. Mommy should not be burdened with housework or other problems. In the presence of stress in the body, the production of prolactin is provoked, which has a suppressive effect on lactation.
What is prohibited during relactation
During the relactation process, you must adhere to some rules:
- There is no need to worry or panic or assume that reintroducing breastfeeding is impossible. You need to be optimistic and not be afraid to seek the help of specialists; they will be able to tell you how to improve lactation.
- You should not check your baby's weight more than once a week. According to standards, a child should gain approximately 125 g in a week.
- If possible, during the first weeks of resuming breastfeeding, do not leave your home, but stay close to the baby all the time.
According to experts, the positive result is largely due to how psychologically the mother is ready for relactation, and how strong her desire is to feed the baby with breast milk.
For this reason, before starting the procedure to resume lactation, you should make sure that you really want to continue breastfeeding and you are not afraid of temporary physical and psychological problems that may arise.
What is needed for stable lactation
In the first weeks after childbirth, the level of prolactin in the body of a nursing mother is very high. This is a key lactation hormone that stimulates the primary formation of secretion in the mammary gland. After a month or a little later, its concentration decreases. Milk production is maintained by frequent stimulation of the breast, namely the nipple and areola. This happens during the process of sucking or pumping.
We can say that the mother's breast works on the principle of “demand creates supply.” That is, the more often breast stimulation occurs, the higher milk production will be. And the more milk comes out, the more is produced. And vice versa. Thus, to maintain lactation, two conditions are needed: frequent stimulation of the breast and its high-quality emptying.
It is important to know that milk will not go to waste if:
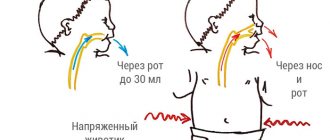
- The baby latches onto the breast correctly. In this case, the mother does not experience pain or discomfort. She hears the baby swallowing, but there are no extraneous sounds (smacking, clicking);
- Mom pumps correctly. There is no painful sensation, but the milk is well separated in drops or streams;
- a harmonious feeding or pumping regime has been established. Babies up to two to three months feed on demand. Older babies breastfeed at least 10-12 times a day. If for some reason the mother is unable to put her baby to the breast, she should pump in the rhythm of feedings and also during the night;
- Night feedings take place. Be sure to apply the baby several times a night. After all, it is at night that the greatest secretion of prolactin is observed.
Therefore, a decrease in milk secretion may occur if:
- there are errors in application;
- pumping is carried out incorrectly;
- less than ten applications or pumping per day;
- there are long breaks between feedings;
- no night feedings.
To reduce milk volume, ineffective breast emptying and infrequent breast stimulation are sufficient. The longer the alveoli are filled with milk, the slower the formation of new secretion will occur. Prolactin levels will decrease and milk supply will decrease.
Measures to restore breastfeeding
To resume breastfeeding after a forced break, it is better to seek the help of a specialist. He will be able to tell you how to act correctly in this situation, and will also give advice on what to take for lactation.
Relactation involves performing the following activities.
Put your baby to the breast frequently
This should be done at least every 2-3 hours. Breast stimulation is required for good milk production. As a rule, when breastfeeding is interrupted, a gradual decline in lactation occurs.
In the process of resuming breastfeeding, it is necessary to stimulate milk production as intensively as possible.
Contact with child
It is necessary to have close contact between mother and baby throughout the day and, if possible, at night. Experts advise walking with your baby in your arms and putting him in your bed at night.
If possible, the breast should be made available to the baby so that he can latch on when he wants to. This will help stimulate milk production.
Massage the chest and interscapular area with light movements
This also helps stimulate milk production. You should not use bottles when supplementing. It is recommended to carry it out using a special system for this procedure.
The optimal supplementary feeding scheme is as follows: breast - supplementary feeding - breast. When additional pumping is carried out, the scheme looks like this: pumping - breast - expressed milk - breast - supplementary feeding - breast.
Thanks to this scheme, the baby will be able to control the volume of milk during supplemental feeding and stop it if desired, if breast milk is in sufficient quantity.
It is important to put the baby to the breast at night, since during this period the mother’s body synthesizes the hormone prolactin, which is responsible for the synthesis of milk, in large quantities.
Breastfeeding at night will help stimulate lactation.
Give up the pacifier
If the pacifier has become such a habit for the child that it is impossible to live without it, you should not try to change the situation. If a pacifier is not essential for a baby, it is better to abandon it.
When your baby sucks on a pacifier, his sucking reflexes are satisfied, so he will need the breast less than a baby who does not use a pacifier. Therefore, breast stimulation will not be sufficient, which is why milk will be produced in less volume.
Pumping and breastfeeding
When a child refuses to breastfeed at first, there is no need to panic. After feeding through a nipple for a certain time, the baby became lazy, he lost the desire to work, and, in his opinion, this is pointless, since milk does not pour out of the breast on its own.
In this case, you will have to be patient and put the baby to the breast, even when he hardly sucks it. Gradually you will notice changes, the arrival of milk is quite possible. To stimulate milk production, if the baby refuses to breastfeed, you need to pump up to 6 times a day.
In addition, as a stimulation for the baby to start taking the breast again, you can use a special supplementary feeding system at the breast, so the baby can get the desired nutrition and at the same time promote rapid milk production.
Help from relatives
At first, when lactation resumes, the mother must significantly change her lifestyle and spend most of the time with the baby. So, before you begin relactation, you will have to tell all your relatives in an accessible language about your own actions, the purpose of such activities, the difficulties that may arise, and the help required from them.
Most often, relatives understand this and offer their help. The first thing that is required is to free the mother from housework for at least 2-3 weeks.
Please be patient
When starting to resume breastfeeding, the mother should understand that a difficult period awaits her, but she needs to be patient and then everything will work out. Relactation can continue in different ways in each case: for some it will take a couple of weeks, for others a couple of months.
When you have the feeling that the result is zero, milk production is poor, the baby does not want to take the breast, you should not give up!
In this case, you need to seek the help of a lactation consultant or pediatrician, they will be able to give advice specifically for your situation.
Why is there little milk in the breast and when does lactation begin?
Hollywood films are replete with scenes of a happy mother putting a baby to her breast immediately after giving birth. Therefore, ordinary people rarely think that this does not happen to every woman in life.
Mine gave birth an hour and a half after giving birth, while she was washed and measured, more than an hour passed before I was stitched up and placed in the ward. In principle, I was very lucky with the maternity hospital: there they did not supplement the children with anything and simply insisted that the child hang on the chest and suck out these unfortunate droplets of colostrum.....
Anastasia
https://www.babyblog.ru/community/post/fanatka/840607
For example, when performing a caesarean section under general anesthesia, the first attachment of the baby occurs only six hours after the operation. There are also cases where a woman is in intensive care for at least 24 hours. Therefore, you also have to forget about early application here.
My child was taken away from me on the first night because... I was coming off an epidural. In this case, the child inevitably receives formula. On the 2nd day, my baby already had little colostrum, and the milk had not yet come. So I asked for a mixture. On the 3rd the milk came. My daughter was on formula for 1 day and absolutely nothing bad happened)) Now we are completely breastfed. So if you have a similar situation, it is better to give your child formula than for him to go hungry.
TattaRainbow pages for babybooks
https://www.babyblog.ru/community/post/obraz_live/3137469
Medical contraindications for early breastfeeding include:
- Rhesus is a conflict situation between mother and baby. The essence of the conflict is that maternal protein penetrating through the placenta to the fetus inhibits antibodies in the blood of the newborn. This leads to hemolytic disease and severe anemia with the destruction of red blood cells. In order to avoid such a pathology, breastfeeding occurs 2–3 days after the birth of a child with Rh conflict.
I am Rh negative, my daughter is positive, they brought me food only on the second day, and then after a scandal with the doctor. My sister also had a disadvantage; they brought her sons to feed her only on the third day, explaining that she was Rh negative. We did not have Rh conflicts during pregnancy. It was a long time ago, then they didn’t give anything to anyone in the delivery room, but positive mothers were brought to feed their babies right away, but ours were first fed glucose and formula for two or three days, maybe there is some kind of dependence?...
Olga
https://www.babyblog.ru/community/post/living/3101207
- The birth of a child very premature. When a baby weighs less than one and a half kilograms and is born before the 32nd week of pregnancy, it is physically difficult for him to latch on to the nipple immediately after birth. These newborns are fed using a special tube.
- Depressed central nervous system of the infant. Weak physical condition and impaired muscle tone do not allow the baby to make sucking movements. Such children are put to the breast five days after birth.
- When assessing the baby's condition on the Apgar scale, it is less than 7 points. In this case, there are deviations from moderate to severe conditions requiring immediate resuscitation.
- In case of severe suffocation and respiratory distress syndrome in a newborn. Urgent resuscitation actions are also carried out here, excluding early breastfeeding.
- If the mother lost a lot of blood during childbirth. In this situation, emergency medical intervention is carried out in order to stabilize the condition of the woman in labor, including blood transfusion.
- Unconscious state of the woman in labor. In this case, the priority is to normalize the mother’s health.
- HIV-positive status or open form of tuberculosis in a young mother. Diseases prohibit not only early breastfeeding, but also lactation in general.
These factors directly affect the timing of lactation. After all, it is possible to establish such a process only after the health of mother and baby improves.
Due to the untimely arrival of milk, mothers are forced to use formula while still in the maternity hospital.
Hi, I myself work in a maternity hospital in the dairy kitchen (I prepare formula). Here we all have the same formula and only those who do not have enough milk are supplemented (and then at the request of the mother), after a caesarean section they are fed with formula while the mother recovers from anesthesia and those who themselves refused to breastfeed. Usually they breastfeed first, and then if there is not enough formula, they supplement with formula.
Anastasia, St. Petersburg
https://www.babyblog.ru/community/post/obraz_live/3137469
The appearance of early transitional milk in the breast occurs on the third or even fifth day after the birth of the baby. The liquid released before this time is not yet milk, in fact. So far we are only talking about thick colostrum, which prepares the newborn’s digestive tract to receive real mother’s milk.
The process of replacing colostrum with mature milk occurs in women with varying intensity. For some it is faster, for others this process is longer. It is known that in primiparous women the process of converting colostrum into mature milk takes longer, in multiparous women it takes less. The individual characteristics of each woman matter.
Elena Nikolina, neonatologist
https://www.7ya.ru/article/Kogda-pridet-moloko-Nalazhivaem-laktaciyu/
Despite the small amount of the substance, you need to immediately apply the baby to each breast in turn.
Proper breastfeeding has a number of nuances
And also be sure to drink enough liquid, especially plain water.
The total amount of liquid drunk before the milk comes in (during the first 3–5 days after birth) should be no more than 800 ml per day, otherwise it will be quite difficult to cope with the symptoms of hot flashes. When milk appears, in parallel with establishing adequate emptying of the mammary gland, it is necessary to gradually increase the amount of fluid consumed to 2–2.5 liters per day.
Nadezhda Ilyintseva Pediatrician, Ph.D. honey. Sciences, CSTO GUZ, Ulyanovsk
https://www.9months.ru/grudnkorm/5599/grudnoe-vskarmlivanie-v-pervye-dni-kak-naladit-laktaciyu-v-roddome
When a woman who has given birth does not have the opportunity to regularly breastfeed her newborn in the first days (after a caesarean section under general anesthesia, when mother and child are separated), it is important to express the incoming milk every two hours to avoid stagnation and “burnout”.
Not a doctor, but a mother who once did not feed her newborn after giving birth. But I tried, right after the birth of my middle child, a drop of colostrum was filtered out of me. And then that's it. We took the little one for a couple of days for research. At this time, the baby was fed formula from a bottle. The breasts, while they were a source of colostrum, were not naughty, but on the fourth day they became distended. Periodically they brought the baby in and I poked my boobs at her, but it’s hard work to suck natural milk. In general, the middle one ate the formula, and my breasts tried to burst from milk. The temperature was rising. Fever and chills as a consequence. Sisi was sick like hell for several days. I think it's five. Then the milk burned out and that was it. I don’t know what kind of developmental trauma befell my daughter, we’ll deal with it later.
Olga Lomakina, mother of many children
https://thequestion.ru/questions/122563/chto-budet-s-materyu-novorozhdyonnym-esli-posle-rodov-ne-kormit-rebyonka-grudyu
From the fifth to the seventh day, breast milk comes in stronger and stronger and is called late transitional. And after a caesarean section under general anesthesia, the changes last up to ten days due to delayed application. The nutritional liquid is distinguished by an increase in the level of carbohydrates and a decrease in the amount of proteins and fats.
Table: composition of human milk depending on the degree of maturity
| Stage of breast milk maturation | Belkov, g/l | Fat, g/l | Carbohydrates, g/l |
| Colostrum release | 23–59 | 29–42 | 42–78 |
| Appearance of transitional milk | 17–23 | 28–45 | 56–79 |
| Formation of mature milk | 8–19 | 32–37 | 72–76 |
After 10–15 days from the moment the baby is born, mature milk appears in the woman’s breast, which is bluish in color and has a thinner consistency than previous secretions. At this time, during the sucking process, contractile movements of the uterus are felt, and unexpected (occurring not during feeding) and abundant flows of milk begin in the chest. This phenomenon indicates the stabilization of oxytocin production and the establishment of milk production in the breast. In order to support the process of milk formation, it is better not to feed the baby according to a schedule. You need to apply it as many times as the baby needs, and to one breast at each feeding. Indeed, in addition to reducing the amount of secretion produced by the mammary glands, infrequent feedings provoke an increase in the level of glucose in the child’s blood.
The final establishment of lactation occurs one and a half to two months after the birth of the child. At this time, spontaneous tides are no longer observed. The breasts of a nursing mother become soft, and there is a feeling of insufficient fullness of the mammary glands. You can understand that lactation has been established by the absence of painful sensations during the arrival of milk.
Now milk is produced not under the influence of hormones (endocrine control), but under autocrine control. This means that continued milk production depends more on how empty the breasts are, rather than on the level of hormones in the blood. Milk is produced according to the principle “demand creates supply”, namely the more the mother breastfeeds, i.e. The more the baby sucks, the more milk will be produced. And accordingly, the less you feed, the less milk there will be.
E. O. Komarovsky, pediatrician
https://lib.komarovskiy.net/anatomiya-grudi-kormyashhej-materi-kak-v-grudi-poyavlyaetsya-moloko.html
Factors influencing a decrease in breast milk production are:
- Using a pacifier or pacifier. Such devices are much easier to suck on, which can cause the baby to refuse to take his mother’s breast.
- Lactation crisis due to changes in the baby's needs for breast milk. Every 2–3 months, the baby’s sucking activity increases as he grows and develops. Milk in the mother’s breast does not always have time to arrive in the required quantity. This is fraught with lactostasis and the introduction of mixtures so that the child does not remain hungry.
- Postpartum infection. In this case, antibiotics are used for treatment, and the mother is forced to interrupt breastfeeding.
- The appearance of cracks in the nipples and the development of mastitis. The main reason for this phenomenon is frequent breast washing. In the process of washing the nipples, a special protective layer disappears, which is responsible for the destruction of infections and the elasticity of the skin on the chest. As a result, cracks appear through which pathogenic microbes, including Staphylococcus aureus (which causes mastitis), penetrate inside.
- Severe infectious and viral diseases in the mother (such as influenza and tuberculosis, tonsillitis and epilepsy).
- Excessive swallowing of air by the baby during feeding. This causes colic in newborns and breast refusal. Which, in turn, leads to a decrease in milk volume.
- The use of medications (camphor, gestagens, androgens, diuretics).
- The tense emotional and psychological state of a nursing woman.
- No night feedings. Since prolactin is produced more actively in the dark, it is important to feed the child, even if he is sleeping. The most productive time is from three to eight in the morning.
- Incorrect attachment of the baby to the breast. From the first days of a baby’s life, it is necessary to ensure correct latching of the nipple in order to eliminate lack of food in the newborn and unpleasant sensations in the mammary glands in the mother.
According to statistics, in three percent of cases, women who give birth completely lack lactation function. The basis of this pathology lies in hormonal disorders on the part of the mother.
In case of disappearance of breast milk that has already appeared, the reasons should be sought among such phenomena as:
- A woman’s psychological attitude is against natural feeding.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Using estrogen-based contraception (this hormone suppresses the production of prolactin).
- Treatment with antihistamines and vasoconstrictors, taking diuretics and pyridoxine.
- A sharp change in the body weight of a nursing mother (especially if it decreases).
Video: why does a nursing mother lose milk?
Mother's diet
Nutrition should be of high quality, and fluids should be consumed in large quantities, not forcing yourself, but also not leading to a feeling of thirst. In addition, the diet must necessarily contain products for lactation of a nursing mother.
To improve breast milk production, a young mother is recommended to consume:
- warm tea;
- caraway seeds and bread with caraway seeds;
- dried fruit compote;
- clean water;
- nuts;
- dill tea;
- herbal tea;
- nut milk;
- low-fat meat soups and broths;
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- hard cheese, Adyghe cheese, feta cheese;
- fermented milk products;
- barley decoction or barley coffee;
- radishes with honey;
- tea to increase lactation with ginger;
- Hercules;
- buckwheat, etc.
Diet of a nursing mother
Hypogalactia may be associated with maternal malnutrition. How to restore lactation in this case? You should adhere to a diet and maintain a drinking regime.
We recommend reading: Calcium during breastfeeding: can you drink it, consumption rate
Medicines should not be taken unless absolutely necessary. While milk production is physiological, its volume can be stimulated by a diet that includes the consumption of lactogenic foods and physical therapy.
Liquid foods should be included in the diet, and the consumption of dry food should be limited. The daily volume of fluid consumed should be at least 2 liters . Water and drinks (compotes, herbal infusions) should be warm.
It is acceptable to use drugs such as Lactogon and Apilactin. These products help avoid problems with lactation.
Products in the daily diet for a nursing woman
A nursing mother's diet must include porridge as the main source of carbohydrates, as well as fresh and stewed vegetables.
- meat products rich in protein (rabbit, turkey, veal);
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- cereals (the main source of carbohydrates);
- vegetables and fruits;
- walnuts, hazelnuts;
- vegetable oils;
- honey;
- ginger.
Prohibited foods for breastfeeding
During breastfeeding, you should temporarily exclude the following foods from your diet:
- smoked and canned products;
- hot spices (namely red and black pepper);
- parsley and mint;
- citrus fruits (if the child has an allergic reaction to them);
- chocolate;
- lingonberry tea and sage decoction.