When teeth start cutting
There is no exact answer as to what time a child’s teeth are cut – the timing varies from person to person. However, you can focus on the average, standard periods of eruption approved by WHO:
- the lower incisors appear at 6–7 months;
- upper – at 7–8 months;
- upper lateral incisors – at 8–9 months;
- the lower ones are closer to a year.
According to the standard, a one-year-old child must have eight baby teeth.
From one year to one and a half years, the child acquires larger teeth - upper and lower molars, and from fifteen to twenty months - upper canines, which are also called “ocular.” The fact is that the optic nerve runs next to them, so these teeth are often more difficult for the child than others. Irritation of the nerve causes sharp pain and sometimes watery eyes.
It can be difficult even for a doctor to understand that the first teeth are being cut. After all, this process is often accompanied by an increase in temperature, changes in stool and mood, and refusal to eat.
When should you start caring for your baby's teeth?
Experts recommend starting to clean your gums with gauze as soon as the first tooth appears, approximately between the sixth and seventh months. The most convenient device for brushing a baby's teeth will be the parent's finger wrapped in gauze. By the way, this method is also suitable for older children if they refuse to use a toothbrush. The next step should be a silicone toothbrush - a massager in the form of a fingertip, put on the parent’s finger. To make a smoother transition for a child to a classic toothbrush, you must first of all interest him, for example, by letting the child look at an adult toothbrush and show him what they do with it, deliberately emphasizing: “Just like mom and dad.” At about a year old, you can give your baby his first toothbrush and try to make learning fun for him and like a game. If he loves the imitation of brushing his teeth, then it will be easier to teach him to seriously engage in this important task.
Kids love that they do everything like adults and get great pleasure from the process of spreading the paste, but they often don’t like its pungent taste. Therefore, use only special children's pastes with a soft, pleasant aroma for children. Dentists warn that it is extremely harmful for children to swallow too much toothpaste containing fluoride, so for very young children it is recommended to use only toothpaste that does not contain fluoride. Such a paste could be “ROKS Baby for children from 0 years old” - the first toothpaste on the Russian market for oral care for children and infants, a toothpaste without fluoride and other components that can cause unwanted reactions in the body, as babies swallow the paste. This paste contains natural linden extract and xylitol, which have a protective effect and give the paste a slightly sweet taste that babies like.
Formation of the dentition
The article tells how to understand that a child is teething, and about ways to help him with pain and inflammation of the gums. But first, a few words about the process of dentition formation.
The formation of absolutely all teeth occurs in the fifth month of intrauterine development. They remain in a “frozen” state and begin to grow immediately before eruption. Therefore, if a child has no teeth by 9-12 months, radiography is prescribed - a study that allows one to evaluate their formation and location.
Ways to care for children's teeth
Primary (baby) teeth require the same quality care as permanent teeth. Early oral hygiene will help prevent tooth decay.
Here are some tips for caring for children's oral cavity.
- Clean your child's gum line with gauze or a soft cloth.
- Provide separate cutlery (bowl, spoon and fork) for your child. Do not allow others to use this utensil as this may cause infection.
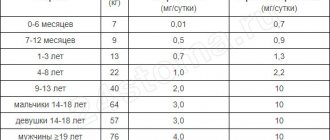
- Give your child foods rich in vitamins and minerals. Your baby needs calcium, fluoride, phosphorus and vitamin C for healthy teeth and gum development.
- Avoid sugary foods and drinks as they damage teeth.
- Teach your child to drink from a glass, not a bottle. Drinking from bottles leads to tooth decay as the slow flow of milk and juices accumulates in the baby's mouth and remains there for a long time.
- As soon as your child turns 18 months old, you can start brushing his teeth.
How to brush baby teeth?
- Dentists recommend using fluoride toothpaste after a child's first tooth appears. But the amount of paste on the brush should be the size of a grain of rice until the age of three.
- After three years, the amount can be increased to the size of a pea.
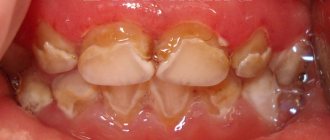
- Too much or too little fluoride can be bad for children's teeth. Too much of it can cause a condition called fluorosis, a common disorder characterized by erosion of tooth enamel.
- Fluoride deficiency leads to dental caries, a condition in which the tooth decays over time due to acid-forming bacteria and saliva-fermentable carbohydrates. Caries develops in the crowns and roots of teeth and affects the primary teeth of infants.
- Replace your child's toothbrush every three months to avoid bacterial infection. Following a consistent brushing routine will help your child become comfortable with oral hygiene early on.
What affects the timing of teething?
Processes in the body are individual, including timing. The age at which the first teeth appear is determined by a number of factors:
- Heredity.
- The intrauterine period and negative factors affecting the fetus (for example, a pregnant woman taking certain medications).
- Nutrition for the expectant mother during the period of waiting for the baby and breastfeeding.
Introduction of complementary foods, etc.
What is milk bite? Formula
The appearance of baby teeth is a signal that the baby is growing up. From the point of view of human development, their appearance indicates the following:
- The child is ready for the transition from sucking to chewing, that is, from mother’s milk (or formula) to complementary foods and a gradual transition to normal food.
- From the intuitive production of individual sounds, the baby moves on to understanding speech addressed to him and even tries to imitate it.
The rudiments of baby teeth are formed in the womb, so the woman’s condition during the first trimester of pregnancy is responsible for the predisposition to “bad teeth”.
How many baby teeth should children have? The temporary bite has 20 teeth, of which 8 are incisors, 4 canines and 8 molars.
In dentistry, there are several ways to designate a temporary occlusion. In ordinary life, this information is unlikely to be useful to the mother, but it can help to better understand the dentist’s explanations and actions during the appointment.
- The classical Zsigmond-Palmer system, which was adopted for a long time in the USSR. In it, the milk row was designated with Roman numerals.
- A modern system accepted throughout the world, including by the International Dental Association. It involves using two numbers to designate each tooth. The first number indicates the quadrant in which the tooth is located (upper left or lower right), and the second number indicates the serial number of the tooth itself.
- An alphanumeric system in which each type of baby tooth is designated by a capital letter, and the index number is a serial number. This method is very convenient to indicate a changeable bite. To do this, you just need to replace lowercase letters with capital ones. This change is immediately noticeable.
- In America, it is customary to designate baby teeth using the letters of the English alphabet, placing them from the upper right molar to the lower right.
- You can also find the group designation of milk occlusion. In it, the number indicates the number of teeth of a certain group, and its location, in fact, the type of tooth.
- Similarly, temporary occlusion can be recorded using an alphanumeric system.
How does the jaw of baby teeth differ from permanent teeth?
There is an opinion among parents that baby teeth grow without roots. This myth appeared because during a change in bite, teeth fall out with reduced (resolved) roots. In fact, baby teeth have roots, and their number completely corresponds to that of permanent teeth. Despite the fact that the teeth of the temporary and permanent dentition are similar in appearance, there are several differences between them that help dentists accurately determine the group affiliation of the tooth.
| Milk bite | Permanent bite | |
| Number of teeth | 20 | 32 |
| Premolars | No | There is |
| Color | White-blue | Yellowish |
| Size | Small | Big |
| Crown sizes | The crown is wider than it is tall | High crown |
| Crown to root size ratio | The crown is more convex, making the roots appear smaller | Traditional ratio of crown to root sizes. |
| Presence of enamel roller | In the area of the neck of the tooth there is a thickening of the enamel, due to which the crown becomes larger. | No |
| Degree of mineralization | Low | High |
| Cavity dimensions | Extensive | Standard sizes |
| Channels | Wide canals and apical foramina | Narrow, sometimes difficult to pass with irregularly shaped branches |
| Root shape | Rounded | Long and elongated |
| Direction of root growth | Moved to the side to make room for the permanent tooth germ | Perpendicular to the jaw bone |
| Root reduction | Eat before changing bite | No |
| Tremas and diastemas (distance between teeth) | Normal physiological state as the jaw grows (from 4 to 6 years) | It shouldn't be normal. |
| Lumps and cutting edges | By the time the bite changes, they are erased (by 6 years) | Well expressed throughout life |
Teething symptoms
- there may be a slight fever;
- anxiety - the child becomes capricious, sleeps poorly, often wakes up at night;
- decreased appetite;
- excessive salivation and, as a result, redness of the skin around the mouth;
- swelling and redness at the site of tooth eruption, possible formation of hematomas on the gum mucosa;
- increased need for the baby to chew on something: pacifier, toys, fingers.
There are children whose teeth appear asymptomatically and even unnoticed by their parents. But, as a rule, this process is accompanied by an individual combination of the signs given in the list above.
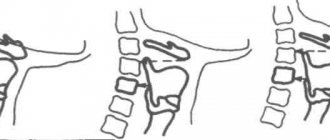
The order of eruption of baby teeth
Everyone is different, but it is still important to know how most babies develop. Children's first teeth usually erupt almost simultaneously on the right and left. The sequence is as follows: first the anterior ones (incisors, canines), then the posterior ones.
It is important to understand that this pattern of teething in children is average, and in your case it may happen in a different order or at a different time. This does not necessarily indicate any violations.
Doctors have compiled an approximate, average diagram of teething in children:
Don't worry if you don't meet these standards for several months. If the parents got teeth late, most likely the children will have the same. Heredity has a very strong influence on development. The teething pattern should not become an unnecessary source of parental anxiety. This is just a guideline, like all other norms.
Both the sequence and timing of teething in children can vary greatly. Only if you are “late” by more than 6 months (for example, nothing appears until a year), it is worth discussing this with your doctor. There are genetic disorders when the rudiments of teeth do not develop at all. However, this is extremely rare. Some diseases also affect the timing of teething, but these conditions in children always manifest themselves with some more obvious symptoms.
In any case, there is no remedy that would “cut teeth” - we won’t pull them out of the jaw. We also do not regulate the cutting order. All that remains is to observe the process in children and take care of their health in general.
Deviations from the norm of eruption
Teething, although a painful process, is still natural for the body, but deviations in the pattern or time may indicate some pathologies. A delay in the appearance of primary incisors by a month or a month and a half is considered an acceptable norm, and if other children erupted their first teeth at six months, and your child’s gums have just begun to swell at eight months, do not sound the alarm. There's nothing wrong with your baby. Each organism develops according to its own rhythm.
However, there are several points that you should pay attention to and seek advice from a pediatrician or dentist.
Early eruption
If a four-month-old baby exhibits signs that are precursors to the first incisors, then most likely this indicates a disruption of the hormonal system. It is better to show the child to the pediatrician and conduct the necessary examination.
“I noticed that after the DPT vaccination, teeth began to be delayed in appearing. The doctor said it could be related to the immune response. The child’s body is busy building immunity, and therefore teeth come in a month late, although our first teeth came out exactly on schedule.”
Excerpt from Irishka_Grishina’s blog on baby.ru
Delay in eruption
A long (more than three months) absence of teething symptoms should cause alarm. The cause of the delay can be either previous infectious or viral diseases, or more serious abnormalities, for example, metabolic disorders, intestinal problems, neurological pathologies.
If by 12 months a child has not developed a single tooth, then this may be a consequence of congenital adentia - an intrauterine pathology in which the rudiments of a primary bite are not formed in the body.
Difficult teething
There are cases when the gums swell, the child develops increased salivation, but the crowns do not appear for two or more weeks. In such situations, it is better to seek dental help. The doctor will advise you on how to help baby teeth erupt into the light. Sometimes this requires surgery.
Violation of the direction of eruption
More often this happens with permanent units of the dentition, because they may encounter an obstacle on their way in the form of a milk tooth that did not fall out on time or a molar “neighbor” that is too large. With this pathology, the tooth does not grow strictly upward, but sideways. As a rule, this most often happens with molars, including the “wise ones”.
Read on the topic: what is an impacted and dystopic tooth - why does it bring discomfort and reduce the aesthetics of a smile.
It is rare, but it happens that the milk is cut to the side of the gum. This indicates displacements of the axis of its location. It is impossible to ignore such growth in both permanent and temporary (mammary) units, because this pathology can lead to malocclusion and even pathological development of the jaw. It is best to correct a defect at the initial stage, therefore, if a child has problems with the position of a growing tooth, you should immediately contact a dentist.
How to relieve a baby’s condition if his gums are swollen and painful?
When the gums are swollen and unpleasant symptoms appear, many pharmacological innovations come to the aid of children and parents that relieve pain and discomfort. You can use traditional medicine recipes that also helped our mothers and grandmothers.
First of all, you need to get a teething toy. It is first placed in the refrigerator or freezer - the cold rubber toy dulls the pain and safely scratches the gums.
If symptoms are intense, especially when the child does not sleep at all and cries a lot, a variety of gels, suppositories or suspensions are suitable.
Homeopathic medicines are popular and should reduce general symptoms.
Medicines
Medicines for children are divided into the following groups:
- local painkillers;
- complex homeopathy;
- painkillers for oral administration.
Local analgesics are presented in gels; almost all modern parents have them in their medicine cabinet. The advantages of such gels include convenient application to the gums, quick effect and antiseptic properties. During the first minute, the mucous membrane “freezes” and becomes insensitive. Among the disadvantages are the short duration of the effect and unpleasant sensations in the mouth. However, the pain relief effect is sufficient until the child falls asleep.
The most famous gels:
- Kamistad Gel (Baby);
- Kalgel;
- Dentinox Gel-N;
- Holisal.
Homeopathic medicines act comprehensively. They affect the entire process as a whole, speed it up and alleviate the baby’s condition. Such products contain only natural and safe ingredients, so they are suitable even for the smallest children. They must be used strictly according to the instructions.
Homeopathic medicines:
- Viburkol - candles;
- Dantinorm Baby - drops (composition of Dantinorm Baby and instructions for use);
- Dentokind - tablets (instructions for use of the drug Dentokind);
- Pansoral - gel, etc.
Analgesics and antihistamines intended for internal use are prescribed only by a doctor. Unlike the first two groups, taking these medications is indicated in the presence of serious symptoms or complications:
- Fenistil drops (from birth) and Parlazin (after 1 year) are antihistamines. They are prescribed to relieve and reduce swelling of the mucous membranes in the mouth and nasopharynx, and eliminate itching or burning of the gums. Antihistamines help reduce runny nose and inflammation.
- For severe pain or fever, taking antipyretic drugs (they also act as painkillers) is recommended. Children's (necessarily age-appropriate) suspensions or suppositories based on ibuprofen or paracetamol (Nurofen, Panadol, etc.) are suitable. Before starting to take the medicine, you should consult your pediatrician. He will assess the need for its use and also select the most suitable product.
Folk remedies
- Tea based on chamomile, lemon balm, lavender and catnip will calm the baby and reduce pain. Dry ingredients must be mixed in equal proportions. Pour a tablespoon of the prepared mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave for 10-15 minutes, then strain. You can drink this tea throughout the day.
- Wipe your mouth with a strong decoction of chamomile or make compresses. If the decoction is diluted with water, it can be drunk as tea.
- Clove oil helps children and adults in dentistry. It disinfects and relieves pain. Pure clove oil will burn, so it needs to be diluted with olive or almond oil in a 1.5:1 ratio. Treat the inflamed area with the resulting solution.
- For rubbing or compresses, a decoction of sage, calendula, and oak bark is used. You can use one component or prepare a mixture. The ingredients relieve inflammation, disinfect, reduce pain and itching.
Chamomile tea is a very effective teething soothing remedy.