Anatomy of permanent teeth
Each molar consists of certain parts:
- crown. This is the part of the tooth that protrudes from the top;
- the root, it goes deep into the alveoli. At the same time, it is attached thanks to special connective tissue bundles. There can be different numbers of roots (1-5 pieces). This moment affects the number of nerves and channels;
- neck. This part is located between the root and the crown.
Tooth tissues are distinguished by their heterogeneity. The enamel is on top and is known for its durability. Once the tooth has erupted, it is covered with a transparent thin layer. This is the cuticle, which eventually changes to the pellicle. The latter is a film that is created from what saliva produces.
Beneath the enamel is dentin, the tissue of the tooth. Dentin is similar to bone when you study how it is built. However, it is more durable because there is a high level of mineralization. In the area where the root is located, the dental tissue is covered with cement. The latter is rich in mineral compounds and is also associated with periodontium. Collagen fibers are used for this.
As for the part of the tooth that is inside, this is the crown and root canal. They are filled with pulp. This is loose connective tissue; it contains nerve endings and blood vessels.
Differences between baby teeth and permanent teeth
Permanent and temporary teeth are built in the same way, but still have certain differences between themselves:
- The enamel on baby teeth is whiter. And the enamel on permanent teeth has a yellowish tint;
- the best indicators of density and mineralization are noted behind the molars;
- the pulp of a baby tooth is large in size, and the dense tissues and their walls are thinner;
- permanent teeth are larger in size, here the length is greater than the width;
- The root of baby teeth is short and thin compared to permanent teeth. When the root of temporary teeth is formed, they expand in width. Therefore, the permanent bud has free space to grow.
Where do teeth come from?
Teeth begin to form and develop when the fetus is still inside the womb (at about 6 weeks). They have their source - the epithelial dental plate. Already by 14 weeks, active formation of dental tissues, which are hard, occurs. Initially, this occurs in the area where the crown will be, and later at the root.
Molars, namely their first rudiments, appear by the 5th month of the embryo. They are located higher than the child’s baby teeth or lower. By the time the child is born, the rudiments are already practically formed in the tissues of the jaw.
Teeth that belong to an additional group (have no predecessors) are formed later. This occurs after about 1 year of life. Why? Because the baby's jaw is still very small and there is not enough space for them.
Why do molars turn black in a 6 year old child?
When a 6-year-old child's molars turn black, parents begin to sound the alarm. Darkening of the enamel can occur even with good oral hygiene. When a child’s radical units turn black, the reasons may be the following:
- Incorrectly composed diet: excessive amounts of sweets, lack of meat and fish.
- Dysbacteriosis can also cause darkening of teeth.
- Hereditary factor.
- Deficiency of calcium and other microelements.
- Development of early caries.
The appearance of dark plaque is an alarming symptom that requires contacting a dentist. You should immediately seek help so as not to start the process.
What does a dental formula look like?
To make it more convenient to describe teeth and their number, special formulas are usually used. Each tooth has its own number, which is used to decipher its location.
When describing a milk bite, Roman numerals are used:
- incisors – I, II;
- canine – III;
- molars – IV, V.
If we talk about the formula for adult teeth, here the teeth are counted starting from the center:
- incisors – 1.2;
- fang – 3;
- molars (small) – 4.5;
- molars (large) – 6,7,8.
8 is a wisdom tooth; not every person has it.
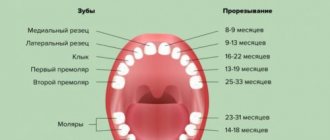
Teething order
Typically, all children start teething at about the same time. Teeth emerge from the molar set at the age of 5, and it is the molars (large ones) that emerge. Then the diagram is as follows:
- Initially, the incisors on the lower jaw change, which are located in the center;
- then the central incisors appear on the upper jaw and the incisors on the sides on the lower jaw;
- at about 8-9 years old, the incisors on the top and sides change;
- up to 12 years of age, molars (small) grow;
- at the age of 13, the fangs change;
- after the child turns 14 years old, the second molars (large ones) come in. They were not included in the milk kit;
- and after another 1 year the third molars (large) appear. This is a wisdom tooth. But he may not appear at all.
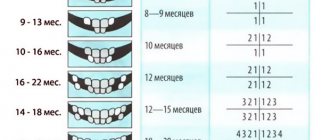
Teeth growth chart
Depending on the baby’s diet and his individual characteristics, the timing of teeth appearance may vary. This is also influenced by hereditary factors. Let's look at the sequence and approximate timing of growth of primary and permanent teeth.
Baby teeth
On the jaws of a newborn baby there are 20 follicles of temporary teeth. Also inside are permanent teeth, or rather, their rudiments (16 appear with the birth of the baby, and the rest are formed a little later).
The gums of the lower jaw are the first to suffer. At the same time, the tooth enamel in children does not contain a sufficient amount of microelements, unlike permanent teeth in adults, and therefore is still very rough and porous. If you do not follow the rules of oral hygiene and do not eat properly, the risk of developing dental caries in children increases. If anyone doesn’t know, baby teeth also need proper care.
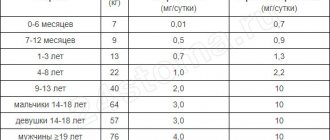
Table. Baby teeth growth chart.
| Name of teeth, photo | Baby's age at birth (months) |
| 6-7 | |
| 7-9 | |
| 9-11 | |
| 11-12 | |
| 13-18 | |
| 14-19 | |
| 15-21 | |
| 16-22 | |
| 21-25 | |
| 25-32 |
Permanent teeth
Molars, which are located at the end of the baby's dentition, are the first permanent teeth to appear in the mouth. Their main feature is the presence of slight depressions on the chewing surface, which is why they are most susceptible to caries. As soon as permanent teeth erupt, they must be properly cared for, because they do not yet contain a sufficient amount of minerals and are therefore very weak. In addition to the rules of oral hygiene, it is necessary to periodically treat the surface of the teeth using special fluoride gels or varnishes. Dentists recommend carrying out this treatment at least 4 times a year. 12 months after eruption, the frequency of the procedure can be slightly reduced.
How to determine that a child will soon have molars?
There are certain signs that indicate that permanent teeth will soon begin to erupt:
- The spaces between the teeth increase. The jaw grows and the free space increases;
- baby teeth become loose as the root gradually dissolves. It cannot be firmly fixed in the jaw tissues;
- in case of loss of a temporary tooth. This confirms that the molar will soon come out as it has pushed out the previous one;
- The gums are slightly swollen and red.
When permanent teeth erupt, the child’s general well-being usually remains the same, the temperature does not rise, and there is no pain.
Timing of baby teeth loss
The last milk units are replaced by permanent ones around the age of twelve. The sixth teeth erupt approximately after fourteen years of age. The last teeth to grow are the 8s or wisdom teeth. They appear at different times from 18 to 28 years. But dentists often encounter situations where eights appear in patients after thirty years of age. This is not a pathology, just like cases when the last molar does not erupt at all. We will consider the timing of the eruption of permanent teeth below.
Initially, a six- to seven-year-old child cuts teeth according to the same pattern as small children. Only by the age of fourteen do additional chewing teeth appear. There is no absolutely accurate data regarding the timing of the eruption of permanent teeth, since everything depends on the individual characteristics of the child. The shift period can pass very quickly or drag on for a long time. By the age of five or six, children have lower and upper central incisors. The lower and upper lateral incisors emerge by the age of eight. Premolars above and below grow between nine and twelve years. Fangs may appear at the age of twelve or thirteen. Second molars on both jaws appear at fourteen, sometimes at fifteen years of age. Although the age at which the molar units begin to erupt may vary, the sequence is almost always maintained. When a 6-year-old child begins to erupt molars, parents should be especially attentive to the issue of oral hygiene.
Possible problems
Permanent teeth have just appeared, but this does not mean that there will not immediately be any problems associated with them. Parents should be aware of possible dental problems:
- lack of molars;
- pain in the molar area;
- crooked position of molars;
- molars fall out;
- injuries.
For any of these problems, it is important to contact a specialist in time to receive qualified help.
How to improve your child's condition
Pain in the teeth is not a pleasant symptom, which is difficult to deal with even for an adult. And it is much more difficult for children to endure toothache. The growth of molars may be accompanied by slight discomfort, as well as general weakness. Therefore, it is better to find out in advance when this period begins in order to help the child at any time. When a tooth erupts, it damages the lining of the gums. This causes slight inflammation. In such cases, dentists talk about an aseptic inflammatory process, which often causes fever and digestive disorders. Standard medications for the treatment of inflammation in the oral cavity are not all suitable for children. Doctors often prescribe Cholisal, which does a good job of eliminating pain and reducing inflammation. This drug also affects bacteria. Before use, be sure to consult a specialist. What else can help:
- Light gum massage.
- A cold compress can be applied several times a day.
- Using special gels with an analgesic effect: Metrogyl Denta, Kalgel. Use no more than four times a day is allowed.
- To eliminate fever, standard remedies are used that a child usually takes when the temperature rises. Carefully monitor how much medicine you give your child so as not to exceed the norm.