General information
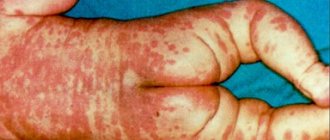
The name of the disease is due to the fact that outwardly it looks like a nettle burn - the skin turns pink and swells, while small blisters can merge into large local spots (angioedema) of irregular shape.
Papules cause itching and discomfort; when scratched, the wound surface can become infected, and then dermatitis and other complications join the underlying disease. The disease is very common; every third person on the planet has suffered from urticaria in one form or another.
Symptoms of urticaria in children
The main sign of urticaria in a child is a rash. Its prevalence and severity may vary, but in most cases the disease follows a single pattern.
- Convex pink and red rashes appear that turn pale when the skin is pressed or stretched. When the blisters merge, the edges of the spots become more intensely colored.
- The appearance of blisters, their disappearance or merging into vast shapeless foci occurs chaotically, and their migration over the surface of the body is unpredictable.
- The rash is accompanied by severe itching.
- The temperature may rise, either slightly or to high values.
- Often - weakness, malaise, joint pain and headache.
- In the complicated form, difficulty breathing or swallowing, nausea and vomiting, and bowel movements.
- An even more severe manifestation is angioedema on the lips, oral mucosa, eyelids, cheeks or genitals.
The localization of the appearance of the rash can be anywhere, including on the mucous membranes - lips, nasopharynx, ears and genitals. Most often, the upper part of the body and arms are affected, while the symmetry of the rashes is not always present; the spots take on the most bizarre coral-like shapes.
In most cases, allergies in the form of urticaria in children are accompanied only by the appearance of an itchy rash, which does not last long, from several hours to several days. Often other pathologies give similar symptoms; in this case, urticaria is not considered as an independent disease.
Information for parents! If a rash in the form of hives is accompanied by even slight swelling in the child, especially in the face and neck, you must immediately call emergency help!
Symptoms and main signs
Urticaria in newborns: what causes the rash? Rashes appear more often in skin folds and in places of contact with clothing. That is why it is so important to choose high-quality fabrics for children's textiles, clothes without seams, which once again provoke irritation.
Hives are not an infectious disease and cannot be transmitted from one child to another.
The skin disease consists of pinkish to red blisters . They form groups of redness, similar to nettle burns, come in different sizes and shapes, appear and disappear, now in one place, now in another.
More often, rashes on the baby’s body are observed:
- on the chin and cheeks;
- on the arms and shoulders;
- on the back and buttocks.
In rare cases, the rash will remain in one place for up to 48 hours or longer. It usually migrates throughout the body. In addition to rashes, serious symptoms include :
- poor appetite;
- dry skin;
- disturbing sleep;
- vomiting for no reason;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- constant anxiety.
Depending on the form of the disease, acute and chronic urticaria are distinguished.
Acute occurs abruptly and appears 1-2 hours after contact with the allergen. This makes it easier to determine the cause of skin irritation. Details about the treatment of acute urticaria in a child are described here.
Chronic is less common. The rash appears on the child's body within several weeks . If urticaria appears in children under one year of age, treatment may take up to 6 months.
Causes of urticaria in children
There can be many reasons for the appearance of hives in a child. In addition, it can be caused by different factors in the same person at different ages. Among the most common pathogens in children, the following groups can be distinguished:
- Food products (citrus fruits, nuts, eggs, seafood, strawberries, tomatoes, etc.).
- Food additives, primarily sulfides, salicylates and various chemical dyes.
- Household allergens (dust, fluff, cigarette smoke, pollen, cosmetics and detergents, synthetic clothing, fumes from furniture varnishes, paints, etc.).
- Medicines and contrast agents for radiography.
- Blood (donated) and drugs created on its basis.
- Vaccinations.
- Insect bites, helminthic infestations.
- Physical, including thermal phenomena (overheating and sweating, cold, physical activity, direct sunlight).
- Psychogenic factors.
- Various infections.
All of these factors can become both the cause of primary urticaria and the impetus for its exacerbation during the chronic course of the disease. In children under two years of age, the vast majority of cases of urticaria are caused by food allergens.
Causes of urticaria
About the cause of urticaria, I would say this - it is a congenital allergic reaction to something. Thus, a person (adult or child) must have a congenital predisposition to this disease.
And since this is an innate reaction of the body, then this is a slightly sad conclusion that there are no radical treatments for this disease and all the remedies currently available in official medicine are, unfortunately, aimed only at combating the symptoms of the disease!
Once again, I draw your attention to the fact that I am talking about official medicine and do not consider different theories, such as that all diseases are caused by “parasites”, “fungi”, “earth”, “water”, “sins”, etc.
The second point about the word congenital - this does not mean that urticaria should appear in a person from birth, it can appear for the first time at any age!
Another important point about the cause of urticaria. They can be roughly, but from a practical point of view correct, divided into two groups.
The first is when the reason is known. Hence the names of the varieties of urticaria: cold - caused by low temperatures, solar - the sun, aquagenic - water, vibration - vibration, allergic - various foods, plants, infections, etc.
The second group is when the cause is unknown (not established) - idiopathic urticaria, which in turn is divided into acute, in which there is a single appearance of blisters lasting less than 6 weeks, and chronic, in which blisters appear daily or almost daily for more than 6 weeks. blisters, each of which lasts no more than 24 hours.
The mechanism of occurrence of urticaria (pathogenesis)
The human body contains mast cells or mast cells, which are specific elements of connective tissue. They are the central element in the development of urticaria, activators of inflammation. When an allergen enters the body for the first time and in small doses, the child does not experience any external manifestations or reactions, but sensitization occurs, which can be represented as the first acquaintance with the allergen, resulting in the production of histamine. It is this substance that causes redness, swelling and other inflammatory factors. It gradually accumulates in mast cells, and when its amount reaches a critical threshold, the cell membrane is destroyed with the release of histamine into the bloodstream and a subsequent cascade of pathological changes in the body.
Classification of urticaria in children
According to the nature of the course, acute and chronic forms are distinguished.
In the first case, the disease manifests itself abruptly; the symptoms of urticaria continue to bother the child from several hours (usually 6-12) to 1-2 weeks. The rash is accompanied by severe itching, the surface of the skin at the site of the rash becomes hot to the touch. If the outbreak is caused by an allergen, then when contact with it is eliminated, the symptoms disappear quickly and without a trace. With an exacerbation of chronic urticaria, the itching and rashes are less intense, but in this case they can persist for a long period - several weeks and sometimes months. The condition is accompanied by weakness, nausea, loss of appetite, headaches, and, less commonly, stool disorders. Sometimes, against the background of sluggish urticaria, neurotic disorders develop, and since the child constantly scratches the itchy papules, a secondary infection occurs and dermatitis develops.
Based on the severity of the disease, the following types of urticaria in children are distinguished.
- Mild form - external manifestations are almost invisible, the child feels well, there is no itching or intoxication of the body. A minor rash goes away within a day at most.
- Moderate - characteristic rashes are clearly visible, accompanied by fever and itching; intoxication of the body in the form of nausea and headache may be present. The papules merge, swelling appears, and there is a risk of the first signs of Quincke's edema appearing.
- Severe - pronounced symptoms. Severely itchy rash, general intoxication of the body with a gastrointestinal reaction, development of Quincke's edema. Requires urgent medical attention.
Depending on the provoking factor, the child may experience the following types of urticaria:
- Contact - has an allergic origin, in 1st place among the causes are pharmacological and biological factors. When contact with them is eliminated, it goes away without a trace.
- Idiopathic - occurs for unknown reasons. It does not respond well to standard treatment and retains symptoms for a long time.
- Vibration - occurs against a background of strong mechanical vibrations.
- Dermatographic - provoked by mechanical irritation of the skin (tight or synthetic clothing, skin folds, etc.). After eliminating the irritant, it goes away very quickly, usually within half an hour.
- Cholinergic - caused by high physical activity, characterized by the appearance of small rashes.
- Thermal - provoked by uncomfortable (high or low) ambient temperature. Accompanied by particularly severe itching and is the most common cause of edema.
- Aquagenic - a reaction to contact with water. The rash is usually small or absent, but is accompanied by severe itching.
Temperature urticaria
As with the types of urticaria described above, the child follows a diet according to A.D. Ado. You should adhere to a gentle thermal regime, avoiding high and too low temperatures. If the effect of thermal factors on the body is inevitable, antihistamines should be taken before contact. In cases of photodermatosis, photosensitizing drugs are discontinued.
For the generalized form, take clemastine 0.1% 2 ml, chloropyramine (suprastin) 2.5%, dexamethasone, prednisone. For mild to moderate cases, take fexofenadine and loratadine once a day. Doctors may also prescribe antihistamines with a stabilizing effect on mast cell membranes.
First aid for urticaria in a child
The primary task is to identify and eliminate the provoking factor. The main problem during this period is not rashes, but itchy skin. When providing first aid, it is important to eliminate it if possible - gently trim the nails, put on protective gloves for infants, apply an available non-hormonal anti-allergic cream (for sunburn, mosquito bites, etc.) to the site of the rash. If there is no cream, you can use a cool compress.
All this is done before medical assistance, which should be provided immediately. In case of development of edema and severe symptoms, it is necessary to call an emergency team.
Treatment of urticaria in children
The choice of treatment tactics for urticaria in children depends on its cause, main symptoms, the age of the child, as well as the stage at which the disease is caught.
Only a doctor can prescribe complete therapy after an accurate diagnosis. The main goals include eliminating precipitating factors, prescribing medications to eliminate symptoms, and treating associated pathologies. The doctor makes the choice of antihistamines and other drugs based on the individual clinical picture. Modern medicine offers new generation drugs that minimize the risk of side effects, have a high level of safety and are easy to use for young children. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required.
Is it possible to bathe a child with hives?
If the disease is not aquagenic in nature, you can and should bathe your child, but it is important to follow the recommendations:
- do not heat the water above +37C;
- do not use washcloths and hygiene products with dyes and fragrances;
- maximum bathing time - 10 minutes;
- the use of herbal decoctions and potassium permanganate should be agreed with a doctor;
- Do not rub the inflamed skin with a towel.
Disease prevention methods
There are no special preventive measures. However, you can minimize the risk of developing the disease by following these recommendations:
- control the child’s diet;
- exclude contacts with potential allergens - food, volatile, contact;
- have an antihistamine in your home medicine cabinet;
- buy your child loose clothes made from natural fabrics;
- do not provoke stress in the child;
- do not trigger chronic diseases.
Sources:
L.V. Luss. Causes and treatment of urticaria in children // Medical Council, 2015, No. 14
I.I. Balabolkin. Urticaria in children: clinical and pathogenetic variants, diagnosis and treatment // Russian Pediatric Journal, 2021, 20(2)
L.P. Sizyakina, A.A. Lebedenko, C.B. Maltsev, A.N. Posevina, L.A. Averkin. Urticaria in children: a modern view of the problem // Medical Bulletin of the South of Russia, Reviews, 2015
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Possible complications and their consequences
Urticaria, despite its apparent harmlessness, can lead to serious consequences, primarily to Quincke's edema. Its characteristic initial symptoms, in addition to the swelling itself, are difficulty breathing and paroxysmal cough with whistling (bronchospasms). Swelling of the internal mucous membranes is dangerous due to disruption of the housing and communal services, the first signs of which are a gag reflex and stool disturbance. From the nervous system, severe cases of urticaria are dangerous due to damage to the meninges, which can be fatal in the absence of medical assistance.
Treatment of urticaria in children
It is impossible to predict the body's reaction to a particular allergen, however, every parent can protect their child as much as possible from contact with the most active well-known allergens, do not bundle up or overcool, and do not use cosmetics and detergents with dyes and strong fragrances.
If possible, prevent the presence of children in rooms with a strong smell of paints and varnishes, avoid stress, infections and excessive physical exertion. It is recommended to examine the child’s endocrine system and not ignore signs of weak immunity. Unfortunately, urticaria is often not taken seriously; however, it is a disease that, if unfavorable, can threaten the life of a child.
SM-Doctor pediatricians are always ready to help your child; their experience and attentive attitude to each little patient are the key to a quick and correct diagnosis and well-chosen treatment tactics.
Reasons for appearance
Delicate children's skin is susceptible to various types of external influences.
When an allergen enters a fragile child’s body, it provokes the production of the hormone histamine.
It increases the permeability of blood vessel walls.
Fluid from the bloodstream intensively enters the surrounding tissues.
This is how the body tries to reduce the amount of allergen on its own. As a result, mothers see redness and swelling on the baby’s body.
Hives can also be triggered:
- Products in my mother’s diet include honey, chocolate, eggs, smoked meats, seafood, tomatoes, mushrooms, strawberries, nuts, citrus fruits, and cheese. Food allergies most often provoke hives in children.
- Physical irritants. These include dry air, friction with a diaper or clothing, contact with synthetic fabrics, and active sun.
- Insect bites - bees, wasps, bugs, mosquitoes and even small flies.
- Impurities in the air in the form of pollen, fluff, dust, tobacco smoke, perfumes.
- Infectious diseases weaken the immune system and increase the risk of disease.
- Medicines, including vitamins, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs.
Excessive care and strong wrapping of a child can also cause blisters and redness on the skin.