Some parents notice a small bubble of liquid on the lip of their breastfed babies. As a rule, this is a common callus, which appears as a result of prolonged and intense sucking of the breast or friction of delicate sponges against the nipple. However, sometimes such a watery blister may indicate the appearance of a disease, which may include herpes, stomatitis or thrush.
In this article, we will look at how to distinguish a normal callus on the lip of a newborn from signs of infection. And we’ll find out what to do to get rid of a baby’s callus.
Why does a callus appear on a newborn's lip?
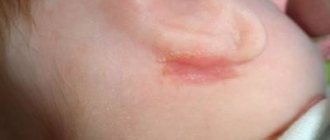
A callus on a baby's lip is a small watery formation with liquid inside, covered with skin on top. Sometimes the formation can become covered with a dense crust, then it becomes dry, hard and dense. Calluses on the lips of newborns can appear as early as 4-14 days of breastfeeding. After a certain time, they quickly disappear, but may subsequently appear again and even become a regular occurrence.
As practice shows, calluses can remain with a child until the end of breastfeeding and last up to 1.5-3 years. When is the best time to wean your baby and stop breastfeeding, read here.
In a newborn, a callus appears due to active sucking. Babies' skin, especially on the lips, is very delicate, soft and sensitive. Therefore, with regular, prolonged and strong friction, it rubs and is slightly injured. Pediatricians note that the presence of such a milk callus indicates the child’s good appetite, normal digestive function and a developed sucking reflex.
Reasons for appearance
A callus on a child’s lip manifests itself in the form of a neoplasm and dropsy on the inside, which is covered with skin on the outside. Sometimes it becomes covered with a compacted and dry crust. This formation can occur on the 4th day or after 2 weeks, when the baby is breastfed. After a certain period, the formation will disappear, but it can appear again or be constantly present.
Causes of the defect:
- if you rub the nipple for a long time and uncontrollably apply the baby to the mother’s breast,
- the mother changed the method of attaching the baby to the nipple during natural feeding,
- The mother's breast has anatomical features,
- milk flows poorly, baby makes efforts to feed himself,
- When artificial feeding, a rough nipple is used.
The callus may remain until natural feeding is stopped and can be observed in a child from 1.5 to 3 years of age. The main reason for the appearance of a callus is the active sucking of the baby. The skin of his lips is delicate, soft and sensitive. Constant, prolonged intense friction contributes to chafing and minor traumatic effects.
Experts believe that a callus is a sign of a baby’s good appetite, signaling a developed sucking reflex and normal functioning of the digestive tract.
Calloused neoplasms will appear on the lip if the child suffers from:
- aphthous stomatitis,
- measles,
- chicken pox,
- scarlet fever,
- herpes,
- thrush,
- diphtheria.
Another such defect will arise due to pathogenic microorganisms introduced onto the baby’s skin and mucous tissues due to ignoring the rules of personal hygiene.
What to do if a newborn has a callus on the lip
- First of all, determine whether it is really a milk callus and not a symptom of any disease;
- As a rule, a milk callus is located on the upper lip of a newborn. It can be observed much less frequently on the lower one;
- A real milk callus does not cause discomfort to the baby, he continues to eat and suck the breast or pacifier, behaves calmly, does not cry or be capricious;
- A true milk callus is white or light in color and has a clear liquid inside;
- Milk callus does not require treatment. It disappears on its own, may appear again and be regular;
- Do not open the bladder or release the liquid, otherwise you will injure the tissues and increase the risk of infection!;
- If the callus bursts on its own, treat the area with hydrogen peroxide;
- If the callus causes discomfort during feeding and provokes anxiety, then an infection has occurred and the disease begins;
- A watery blister with yellowish liquid and bright redness around indicates the presence of stomatitis or thrush;
- An elevated temperature and the appearance of several watery formations are signs of herpes;
- Herpes, stomatitis and thrush must be treated.
Varieties and causes of occurrence
A callus on the upper lip of a baby is a patch of keratinized skin that appears due to strong friction. This is how the body protects the deep layers of the epidermis from damage.
There are several types of formations:
- dry - a hard crust consisting of dead particles of the epidermis;
- wet - under the rubbed layer of skin there is a bubble filled with lymphatic fluid;
- bloody - there is an admixture of blood in the fluid of the callus.
Dry calluses can most often be seen on the lips of infants. Delicate skin is damaged due to the following factors:
- rough tip of the nipple during artificial feeding;
- long and frequent friction on the nipple in the absence of a feeding regimen;
- improper latching of the breast by the child;
- features of the anatomical structure of the mammary gland;
- difficulty releasing milk.
Usually, a milk callus on a baby’s lip appears 2-3 weeks after the birth of the child and does not bring him significant discomfort. If the skin has become rough as a result of active sucking, such a neoplasm does not require special treatment. After a few days, the hardened crust will fall off, leaving no scars. In some cases, the skin finally heals only after the introduction of complementary foods, when the pressure on the lip is reduced.
Regardless of the reason that caused the appearance of a callus, it is forbidden to rip it off or pierce it . Such actions can lead to the entry of pathogenic bacteria into the wound. It is also not recommended to lubricate the formation with alcohol-based antiseptics, including iodine and brilliant green. The use of various traditional medicines can cause an acute allergic reaction, including suffocation.
If the blister opens on its own or is accidentally touched while swimming, it is necessary to lubricate the damaged area with hydrogen peroxide, Miramistin or an aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine. After this, the wound will dry out within 2 hours.
Stomatitis in a baby
Stomatitis involves inflammation of the oral cavity, damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue and gums. In this case, the baby feels anxious, refuses to eat, eats poorly and sleeps poorly. Three days after the onset of infection, a white coating forms on the tongue, which subsequently spreads to the hard palate, mucous surface of the cheeks and the entire mouth. In this case, cracks, “jams”, and a watery blister with a pronounced red shell and a yellowish liquid inside appear in the corners of the mouth and lips.
If stomatitis is detected, improve the hygiene of the baby and nursing mother, be sure to sterilize dishes and toys. After this, the infection will clear up in five to seven days. To speed up recovery and alleviate the baby’s condition, if the baby is not allergic to parsley, give the child an infusion with this herb. To do this, chop the parsley root and pour a tablespoon of the plant with cold water, bring to a boil and leave covered for an hour. Then strain and use a teaspoon all day long.
The mucous membranes of the mouth can be wiped with a solution of baking soda after feedings or naps, and treated in the morning after a night's sleep with sea buckthorn oil and aloe juice. They disinfect areas of the skin, tighten and heal wounds in a short time.
For severe forms of infection, the doctor may prescribe special antifungal ointments. Do not use medications without consultation and prescription of a specialist! How to cure stomatitis in infants and nursing mothers, see the link.
Thrush in a newborn
With thrush, a white coating with a red rim forms on the baby’s gums, tongue and cheeks. In addition, a rash and redness may appear on the body, and yellowish blisters or blisters on the lips. At the same time, the baby is capricious, refuses to eat, sleeps poorly, and feels discomfort.
In this case, it is also important to improve hygiene, disinfect things and objects that can get into the baby’s mouth. Products are boiled or sterilized for at least twenty minutes. To cure thrush, you can also treat your mouth with a soda solution up to eight times a day. To prepare this remedy, dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of boiled warm water.
Stomatitis and thrush can be caused by poor hygiene, too early or incorrect complementary feeding, fungus and thrush on the breasts of a nursing woman. To prevent the development of infection, maintain your hygiene and the hygiene of the mine. Be sure to clean your mouth after each feeding and burping, and remove any remaining milk or food from your baby’s lips. Thoroughly clean and sterilize bottles, nipples, baby dishes, toys and other objects with which the baby has constant contact.
Brush your mouth, tongue and teeth regularly. Up to six months, use special finger wipes or a sterile gauze bandage, after six months they switch to silicone finger brushes, and after a year you can already use a children’s toothbrush with soft bristles. Read more about oral and dental hygiene for a newborn in the article “How to properly brush your child’s teeth.”
Milk callus or herpes
Herpes is another unpleasant disease that can be accompanied by the formation of a watery blister on the lip. Moreover, it can only develop in a baby inside the womb or during childbirth. If the mother has acute herpes, the risk of the child getting sick is 75%.
Herpes can appear as early as the second week after the baby is born.
In this case, bubbles and blisters form not only on the lip, but also on other parts of the body. In addition, the infection is accompanied by fever, drowsiness, and lethargy. The baby may experience convulsions and decreased muscle tone. Herpes is very dangerous for newborns, so urgent and competent treatment is required. Be sure to consult a doctor! Subscribe to our VKontakte group
The difference between milk callus and pathologies
Most parents of infants do not have higher medical education, so they can easily confuse a harmless milk callus with a dangerous pathological rash.
We recommend reading: Signs of stomatitis in infants
To prevent this from happening, you need to know the main differences between them:
- The callus from sucking has a round shape, resembling a bead with a diameter of up to 5 mm. It is located in the middle of the upper lip (very rarely on the lower lip). The color of the safe callus matches the color of the child's lips. This is a single neoplasm that is not accompanied by other rashes;
- pathological inflammation has a white, gray or yellowish color, accompanied by the appearance of white ulcers, blisters or plaque both in the child’s mouth and in other areas (in the corners of the mouth - “zaids”, genitals, face, soles). First of all, it is recommended to examine the baby’s mouth: the inside of the cheeks, tongue, palate, neck. The presence of inflammation in the mouth can be a manifestation of herpes, infectious stomatitis or thrush.
To recognize danger, you need to focus on the child’s general well-being
Symptoms indicating the inflammatory nature of the neoplasm:
- increased body temperature;
- irritability and moodiness;
- loss of appetite;
- change in stool (constipation or diarrhea, sour odor, green color);
- severe regurgitation in infants and vomiting in one-year-old children;
- sweating;
- increased salivation;
- rash, redness of the skin.