About the disease
Staphylococcal infection combines a number of diseases that can manifest as purulent lesions of the child’s skin, pathology of the digestive tract, involvement of ENT organs or even bones in the process.
It is important to consider that the severity of the clinical picture and the danger of the pathology for the patient directly depends on the type of staphylococcus that caused the inflammation. The disease develops sporadically (unsystematically). The risk of infection largely depends on the baby's immune defense. Traditionally, there has been an increase in the number of episodes of staphylococcal infection in newborns. This is due to insufficient secretion of the natural factor IgA, which is responsible for protecting the mucous membranes throughout the human body.
The most common types of staphylococcal damage to the body are:
- digestive disorder caused by staphylococcus;
- septicemia (spread of bacteria in the blood);
- staphylococcal tonsillitis (angina);
- osteomyelitis.
The specialists of the SM-Doctor clinic have many years of experience in successfully treating children of any age who are faced with diseases caused by staphylococcus.
What is cutaneous staphylococcus?
The content of the article
Staphylococcus epidermidis, a close relative of MRSA bacteria. It is so common that it is found on almost every person's skin. Cutaneous staphylococcus is part of the natural bacterial flora and is not dangerous when you are healthy - it is a deadly microorganism that is found throughout the world and remains dormant in most cases.
This type of staph is often ignored in clinical trials, and due to its ubiquity, it can evolve and genetically mutate between bacteria very quickly.
The problem with cutaneous staphylococcus occurs when immunity is reduced - then infection with Staphylococcus epidermidis can cause a number of complications and become a risk factor for many diseases. Cutaneous staphylococcus is especially dangerous for people who have undergone invasive procedures.
Symptoms of staphylococcus
The clinical picture of the disease in children can vary significantly. With sufficiently active immunity, the phenomenon of asymptomatic bacteremia can even be observed, when the pathogen is detected in the patient’s blood, but does not affect his well-being and the functioning of his internal organs. Factors that influence the severity of the pathological process are the individual characteristics of the child’s immune defense, his age, the type of bacteria, and the amount of pathogen that has entered the body. Possible symptoms of the disease are:
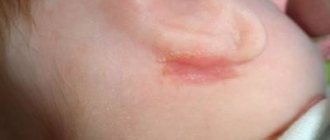
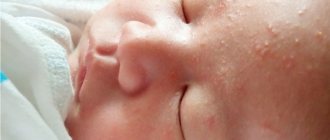
- pustular skin lesions with the formation of boils or even carbuncles;
- itching of the skin, the appearance of red rashes or areas of increased pigmentation;
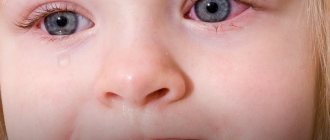
- local inflammation of the oral mucosa (stomatitis), eye conjunctiva (conjunctivitis) and the like;
- increased body temperature;
- emotional lability;
- general weakness, loss of appetite, disruption of normal sleep rhythm;
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, flatulence, diarrhea;
- enlarged tonsils and redness of the throat.
If at least a few of these symptoms are detected in a child, you should immediately seek help. Specialists will be able to quickly determine the type of pathogen and the cause of the deterioration of the baby’s condition, and will also prescribe adequate drug treatment.
Types of pathogenic staphylococci
Several types of bacteria are dangerous to humans. The most common:
- Staphylococcus aureus: golden. It got its name because of the characteristic yellow pigment on the surface. Penetrating into the body, it synthesizes the enzyme coagulase and can cause purulent inflammation of almost any internal organs. This type of pathogen quickly adapts to the effects of antibiotics, forming resistant forms.
- Staphylococcus epidermidis: epidermal. It usually affects the skin and mucous membranes. It often becomes a factor in inflammation of injuries, postoperative sutures, the development of purulent conjunctivitis, and respiratory tract infections.
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus: saprophytic. Its specificity: affects the mucous membranes of the urinary organs, provokes cystitis, urethritis, and kidney inflammation.
- Staphylococcus haemolyticus: hemolytic. Dangerous for mucous membranes and tissues of internal organs. It becomes a provocateur of the development of endocarditis, pneumonia, nephritis and other severe pathologies.
Almost all types of pathogenic staphylococci are prone to mutations as a result of improper or insufficiently long treatment.
Causes of staphylococcus
All types of staphylococcal infections occur against the background of the activity of the bacteria of the same name.
It is capable of producing exo- and endotoxins, which negatively affect the functioning of the child’s internal organs and systems. In practice, doctors at the SM-Doctor clinic encounter the following variants of staphylococcus:
- Saprophytic. It is rarely found in children; it most often affects the organs of the genitourinary system.
- Epidermal. It affects the baby’s skin, but with the development of primary or secondary immunodeficiency. The bacterium can be present on the surface of the child’s skin without provoking purulent lesions.
- Hemolytic. The pathogen can affect almost any part of the patient's body, even the endocardium (the inner wall of the heart). In the absence of adequate treatment, a septic condition develops.
- Golden. The most aggressive strain of bacteria, which causes a pronounced clinical picture with an increase in body temperature and a serious deterioration in the child’s well-being.
Staphylococci are transmitted from sick people by airborne droplets, nutrition or contact. Schoolchildren often get sick from eating unwashed foods, infants get sick through the air, etc.
What is staphylococcus
These are bacteria of the Staphylococcaceae family that attack various organs and systems of the body. The most common infection is staphylococcus in children. The infection enters the body through airborne droplets, through contact and through consumption of contaminated products.
Children are most often found to have one of the following three types of bacteria:
- Saprophytic. The most rare type in children. It attacks the organs of the excretory system and is fraught with acute inflammation of the urethra and bladder. This is the most harmless type for babies and can be cured in a few days.
- Epidermal. It multiplies on the skin and mucous membranes. Leads to conjunctivitis, purulent urinary tract infections and complications after operations. In the most severe cases, endocarditis and sepsis occur.
- Hemolytic. It makes itself felt by the development of purulent inflammation in the internal organs. If the child’s immunity is weakened and proper treatment is not provided, sepsis may develop.
- Golden. It is the most dangerous for humans. It can affect almost all organs, causing severe purulent inflammation in them. Staphylococcus aureus is characterized by high pathogenicity and causes the formation of boils, catarrhal tonsillitis, etc.
It must be said that pathogenic cocci of these bacteria are not always dangerous for a child. A body with a strong immune system can cope with them on its own. But for weakened children, staphylococcus threatens ENT diseases, digestive disorders, damage to bone tissue, pustular skin inflammation, etc.
Symptoms
There are two forms of the disease - early and late. In the first case, signs of the disease appear within 24 hours. In the second - only after 48-120 hours.
How staphylococcus is treated is determined by a pediatrician or infectious disease specialist when the following symptoms appear:
- pustules on the skin,
- furunculosis,
- rashes and pigmentation on the skin,
- stomatitis,
- conjunctivitis,
- temperature rise to 38° C,
- moodiness,
- general weakness,
- decreased appetite,
- bad dream,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- stomach ache,
- diarrhea.
In the worst cases, sepsis (general infection of the body) is possible.
Diagnosis of staphylococcus
Naturally, it is impossible to make a diagnosis and determine the type of pathogen at home. Therefore, if you suspect that your child has staphylococcus, symptoms and treatment should be correlated with the diagnosis and prescribed only by a qualified doctor. It is necessary to show the child to a pediatrician as soon as possible.
To diagnose the disease, a series of tests are prescribed. It includes:
- blood serology,
- throat and nasal swabs,
- urine or stool test
- endoscopic examination of the colon (in case of development of colitis),
- laryngoscopy (if the infection has “sank” below the throat and affected the larynx).
Additionally, PCR tests and analysis of the mother's expressed breast milk may be prescribed.
Diagnosis of staphylococcus
“SM-Doctor” is a multidisciplinary clinic, which is equipped following the example of leading clinics in Europe. Thanks to our own laboratory and modern equipment, our doctors can quickly and accurately identify the cause of deterioration in the condition of a child of any age and determine the strain of bacteria in order to select an effective treatment. Diagnosis of staphylococcal infections begins at the stage of the first consultation. Our specialists collect anamnesis, carefully analyze the complaints of the parents or the patient himself and conduct a comprehensive examination. This allows you to almost immediately decide on treatment tactics. To clarify the diagnosis, the following procedures are used:
- a set of standard laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood and urine tests);
- bacteriological examination of blood, skin scrapings, feces, urine;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) - the technique allows you to identify specific antibodies to a specific pathogen;
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is one of the most effective diagnostic methods, which makes it possible to detect DNA or RNA particles of any bacterium in a minimal amount of test material.
In addition, all young patients are examined by related specialists.
In case of staphylococcal infection, consultation with a cardio-rheumatologist, sometimes a nephrologist, neurologist and other doctors is required. Our specialists pay special attention to the fact that in the absence of timely treatment of staphylococcal infection of any origin, it shows a tendency to generalize, which is fraught with septic conditions and death for the patient.
Cutaneous staphylococcus - treatment
Scientists from the Milner Center for Evolution at the University of Bath have identified 61 genes in staphylococcal skin bacteria that can cause deadly diseases. The samples were taken from patients who had infections following hip or knee replacement surgery and fracture fixation, and were compared with skin swab samples from healthy volunteers.
Surprisingly, even more deadly forms of the bacteria were found in some of the healthy people who took part in the study. Staphylococcus epidermidis has also been found to form biofilms, which increase the body's resistance to antibiotics.
Treatment of cutaneous staphylococcus involves the use of antibiotics. Unfortunately, some antibiotics do not work against some types of cutaneous staphylococcus - the drug resistance of cutaneous staphylococcus is similar to that of Staphylococcus aureus.
For highly drug-resistant strains, vancomycin or teicoplanin are used, which are effective against staphylococci, including methicillin-resistant strains.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Treatment of staphylococcus
Treatment of staphylococcal infection is always individual and depends on the characteristics of each specific case.
SM-Doctor doctors have more than 10 years of experience working with such patients and know what remedies need to be used in each case. The clinic applies diagnostic and treatment standards approved by the global community of doctors. To combat the pathogen, the following are traditionally used:
- antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones). Depending on the location of the pathological focus, the doctor may prescribe a remedy in the form of ointments, tablets, injections;
- antipyretic medications (paracetamol, ibuprofen) to combat fever above 38°C;
- local antiseptics (“zelenka”, hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin).
Cutaneous staphylococcus - symptoms
Symptoms of activation of staphylococcal infection:
- skin changes;
- boils and skin rashes;
- pain at the site of a staph infection;
- ulcer formation.
Staph Infection
Symptoms of cutaneous staph are nonspecific—each case of cutaneous staph may have slightly different symptoms depending on what part of the body is affected. People undergoing surgery should pay attention to the symptoms of cutaneous staphylococcus.
Prevention of staphylococcus
To prevent infections associated with staphylococcus, it is recommended:
- washing hands before eating and after going outside;
- treating any cuts, abrasions and wounds with antiseptics;
- strengthening the immune system through hardening, proper nutrition and exercise.
“SM-Doctor” is a clinic where real professionals work. If you detect the slightest signs of infectious processes in a child, you should immediately seek help. Timely initiation of proper treatment is the key to the health and well-being of every child. Contact us!
Cutaneous staphylococcus in a child
A child's immune system is more sensitive than an adult's, so cutaneous staphylococcus can be dangerous even for the youngest. If a child has skin lesions, he should be carefully treated, dressed and protected from external factors to avoid infection. If your child has skin changes for no reason, consult a doctor.
Staphylococci in a child can cause folliculitis, staphylococcal sycosis, and multiple abscesses. Conditions such as bullous impetigo, bullous inflammation and peeling skin can occur as a result of staph infection in newborns.