Neonatal screening of newborns: why is it needed and how is it carried out?
The main issue that concerns parents of a newborn baby is the health of the child. Many congenital diseases are insidious and do not manifest themselves in the first year of life. It is for this reason that a research method known as newborn screening was developed. This is a simple test that allows you to detect the presence of many congenital diseases in the first days of a child’s life.
What is newborn screening
Newborn screening is a blood test that allows for early diagnosis of at least 50 congenital diseases.
The method is the most accurate method for early diagnosis of genetically determined pathologies to date. According to WHO recommendations, newborn screening is included in the list of mandatory medical tests for babies. Note: In Russia, many mothers call newborn screening a “heel test,” since blood is taken from the baby’s heel.
You should know that a positive result does not always mean that the child actually has a particular disease. To be completely sure, parents will be given a referral for additional examination by an appropriate specialist.
When is neonatal screening performed in newborns?
This test is carried out in the first 10 days of a child's life, but the exact date may vary significantly depending on the circumstances.
Screening of newborns is not recommended in the first 2-3 days of life, since testing carried out so early carries the risk of error - the result may be false negative or false positive.
Usually, blood for analysis from babies born at term is taken in the maternity hospital on the 4th day of life. For premature babies, the test is performed on the 7th day. If the mother and baby have already been discharged from the maternity ward by this time, blood for screening is taken at home or in the clinic.
Such early timing of the analysis is explained by the fact that some genetically determined diseases manifest themselves in the very first weeks of life and it is extremely important to diagnose them in time in order to begin therapy. However, an expanded test that includes the diagnosis of more diseases can be performed later. Starting from the age of three months, blood for analysis is no longer taken from the heel, but from the finger.
What studies are included in the mandatory screening program for hereditary diseases?
Since there are a lot of diseases that can be detected through this study, the list of pathologies for mandatory screening has been reduced to the five most common:
- Hypothyroidism . Pathology of the thyroid gland, which can lead to delays in physical and mental development. Today, timely diagnosed hypothyroidism responds well to hormonal therapy. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case in 5 thousand.
- Androgenital syndrome . Pathology of the adrenal cortex, in which the normal production of the hormone cortisol is disrupted. It can manifest itself in the form of delayed development of the reproductive system, problems with blood vessels and the heart. This syndrome cannot be completely cured, but it can be kept under control with the help of hormonal therapy. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case in 15 thousand.
- Cystic fibrosis . The disease is manifested by a noticeable thickening of secretions in the digestive tract and lungs, which leads to damage to the liver, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system and other organs. Treatable. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case in 3 thousand.
- Phenylketonuria . A disease characterized by impaired production of certain enzymes. The consequences are quite severe. First of all, these include lesions of the central nervous system. However, they can be avoided with a special diet. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case in 15 thousand.
- Galactosemia . This is the name given to the deficiency of the enzyme that breaks down galactose, one of the sugars found in lactose and other substances. The consequences of a lack of this enzyme appear after a few weeks of life. The child begins to develop jaundice, vomiting, and loss of appetite. Over time, severe liver pathologies develop, mental and physical development slows down, and vision deteriorates. This congenital pathology is dangerous and quite rare. Prevalence: 1 case in 30 thousand.
These diseases were also chosen because with early diagnosis they can be cured or at least significantly alleviate the consequences. However, the list of pathologies that can be determined by screening is much wider, and parents can conduct additional tests if desired. In some countries, newborn screening includes the diagnosis of more diseases, for example, in the USA - 40, and in Germany - 14.
How to prepare your baby for research
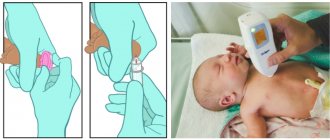
For the results to be as accurate as possible, blood should be donated on an empty stomach, 3 hours after the last feeding. The test is usually carried out at least 4 days after the start of breastfeeding. Preparing for newborn screening is very simple. Before taking blood, the child’s leg is washed with soap, wiped with alcohol and wiped dry with a sterile napkin - this is where the preparatory measures are limited.
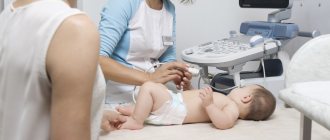
How is blood drawn?
This procedure is a fairly simple set of actions. A small puncture is made on the child's heel. The first drop of blood is removed with a sterile wipe. Then the nurse lightly squeezes the baby's heel and applies the resulting blood to a special paper test form so that the blood soaks through the porous paper. It contains all the information about the newborn, as well as about the institution where the blood was drawn. The form is dried at room temperature for 2–4 hours, placed in an envelope and sent to a laboratory or medical genetic center.
Interpretation of analysis results
It takes 10–14 days to process the samples, after which the parents receive a genetic examination report. The results can only be interpreted by a specialist. Remember that newborn screening results are not a diagnosis. An opinion can only be given by a doctor of the appropriate profile based on additional research.
Although newborn screening is quite accurate, it sometimes produces false-positive or false-negative results (most often due to improper blood sampling technique). If the test result is positive for any disease, parents are offered a repeat test. In case of a repeated positive result, the baby is sent for a detailed examination.
Useful information Most often, a false-positive result when screening newborns is given by a test for cystic fibrosis.
What is advanced neonatal genetic screening using TMS?
Despite the fact that the mandatory newborn screening program includes only five diseases, there are many more genetically determined diseases - about 500. Fortunately, most congenital pathologies are very rare. However, many conscious parents want to receive as complete information as possible about the child’s health and undergo extensive neonatal screening. It allows you to identify congenital metabolic disorders in the first weeks of a baby’s life.
This screening is carried out using tandem mass spectrometry (TMS) and makes it possible to test a child for 37 genetic diseases, including leucinosis, methylmalonic acidemia, biotinidase deficiency, argininemia and many other diseases. From the mandatory list, only phenylketonuria is included in such a study.
The technique for collecting blood for advanced screening is no different from the procedure for a routine study. Test results can be obtained in 2–3 weeks.
Expanded neonatal screening reveals changes in the concentration of metabolites in one direction or another, that is, increased or decreased levels of these substances may indicate the presence of a genetic disease. For example, in phenylketonuria, phenylalanine is increased.
As with mandatory screening, in case of serious deviations from the norm, the doctor refers the baby to specialists to conduct additional research and develop a treatment regimen if the diagnosis is confirmed.
Genetic screening of newborns is especially necessary if there have been cases of hereditary diseases in the family, albeit in the distant past. Quite often, healthy parents are still carriers of defective genes and can pass them on to their offspring. But even if no one in your family suffered from genetic diseases, such expanded screening of newborns is still worth doing, since the child still has a risk of having these pathologies.
Descriptions and main objectives of the study
“Genes are the material that contains all the information about an organism. If any disturbances occur in it, first of all, they occur in the structure of the genes. This is especially true for hereditary diseases,” comments pediatrician Kristina Kusochkova.
What benefits does genetic analysis provide and why does a child need it? To find out about the tendency to hereditary diseases, sensitivity to any medications and products, find out what type of physical activity, daily routine and type of nutrition is suitable for a particular child - all this helps to determine the child’s DNA test. The study identifies all risks and health features. A DNA aptitude test is also carried out. The gender of the child does not matter.
Why else is it worth conducting a genetic test for a child? The result you get will remain with the baby for many years, because genes do not change. That is, by doing a DNA test once, you receive important information about the child’s health for the rest of his life. He will be able to use the data obtained as an adult, and the DNA test will provide a lifelong contribution to his health. Mothers and fathers generally understand the determining role that genes play in the lives of their children.
© MyGenetics
How to carry out screening?
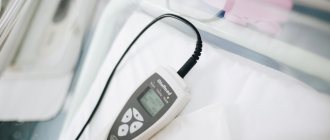
The main method for identifying critical congenital heart disease is pulse oximetry [1–6].
During pulse oximetry, the degree of blood oxygen saturation is assessed in different loci - on the child’s right arm (SpO2 preductal) and his right or left leg (SpO2 postductal) [1-4]. The measurement can be carried out simultaneously using two sensors or alternately using one sensor [2].
During pulse oximetry, the child should be in a calm state. The baby's hands and feet should be warm. After applying the sensor, you should check the tightness of its fit and wait until a stable, continuous pulse curve without artifacts appears on the monitor [5].
The average time for pulse oximetry in a newborn is 3.5–9 minutes [3].
Pulse oximetry may give a false result if there is a bright light source nearby, the sensor is loose, or the child’s extremities are cold [2].
DNA analysis for newborns
An analysis for genetic diseases in a child allows us to identify pathologies at an early stage and predict the risk of developing certain diseases. It is worth doing it not so much if there are hereditary pathologies in the family, but rather in order to know which correct habits will have the best effect on the child’s health.
The test will help doctors “catch” the slightest problems with the health of the newborn and begin correcting the diseases in time. A child’s blood test does not give such an accurate result. Pregnancy, as a rule, proceeds more predictably if genetic research is carried out during this period.
© MyGenetics
Indications for genetic testing of a child
Genetic analysis should be carried out not only if it is known about pathologies in the family that are inherited. The fact is that not all diseases appear immediately, or even appear at all. But experts recommend carrying out genetic analysis regardless of the diseases that relatives suffer from.
Doctor Kristina Kusochkova confirms: “A genetic test provides complete information about a person. On the one hand, this is a huge plus for pediatricians and general practitioners. The doctor will know in which direction to work, what to pay attention to first, and will correctly formulate advice on preventive measures. On the other hand, mothers sometimes misinterpret the test, begin to show overprotection, and control the child in everything that is not good. Therefore, consultation with a specialist after such a test is mandatory. It is necessary to explain the results to the mother and correctly determine further tactics for preventive measures to prevent possible pathologies.”