A wet cough in a child is a sign of infection
There can be dozens of causes of cough: infection, pathologies of the ENT organs (nose and nasopharynx), gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, asthma, allergies and even the psychological state of the child. As you know, “there is no smoke without fire,” so if a child starts coughing, you need to see a doctor to find out the reasons and prescribe adequate treatment, since parents cannot always cope on their own, and sometimes even worsen the situation. When you see a specialist, try to provide complete information, namely, when the attacks began and in what cases they recur, for example, when the child is sleeping or walking. Some experienced parents can determine by ear the type of cough a child has: a dry, barking cough or a wet cough that produces sputum.
Main causes of morning cough
Coughing is a response to irritation - a reflex attempt to clear the airways. However, sometimes babies experience strange seizures after waking up. If this phenomenon recurs periodically, you should consult a doctor to identify the cause and eliminate the cough syndrome.
Let's look at some of the most common causes of children's cough in the morning, which will require the intervention of specialists.
- Cough that plagues a baby during sleep: contributing factors and ways to alleviate the condition
Allergy reaction
A sleeping baby is irritated by many factors that can cause an allergic cough. If you can identify the irritant: a smell, feather filling in a child’s pillow, a flowering tree near a window, it is enough to simply eliminate it. Sometimes you have to use antihistamines. However, even after eliminating the problem, you should not neglect consulting a specialist so as not to miss the development of allergies in your child.
Accumulated mucus in the nasopharynx
Sometimes, during the night's rest, mucus accumulates in the baby's nasopharynx. It can be produced in the nose or in the stomach, entering the pharynx area during prolonged horizontal position of the body. To find out the origin of the mucous mass, you should contact your pediatrician, who, after conducting an examination, will refer you to either an ENT specialist or a gastroenterologist.
If a child develops bronchitis or pneumonia, he will also be bothered by a wet, productive cough in the morning. In this case, suspicions will be confirmed by a high temperature, the presence of which should be a reason to consult a doctor.
A morning cough can also be a residual cough after an inflammatory lung disease. This symptom does not pose a threat to the child's health.
How to distinguish between bacterial and viral cough with sputum in a child
Most acute respiratory viral diseases begin with a dry cough (the first hours), then sputum appears. For your information, children under four years old do not know how to cough, so the sputum is simply swallowed. If possible, note the type of sputum and its color. Transparent sputum is a sign of a viral disease, while whitish and cloudy sputum with a greenish-yellow tint indicates the presence of a bacterial infection. With ARVI, a child may experience difficulty breathing. To understand whether such a symptom exists, you need to compare how your baby breathes in a healthy state, noting rapid, noisy breathing. With nasal congestion, the child may begin to breathe through the mouth. In winter, on the street, breathing through the mouth, a child captures cold air immediately into the respiratory tract; the cold air does not have time to warm up, as when breathing through the nose. The lack of oxygen that the body does not receive with this method of breathing has a negative effect on overall health. A persistent or nighttime cough in a child should alert parents.
What should parents do if their children have a morning cough more often than usual?
1. Eliminate the allergic component of the cough, if necessary, take allergy tests in order to know the pathogens that will need to be disposed of urgently.
2. Check whether or not there is an increase in body temperature.
3. Examine the child’s skin for rashes.
4. If the baby is already talking, check if his throat hurts or if he feels any other discomfort.
5. Observe how the child behaves during the day - does he cough, does he eat well, how active is he, etc.
6. Humidify the air in the room; perhaps its dryness is the cause of the cough.
7. Reduce the room temperature to a maximum of 22 degrees Celsius.
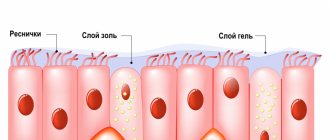
Barrier function of the mucous membrane
The first barrier to pathogens is the oropharynx. Thanks to the structure of the organ and the composition of the mucus lining it, comprehensive protection is provided. Natural purification mechanisms provide air filtration and mucus transport.
Epithelial cells are able to attract and retain molecules that are involved in immune processes. The mucous membrane of the respiratory tract has a protective effect due to the presence of local immunity factors in the mucus and submucosal layer. Lymphocytes, phagocytes, a complex of protective proteins, interferon (IFN), and lysozyme, the concentration of which in the tonsils is 300 times higher than in the blood serum, participate in the formation of local immunity. Immunoglobulin A helps prevent the replication of viruses; it has the property of combining with foreign protein agents, excluding them from circulation.
Interferons enhance the synthesis of antiviral proteins, which inhibit the multiplication of the virus inside the cell and protect healthy cells from infection. However, viral infections can cause an imbalance in the interferon system. Prolonged presence of bacteria and viruses can cause chronic respiratory diseases.
The mucus covering the epithelium from the nasal cavity to the lower sections of the bronchi moisturizes the mucous membranes, protecting them from drying out, mechanical, chemical influences, pathogenic microorganisms and is capable of absorbing dirt particles from the inhaled air.
Rhinobronchial secretion can be thought of as a constantly renewed filter; “waste” material is removed from the respiratory tract using the oscillatory movements of the cilia of the mucosal epithelium or cough.
Mucociliary transport ensures the sanitization of the respiratory tract and performs the barrier, immune and cleansing functions of the respiratory tract. Clearing the respiratory tract of foreign particles and microorganisms occurs due to their settling on the mucous membranes and subsequent elimination along with mucus.
The rhinobronchial secretion contains such natural helpers in the fight against infection as lysozyme - breaks down the cell walls of most bacteria, lactoferrin - a protein that can bind iron ions, making it unavailable for bacterial metabolism, fibronectin prevents the adhesion of bacteria; interferons have antiviral activity. However, the body’s own strength in resisting infection may not be enough, so children under 5-6 years old can suffer from respiratory diseases up to 6-7 times a year. Cough and runny nose are some of the leading symptoms of acute respiratory infections.
Prevention and treatment of ARVI
It is known that respiratory viruses are spread by sneezing, coughing or talking, that is, it is an airborne infection. The virus invades the cell of the respiratory tract mucosa, where it multiplies, after which the cell dies with the release of new viral particles and infection of new cells. From the moment of infection to the appearance of symptoms, it can take from several hours to several days. It is important to respond to infection as soon as possible, because only in this case do we prevent the virus from spreading widely in the body and causing significant harm to organs and systems. Experts advise starting antiviral treatment with the first symptoms of ARVI (sneezing, coughing, sore throat). To treat ARVI, in addition to suppositories, VIFERON Ointment or Gel can be applied to the nasal mucosa. VIFERON Gel is also used to prevent colds.
Treatment regimen with VIFERON Candles (suppositories)
For ARVI, the drug is prescribed according to the following scheme:
– Children under 7 years old, incl. newborns and premature infants with a gestational age of more than 34 weeks are prescribed VIFERON Suppositories (suppositories) 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued. The break between courses is 5 days.
– Children over 7 years old are prescribed VIFERON 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every day for 5 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued.
The preparations VIFERON Gel and VIFERON Ointment are also used in the treatment of a wide range of acute respiratory viral infections in children. The product is applied in a thin layer to the mucous membrane of the nasal passages 3-5 times a day for 5 days.
In order to prevent ARVI and influenza during the period of rising incidence, a strip of gel no more than 0.5 cm long is applied to the previously dried surface of the nasal mucosa and/or to the surface of the tonsils 2 times a day for 2-4 weeks.
The modern strategy for preventing viral diseases accompanied by cough, in a few words, is vaccination and rapid tests (for viruses and bacteria). The main disadvantage of diagnostic tests is that it takes a day or two to obtain results. The most accurate one today is PCR diagnostics. Naturally, if a child is sick, even without a fever, he should not be taken to kindergarten or school, where he can infect others.
In approximately 25% of cases of ARVI, it is not only a viral, but also a bacterial infection, which must be treated comprehensively. Studies have shown [1] that combination therapy for children of different ages using the drug VIFERON Suppositories made it possible to achieve positive dynamics faster, on average two days earlier than in the control group:
- normalization of temperature;
- reducing signs of intoxication;
- stopping or reducing the intensity of cough, runny nose;
- easier breathing
In a hospital where patients used VIFERON, the likelihood of contracting a nosocomial infection was halved [1].
I would like to touch a little on the topic of using antibacterial agents for sore throats and coughs. Considering that the majority of respiratory diseases are caused by viruses, modern scientists are inclined to believe that the use of antibiotics is justified in 24% of cases, while in 62-95% of home medicine cabinets of our compatriots, depending on the region, there are antibacterial drugs “just in case” "
Viral infections can be accompanied by complications, especially in young children, children with chronic diseases, and children who are often ill. Experts believe that a lack of protein in a child’s diet reduces immunity. Children with underweight and nutritional deficiencies are more susceptible to infectious diseases.
How to determine the source of health problems
First of all, you should figure out what kind of cough is called wet? The described spasms are also referred to as “productive.” This means that during a reflex contraction of the chest, the child actively expels sputum. In most cases, after such an attack, it becomes easier for the patient to breathe.
Before visiting the hospital and starting treatment, it is important to make sure that the spasms are pathological. There is an interesting statistic that babies can cough 10-15 times a day. Irritation is associated with the penetration of dust and other weed particles into the body. There is no need to interfere with the removal of mucus - this is normal.
In order to identify the cause of deterioration in health, you need to understand the processes occurring in the child’s body during a wet cough. The respiratory tract constantly produces mucus, which is responsible for “filtering” air coming from outside. Irritation occurs when there is excess production of mucus. Therapeutic actions are necessary to facilitate expectoration and prevent dangerous complications of intoxication.
General principles for treating a viral disease if a child has a runny nose and cough:
– adequate water load plus diet, that is, feeding according to appetite, there is no need to force the child to eat, food may not be digested;
– antiviral drugs, among which VIFERON, an original broad-spectrum antiviral immunomodulatory drug, is the most commonly prescribed drug* and can be used even in infants, starting from birth;
- symptomatic remedies. It is important to understand that while the cough is dry during the first hours or days, it is not advisable to use expectorants; when the cough becomes wet with sputum, you can give expectorants and do inhalations as recommended by your doctor; Many herbs contain allergens, so they are not prescribed to children without the approval of a specialist.