Humanity has been fighting diseases for more than one millennium. Unfortunately, modern medicine is not yet able to effectively prevent possible congenital pathologies.
They are very different and disrupt the proper functioning of internal organs, cause discomfort and other inconveniences, as well as health problems.
Congenital inflection of the gallbladder is a pathology that is considered quite common.
However, there are certain problems in identifying and diagnosing it.
The fact is that the disease very often occurs without any clinical manifestations and does not cause any concern to the patient.
The clinical picture depends on the shape of the bend and its multiplicity.
Congenital inflection is most often fixed and unchangeable. It is considered the most dangerous type of disease.
What it is?
For this disease, it is recommended to use choleretic drugs and antispasmodics.
An inflection is a change in the physiological shape of an organ. As a result of such a change, there is a violation of its functionality.
The gallbladder is important for food digestion processes.
Bile (an enzyme necessary for digestion) secreted by the liver is stored in the gallbladder and, when needed, is expelled into the digestive system.
This occurs due to the contraction of the muscle tissues that make up the organ.
If the shape of the gallbladder is disrupted, the ability to contract is reduced, therefore, the process of releasing bile into the digestive system is disrupted. This leads to disruption of the entire gastrointestinal tract system.
The disease may be single or multiple . The shape of the organ changes in various ways (in particular, the organ can resemble a horseshoe, a question mark, a hook, the letter S).
The disease can be labile , when the gallbladder periodically takes a normal, natural form for a given organ, and then returns to a pathological state, or fixed .
The fixed bending form is considered the most dangerous. If with a labile bend the gallbladder periodically empties, with a fixed form this is not possible.
Consequently, bile stagnates in the cavity of the gallbladder, stretching the walls of the organ. As a result, prerequisites are created for the development of other gallbladder diseases (cholelithiasis, cholecystitis).
This is what a congenital gallbladder may look like
Bend of the gallbladder in a child
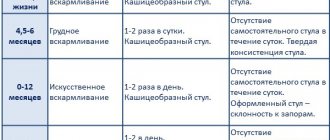
Anomalies of the gallbladder in the form of constrictions and kinks are registered in 30% of children already in the neonatal period. Torsions and kinks, along with other malformations of the biliary tract, can cause obstructive jaundice at this age. The congenital anomaly manifests itself in infancy with regurgitation, bloating, digestive and stool disorders. In addition, these symptoms often become pronounced when switching to solid food, which forces the child to be examined.
Most of the identified kinks in older children are functional and are associated with the rapid growth of the child and the gallbladder. As the child grows, these kinks may appear and disappear. Therefore, it is a mistake to make a diagnosis of “dyskinesia” based on the identified functional excesses. Functional excesses rarely impede the flow of bile, but they are predisposing factors.
Dyskinesia and bending of the gallbladder in a child of school age and adolescence are more pronounced, which is associated with a violation of the diet, consumption of unhealthy foods (chips, hot crackers, fried foods, etc.). Children experience periodic nausea and vomiting associated with dietary errors.
The child may complain of a dull pain in the right hypochondrium, decreased appetite, bitterness in the mouth, and belching with the smell of rotten eggs. Pain syndrome is associated not only with food intake, but also with overeating, as well as with physical activity. There are painful attacks, after which there is discoloration of the stool, and with prolonged disruption of bile outflow, there may be yellowing of the sclera. Of course, this condition of the child requires drug treatment.
Komarovsky notes in his comments that treatment should be carried out only in the case of fixed kinks and if the child has complaints. Usually the child is diagnosed with biliary dyskinesia. Treatment should begin with normalizing the rhythm of nutrition and eliminating prohibited foods.
It is useful to include in the diet foods with a choleretic effect: pumpkin, pumpkin juice, corn oil, bran (wheat, corn or oatmeal), carrots and beets in any form, dried apricots, plums, apples, strawberries, whole grain cereals. Pumpkin can be baked and little by little added to various porridges. You also need to ensure that the child drinks enough fluid to prevent bile thickening. If nutritional correction does not provide a significant improvement, then children are prescribed medication and herbal medicine.
In general, treatment is no different from that in adults. In the hypertensive form, antispasmodics are prescribed to relieve pain: Dibazol , No-shpa , Papaverine . They are prescribed in a short course (up to 5 days). Among antispasmodic drugs, a good effect is observed with the use of Buscopan . It is prescribed to children from six years of age, 1 tablet three times a day. Duspatalin is also widely used (approved in children over 12 years of age). The drug is prescribed before meals 2 times a day; if necessary, it can be used for a long time.
After pain relief, choleretic drugs are recommended. Modern drugs of plant origin and synthetic have a combined effect: antispasmodic, choleretic, hepatoprotective and cholekinetic. In children Olimethin , Holosas , Cholagol , Gepabene , Odeston , Khofitol , Galstena , Hepel .
For children of any age, it is important to optimize their daily routine and lifestyle. First of all, it is necessary to ensure that the child has a full night's sleep to restore regulatory processes in the central nervous system. In adolescence, 8 hours of sleep is physiological; in younger schoolchildren it should be 9-10 hours.
If a child is asthenic, he needs additional daytime sleep. For all ages, it is important to limit the time spent at the computer and watching TV (no more than 2-3 hours a day). At the same time, sufficient physical activity and walking are recommended - this is an important therapeutic component for biliary dyskinesia.
Causes of pathology
Congenital inflection of the gallbladder develops due to improper intrauterine formation of the fetus.
The prerequisites for the occurrence of pathology appear around the 5th week of pregnancy, when the most important internal organs, such as the liver and bile ducts, are formed in the fetus.
This situation can be caused by such unfavorable factors as infectious diseases suffered by a pregnant woman at the very beginning of pregnancy, poor lifestyle of the expectant mother, uncontrolled use of medications, including vitamin complexes.
Clinical manifestations
The disease does not manifest itself in any way for a long time, especially if we are talking about a labile (mobile) form of the pathology. Most often, the first signs of pathology appear in adolescence, sometimes even in adulthood.
At the same time, congenital inflection of the gallbladder does not have any clinical picture that characterizes this particular pathology; the manifestations of the disease are similar to the signs of other pathologies of this organ. The patient may be bothered by symptoms such as:
- Feeling of heaviness after eating;
- Difficulty in digesting food;
- Nausea, urge to vomit;
- Increased gas formation;
- Lack of appetite;
- Abnormal stool (constipation, or vice versa, diarrhea);
- Pain in the right hypochondrium, epigastrium.
Urgent symptoms
A bend located in the cervical area is considered the most dangerous condition, as it can lead to permanent loss of functionality of the organ, necrosis of its cells and tissues.
This condition has more pronounced symptoms:
- In the area of the right hypochondrium there is an acute and severe pain, radiating to the right shoulder blade;
- Body temperature rises;
- Change in skin color (yellowness);
- Severe diarrhea;
- Increased sweating;
- Changes in the color of stool (discoloration) and urine (darkening).
General information
Normally, the gallbladder is pear-shaped; it has a fundus (the wide end of the organ), a body and a neck (the narrowest part).
This organ is a reservoir of bile (holds 40–60 ml), which enters the duodenum after food enters it. With a normal structure, there are no obstacles to the exit of bile into the duodenum and the biliary system functions correctly, without causing discomfort in a person. Various abnormalities in the shape of the bladder can cause dysfunction of the biliary system, which in the clinic is manifested by a variety of symptoms. Anomalies in the shape of the gallbladder include constrictions, curvature, sagittal septa, kinks, hook-shaped and S-shaped, double bladder.
Congenital bending of the gallbladder is not a disease, but a stable deviation from the norm, one might say a feature of the organ. Most often, the detection of an inflection is an accidental finding, since the patient has no complaints. But you need to know about this pathology and, in order to avoid complications, follow certain dietary recommendations, as well as monitor your physical activity. Typically, the bend occurs in the transition area of the body and into the bottom of the bubble. Sometimes there are several kinks, which gives the bubble a variety of shapes: hourglass, boomerang, S-shape.
The importance of this problem lies in the fact that various variants of deformations of this organ disrupt the passage of bile to varying degrees, contribute to the development of cholestasis (stagnation of bile) in the biliary system, hyperconcentration of bile and cause the possibility of stone formation. Even good contractile function of the bladder does not exclude its slow emptying. Congestion causes dystrophic processes in the wall of the bladder and an inflammatory process, which leads to disturbances in its contractile function and motility - various types of dyskinesia (hypomotor and hypermotor).
The largest proportion of motor disturbances is observed with constrictions in the area of the bladder neck, somewhat less often it is caused by kinks in this area. There is a dependence of motor disorders of the bladder on the localization of deformations. Most often, dyskinesia of the hypotonic type develops with deformations that occur in the cervical part of the gallbladder. With lesions in the cervical area, hyperkinetic dyskinesia is rare. Disturbances in the function of the bladder due to deformations in the area of its bottom are rare (15-20% of cases). With long-term inflammation of the gallbladder, pericholecystitis (inflammation of the serous membrane that covers the gallbladder from the outside), which involves nearby organs (most often the duodenum) in the adhesive process. This aggravates the course of the disease.
Diagnostics
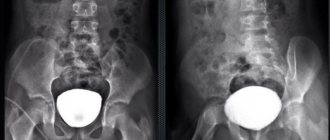
To make a diagnosis, the doctor conducts a survey and visual examination of the patient, and palpates the area of the gallbladder. In addition, special hardware examinations are required. Ultrasound is considered the most effective method for diagnosing pathology.
This method allows you to identify the bend, determine the shape of the gallbladder, and assess its condition. To identify the type of pathology (labile or fixed), ultrasound is performed twice. The first time the study is performed on an empty stomach, the doctor records the original shape of the organ.
After this, the patient eats a breakfast of 2 egg yolks (this product is considered choleretic), and after a while is examined again. With a fixed type of pathology, the shape of the gallbladder remains unchanged.
The disease is detected using ultrasound
Treatment of pathology
Most often, treatment is conservative. That is, the patient is prescribed to take special medications, follow a diet and a special lifestyle.
At home, folk recipes are widely used. In some cases, when the pathology is dangerous to the patient’s health and threatens his life, emergency surgery is prescribed.
Drug treatment
In the case of a congenital form of the pathology, the patient is prescribed drugs that facilitate the outflow of bile and the process of emptying the gallbladder, preventing the development of cholelithiasis.
Such drugs include Allochol, Gepabene. It is important to remember that the use of choleretic drugs must be prescribed by the attending physician, since these medications cannot be taken if there are stones in the gall bladder, as this can provoke blockage of the ducts of the organ.
And this is a life-threatening condition.
The patient is also prescribed drugs that change the viscosity of bile, making it more liquid (Ursohol). These products not only promote the flow of bile, but also dissolve small stones in the gallbladder area.
If the process of bile stagnation continues for a long time. An inflammatory process may occur in the gallbladder and its ducts. In this case, it is necessary to take anti-inflammatory drugs.
To relieve pain, painkillers are prescribed (No-shpa, Papaverine).
Surgery
Sometimes dangerous situations may arise when urgent surgical intervention (removal of the gallbladder) is required. This is necessary if multiple bends occur, since in this case the development of peritonitis and general severe intoxication of the body is possible.
Surgery is also prescribed when conservative treatment does not produce a positive effect, and the inflammatory process continues to develop in the area of the affected organ.
Treatment at home
A procedure such as tubage using a magnesium solution can have a positive effect. To prepare it, 20g. Magnesium sulfate is diluted in 70 - 100 ml. boiled water (proportions and quantity of the ingredient are determined depending on the patient’s body weight).
The resulting solution is drunk on an empty stomach, after which a warm heating pad is placed on the right side. The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes. A solution of magnesium has a strong choleretic effect; as a result of its action, accumulated bile is released into the digestive tract.
As a result, after the procedure, the consistency and color of stool may change; it becomes more liquid and acquires a green tint. This phenomenon is considered normal. It is important to remember that this method can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
Contraindication – the presence of even small stones.
Do you need a diet?
Undoubtedly. Without following a special diet, successful treatment is impossible. It is necessary to avoid spicy, fatty, fried foods, spices, sweets, dried fruits, grapes, and alcohol.
It is recommended to give preference to light dishes of plant origin. This is necessary because if the gallbladder is bent, the process of digesting food is already difficult, and heavy food will create additional stress on the organs involved in its digestion.
It is important to remember to adhere to the liquid regime. It is recommended to drink at least 1.5 liters. clean water. This helps to liquefy bile and cleanse the bile ducts.
Symptoms of a bent gallbladder
If the bending of the gallbladder does not cause stagnation of bile, then symptoms may not be observed. If the outflow of bile is disrupted, patients experience pain of varying intensity, bitterness in the mouth, nausea, belching, heartburn , bloating , and upset stools (alternating constipation and diarrhea ). The severity of symptoms depends on the speed of development of the inflection. If the bend or twisting occurs rapidly for some reason, then the clinical manifestations will be pronounced: severe pain, nausea, vomiting, weakness, sweating, increased heart rate. This is an urgent condition and the patient must be hospitalized.
With the gradual development of the inflection, the symptoms increase slowly, there may be an improvement in the condition and periodic deterioration. For all locations of kinks, the symptoms are almost the same. But of all the localizations of kinks, ties and torsions, the most dangerous is the localization in the cervical region, since the passage of bile is significantly impaired. Symptoms of a bend in the neck of the gallbladder include sharp pain, which is localized not only in the right hypochondrium, but also between the shoulder blades, attacks of nausea, vomiting, discoloration of feces due to the fact that the flow of bile into the intestines stops, and yellowness of the skin. Multiple kinks of the bladder are less common and are severe with symptoms of severe pain and dyspepsia and are an indication for urgent hospitalization.
Against the background of kinks in the bladder, sooner or later dysfunction of the biliary tract occurs, which has various clinical manifestations. When there is a bend in the neck of the bladder, hypokinesia , and when the body of the gallbladder is bent, a hyperkinetic variant of dyskinesia .
With the hyperkinetic variant, colicky pain appears in the right hypochondrium, which radiates to the back between the shoulder blades and to the left half of the abdomen. There is a connection between the occurrence of attacks and psycho-emotional stress, and they appear much less frequently after meals and after physical exercise. In most cases, the pain goes away on its own.
In the hypokinetic variant, the patient is bothered by almost constant dull, bursting pain in the right hypochondrium. They intensify with changes in body position, as intra-abdominal pressure increases, after eating or physical activity. Common to both forms are: bloating, bitterness, unstable stool, which is associated with impaired flow of bile into the intestines.
Prevention
As is known, the prerequisites for the development of congenital pathologies are laid in the first weeks of intrauterine development of the fetus.
Therefore, the expectant mother needs to take care of her health even during pregnancy planning. And when pregnancy has occurred, it is necessary to visit a doctor in a timely manner and carefully follow all his recommendations.
Performing this gymnastics helps get rid of pathology