Article:
At some point, parents begin to notice that almost every night strange sounds are heard from the children's room - grinding, knocking, slurping. No, it’s not a monster under the bed or a pet gobbling up its supplies. This is a child grinding his teeth. This phenomenon has a medical name - bruxism. According to statistics, up to 5 years of age, about 50% of children suffer from it; after 5 years, the figure drops to 20%. How dangerous is this, should I be concerned and should I do anything?
Causes
Finding out why a child grinds his teeth in his sleep is definitely not a good idea to ask your neighbor’s grandmother. “People’s” versions of what is happening can be shocking: from the evil eye (allegedly someone was jealous and wished harm) to sadistic tendencies (allegedly he will grow up to be a monster and a flayer). There is no need to listen to such horror stories and attach importance to them.
The primary task of parents is to understand the real causes of the phenomenon and take appropriate measures. The problem is that provoking factors can be very different, and each of them needs to be analyzed and tried to be “fitted” to the current situation.
Psychological reasons:
- emotional instability;
- stress (for example, babies often grind their teeth if the mother decides to refuse lactation);
- frequent affective states;
- overvoltage;
- sleepwalking;
- age crises of 3 and 7 years.
Neurological:
- disruption of the functioning of both nervous systems - central and peripheral, which leads to neurological and motor disorders;
- damage to motor neurons of the trigeminal nerve;
- extrapyramidal side effects of psychotropic drugs;
- functional disorders of the spine.
Dental:
- teething;
- dental anomalies: adentia (the absence of several teeth in the oral cavity), supernumerary teeth (additional teeth trying to fit into a fully formed dentition);
- malocclusion;
- change of teeth;
- incorrectly selected braces;
- unsuccessful dental treatment;
- arthritis or arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint.
Osteopathic:
- birth injuries;
- recent traumatic brain injury;
- blocking of cranial sutures;
- disturbance of craniosacral rhythm.
Other reasons:
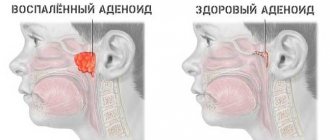
- nasal breathing disorders: adenoids, deviated nasal septum, frequent rhinitis;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- helminthiasis (ascariasis, enterobiasis);
- unhealthy diet (unbalanced, insufficient, lack of routine);
- abuse of chewing gum;
- side effect from taking sleeping pills or antidepressants.
The causes of bruxism indicated in the last block are only hypotheses and are not confirmed by official medicine, since they are not based on any scientific research.
If a child grinds his teeth during the day, you need to observe at what moments this happens. If there is no pattern, the problem is most likely neuralgia. If this is a reaction to stress, psychotherapy can help.
Now you know the possible scenarios for the development of events, why the child grinds his teeth, what it could be and in what direction to look for the cause. It is necessary to find out, otherwise the problem will not be solved.
Origin of name. The term “bruxism” comes from the ancient Greek word “βρυγμός,” which translates to “teeth grinding.”
Treatment methods
It is imperative to provide psychological support to a child who suffers from bruxism. An experienced child psychologist will help the baby overcome the problem. A dentist can treat complications of bruxism. Drug therapy involves taking special medications. Sometimes children are prescribed Tenoten or Glycine to relieve stress and normalize sleep. The following will be useful:
- Soothing baths.
- Massage.
- Warm compresses on cheekbones.
- Wearing a night guard.
If you suddenly notice regularly recurring teeth grinding in your child, you need to immediately pay attention to this. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. After an examination, a competent doctor will prescribe additional tests to correctly diagnose the disease.
If a 2.5 year old child grinds his teeth, you should pay close attention to this phenomenon. If we are talking about pathology, then serious treatment may be required, the regimen of which should be drawn up by a competent and experienced doctor.
Signs
After identifying the cause, it is necessary to observe what additional symptoms accompany this pathology.
First, you need to track when exactly this happens. It turns out that bruxism doesn't only occur at night. It can be observed at any time of the day. Some parents notice that their child grinds his teeth during the day. This causes much more inconvenience because the unpleasant sounds are heard by others. The faster you need to solve the problem.
How it usually happens:
- teeth grinding continues for several seconds or minutes;
- attacks can be repeated several times during the night (or during the day);
- Most often the child does not wake up.
Secondly, you need to check whether there are any complaints about your health during this period. As a rule, when children begin to grind their teeth, a whole complex of symptoms develops in parallel. He will tell you whether the cause of bruxism has been correctly identified and in what direction to move forward.
If the functioning of the central nervous system is disrupted, teeth grinding is most often accompanied by symptoms such as:
- sleep disorders (somnambulism, insomnia, snoring, nightmares, apnea);
- enuresis;
- tremor of the limbs;
- epilepsy.
During the day, the child may complain of pain in various parts of the body:
- head;
- jaw;
- dental (when closing the jaws);
- facial (facial muscles and nerves hurt);
- in the temporomandibular joints;
- in the ears (otalgia);
- in the paranasal sinuses;
- in the neck, shoulders, back.
Pain syndromes are especially severe in the morning (if the child grinds his teeth at night). Other symptoms that may accompany bruxism:
- ringing in the ears (tinnitus);
- dizziness, in which orientation in space is lost (vertigo);
- weakness and weakness in the morning, the child wakes up exhausted and refuses to get up;
- loss of appetite;
- irritability, sudden mood swings, tension;
- high eye sensitivity;
- muscle spasms (usually jaw, chewing).
In addition to this symptom complex, parents should observe what happens to the child exactly at the moment when he grinds his teeth:
- often grinds his teeth and tosses and turns - a sure sign of mental problems;
- At the same time, he makes involuntary grimaces (wrinkles, actively moves his facial muscles) - this is neurology;
- wakes up frightened after this, cries, screams, does not want to go to bed anymore - disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- grinds teeth and coughs - the cause should be sought in nasal breathing disorders, you need to go to an appointment with an otolaryngologist.
Bruxism is extremely rarely manifested only by the child grinding his teeth. Attentive parents will notice that the matter does not stop there. Any changes accompanying this phenomenon should be described in detail to the doctor at the appointment.
The child grinds his teeth in his sleep
This phenomenon occurs frequently, which makes questions about what is happening very relevant for worried and caring parents.
Frequent teeth grinding by a child is regarded by some parents as a harmless and not at all dangerous habit. In fact, this is a physiological disorder that is fraught with unpleasant health consequences and requires the help of specialists. This phenomenon occurs not only in children, but also in adults.
In medicine, teeth grinding is referred to by several concepts, such as bruxism, odonterism, and the Carolini phenomenon. When such a phenomenon occurs in a child’s life, the baby does not always experience unpleasant sensations. If cases of bruxism are not frequent and short-term, then they will not affect the health and condition of the child in any way, but constant and prolonged attacks can greatly harm the baby. Teeth grinding in a child is characterized by the following indicators:
- teeth become loose;
- sleep becomes restless and intermittent;
- There may be a feeling of ringing in the ears;
- discomfort in the neck area;
- influences the formation of correct bite;
- the baby may have a headache;
- increased abrasion of the enamel of baby teeth (especially fangs and incisors);
- discomfort while chewing.
When a child grinds his teeth, a frequent contraction of the masticatory muscles occurs with a special creaking-clicking sound. In addition to such involuntary and unconscious contractions of the masticatory muscles, other processes in the child’s body are also subject to changes: breathing, heartbeat, blood pressure and other important vital signs change.
The duration of a muscle spasm can last from a couple of seconds to several minutes. Each baby may have its own peculiarity of the occurrence of this phenomenon, with its own frequency and duration (there are also rare manifestations).
Bruxism is a common phenomenon among preschool children (every second child has it), but medicine still cannot give it a clear explanation or determine its true cause.
Make an appointment
Age characteristics
Before you go for a consultation with a pediatrician, parents should know that teeth grinding at night, heard from the children's room, is often due to age-related characteristics.
7-8 months
The main reason: an excess of emotional impressions during the day, as an option - stress due to weaning;
Accompanying symptoms: anxiety, crying, whims, refusal to eat, disruption of feeding and sleep patterns.
What to do: provide the baby with the most comfortable environment possible, postpone weaning to another period, less noise during the day, soothing baths before bed.
9-10 months
Main reason: teething.
Accompanying symptoms: swelling of the gums, fever, crying, excessive salivation, the desire to put various objects into the mouth.
What to do: give painkillers orally (Vibrukol, Panadol, Nurofen), lubricate the gums with cooling gels (Cholisal, Kamistad, Dentinox), use anti-inflammatory toothpastes for children (Weleda, SPLAT Junior, SPLAT Magic Foam).
11-12 months
The main reason: improper transition to regular food for adults, as a result of which various vitamin deficiencies and deficiencies of micro- and macroelements are observed.
Accompanying symptoms: developmental abnormalities, lethargy, sleep disturbances, pale skin, loss of appetite, convulsions.
What to do: seek help from a pediatrician as soon as possible.
1-2 years
The main reason: at 1 year of age, nasal breathing disorders and various inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx are most often diagnosed.
Accompanying symptoms: adenoiditis, sinusitis, difficulty breathing, cough, rhinitis.
What to do: promptly treat any colds and infectious diseases, engage in ongoing prevention, seek help from an otolaryngologist.
If parents do not take care of the fact that the baby grinds his teeth more and more often, this can lead to the development of chronic diseases of the nasopharynx and improper formation of the jaw.
3-4 years
The main reason: the age crisis of 3 years, accompanied by adaptation to kindergarten.
Accompanying symptoms: whims, hysterics, disobedience, refusal of the usual daily routine.
What to do: be patient, help in adapting to kindergarten, wait out the age crisis.
5-6 years
The main reason: improperly formed bite, neuralgic problems.
Accompanying symptoms: tension and spasms of the facial muscles, incorrect placement of teeth, complaints of pain of various types. Most often, at this age, children grind their teeth during the day.
What to do: correct the bite (wear removable structures: mouth guards, trainers, slings, plates), engage in myotherapy and orthodontic treatment, and also seek advice from a neurologist.
7-8 years
The main reason: the age crisis of 7 years, accompanied by adaptation to school.
Accompanying symptoms: self-willed, tries to imitate adults, demands independence.
What to do: be patient, help in adapting to school, wait out the age crisis.
If a child grinds his teeth due to age-related characteristics, with the correct attitude of the parents and timely measures taken, this will quickly go away.
Causes of daytime teeth grinding in children
When chewing organs appear in children, many new sensations arise. An 8-month-old toddler is interested in what sounds are made when the units touch. Therefore, the crumbs can tap and rub their teeth against each other. Over time, the child gets used to it and stops doing it. Of course, this is not the only reason for grinding.
- Often, babies rub the edges of the crowns to relieve discomfort and itching in the gums when the chewing organs are born. As soon as the unit breaks through the gum tissue, the baby stops rubbing.
- The reasons for grinding teeth during the day may be the expression of negative emotions. Anger, stress, whims, nervous system disorders are frequent companions of grinding.
- Spasmed muscles due to diseases of the facial joint nodes, as well as malocclusion, cause grinding.
- Sometimes bruxism precedes an attack of epilepsy.
- It happens that the disease is inherited.
- Grinding occurs due to mechanical trauma to children's teeth.
- The provoking factor is enlarged adenoids.
- Friction due to inflamed or misaligned jaws is common.
- If the body lacks the necessary minerals, children chatter their teeth.
- The age of the child is also of great importance for such an unusual condition. A child grinds his teeth during the day when he is 2 years old, when all his chewing organs have not erupted. This way it relieves itching and pain.
Diagnosis and treatment
Most parents are too calm about the fact that their child grinds his teeth and expects everything to go away on its own. This is mistake. In what cases should you consult a doctor with this problem:
- the child grinds his teeth so hard in his sleep that he later complains of pain in the jaw or neck;
- grinds his teeth even during the day and is unable to control this process;
- it lasts more than 3 weeks;
- bruxism is accompanied by additional symptoms and provokes a deterioration in well-being;
- complaints of pain syndromes.
You should first make an appointment with your local pediatrician, who will:
- will listen to complaints: how and when the child grinds his teeth, what additional symptoms this is accompanied by, whether there are any health problems;
- will study the medical history;
- examine the oral cavity, in which the naked eye can observe inflammatory processes of periodontal tissues, caries or abrasion of enamel due to injury to the teeth during spastic contractions of the lower jaw;
- will conduct polysomnography to record a specific pattern of spastic contraction of the masticatory muscles and exclude epilepsy as one of the causes of bruxism.
Based on the diagnostic results, he will give a referral to a more specialized specialist. Depending on the suspected cause, this could be a psychologist, psychotherapist, neurologist, dentist, osteopath, or less often a gastroenterologist, otolaryngologist, helminthologist and even a nutritionist.
Depending on the main reason, they may prescribe:
- a course of psychological consultations on how to relieve emotional stress;
- psychotherapeutic sessions to bring the child’s psycho-emotional state back to normal;
- drugs for the treatment of the affected trigeminal nerve: anticonvulsants, muscle relaxants, vitamins;
- sanitation of the oral cavity.
Additionally, they may assign:
- dieting (balanced meals by the hour);
- vitamin therapy;
- irrigation (rinsing with saline solution) and irrigation-elimination therapy for nasal breathing disorders;
- anthelmintic drugs when confirming diagnoses such as ascariasis or enterobiasis: Piperazine, Pyrantel, Mebendazole, Albendazole, Levamisole, Vermox, etc.;
- hypnosis;
- acupuncture;
- neurotherapy;
- massage of the spine and deep paraspinal muscles.
Treatment depends on the doctor's specialization dealing with this problem. But it is always aimed at eliminating the main cause and the entire accompanying symptom complex, as well as preventing the development of hazardous consequences for health.
How can you help your baby?
To avoid damage to baby teeth and the occurrence of specific sounds, it is recommended to contact a pediatric dentist to make individual protective applicators (mouth guards), according to age characteristics;
- Try doing relaxing exercises for the facial muscles;
- After consultation with a pediatrician, you can use vitamin preparations that help reduce convulsive activity and tension in the masticatory muscles;
- Load the masticatory muscles as much as possible during the day (offering to chew solid healthy food), this is how muscle relaxation occurs;
- Before going to bed, walk more often in the fresh air, bathe the baby in a warm bath, do stroking massages for the lower part of the baby’s face; this way the baby will calm down and relax faster;
- Give the child the opportunity to chew special toys in the mouth - teethers, especially in the active phase of the eruption of baby teeth.
The health and well-being of your baby comes first! Do not ignore any strange manifestations in your child. In such cases, you should not be careless or “heal” the child yourself, following common “myths”. Be careful, listen to your child and trust only qualified specialists.
Make an appointment at our Babydent !
Show more tips
Tips for parents
Often the matter is not limited to treatment alone. In order for teeth grinding in sleep to stop once and for all, parents must provide the child with appropriate care.
First, you need to seek help from a dentist, regardless of the cause of bruxism. He will select a special mouth guard based on the shape and size of your teeth. It will need to be put on the child’s upper teeth when he sleeps. It does not cure or eliminate the problem, but it prevents the development of undesirable consequences.
Secondly, teach your child to relax before bed in order to relieve stress and tension accumulated during the day:
- stop watching TV and playing computer games;
- exclude overeating and consumption of fatty and long-digesting foods;
- listen to soft, calm music or white noise;
- read books;
- take a walk (do not play noisy and active games in the yard), but just walk down the street, talk about something pleasant;
- take a relaxing bath.
If a child grinds his teeth during the day or wakes up at night, he must first be reassured and reassured that he is safe. It is recommended to give a glass of water, soak a small towel in warm water and apply it to the forehead. Hug, stroke, offer to do a few simple breathing exercises. There is no need to tell in detail what happened. On the contrary, it is advisable to distract with conversations on unrelated topics.
Thirdly, to normalize the emotional and mental state and improve the child’s well-being, parents must ensure:
- strict adherence to the daily routine: go to bed, get up in the morning, walk, eat - strictly according to the clock;
- a balanced diet with the exclusion of harmful foods from the menu (soda, fast food and sweets);
- minimal load on the jaws: during this period, chewing gum, nuts, dried fruits, crackers should not be given; the diet should include more purees, cocktails and broths;
- balance of physical, emotional and mental stress appropriate to age;
- a favorable, friendly atmosphere at home (no conflicts or quarrels between relatives in a raised voice).
The more accurately and regularly parents follow medical recommendations, the faster the child will stop grinding his teeth.
Diagnosis of bruxism
If parents notice symptoms of bruxism, they should carefully monitor their child's sleep. It is also necessary to check how often the attacks last and at what time the grinding occurs. It is also very important to determine whether there are any associated problems and what the general condition of the child is. Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause of the problem and prescribe effective treatment. More often, doctors recommend polysomnography. Diagnostics will help identify involuntary contractions of the jaw muscles.
This technique will make it possible to distinguish bruxism from hidden serious pathologies. This study is especially relevant for children with an increased risk of developing epilepsy. A pediatric dentist can diagnose bruxism. Bruxism can be accurately determined by a special mouthguard that children wear at night. In the morning, the condition of the product is assessed. If deformed areas are found on the mouthguard, it means that there was a load in these places. It is also advisable to consult with a neurologist and child psychologist.
Consequences
If parents let the situation take its course and do not consult a doctor, this can have dire consequences. Lack of necessary treatment and recommended care in the future can lead to:
- chips, abrasion and microcracks in tooth enamel;
- development of periodontitis;
- changes in bite and other transformations in the structure of not only the jaws, but also the facial joints;
- chronic migraine;
- neuralgic diseases;
- spasms of facial muscles;
- sleep disorders;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx.
So grinding your teeth while sleeping can have serious consequences for the health of a child at any age. To protect him from them, timely medical assistance and appropriate parental care are necessary.
Physiological explanation of bruxism
Teeth grinding occurs due to spasm of the chewing muscles, clenching of the jaws and their strong movement. The peculiarity of the disease is the fact that it occurs involuntarily. Most often this occurs during the patient's sleep at night, but some also worry during the daytime. In the first case, the pathology is called bruxism, in the second - bruxiomania. During the period of primary occlusion formation, the disease manifests itself in at least half of children. This is considered normal if it goes away by age 7.
Prevention
If you don’t want to hear your child’s teeth grinding in his sleep, or you don’t want to face such a problem, it’s enough to take a number of preventive measures.
- Constantly ensure that the child is not in a state of stress, much less depression. Monitor your psycho-emotional mood. Help resolve any problems and conflicts.
- Don’t overload: don’t let you do backbreaking physical work, don’t force you to sit until late at homework, don’t enroll in five sections and clubs at once.
- Ensure a balanced diet in accordance with age and proper drinking regimen.
- Introduce sports: exercise and walking are required daily.
- Ventilate the nursery before bedtime and in the morning.
- Have preventive examinations at the dentist twice a year. Treat caries and other diseases in a timely manner. Follow all doctor's recommendations.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- We allow contact only with vaccinated animals.
- Do not self-medicate.
- When prescribing powerful medications or a course of therapy that is too long, learn about side effects and the possibility of eliminating them.
The child's body is in constant development, and this sometimes forces parents to ignore some symptoms. Indeed, you shouldn’t run to the doctor with every sneeze and scratch. However, the situation when a child begins to grind his teeth is not an ordinary situation and requires close attention from adults. The sooner the cause is determined and treatment is carried out, the less chance there is of developing dangerous consequences.
Treatment methods
Treatment of bruxism in children begins with eliminating the causes that caused this disorder. Medication, physiotherapy, psychotherapy are used, and dental defects are corrected.
There is no specific drug therapy for bruxism, since it is not a disease, but rather a symptom of certain disorders. However, the doctor can prescribe medications that correct the function of the masticatory muscles and normalize sleep. These include the following:
- B vitamins,
- magnesium and calcium preparations,
- sleeping pills,
- sedatives.
Warm compresses, pine baths, a course of restorative massage, and swimming can be prescribed as methods to normalize sleep and muscle tone in the absence of contraindications.
Psychological correction has no contraindications and is used in many cases. If you suspect that episodes of disturbance were preceded by stress, you may want to consult a child psychologist. Lack of attention from loved ones, conflicts in the family or school community, life changes, a state of loss - all these are reasons to visit a specialist. Various techniques are used to treat children: art therapy, sand therapy, hippotherapy, dance-movement therapy, etc. In addition, a child psychologist will give recommendations on organizing the child’s leisure time, interacting with him and building relationships within the family, creating a calm and favorable atmosphere in home.
Dental therapy methods are designed not only to cope with the causes of bruxism, but also to eliminate its consequences. So, if there are malocclusions or crowded teeth, premature loss of baby teeth, the doctor will offer the optimal solution. According to indications, treatment of caries and inflammatory diseases is carried out, restoration of damaged teeth with composite materials, in order to get rid of hypersensitivity - fluoridation and remineralizing therapy.
To treat the disorder in children over 10 years of age, protective mouthguards can be used - devices made of soft material that are fixed on the teeth before bedtime and help protect the enamel from friction. You can purchase ready-made mouthguards or have them made at a dental clinic. The second solution is more optimal, since it involves preliminary taking an impression and making a structure exactly according to the parameters of the child’s dentition. Therefore, the mouthguards fit more tightly, which means they protect the teeth more reliably. In addition, the doctor will tell you everything about caring for the aligners and when to replace them.
A pediatric orthodontist will tell you how to treat bruxism in children suffering from malocclusion. As a correction method, he may suggest plates, orthodontic aligners, wearing special devices or braces - it all depends on the specific case, the type of malocclusion, and the age of the child. It is easier to correct your bite when your jaws are still developing.
General recommendations:
- It is important to prevent emotional overexcitation in a child, including those associated with positive emotions. All active events should be planned for the first half of the day;
- communicate and build trusting relationships with your child, maintain a healthy, calm atmosphere in the family;
- Switch your child’s attention from computer games and watching cartoons in the evening to inactive leisure. It is better to devote 2-3 hours before bed to reading books and quiet games;
- Do not feed your baby 3 hours before bedtime. You should not overload your digestive system at night.
Treatment of bruxism
The treatment regimen is selected individually, taking into account diagnostic data and the patient’s age. In children under 6-7 years of age, the disease does not require emergency intervention. The patient is monitored by a dentist, but all symptoms in most cases go away on their own, without treatment.
In adults, when signs of bruxism are detected, a set of methods is prescribed. They depend on the form of the disease and its severity, as well as accompanying symptoms. The treatment regimen may include several areas:
- correction of bite and elimination of dental defects;
- drug therapy;
- psychotherapy;
- relaxation techniques;
- massotherapy.
At the first stage, it is important to eliminate all dental problems that can cause spasms of the masticatory muscles. Modern medicine allows you to correct your bite with the help of rigid fixation devices, which also help with anomalies in the location of individual teeth. Missing fragments are successfully replaced with prostheses or implants - the prosthetic method is selected individually. Selective grinding of tooth surfaces may also be necessary. First, it is necessary to completely eliminate those pathologies that interfere with the normal functioning of the temporomandibular joint. When all the symptoms of night grinding disappear, you can begin to eliminate aesthetic problems: restoration of defects, installation of fillings or veneers. Treatment of periodontitis also occurs after the attacks of night grinding stop.
To stop attacks, a course of drug therapy may be necessary. It includes sedatives and sleep aids. Solutions of magnesium, calcium, and B vitamins are also effective - they have a positive effect on the processes of neuromuscular conduction and normalize the functioning of the central nervous system. Treatment tactics are aimed at reducing the manifestations of convulsive syndrome.
The use of soft mouth guards may be necessary as symptomatic therapy. They are made of rubber or soft plastic and perform a protective function. These devices are designed to be worn at night, when the patient cannot control the functioning of the chewing muscles, and spasms occur involuntarily. Soft materials prevent abrasion of dental surfaces and the development of dangerous complications. However, they cannot reduce the frequency of attacks or prevent their occurrence.
Additional methods for treating bruxism
The psychotherapy method is considered effective for bruxism. Attacks of teeth grinding often occur against the background of a weakened psycho-emotional state, so self-control and relaxation practices come to the fore. The approach to each patient is determined individually by the doctor. It may be impossible to discover the root cause of problems on your own.
At home, you can massage your jaw, neck and chin. You should perform smooth movements with your fingers in the upper part of the neck, as well as on the side surfaces of the jaws. The procedure should not be accompanied by painful sensations. Its essence comes down to mechanical relaxation of muscles, as a result of which their spasms occur less frequently. Exercise therapy, a simple set of exercises to increase muscle elasticity, has a similar effect. Throughout the day, it is important to ensure that you keep these muscles relaxed and do not clench your jaw.
Breathing exercises are also useful. It allows not only to cause relaxation of the masticatory muscles, but also to ensure a sufficient supply of oxygen to the tissues of the nervous system. These exercises are also part of the system of self-control practices that are recommended for involuntary teeth grinding. At home, it is enough to practice deep breathing: air is slowly inhaled through the nose so that it fills the lungs as much as possible, and then exhaled through the mouth.
Possible consequences and complications of the disease
Bruxism, if left untreated, gradually progresses. Attacks occur more often and begin to occur even during the daytime. At the same time, a person’s sleep quality deteriorates, performance, memory concentration and attention decrease. The functioning of the central nervous system is also disrupted, and constant daytime sleepiness develops. In addition, the disease can cause more dangerous complications:
- abrasion of the surfaces of individual teeth or dentition, which is accompanied by pain and increases the risk of developing caries;
- inflammatory diseases of the structures surrounding the teeth;
- bleeding gums, which are damaged when the jaws involuntarily close;
- weakening and inflammation of the temporomandibular joint - pain increases while eating or any other jaw movements;
- tension often spreads to the cervical vertebrae, which can trigger the development of osteochondrosis.
It is worth understanding that complications develop only in advanced cases. Modern medicine has all the necessary means and methods for treating bruxism, which allows you to get rid of its manifestations at any age. Despite the fact that attacks occur mainly at night, they are not the only symptom of the disease. Feeling of discomfort, tension and pain in the temporomandibular joint, increased sensitivity of the teeth - these problems should be addressed to a specialist.
Diagnostic methods
Since bruxism is considered a polyetiological disease, before starting its treatment it is important to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis. To begin with, a standard procedure is prescribed using brux checkers. These devices are mouthguards to be worn at night. After the patient wears them overnight, the impression is sent to the dentist for analysis. This way you can determine which teeth are experiencing overstrain, and how much the disease is related to the bite and location of a person’s teeth.
In order to diagnose pathologies of the masticatory muscles, electromyographic analysis is used. This research method will allow you to assess the condition of the muscles at rest and in motion. This way you can determine myofascial pain syndrome, and by the location and function of the muscles, you can identify incorrectly selected and installed prostheses. In children, the mechanism of development of the disease is often associated with the process of teething. Symptoms of bruxism will help parents identify and pay attention to their child’s malocclusion in the early stages.
You may need to consult a neurologist, otolaryngologist, psychotherapist, or maxillofacial surgeon. Based on the data of a comprehensive examination, a final diagnosis can be made and a suitable treatment regimen can be prescribed. The Clinical Brain Institute employs qualified specialists who have successful experience in treating bruxism in patients of all ages. There are also all conditions for examination using instrumental methods.