Experts Ask a Question
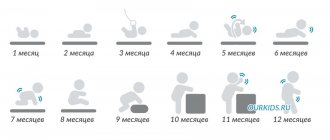
During the first month of life, the baby needs constant monitoring. This makes it possible to detect any disturbances in the functioning of the body, after which therapy can be prescribed in a timely manner. When the mother and baby are discharged from the maternity hospital, the child is examined at home by a pediatrician and a nurse. During the visit, the doctor examines the child, the umbilical wound, reflexes and explains techniques for caring for a newborn. When the baby is one month old, the child must undergo his first major medical examination (pediatrician and specialists).
What you need to know about documentation
Immediately after the baby is born, he is examined by a pediatrician, neurologist, and neonatologist. This is a mandatory procedure for all children. At this stage of life, medical professionals focus on the level of reflexes and skills of the newborn.
For the first appointment with the pediatrician, the mother must provide an extract from which the doctor will receive the following information:
- information about the woman in labor - how her pregnancy proceeded, whether there were any complications during pregnancy, features of labor. It is indicated what methods were used to alleviate the condition of the woman in labor, whether there was a cesarean section or episiotomy, whether anesthesia was used;
- information about the baby - the document indicates the day, month, year and time of birth, height and weight measurements, Apgar scores that were used in the delivery room. It is indicated whether the baby was put to the mother’s breast, what condition it was in for several hours after birth;
- The card indicates how the baby developed and how he behaved in a medical facility, how much weight he lost, how much he gained, and his growth indicators. It is indicated in what condition the umbilical wound is, when exactly the umbilical cord fell off (if this happened in the maternity hospital)
- These documents indicate whether the baby has been vaccinated, and whether the parents refuse vaccinations. The number and series of the vaccine that was used to administer to the baby is listed. If vaccination was not carried out, the reasons for its absence must be listed;
- The documentation lists laboratory tests and blood test results. Be sure to indicate if there is a Rh conflict between mother and child;
- if there are additional examinations, for example ultrasound, all results are recorded in the card. Information is also written here about whether there were consultations with narrow specialists, whether there are recommendations or appointments of narrowly specialized specialists;
All this documentation must be given to the pediatrician. He and a nurse will monitor the newborn's condition after he is discharged.
During your visit when your baby is six months old, your doctor will likely do the following:
- Weigh the child and measure his height.
- Get the vaccinations required at this stage (most likely, these will be vaccinations against hepatitis B, diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough (DTP), polio and a vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae).
- Assess the child's development, temperament and behavior.
- He will tell you how to form a correct sleep schedule for your child.
- Will evaluate the degree of safety of the surrounding space, since now the baby comes into contact with a large number of things every day and will soon begin to walk.
Features of newborn development
During the first month, young parents learn to live with their child and care for him. Mom and dad learn to bathe the baby, a breastfeeding or formula feeding regimen is developed, and sleep improves. Mom's body gradually begins to return to normal.
At one month old, the baby can already lie on his tummy for a short time and begins to focus his gaze on the face of his mother or father. Some babies already know how to respond to loud sounds and follow movements at close range. The baby can lift his head from a position on his tummy; some hold his head in a vertical position. Children already begin to spontaneously smile, make enthusiastic sounds, and coo.
This time is an adaptation period. The child’s body adapts to life, so it is very important not to neglect examination by doctors. The visiting nurse and the pediatrician assigned to the baby will visit the mother and child once every seven days for a month.
The baby is examined, auscultation (listening) of the lungs and heart, and examination of the abdomen is carried out. The doctor gives recommendations for caring for a newborn. The doctor shows how children are bathed, how they are fed and swaddled. At this stage, it is very important for the mother to establish breastfeeding, so she can seek help from a doctor so that he can show how to properly latch on to the baby.
For what reasons do newborns need to visit a medical facility at 3 months?
At 3 months, the child must go through a rather serious trip with his parents to a medical children's hospital so that doctors can assess the general condition of the children and observe its development.
Sometimes local pediatricians offer parents to make the first visit in the 1st month of life, but most often it is postponed until the child is almost an adult, that is, at 3 months. This procedure must be mandatory, so you need to carefully prepare for it and in no case neglect it. When a child undergoes mandatory medical examinations, parents will be able to know exactly how the baby is developing and what its general health status is. To make a correct diagnosis for a 3-month-old baby, the doctor must be a real professional, because any disease in small patients is not so easy to identify.
First inspection
During the first examination, the pediatrician measures height, weighs, and evaluates weight gain. The doctor measures the circumference of the baby's head and chest. The pediatrician also uses a stethoscope, listening to the child’s heartbeat, palpating the tummy and thighs. The reaction of the eyes is checked, so the doctor determines whether the child’s reflexes are normal and whether he can focus his gaze.
The lymph nodes are palpated and the fontanelle is examined. The pediatrician also examines the area of the external genitalia and skin. Based on the entire examination, an assessment is made of the dynamics of the child’s overall development.
There must be a mandatory weight gain per month. Over the next two months, weight is gained by an average of 200 grams per week.
Examination by a pediatrician
The most important doctor for a 3-month-old baby is a pediatrician. It is this specialist who will maintain a special table that takes into account the child’s development. The table shows the following parameters:
- height and weight indicators;
- head and chest circumference;
- abdominal cavity circumference indicators.
In addition, the local pediatrician must examine the site of the vaccination, which was done in the maternity ward, measure its indicators and enter them into the table too.
Next, the pediatric specialist will examine the oral cavity and listen to the heartbeat of children at 3 months and their lungs. If at 3 months children already have their first teeth, their condition is also carefully studied. When examined by doctors, parents will be able to ask any questions regarding the baby’s health and tell them what the child can do, how long he sleeps and stays awake, what he eats and how he defecates. All additional information is very important for all doctors who need to undergo a routine examination to accurately determine whether the newborn is developing at the proper level at 3 months.
After the pediatrician has fully examined the child, parents will receive all the answers to their questions. The doctor will establish a health group for the patient, whose age is 3 months, and give advice on visiting other specialists. But if the condition of the newborn does not cause any concern, then the routine examination can be completed after the conclusion of the pediatrician.
What is recommended to take with you to the examination?
To ensure a comfortable stay for a newborn in a medical facility, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to packing the bag. The following things are needed:
- diapers, it’s better to take several;
- pacifier;
- a rattle or toy that can distract the child and keep him occupied while waiting for an appointment;
- a bottle of water if the child is fed with adapted formulas. When feeding with mother's milk, this attribute is not needed;
- results of preliminary tests and ultrasound examinations, if they were previously prescribed by doctors;
- You can take a notepad and pen.
These recommendations will help a young mother not only when her baby is one month old, but also in the future. You will need to visit the doctor every month until the first year.
What does the pediatrician do during the examination:
- the doctor weighs the child, assesses his weight gain or loss;
- height measurements are taken;
- chest and head circumference are measured;
- the doctor examines the condition of the skin, whether there is any irritation, prickly heat, irritation or redness in the folds on the neck and behind the ears;
- performs an examination of the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, eyes, and genitals;
- listens to breathing and heartbeat;
- palpates the lymph nodes, thyroid gland, fontanel.
The pediatrician will explain the need for vitamin D prophylaxis.
Visit to the surgeon
The surgeon can determine the following pathological changes:
- phimosis - this pathology is manifested by a narrowing of the foreskin in boys;
- inguinal or umbilical hernia, which appear as a result of various developmental defects;
- cryptorchidism, in which the testicles do not descend into the scrotum after birth;
- hemangiomas are vascular tumors on the surface of the skin that are benign.
If pathologies are detected on time, they are treated in a timely manner. This allows you to prevent the development of consequences and complications. The older the child becomes, the more difficult it is to treat pathological processes.
Health groups for six-month-old babies
There are the following health groups for six-month-old children:
- 1 group. These are physically healthy children with a developed psyche. They rarely get sick, their body is highly resistant.
Healthy child
- Group 2 – these are children with some functional developmental deviations. They do not have chronic diseases.
- Children of the third group have compensated chronic diseases. Their body resistance is reduced. Such children must be registered with a dispensary.
- Group 4 – these are children with chronic diseases in the subcompensated stage. They may have a congenital pathology or a developmental defect. In children, this condition occurs after an exacerbation of the disease, a deterioration in general health. Their body's resistance is sharply reduced.
- Children of group 5 have chronic decompensated diseases. This also includes patients with disabilities, cancer and other serious conditions.
Visit to an orthopedist
An orthopedist examines the baby's musculoskeletal system. He spreads the legs at the hip joint and examines whether the gluteal folds are symmetrical. These are methods for visual diagnosis of hip dysplasia. A timely diagnosis and timely initiation of therapy help get rid of the pathology much faster than in adulthood.
An orthopedist can also determine the following pathological processes:
- dislocations;
- congenital clubfoot;
- torticollis.
What specialists does a six-month-old child need?
Why does a child’s runny nose persist for a long time?
By six months, the child must undergo several doctors. Under no circumstances should medical examinations and medical recommendations be ignored.
List of doctors
| Pediatrician | This is the most important doctor in the life of every baby. It is recommended to visit this specialist monthly until the baby is one year old. He must weigh the child, measure the circumference of the head and chest. The most important task of a pediatrician is a comprehensive examination of the baby. It will help to find out if there are any delays in its development. If alarming symptoms are noticeable, the child is sent for additional examination. The pediatrician should tell you when to do routine vaccinations. |
| Neuropathologist | A visit to a neurologist in the sixth month of life is mandatory. The doctor should evaluate the baby's muscle tone and reflexes. It is also important to assess the infant's mental health. |
| Orthopedist | This doctor looks at whether the folds on the legs are symmetrical and how they are separated. This procedure helps detect hip dysplasia at an early stage. |
| Cardiologist | A visit to this doctor is mandatory if there is a referral from a pediatrician. |
| Surgeon | This doctor detects hernias, congenital dislocations, and torticollis. In addition, he examines the genitals. This is especially important for boys because it helps detect cryptorchidism. |
| ENT | The doctor checks the patient's hearing acuity, as well as the condition of the nasopharynx. A visit to this doctor at six months is mandatory. |
| Dentist | This specialist examines the little patient’s mouth and monitors the normal eruption of baby teeth. |
Appointment with a neurologist
Appointment with a neurologist
During the examination, the neurologist monitors reflexes and other parameters. The specialist determines whether there is a syndrome of central nervous system depression or a syndrome of increased neuro-reflex excitability. The neurologist also examines the following parameters:
- innate reflexes;
- motor skills;
- muscle tone;
Several years ago, in the maternity hospital or at the first appointment with a pediatric neurologist, the recommended neurosonography was performed. This is an ultrasound examination of the brain, which is performed through the fontanel. The problem is that this procedure was prescribed to all children, even those who do not have obvious signs of pathological processes.
What does a pediatrician check for a six-month-old baby?
By this age, the child can sit down or prepare to sit down. His back straightens. The little one pulls all surrounding objects into his mouth, so he actively learns and studies the world.
At six months, the doctor gives the child many vaccinations. The places where they are made can be somewhat painful. In addition, your baby's temperature may rise slightly after vaccination.
Note! An increase in temperature after vaccination indicates that the baby’s immunity is properly formed. Temperature and pain can be reduced with children's paracetamol.
During the visit, the doctor performs the following actions:
- Weighs the child and measures his height.
- Makes the list of vaccinations required at his age (against hepatitis B, diphtheria, whooping cough and tetanus, polio, hemophilus influenzae).
- Evaluates the child's overall development and behavior.
- Gives advice on healthy sleep.
Child's visit to the pediatrician
When assessing your baby's overall development, your doctor will need additional information. You should clearly and most importantly answer the doctor’s questions correctly:
- Has the child had an appointment with a specialized doctor? If so, for what reason and what was the result of the inspection, were all recommendations followed?
- Are teeth appearing?
- Does the baby make any sounds? The doctor may ask you to describe everything that the baby “gives out”: screams, laughter, muttering.
- Does the child play with objects? Does he pull them into his mouth or throw them? It is important for the mother to describe what the baby can already do, whether he can search for and catch small objects.
- Does the child sit down (on his own, or does he need the help of an adult).
- The doctor is also interested in whether the baby can bear weight on his lower limbs if the mother tries to position him in an upright position.
- If the mother enters the room silently, does the baby turn his head?
During a 6-month-old child's visit to the doctor, it is necessary to discuss the following points:
- dangers and risks of food allergies;
- possible sleep problems;
- the advisability of taking dietary supplements;
- what to do if the baby does not respond to sounds and looks pale.
Important! All children are different in their development. Any doubts regarding the baby’s development should be discussed only with a pediatrician.
Visit to an otolaryngologist
This specialist examines the nasal passages and their mucous membranes. Also examines the throat. The doctor examines the ears for wax plugs and checks the nasal passages to make sure they are developing correctly. To check the quality of hearing, a specialist performs an otoacoustic diagnosis.
If any pathological processes or abnormalities are detected, the otolaryngologist issues a referral to specialists at the audiological center. More in-depth research is being done there. With the help of early diagnosis, it is possible to prevent the development of negative consequences for the mental and speech development of children.
Visit to an ophthalmologist
Ophthalmologists say that even in young children a tendency to strabismus can be determined. At the reception, the specialist examines the baby’s fundus and assesses the condition of the tear ducts. When examining the tear ducts, it becomes possible to detect their blockage and begin timely treatment.
Thanks to the examination of the fundus, it is possible to determine the presence of retinal pathologies and inflammatory processes. Increased intraocular pressure may also be detected. Some children develop various vision problems after birth. Diseases such as dacryocystitis and conjunctivitis may develop. It is early diagnosis that will allow timely treatment to begin and prevent the development of negative consequences.
Why should a baby undergo examinations?
A routine examination should not be ignored, because it is at one month of age that important developmental disorders can be identified. Thanks to timely measures taken, the child can be helped. There are a number of characteristics of newborns in which it is enough to provide proper care for the baby in order to prevent the beginnings of the disease from developing and becoming a problem.
The first month of a child’s life is the most difficult for his mother from a psychological point of view. She, who has just been discharged from the maternity hospital, has not yet recovered, and her daily responsibilities include a small child who requires a lot of attention and time.
Often women are extremely dissatisfied with patronage due to the fact that they feel unwell, are often not satisfied with their appearance, but are forced to accept a stranger. When a mother receives information that she needs to see several specialists in a month, this can completely throw the woman out of her mental balance.
Due to a lack of strength and desire to see doctors on time, many children receive diagnoses that could have been avoided. These include:
- dislocation of the hip joint;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- CNS disorders;
- various neurological disorders.
Appointment with a neurologist
Attention! Timely diagnosis is a guarantee of good health for the baby and the elimination of many problems associated with it.
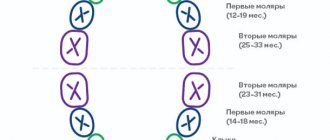
Visiting the dentist
Many parents are surprised that babies need to be examined by a pediatric dentist. Even though the baby has no teeth, a consultation with a dentist is necessary. An examination by this specialist allows you to determine possible anomalies in the structure of the oral cavity. If this problem is ignored, in the future there will be difficulties with teething, they will be crooked, the bite will be deformed.
During a medical examination of a child at 1 month, a specialist assesses the condition of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, determines inflammatory processes and plaque.
Necessary doctors for rounds in 2 months
Massage for a 3 month old baby
If, after visiting any of the specialists in 1 month, closer monitoring of the child is required, an additional appearance may be scheduled. For example, when a neurologist believes that a month-old baby has problems with muscle tone or any other abnormalities, he refers him to an ultrasound scan of the brain. After receiving the results, already at the age of 2 months, the baby should visit the neurologist again for a diagnostic assessment.
It is not planned for a two-month-old child to go through a full list of specialists without identifying problems. The exception is the pediatrician, who monitors the dynamics of the baby’s weight gain and body length, and also refers him for routine vaccinations.
Additional tests
In order to undergo additional types of diagnostics, you need to get a referral from a pediatrician. Additional examination during a medical examination at 1 month may be necessary if the doctor suspects any disturbances in the functions of the baby’s internal organs.
A one-month-old baby may need the following examinations:
- an ultrasound diagnostic specialist performs an examination of the abdominal organs, examines the gallbladder, liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, neurosonography;
- Electrocardiography and cardiac ultrasound are performed. These examinations will help assess the condition of the heart and blood vessels;
- To prevent the development of anemia and various inflammatory processes in the baby’s body, doctors give a referral for a general blood test. No additional preparation is required for this;
- Your doctor may order a general urine test. This can be done using a urine bag. You can purchase it at any pharmacy chain. It is attached to the baby's external genitalia, after which its contents are poured into a sterile container for collecting urine. The main condition is to wash the child before collecting urine;
- if physiological jaundice is suspected, the child is referred for biochemical blood tests. In this case, an important indicator is the level of bilirubin.
Features of early diagnosis
Thanks to early diagnosis of pathological processes, it is possible to quickly solve existing problems, prevent the development of complications, and perform correction.
One of the methods of early diagnosis is ultrasound examination of the brain. For a one-month-old baby, this is a very important examination, since it can help determine deviations in the development of the central or peripheral nervous system.
This diagnosis is indicated in the following situations:
- if the baby was born premature;
- if there were any complications during the birth process;
- if after childbirth the neonatologist gave low scores on the Apgar scale;
- in the presence of muscle hypertonicity or hypotonicity;
- if there is a delay of a physical, mental or neurological type.
Using neurosonography, you can determine the presence of congenital and genetic abnormalities of the nervous system, cystic formations. If the child was injured during childbirth, the specialist carefully examines the tissue to determine whether there are intracranial hemorrhages.
Ultrasound examination of the hip joints helps determine possible pathological processes, dysplasia, and congenital dislocations of the hip joints. During the first year, treatment of these pathologies will be most effective, since the child does not yet walk and the load on his musculoskeletal system is less. If problems are identified during an examination of a child at 1 month, the orthopedist will refer him to a course of massage and give general recommendations. The doctor writes out a referral for the necessary procedures, with the help of which recovery occurs much faster.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity is a necessary procedure for newborn babies. This examination helps determine whether there are any congenital abnormalities. During the planned procedure, an assessment is made of the suitability of the internal organs for the child’s age category. There are certain criteria for the relationship between age and the size of internal organs; these indicators are taken into account when assessing development.
Ultrasound examination of the heart is performed from one to one and a half months. This procedure is absolutely safe for the child. It is informative and can be used to assess the state of the cardiovascular system. There are no contraindications to echocardiography.
List of specialists for examinations at 2 years
Examination of a child by an ophthalmologist
At 2 years old, the child will need to visit the following specialists:
- Pediatric neurologist. This is one of the main doctors you need to see regularly. He will be able to identify problems such as developmental delays, irregular speech, hypertonicity or hypotonicity of muscles, impaired coordination of movements and many other different conditions that parents often do not see. A neurologist will help you choose the right treatment and, if necessary, prescribe massage, exercise therapy, and special educational games for your child.
- Surgeon. This specialist should be contacted every year of the child’s life until he reaches the age of 5 years. Even if there are no visible reasons for concern, it is imperative to visit a surgeon: he will identify possible postural disorders, curvatures of the spine, problems with flat feet, various defects in the development of joints, such as dysplasia, and in boys he will check the correct development of the genital organs. Sometimes surgical problems do not appear outwardly and become known only after an appointment with a doctor.
- Oculist. The doctor will check the baby’s fundus, visual acuity and, if necessary, based on the examination results, prescribe corrective treatment. At 2 years old, children's eyes can still be corrected very well.
- Dentist. Even though two-year-old children have not yet grown all their teeth and they have baby teeth, they should see a dentist every year. During the examination, this specialist will recommend to parents proper oral care for the baby, examine the gums and existing teeth and issue a conclusion whether the child needs further treatment. If there are manifestations of caries on baby teeth, then the pathology must be cured, because infections from the oral cavity pass inside with food and, accordingly, problems with the gastrointestinal tract may appear in the future.
- Pediatrician. This doctor will not only help parents correctly make a list of which doctors to see at age 2, but will also provide directions for blood, urine and stool tests, which need to be taken regularly. The doctor will also give advice on nutrition and care for a two-year-old baby.
Audiological screening
Using this examination, it is possible to determine the presence of pathological processes in the development of the visual and auditory apparatus. If any disorders are detected in a timely manner, they can be treated in time when the pathological processes are in the initial stages of development. In this case, the therapy will have maximum effect. This diagnostic procedure is performed for children up to three months.
During the inspection, innovative examination methods are used. According to the protocols, audio screening should be carried out in the maternity hospital. If such an examination is not carried out within the first few days after the baby is born, it must be performed later.
Using a special device, a specialist performs a hearing test. This allows us to exclude developmental anomalies such as deafness or hearing loss.
Is it possible to skip doctor visits?
During the first scheduled examination of a child at 1 month, consultation with specialized specialists is needed to assess the child’s condition and development. Additional diagnostics may also be needed. All this is necessary in order to make sure that the baby is developing according to his age category, that he does not have any developmental abnormalities, diseases or pathological processes. Therefore, it is recommended not to ignore the child’s first examination at 1 month.
There are objective reasons why a mother may not come with her child for an examination:
- being in hospital;
- acute infectious disease;
- It is temporarily impossible to get to the doctor.
When undergoing a routine medical examination, parents can ask any questions and inquire about the results of the examinations. The doctor tells you what processes are happening in the baby’s body and gives advice on caring for him. The first month is the period of adaptation of the newborn’s body to external circumstances.
How is the medical examination carried out?
Every minor child under 17 years of age has the right to a free medical examination.
- To undergo a medical examination, the child must be made an appointment with a local pediatrician.
- At the appointment, parents (or the child himself, if he is over 15 years old) will need to fill out informed voluntary consent
. The doctor will give recommendations on the procedure and write out referrals for tests and consultations with specialists. - If necessary, the local doctor may refer the minor for additional consultation or research.
Based on the results of the preventive examination, the doctor will determine the child’s health group and medical group for physical education.
In what cases is an unscheduled visit to the doctor required?
Sometimes there is a need for an unscheduled visit to the doctor. If the child is less than a month old, you can consult a pediatrician unscheduled in the following cases:
- if there is no increase in body weight;
- if body weight is gained very slowly or the weight does not increase at all. The cause of this problem may be a lack of proper feeding. For example, a nursing mother has too little breast milk, the baby cannot grasp the nipple correctly, and it is very difficult for him to suck. Also, underweight can be provoked by various diseases of the digestive system, lactase deficiency, hidden infectious processes or developmental abnormalities;
- The baby begins to vomit or regurgitate very profusely; almost all the milk consumed flows out. It is especially important to consult a doctor if severe regurgitation or frequent vomiting is accompanied by underweight. These are the first signs of abnormalities in the development of the gastrointestinal tract;
- if two weeks after the baby is born, the umbilical wound does not heal. The reason for this condition may be lack of care, penetration of pathogenic microorganisms;
- in the presence of physiological jaundice for more than two weeks. The pediatrician must definitely examine the child; additional laboratory testing of biochemical blood parameters may be necessary to determine the level of bilirubin and draw up the most correct treatment regimen;
- in the presence of hyperthermia, the temperature exceeds 37.5 degrees. If parents, after measuring the child’s body temperature, see that the readings exceed the specified mark, it is necessary to call an ambulance or independently go to a medical facility for help;
- if blood streaks, drops or clots appear in the stool. This may indicate the development of dangerous diseases, including intestinal obstruction. You should contact a doctor immediately.
Thanks to a timely visit to the pediatrician, you can prevent the development of various pathological processes and, if necessary, begin timely treatment for your baby.