Get an ECG done for a child at the Paracelsus Clinic, Sergiev Posad
ATTENTION:
Online consultations with doctors (more than 18 specialties) are available.
Electrocardiography
of a child in pediatrics is a screening method that is used to analyze the functioning of the cardiovascular system. ECG for children is a highly informative type of research in pediatric cardiology, as the first stage of examination. The functioning of the cardiovascular system in children of different ages has many features. Therefore, it is important that the ECG results are interpreted by a competent pediatrician or cardiologist.
Features of children's ECG
The technique of studying the heart using ECG has been used in medicine for a long time, but due to the lack of necessary equipment, pediatric cardiology for a long time dealt mainly with congenital heart defects. In our Child Health Center, new generation equipment is used to conduct ECGs for children, which makes it possible to diagnose various disorders of the heart at the earliest stages.
It would seem, why does a small child need an ECG? Indeed, the heart and blood vessels of babies do not suffer from chronic infections and intoxications. However, in the first years of life, congenital heart defects and disorders of the circulatory system cannot be excluded, and at school age, children may experience hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias and rheumatic lesions. Functional disorders of the cardiovascular system such as autonomic dystonia, cardiomyopathies, and arterial hypertension have recently become especially common. The reason for this is unhealthy diet, improper daily routine, stress, and sedentary lifestyle. An ECG is required to be performed by our specialists when concluding a contract for medical care for children of different ages.
| This is important to know ! Don’t worry if, when you decide to measure your newborn’s pulse, you find that your baby’s heart is beating very quickly. Normally, the pulse in newborns is 130–140 beats per minute and only by adolescence it slows down to adult levels (60–80 beats per minute). In addition, the baby’s pulse may increase when crying, anxiety, high temperature, or physical stress. But blood pressure in newborns, on the contrary, is significantly lower than in adults - only 35–50 per 70–80 mmHg. |
Each child has its own ECG standards and its own “seam allowances,” that is, permissible deviations from these standards. What is normal for a newborn can be dangerous for a baby, and so on. Therefore, it is better to conduct an ECG for a child in a specialized children's medical institution, using good equipment, and entrust the interpretation to an experienced pediatric cardiologist.
ECG for a child - general information
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a hardware method for studying the heart. Its essence is to register and graphically record the electrical potentials that arise in the heart during its operation.
The procedure is intended to diagnose heart defects, arrhythmias, myocarditis and other pathologies of the heart muscle. It is also needed during preventive examinations.
Special types of electrocardiography
In some cases, as prescribed by a pediatrician or pediatric cardiologist, special electrocardiographic studies may be prescribed for older children.
Bicycle erogmetry (stress test): when a cardiogram is taken during dosed physical activity (rotating the pedals of an exercise bike). This study allows you to see how a child’s heart reacts to physical activity.
Holter monitoring : For an in-depth study of arrhythmias, a long-term ECG recording of 15-20 minutes may be required. To identify hidden disturbances in the blood supply to the heart and the rhythm of its work over a long period of time, ECG Holter monitoring is used. In this case, electrodes are attached to the child's skin, and a small computer-cardiograph is hung on the child's neck or belt, which constantly records the ECG.
How is an ECG performed on a child?
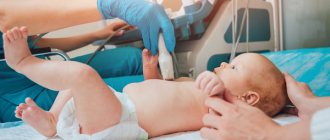
To conduct electrocardiography, special sensors are attached to the body: one on the arms and legs and six on the chest. These sensors record the electrical current from the heart and transmit it to an electrocardiograph, which converts it into a graphical recording on tape. The procedure is absolutely painless and does not cause any discomfort; the whole process takes up to 10-15 minutes.
Before the examination, the child should be undressed to the waist, bare wrists and ankles, and placed on a table. At the same time, parents can be nearby, support and reassure him.
What is an ECG?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a proven, simple and informative method for studying the heart muscle. Electrical potentials resulting from the work of the heart are recorded using special sensors attached to the body. The pulses, amplified 600–700 times, enter a device called an electrocardiograph, which deciphers the information received and displays it in the form of graphs on a moving paper tape. An ECG is absolutely painless, does not take much time and, due to its safety, can be used in both adults and children for the diagnosis and prevention of many dangerous cardiovascular diseases.
What can you find out with an ECG?
First of all, an electrocardiogram allows you to evaluate the frequency and regularity of heart contractions. In addition, using an ECG, you can identify metabolic disorders - deficiency of calcium, magnesium, potassium and other electrolytes. An ECG of a child’s heart helps detect serious diseases such as:
- congenital heart defects, acquired heart defects, myocarditis;
- myocardial infarction;
- hypertrophy (abnormal enlargement) of various parts of the heart;
- angina pectoris;
- disturbances of heart rhythm and intracardiac conduction (heart block);
- pulmonary embolism;
- metabolic disorders in the myocardium against the background of various diseases and pathological conditions.
Benefits of ECG
This method has many compelling advantages. He:
- easy to carry out (does not require special training and subsequent rehabilitation);
- affordable;
- allows multiple repetitions without harm to health and allows doctors to track the development of a small patient’s heart over time, which is especially important for a child in the first years of life.
All this has made ECG a procedure indispensable for the work of both adult and pediatric cardiologists.
ECG monitoring in children
Holter monitoring
ー method of recording an electrocardiogram for 24 hours. To do this, a set of electrodes is attached to the child’s chest, and a signal receiver from the electrodes is attached to the belt. During the day, the little patient should maintain his usual daily routine: sleep, eat, play, run, etc. Parents need to record his actions in detail, indicating the time, so that the doctor can compare changes in the electrocardiograph readings with what the child was doing at that time.
How to prepare a child for an ECG?
No special preparation is required for an ECG of a child's heart. The main thing is that the little patient behaves calmly during the procedure. With an older child, you can play “doctor” the day before, using dolls to show him what awaits him. It is advisable to bring infants for an ECG either during sleep or after eating, when they are in a peaceful state.
| This is important to know ! The calmer the child is at the time of the ECG, the clearer and more objective the results of the study will be and the more accurately the cardiologist will be able to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. An ECG can be performed on a sleeping child, so you can guess the time and record your baby for an electrocardiogram at the moment when he usually sleeps. Call +7 (495) 229–44–10, +7 (495) 954–00–46 , and our administrators will select the best recording option for you. |
It is also recommended to think through the child’s clothing in advance and equip him so that in the ECG room you do not have to fiddle with buttons and ties for a long time.
Indications for ECG in children
Main indications for electrocardiography:
- in infancy for early detection of congenital heart defects;
- a newborn's skin color is not pink, but pale or bluish. Particular attention should be paid to the color of the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle. When crying, the cyanosis usually increases;
- in the first year, during feeding, perspiration is observed, he quickly gets tired, and does not gain weight well;
- preschoolers and schoolchildren experience shortness of breath, they look weaker than their peers, and prefer to avoid active games;
- for pain in the heart area, high blood pressure, sensations of irregular heartbeat, fainting and pre-syncope, murmurs in the heart area, pain behind the sternum, blue discoloration of the nasolabial area and fingertips, dizziness, swelling of the legs;
- mandatory before visiting sports sections
ECG abnormalities can occur in children who have had severe tonsillitis, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, acute intestinal infection, pneumonia, influenza, etc. After these diseases, in order to early detect cardiac disorders (for example, acquired heart defects), an electrocardiogram should be performed on the child.
Do not refuse timely medical care to your child - get an electrocardiogram if indicated or prescribed by a doctor.
When is an ECG prescribed for children?
In addition to the preventive procedure as part of the medical examination of children from 1 to 17 years of age, the attending physician will refer the child for electrocardiography in the following cases:
- shortness of breath when walking;
- pain in the chest area;
- dizziness, loss of consciousness;
- past infectious diseases;
- fatigue during normal physical activity, paleness of the skin;
- cardiac arrhythmia;
- heart murmurs on auscultation;
- high blood pressure;
- swelling of the arms and legs;
- playing sports in the section;
- family history of cardiac pathologies.
According to indications, electrocardiography in children can be taken at any age, including in the fetus, starting from the 14th week of pregnancy or during childbirth.
Dangerous diseases
The ECG shows changes characteristic of such heart diseases:
- congenital heart defects (ventricular or atrial septal defects, enlarged chambers, abnormal arrangement of blood vessels);
- inflammation of heart tissue (endocarditis, myocarditis);
- impaired conduction and contractility of the myocardium of the heart, arrhythmia, angina pectoris;
- imbalance of electrolytes, metabolic disorders in the heart muscle, characteristic of non-cardiac diseases (gastrointestinal, diabetes mellitus, etc.).
ECG in a newborn during the first two days of life
In the ECG of children, individual fluctuations are observed during the first two days. Immediately after birth, the heart rate is 157 per minute, and after cutting the umbilical cord - 142 per minute. In the first hours after birth, doctors note fluctuations in the RR interval from 0.44 to 0.54″, the heart rate is 123.0±1.8 per minute. To perform an ECG on an infant, it is important to swaddle him well. This is necessary to ensure that the recording of the electrocardiographic curve is correct. The child should be warm and motionless. Swaddling is abandoned only if the child is in serious condition and practically does not move. It is recommended to record an ECG 1.5-2 hours after feeding and before X-ray examinations and physical procedures.
Physical basis of electrocardiographic study with stress.
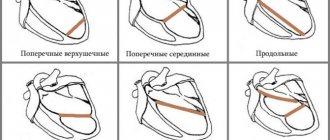
During operation, the electrical activity of the heart constantly and rhythmically changes in accordance with the stages of compression or relaxation (systole and diastole). An electrocardiograph records the difference in electrical potentials between two areas of the heart's projection onto the surface of the child's body and displays the results in the form of a characteristic graph - a cardiogram on a strip of paper or a computer screen. The number of waves per minute on the graph shows the heart rate, the distances between identical elements of the cardiogram - heart rate. Waveforms show how the heart's electrical impulses are formed and how well the individual parts of the heart work together. Based on the shape and size of the elements of the cardiogram, the doctor can judge the quality of the child’s heart and determine signs of possible diseases.
During exercise, the body needs additional oxygen. The heart and lungs must work harder than usual to supply the body with extra oxygen. When performing physical exercises, the heart begins to work harder: it contracts more often and stronger in order to increase the output of pumped blood and maintain blood supply to the muscles and other involved organs at a level adequate to the load. At the same time, the heart muscle itself begins to consume more oxygen supplied with the blood through the cardiac blood vessels.
Electrical activity from the surface of the body is recorded through small metal plates (electrodes) that are placed in specific places on the child's chest, arms and legs. The electrodes are connected to the cardiograph by wires through which information is recorded. During exercise, the electrocardiograph will record changes in heart rate, heart rate, blood pressure, and other symptoms as your child exercises—at first at a slow pace, then faster and faster until he reaches the highest level. All obtained electrocardiogram data will be measured, analyzed by a computer and a doctor, who will form a conclusion based on the results of the study.
What stress tests will a cardiologist suggest?
The type and duration of EGC examinations differ. Depending on the indications and goals, the cardiologist may offer the following tests:
Load tests (Step test). A simple type of diagnostics that does not require special equipment. First, an electrocardiogram is taken from the patient at rest. Then he performs several exercises (running, walking in place for 2 minutes, 20-30 squats). After this, another cardiogram is recorded, the data of which is compared with the first results. In some cases, another ECG is performed, for example, 3 minutes after exercise.
Bicycle ergometry. A person exercises on a bicycle ergometer (a special bicycle connected to a computer). In this case, the intensity of the load may change. It all depends on the purpose of the examination. The device records indicators at rest, during the test and after exercise.
Treadmill test. It is carried out on a treadmill, which allows you to more accurately change the load and speed of the moving belt, adjusting it to each person being examined, even for a child.