The ability to see and hear: when the baby’s abilities manifest themselves
The vision of a newborn baby undergoes a number of changes in the first month of life. A baby is born with vision called peripheral vision. Peripheral vision makes it possible to see those areas that are located on the sides of the baby. Gradually, the child masters the ability to focus his gaze on a point located in the center of his field of vision.
By the end of the first month of life, vision develops to the following level:
- the baby is able to fix his gaze on objects that are nearby at a distance of up to 30 cm;
- parents may notice that at times the baby’s eyes seem to “run away”, from time to time the child may cross his eyes;
- the baby prefers to look at contrasting patterns, but black and white pictures are of greater interest to him;
- The child enjoys looking at human faces.
How to determine hearing or vision impairment in a newborn?
The main methods of testing hearing and vision include checking the reaction in the first weeks of life to:
- rustle of paper;
- movement of objects starting from 3 months;
- changes in intonation, timbre and volume of voice;
- strong light and sound stimuli.
At the same time, to determine pathological disorders of the visual and auditory apparatus, it is important to take into account the child’s analytical abilities.
Children will be able to talk about visual acuity or the color scheme of objects only after they learn to express their thoughts.
Parents should immediately seek advice from an ENT doctor, pediatrician or pediatric ophthalmologist in the following situations:
- after 1 month after birth, there is a lack of interest and focus when moving large objects;
- the baby does not respond to loud sounds and bright sources of light;
- by 4 months, the child does not distinguish parents and relatives who care for him for a long time from strangers;
- does not try to repeat combinations of sounds, does not look at objects and does not reach for brightly colored toys;
- did not start talking by 7 months - the causes of speech impairment may be caused by a pathological disorder of the hearing aid;
- upon reaching 1 year from the moment of birth, he does not orient himself in space, does not play and does not respond to light and sound stimuli.
While playing or caring for a child, parents may notice visually visible defects and developmental anomalies. They manifest themselves in squinting or diffuse strabismus, frequent horizontal or vertical movements of the eyeballs.
Signs of pathologies
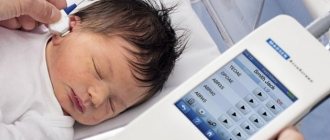
With diseases of the hearing system, the child does not respond to sources of loud noise. When a loud sound appears, a newborn should freeze, become frightened, or close his eyes. If at 2-3 months the baby is indifferent to the voice addressed to him or the noise of rattles, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a pediatrician or audiologist.
In rare cases, infants hear only low and mid-level frequencies, while high-frequency sounds do not cause any response. In such a situation, the development of hearing loss of varying severity is possible. To exclude the presence of pathology, you should pour semolina into a glass or metal container and shake it over the newborn’s head. Normally, he should try to turn towards the source of the noise.
Upon reaching 1 month, the pupil's reaction to light should be checked. If it does not narrow, you need to visit an ophthalmologist. The cause of concern may be the lack of reaction at 12-14 weeks of life to silent objects, as well as if the child does not focus his gaze on various objects. In this case, the baby will not follow the direction of the mother’s gaze and movements. Children with visual pathologies do not distinguish parents from strangers.
It is recommended to visit a pediatric ophthalmologist as a preventive measure at 1, 3, 6, 12 months of a child’s life. Premature babies or newborns who have suffered acute hypoxia during childbirth or cerebral ischemia are at risk. Pathologies are observed in the presence of hereditary diseases in one or both parents, Rh conflict.
What does a newborn baby see?
A child who is only a few days old is very sensitive to bright light. His pupils are very small, this is provided by nature itself, so that excess light rays do not penetrate into the eye. Upon reaching two weeks of age, the pupils begin to gradually dilate. This gives the baby the opportunity to perceive a wider range of light and shadows.
A newborn child sees the environment around him with certain features:
- in the first weeks after birth, the baby does not yet hold his gaze on objects for more than 5 seconds;
- a newborn may “squint” his gaze for the reason that using both eyes at the same time is a skill that is learned over the next 6 months. At first, it is still difficult for an infant to control his vision;
- after 4 weeks of life, babies begin to see better and are able to focus their gaze well on a bright object, but only for a short time, more “sliding” their eyes over its surface.
The retina also trains and develops daily, and as this light-sensitive tissue matures, the child's ability to detect more complex patterns improves.
The world through the eyes of a baby
When newborn babies begin to see and hear, all mothers should know. While in the maternity hospital, doctors check the baby's vision. Special devices are used to determine the baby's pupil reaction to bright light. A newborn is not able to see this huge world for him in bright colors. In the first month of his life, he sees everything in blurry colors and is able to distinguish only light and dark.
Sometimes it is difficult for a baby to open his eyes, because birth is a lot of stress for his body. Bright colors and light are unusual for him and only gradually will he gain good vision. The mother should take all this into account and not worry about when the newborn begins to see normally. In the first month of his life, the little man looks at this world especially:
- he cannot consciously hold his gaze on anything for more than 5 seconds;
- infants cannot see with both eyes at once, so they often squint, which is quite normal;
- Only by the end of the first month does the newborn begin to fix his gaze on brightly colored objects; during this period it is recommended to hang bedside rattles at a distance of 30 cm.
“There is nothing more interesting than watching a baby. He needs the help of adults, his vision needs to be developed and this should be done correctly.”
Features of hearing in newborns
The first hearing test for a baby will be carried out in the maternity hospital, immediately after birth.
We answer the question when newborn children begin to hear - a healthy baby begins to hear voices and sounds in the first days of his birth. Moreover, children not only hear what surrounds them, but are also able to remember some of the sounds. Interesting fact!
If during the last stages of pregnancy you read fairy tales aloud, then after birth, hearing these stories again, the child can “remember” them, calming down and listening to your voice.
Hearing development in an infant by the end of the first month of life:
- the baby's hearing is fully developed;
- the baby is able to recognize some of the sounds;
- the child turns his head towards a familiar voice or sound source.
In the first month of life, the baby will listen to human voices with great attention. You will notice that if you turn your speech to the baby, “coo” with him, he will turn to you so that you are in his field of attention and will listen carefully to your voice. That is why, wondering how many days later children begin to see and hear, rest assured that the infant sees and hears you from birth.
What you need to know about hearing development in babies
Can newborns hear? The fetus develops hearing even before it is born. This occurs approximately at 16-17 weeks of intrauterine development. The phenomenon of “Recognition” has been scientifically confirmed in children. If the baby is regularly played music in the womb, then after birth he will be able to recognize it. Recognition is manifested in the baby's animation, he waves his arms and legs, and often smiles.
The peculiarities of the newborn's auditory system are that he hears only loud sounds. That is why he may not be disturbed by a noisy vacuum cleaner or a running TV. Parents can always test their baby's hearing at home. To do this, clap your hands near the left and then the right ear. You can also use musical toys that make not too quiet sounds.
The reaction of a toddler who hears your conversation or music should be as follows:
- Freezing or flinching.
- Turn the head and move the eyes in search of the sound source.
- Change in facial expressions.
- Movement of legs and arms.
When testing a baby's hearing, the main thing is not to overdo it. You can easily scare a child. In this case, you will observe convulsive movements and crying. If your baby gets scared of something and throws a tantrum, don’t worry, because this is a completely normal reaction.
All the little man’s senses are heightened. To prevent such a situation, talk to the baby calmly, do not shout. This is extremely necessary at least in the first months of life. Talk to your son or daughter more often, turn on calm music, read poetry and fairy tales. In addition to developing hearing, this will contribute to the formation of speech in the future.
Favorite objects – attracting the baby’s eye
Most of all, the baby likes to look at objects located directly in front of him at a distance of 20-38 cm. These can be rattles of different colors, or pictures hung along the sides of the crib. To establish contact with your baby and help him focus his eyes, you can practice simple and useful exercises.
- We learn to keep our gaze on an object. To develop this skill, you need to carefully turn the baby's head from side to side, while keeping his gaze turned to your face. Be sure to accompany the exercise with emotions - a smile, a wink, humming.
On a note!
This exercise can also be done using a toy. Show your child an object of bright color (orange, red) and slowly move it left-right or up and down. The item should be quite large in size. Keep the toy at a distance where the child can focus his gaze. Over time, the movement of the object can be accelerated and smaller objects can be used for the exercise.
- Children 2-3 weeks of age are better able to focus their gaze on objects in a vertical position. Carry your baby in your arms more often, even if at first it seems to you that the baby is not looking at anything around you. The baby needs time to concentrate on the subject. Take your time and give your baby time to look at the bright objects in the environment.
- Train your child's vision with toys of different colors, show him images of simple faces, bright contrasting stripes, circles, and squares. The baby's visual organs develop very quickly, and very soon he will be able to perceive the difference between red, blue and yellow colors.
By the end of the first month of life, the child will be able to briefly focus his gaze on objects distant from him at a distance of 90 cm. At this time, it’s time to hang a funny pendant or a singing carousel over the crib - they will undoubtedly attract the baby’s attention.
When, what and how do newborns see?
The baby begins to explore the world around him immediately after birth. 90% of infants see only blurry shapes of objects. The visual organs need time to fully adapt. Due to low fitness, children close their eyes and often squint, protecting the retina from bright light.
In some cases, babies open their eyes wide 1 hour after birth, receiving information about nearby objects and people.
How do newborn babies see?
Pediatricians explain to parents how a newborn sees and help to identify pathologies in time:
- at 1 week of life the child begins to focus his gaze on objects for 4 seconds;
- at 2 months, visual acuity increases, so the gaze glides over objects without stopping;
- Focus is fully formed by 4 months.
Up to six months, infants squint their eyes. This phenomenon is due to the child’s inability to control both organs of vision and combine their movement. Therefore, up to 6 months of life, it is normal if a child, after looking at a new toy for a long time, suddenly becomes interested in his own nose bridge or squints one eye at another object.
What does a newborn see?
Parents are interested in what the newborn sees when he begins to focus his gaze on one point for a long time. After leaving the birth canal, the baby reacts only to the presence of light sources. At 1 month, children see only large objects. They can then track the movements of large objects and parents. At 12-16 weeks of life, the child distinguishes smaller toys and begins to distinguish between their movements. At 6 months, the baby recognizes the faces of relatives, distinguishing them from strangers. During this period, visual acuity stops increasing, vision completely adapts.
What does your baby like to look at?
When a child begins to see, the faces of his parents are of greatest interest to him. Familiar traits evoke positive emotions in children, which are observed in fathers in 80% of cases. This phenomenon is due to the fact that men have a beard, mustache, large facial lines and other well-remembered features. If changes occur in the appearance of relatives, the baby will not recognize him and will take him for a stranger.
Black and white drawings, high quality photographs and geometric shapes attract the attention of newborns.
When does a newborn begin to see?
When a newborn first opens his eyes, he has peripheral vision. As a result, the child sees areas on the sides of his body. The central objects remain blurry. Children learn to control the lens within 6 months. On days 30-36 of life, the child fixes his gaze on objects that maintain a distance of 30 cm from his body.
There are no light sources in the womb, so the embryo's eyes cannot distinguish between the surrounding organs and the placenta. The fetus reacts only to bright rays that can penetrate the layer of skin and muscles of the mother’s body.
How to make contact?
To help your baby learn to recognize faces, here are a few tips:
- newborns focus their gaze in a vertical position and wait until the child concentrates;
- the face or object must be within 20-25 cm;
- the voice should be calm and quiet, you must smile and actively use facial expressions;
- toys in the cradle should be located in the foot area or on the side of the crib.
Such actions will help to get the baby's attention. Newborns begin to hear early, so a high pitch of voice can provoke a negative reaction. When a child begins to recognize his mother or father, he smiles or laughs.
Why do newborns' eyes cross?
When a newborn 1-2 months old begins to squint his eyes, this is normal. At this time, their visual organs are not coordinated, so it is difficult for the child to control them at the same time. Children's eyes are characterized by intermittent movements.
When trying to look at an interesting object and in strong concentration, one or both visual analyzers may shift to the bridge of the nose.
If the eyes diverge in different directions, then this indicates the development of a pathological process:
- congenital disease;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- birth trauma.
For prevention, you need to visit a pediatrician. A doctor should conduct an examination if the child's strabismus gets worse or does not go away for a long time.
Stages of development after birth
Vision and hearing are formed gradually, going through various stages of development. After birth, the child does not perceive three-dimensional objects and does not remember the tone of voice. He reacts only to simple stimuli:
- light and noise sources;
- large size objects.
The baby does not notice differences in color.
Newborn
Vision is fragmented, causing the infant to see only isolated images and images. Afterwards, vision is narrow, so the child does not observe small things located on the sides of the body. A newborn can distinguish between two objects if only one is shown to him. The image received from both eyes is not combined into one picture.
The child reacts to bright light sources, cries and screams. He hears people's voices that seem loud to him. Any sounds irritate the delicate ear.
3 weeks after birth
The child adapts to the world around him. At this stage of development, he does not distinguish between colors and intonations in the voice. Children constantly squint, trying to get used to the lighting. They see objects in a two-dimensional plane. Farsightedness is observed, so the baby cannot distinguish objects at a distance of 40 cm.
1 month
The baby learns to distinguish between white and dark shades, reacts to the absence or presence of light sources. Objects are perceived vaguely, of the same color range. On the 30th day, visual acuity increases 2 times. The gaze glides over the surface of objects. The child learns to recognize intonation in the voice.
2 months
Children begin to see objects at a distance of up to 80 cm. They are interested in large objects of a uniform shade that they can concentrate on. In this case, objects should not move.
3 months
At 12 weeks of life, the baby is interested in simple geometric patterns. Children look at faces, but do not remember what they see. Infants begin to follow moving objects.
4-5 months
At this time, the child begins to distinguish the distance between objects. It focuses the gaze on both near and distant objects. Lateral vision is actively developing. If children detect movement in the periphery of the visual field, they turn towards the moving person or object.
The baby distinguishes red and yellow colors, but does not distinguish shades by their depth.
Thanks to the development of visual memory, the child remembers the emotions on the faces of his parents, their gestures and clothes.
6 months
Binocular vision allows you to combine the visible image of both eyes into a single whole. In addition to lateral objects, children are good at distinguishing objects located in front of them. The child has good control of the lens and is attracted to bright shades and depth of color. Children look at contrasting images and complex drawings for a long time.
7 months and older
During this period, memory is actively developing, so the child actively reacts to his name. Infants are able to associate the name of an object with its visual shape. Babies begin to see clearly, and visual acuity stops changing. The eyes are fully formed and must fully convey visual information.