Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations of dacryocystitis in newborns are externally similar to the signs of another purulent eye disease - conjunctivitis:
- In the second week of the baby's life, purulent discharge from the eyes appears.
- Pus is released from the lacrimal openings if you press lightly on the area where the lacrimal sac is located.
- The conjunctiva and skin at the inner corner of the eye turns red.
- The eyelids swell and swell.
- Tears flow from the eyes even when the child is not crying.
- When the baby wakes up, his eyelashes are stuck together.
- Such manifestations can occur in both eyes at once, or in one.
How to get rid of the problem
Treatment for this disease is carried out in the following ways:
- Massage of the tear duct. Its goal is to destroy the obstacle that physically blocks the outflow of contents from the lacrimal sac. As soon as patency is restored, the liquid can flow out and the process will begin to decline.
- If this cannot be achieved through massage, you will have to resort to probing. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The probe is designed to break through the film or “break through” the plug blocking the nasolacrimal duct. Usually one manipulation is enough; in exceptional cases, repeated probing is required.
Massage for dacryocystitis in newborns is performed in the following way:
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- Treat the massage area with an aqueous solution of Furacilin, carefully removing all accumulated secretions.
- Place the pad of your index finger on the inner corner of the eye.
- Very lightly pressing on the place of the lacrimal sac, gently stroke the area of the eye, as if trying to remove a blockage in the duct. This action will help open the canal and allow accumulated fluid and pus to drain out.
- Up to 8 hikes of approximately 10 movements are done daily.
- All fluid and pus released during the procedure must be removed with a soft swab soaked in Furacilin solution.
- The procedure is completed with antibiotic eye drops, which should be prescribed to the child by a doctor.
Dr. Komarovsky emphasizes that such treatment should not frighten parents; without it, the consequences can be much more dangerous and painful. Advanced dacryocystitis can lead to the following consequences:
- Phlegmon of the century.
- Abscess or phlegmon of the orbit.
- Phlegmon of the lacrimal sac.
- Panophthalmitis is an inflammatory process with abundant formation of pus, developing throughout the entire eye and leading to loss of vision.
- Secondary meningitis, that is, inflammation of the meninges resulting from the transfer of infection from the eye area.
All these consequences are very serious and it is in the interests of the child’s health to avoid their development in every possible way.
Therefore, it is important to contact a pediatric ophthalmologist in a timely manner at the slightest suspicion of dacryocystitis, and then carefully and carefully follow all his recommendations and instructions.
Causes of dacryocystitis in newborns
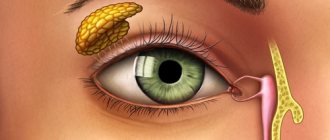
| 1. Lacrimal canaliculus (8 mm) 2. Ampoule (2 mm) 3. Lacrimal sac 4. Nasolacrimal canal (12 mm) 5. Orifices of the nasal canal |
Obstruction of the nasolacrimal ducts in a child develops if, after the birth of the baby, the special thin membrane that protected the eyes from the penetration of amniotic fluid during intrauterine development does not rupture. The unnecessary film interferes with the normal outflow of tear fluid, it stagnates, infection occurs - as a result, purulent inflammation of the lacrimal sac is formed (dacryocystitis).
What is dacryocystitis
The disease occurs when the tear duct is blocked in newborns. This is an inflammatory process caused by the accumulation of fluid in the lacrimal sac. Microorganisms settle on the nutrient moisture and begin to rapidly develop. The fluid turns into pus, and the surrounding tissues and the lacrimal sac itself become severely inflamed.
It is impossible to prevent the formation of obstruction of the lacrimal canal in a newborn child, but preventing the development of dacryocystitis is quite possible. To do this, young parents must follow the recommendations of experienced pediatricians and perform a simple massage from the first days of the baby’s life. If the disease does begin, you need to seek medical help as soon as possible and begin proper treatment.
How is dacryocystitis in newborns treated?
In some cases, the problem resolves on its own by the end of the second week. But sometimes a protective film remains on the eyes - and here the help of a pediatric ophthalmologist is required. It is important to carry out treatment in a timely manner so as not to provoke a serious complication - phlegmon of the lacrimal sac, which can lead to the formation of fistulas.
For treatment, massage of the lacrimal canal may be prescribed. The doctor teaches the parents the technique, and then they perform the massage themselves, at home. Special massage movements are designed to increase pressure in the nasal ducts, causing the embryonic membrane to rupture. The massage is performed every day four to seven times. And in the second or third month of the child’s life, the obstruction disappears.
The massage is complemented by the use of drops that relieve inflammation.
Treatment of dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis can often be confused with conjunctivitis, so you should never treat a child yourself. As soon as you notice the above symptoms, consult an ophthalmologist immediately. It is very important that an accurate diagnosis is made and the necessary course of treatment is prescribed.
Treatment of dacryocystitis must begin immediately after an accurately established diagnosis. In most cases, antibacterial and drug therapy, lavage of the lacrimal ducts and jerky massage of the lacrimal sac from top to bottom are prescribed, which allows breaking through the connective tissue barrier of the nasolacrimal duct. If after 7–10 days the child has not recovered, the doctor will refer you to a procedure for probing the nasolacrimal duct . If there is no positive effect, the probing is repeated after some time.
Of course, the success of any treatment depends on timely diagnosis of the disease. The earlier dacryocystitis is detected, the easier it is to deal with it by washing and the less often you have to resort to probing.
What if massage didn't help?
When the appointment of a massage does not give the desired effect by the age of two or three months, additional diagnostics are required. Based on its results, probing of the nasolacrimal duct may be prescribed, and in some cases, repeated probing of the nasolacrimal duct.
The doctor at our clinic first explains to parents how probing of the nasolacrimal duct is done for children. This is a minor surgical procedure that is performed under local anesthesia and takes five to ten minutes.
- The doctor puts painkilling drops into the child's eyes.
- Then a special instrument, the Sichel probe, is inserted into the lacrimal ducts. This allows the lacrimal openings and nasolacrimal ducts to expand.
- A longer Bowman probe is then used and lowered to the required depth to break the no longer needed film.
- At the end of the operation, the canal is washed and disinfected.
As practice shows, up to the age of eight months, this procedure is 99% effective. If nasolacrimal duct obstruction persists in children, repeat probing of the nasolacrimal duct in newborns may be performed.
If your doctor suggests that you undergo such a procedure, you should listen to the recommendations, since obstruction can lead to serious consequences.
Sounding is carried out at the Optic Center clinic at 40 Let Oktyabrya, 15/1. or you can make an appointment with the clinic administrators by phone, or by calling the toll-free number 8-800-775-78-58
Sign up for a comprehensive examination
How to massage
First of all, you need to prepare for the massage. To do this, the mother or another person should thoroughly wash and rinse their hands to remove alkali many times so that soap residue does not get into the baby’s eyes. Then, as far as possible, cut your fingernails short, warm your palms and fingers so that the child feels comfortable and pleasant from the touch of his mother’s fingers. The finger that will be used for massage should be lubricated with baby cream or oil. It is better to remove excess cream with a napkin. Babies have delicate skin, so all these precautions are completely justified.
Massage in the initial stages of dacryocystitis will allow you to recover as soon as possible.
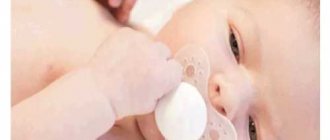
In addition to the mother, the child also needs to be prepared. First of all, the eyes are washed and cleansed. For better disinfection, cotton pads, which will remove purulent and mucous secretions, should be kept in a solution of chamomile or other herbs (chain, calendula), and if an allergy occurs, then in a solution of furatsilin.
Then a cotton pad soaked in a herbal solution is drawn from the outer edge of the eye to the inner. The same should be done with the other eye, but at the same time change the cotton pad.
Even if the other eye does not fester, it should also be instilled so that the infection does not spread from the diseased eye to the healthy one.
In addition, you can wash the eyes, in other words, a little herbal solution or furatsilin is instilled into each eye. Children do not like such procedures, so all this should be done quickly. The baby's head should be placed on its side and quickly drop one or two drops of the solution and make sure that the liquid flows to the spout. If there is no discharge from the eyes, then this procedure can be skipped.
Then comes the massage itself. The baby should be placed on a flat surface, such as a changing table or mattress. Some mothers have gotten used to putting drops in their baby's eyes while breastfeeding.
In order to properly perform a massage, you must:
- Select the finger that will be used for the massage. Some mothers find it convenient to massage with their index finger, while others choose the little or ring finger. With this finger, pressing lightly, you need to feel the dense lacrimal sac, which is located between the eyebrow and the corner of the eye.
- Fix this position and use sliding movements to apply light but noticeable pressure from the eye to the nose. The procedure should be repeated five to ten times. Such movements will lead to the disappearance of the blockage and ultimately to complete rupture of the membrane.
- After the procedure, apply the drops prescribed by the doctor to the child’s eyes.
Surgical intervention
If dacryocystitis was diagnosed after six months, then it is almost impossible to eliminate it with massage. In this case it is prescribed:
- Probing is a simple and painless procedure for the child, performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. It takes no more than 15 minutes, during which the ophthalmologist inserts a special probe into the nasolacrimal canal, removing the resulting plug. After this, rinsing with antiseptic solutions is carried out. In 70% of cases, a single probing is enough to completely eliminate the problem, and in 30% a second procedure is required.
- Surgical intervention prescribed in the absence of a therapeutic effect from conservative treatment and probing. As a rule, it is necessary for serious physiological pathologies and the chronic stage of dacryocystitis. Low-traumatic laser dacryocystorhinostomy is indicated for infants. Most often, the operation is performed through the nose, which avoids an unaesthetic scar on the face.
Dr. Komarovsky claims that any surgical interventions should be performed only if massage does not bring relief even after a two-week course. You should not avoid probing, as it will subsequently eliminate the risk of developing serious inflammatory processes. In addition, the sooner this is done, the less discomfort the child will feel during the manipulations performed.
Dacryocystitis in children (newborns)
Dacryocystitis during infancy is extremely dangerous, as it can provoke purulent-septic complications from the subcutaneous tissue of the face and soft tissues of the orbit. Of particular concern are possible brain injuries (purulent encephalitis, meningitis, brain abscess).
Congenital dacryocystitis does not depend on the sex of the child and occurs in 1 to 6% of all newborns. Violations are most often associated with impaired patency of the nasolacrimal duct. Ophthalmologists consider the valve of Hasner to be one of the key causes of congenital dacryocystitis. It is located at the exit to the nose and is covered with a film of embryonic tissue before birth. Normally, it resolves in the first months after birth, but sometimes this does not happen and blockage of the nasolacrimal duct occurs.
Fortunately, neonatal dacryocystitis does not occur in all cases of blockage. This gives reason to believe that there are additional factors in the development of pathology, such as neonatal infection, etc.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis
Acute dacryocystitis has a number of symptoms. The patient experiences severe redness of the skin, and a painful swelling appears in the area of the lacrimal sac. The swelling causes a narrowing or complete closure of the palpebral fissure, and the patient's temperature rises sharply. In the acute course of the disease, jerking pain in the area of the eye orbit and obvious signs of intoxication of the body may appear. Over time, the swelling can transform into an abscess, which spontaneously “opens up” (pus leaks out).
The chronic form of dacryocystitis is more typical: increased lacrimation and quite noticeable swelling in the affected area. If you press lightly on it, a mucopurulent or purulent secretion appears. If you ignore the disease, dacryocystitis in chronic form can provoke a series of related diseases: blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, etc.