The essence of the reflex in children
The Moro reflex - in simple words, the fear reflex - is one of the innate unconditioned reflexes in a child in the first months of life. Normally, by the age of six months the reflexive reaction to a potential threat is completely replaced by a conscious response.
The essence of the reflex is the baby’s response to a loud sound that is unexpected for him in the form of throwing up and spreading his arms wide to the sides. At the same time, the fingers of the hand are extended, and the pose is maintained for several seconds. After this, the hands return to their original position, the fists clench again, and the child tries to assume the fetal position.
Note! Such testing often provokes the baby to cry, which is completely normal.
Why do reflexes change?
A reflex is the body’s response to a specific stimulus. By their severity and strength one can judge the state of the baby’s nervous system. Normally, the Moro reflex is observed from birth. If it is expressed unevenly, one side reacts more brightly than the other, hemiparesis is suspected. This is a pathological lesion of the nervous system on the part of one hemisphere, leading to weakness in the arm and leg, up to the complete impossibility of independent movements. If a traumatic brain injury occurs during childbirth, then automatism is absent immediately after birth; in a mild form, it may appear after 1-2 days.
The Moro reflex changes in intracerebral hypertension. The higher the intracranial pressure, the less pronounced the automatism, sometimes it becomes incomplete: when hitting the table, the baby spreads his arms slightly to the sides and immediately returns them back.
With pathology of the nervous system, not only long-term preservation of automatism is observed, but also its appearance at the wrong moment. It can appear during normal manipulations, during crying and restlessness of the baby.
Reflex responses of newborn children are direct signs of normal functioning of the nervous system. Not only the long-term persistence of the response is dangerous, but also its disappearance ahead of time and a change in activity. Therefore, children who have suffered acute hypoxia during labor and extraction using a vacuum extractor should be observed by a neurologist.
How is the reaction in a newborn checked?
Before testing begins, the child must be completely healthy, reasonably fed and well rested.
The most optimal time is the first half of the day, 1.5-2 hours after feeding.
The reflex is tested in several ways:
- Clap your hands loudly in front of the baby's face.
- The child is picked up, lifted up, and then sharply lowered down.
- The newborn lies on his back. The child's legs are straightened and sharply raised upward along with the pelvis. The response should manifest itself in a similar way if you press the baby’s arms tightly to his chest and then abruptly release them.
- At a distance of approximately 20 cm from the head of the lying child, make a sharp clap on the surface of the mattress.
During any of the listed test options, the child opens his arms wide to the sides with open palms, and then returns them to their original position. The mechanism of action is very similar to the fact that the baby is urgently trying to grab onto someone or something at this moment of perceived danger.
It is best to conduct dynamic testing during a massage or playing with a child. It is definitely worth taking into account the peculiarities of the child’s nervous activity. How bright the reflex is will depend on this. For example, an easily excitable baby will have an active reaction, while a phlegmatic baby may react rather sluggishly, but this is still not a reason to talk about deviations from the norm.
It is advisable to repeat the test periodically for as long as the reflex should be present: until the baby is 6 months old. The best option is once every 14 days.
Reference. The initial purpose of testing is to check the full functioning of the child’s central and peripheral nervous system. The manifested reflex causes a high degree of stress in the baby with the release of adrenaline, rapid breathing and heartbeat.
No matter how comical the child may look, it is strongly not recommended for young parents to use such a test for fun.
Formation of a dynamic stereotype
The nervous system is usually affected by a large number of stimuli, some of which excite, others inhibit one or another activity of the body. Thanks to the interaction of excited and inhibited areas of the brain, each individual reflex does not occur in isolation, but depends on the entire system of nervous processes occurring in the cerebral cortex.
The system of brain processes is dynamic and constantly changing. A certain combination of the same conditioned reflexes becomes reinforced when they are repeated for a long time. I. P. Pavlov called such an established system of conditioned reflexes, carried out in a certain sequence, a dynamic stereotype
. When a dynamic stereotype is formed, actions each time leave a kind of trace, just as a person walking across a field always leaves behind a barely noticeable path of trampled grass. As soon as a second person follows one person, then a third, the grass gets crushed more and more, the barely noticeable path turns into a path. It is always easier to follow the beaten path than on virgin soil.
It’s the same in the nervous system - if a new impulse runs along an already “laid” path, it will strengthen and expand the existing nerve trace.
The formation of a dynamic stereotype is possible as early as 4-5 months, which greatly facilitates the child’s response to the surrounding external conditions. A child who has learned, through strict adherence to a routine, to always get up at the same time, make the bed, wash, etc., does this willingly, quickly, easily, without the need for additional explanations or reminders. For example, it is enough to say “now let’s go for a walk!”, and the children themselves, without a reminder, finish playing, put away their toys, run to the toilet, and then begin to get dressed.
Breaking a stereotype caused by changes in living conditions occurs with difficulty and is often accompanied by negative experiences and a feeling of displeasure; The child’s behavior becomes disorganized - he begins to be capricious, becomes disobedient, etc. Therefore, strict adherence to the regime is very important for organizing all educational work in the family and in a child care institution.
The formation of any stable habit is possible only if the child follows the rules of behavior systematically, constantly, regardless of the circumstances. For example, wash your hands before eating not only in the nursery, but also at home, at a party, and regardless of whether an adult is present or not.
Manifestation in a dream in a baby
The Moro reflex during sleep manifests itself in the form of spontaneous twitching and this is a fairly common phenomenon.
Involuntary sudden movements can appear at any, even the deepest, phase of the baby’s sleep.
The reflex can be triggered by loud sounds made by pets, any noise, or a careless sudden movement of one of the parents.
Over time, the baby's violent reaction to external stimuli will fade away more and more, and the reflex will manifest itself only selectively.
Features of the development of higher nervous activity
I.P. Pavlov gave a precise definition of higher nervous activity - this is the activity of the cerebral hemispheres and the nearest subcortical centers.
The activity of the nervous system is carried out reflexively in response to any irritation.
The term “reflex” was introduced into physiology in the 17th century by the famous French naturalist Rene Descartes. At that time, only the simplest reactions were explained by reflexes, and only our famous compatriots I.M. Sechenov and I.P. Pavlov at the beginning of the 20th century proved that they (reflexes) form the basis of all processes occurring in the body of humans and animals. At the end of the last century, I.M. Sechenov, observing the development of child behavior, came to the conclusion that mental development begins in infancy. Russian scientists worked successfully in the same direction - V. M. Bekhterev, N. I. Krasnogorsky, A. G. Ivanov-Smolensky, N. M. Shchelovanov and others.
Reflexes are called
natural responses of the body, carried out through the central nervous system, to external and internal stimuli. Reflexes are of two types - unconditioned and conditioned.
Pathological manifestations
The Moro reflex is also characterized by spontaneous manifestations. Even if any external irritant could not cause such a reaction, the baby can throw up his arms and spread them to the sides. In some cases, this indicates increased intracranial pressure in the infant and requires consultation with a neurologist.
An incomplete reflex reaction is also considered a deviation from the norm: the child only slightly spreads his arms. As a rule, this indicates hypertension. If the baby holds his arms apart for a long time with his fingers open, this is a sign of damage to the central nervous system to one degree or another. And the lower the threshold for the manifestation of the reflex, the higher the likelihood of problems with the central nervous system.
An asymmetric reaction, when the baby moves to the side, for example, only the right arm and right leg, may be a symptom of Erb's palsy or cerebral palsy.
In premature babies or those who have experienced asphyxia during childbirth, the reflex may appear late. With timely treatment measures, proper care and nutrition, the reaction will manifest itself over time.
Description of tonic automatisms
This term refers to movements caused by the child’s unconditioned motor reflexes as a result of changes in body position or touching various parts of the body. The function is directly related to changes in the baby’s muscle tone. There are 10 tonic reflexes, the main of which are:
- Labyrinth tonic;
- Symmetrical cervical tonic;
- Asymmetrical cervical tonic.
These reactions fade away by 3 months of a newborn’s life.
Reflexes show the dependence of muscle tension of different parts of the body on its position in space
At 2 months of age, the labyrinthine reflex is of particular importance, thanks to which the baby begins to hold his head
Labyrinthine
Occurs as a result of a change in the position of the child’s head in space. When the baby is in the “lying on his stomach” position, the toddler’s head drops to the chest or, conversely, tilts back. At the same time, the back arches, the arms fold on the chest and form fists, the legs are tucked towards the stomach. After some time, the baby begins to make swimming movements first, and then moves on to crawling.
Magnus-Klein
Reminiscent of a fencer's pose: if the child's head is turned to the right side, he will bend his left arm and left leg, while extending his right leg and right arm. This reaction is aimed at optimizing the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Neck reflexes
There are 2 types of these reactions:
- ASTR (asymmetric cervical tonic reflex). It manifests itself in the fact that if a child turns his head to the side, the arm on the side of the face extends, the leg bends, and on the other side the opposite reaction occurs (the arm bends, the leg extends);
- SSTR (symmetrical cervical tonic reflex). When the baby bends his head, the upper limbs bend and the lower limbs straighten. If you return your head to its previous position, the opposite reaction occurs.
We determine the reflexes of a newborn ourselves
Each mother observed how the pediatrician performed certain manipulations with the baby, and then made a conclusion about the baby’s health in terms of psychomotor development.
This is not difficult to do at home, you just need to know what reflexes a newborn should have and how to check them. Don't be afraid of unclear names. Mothers, without even knowing it, are daily faced with the unconditional reaction of their baby to certain manipulations.
Reflex reactions of newborns are divided into oral (providing sucking) and spinal (motor).
Oral reflexes:
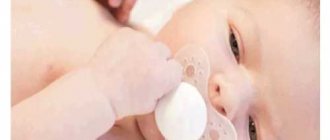
Sucking reflex
All women who have given birth know that immediately after the baby is born, the doctor places it on the mother’s breast. In this way, the main and most important of the unconditioned reflexes of newborns is tested - reflexive sucking. Further, if any object (pacifier or finger) gets into the baby’s mouth, he begins to intensively reproduce the same movements with his mouth and tongue, as when sucking his mother’s breast. The sucking reflex lasts up to 1 year, in some children it manifests itself for a longer period.
Proboscis reflex
The picture is touching when the mother touches the corner of the child’s mouth with her finger (without touching the lips), and the child in response folds his lips into a tube (proboscis). This occurs due to involuntary contraction of the baby’s mouth muscles to an external stimulus. The reflex can be observed for up to 3 months.
Kussmaul reflex (search)
In continuation of the above-mentioned reflexes of newborns, the baby, when touched by a finger to the corner of its mouth, begins to intensively search for the mother's breast. The child opens his mouth slightly and reaches for his mother’s finger. This reflex is observed only up to 3-5 months.
Babkin reflex
It is even more interesting to observe when, with light pressure with a finger on the baby’s palm, he begins to reach out to the person performing the manipulation, while opening his mouth. The baby exhibits a similar reaction in the first 2-3 months of life.
Spinal reflexes:
Defense reflex
It appears already in the first hours of life and is characterized by turning the baby’s head to one side when laying him on his tummy. In this way, nature protected the little man from a lack of oxygen in an uncomfortable position for him.
Monkey reflex (grasping)
Be sure that if the baby grabs something with his small hand, it will be quite difficult to unhook it. This reflex makes humans similar to mammals, whose young cling very tightly to their mother.
Robinson reflex
Continuing the theme of the “tenacious grip,” you can test another reflex: a baby caught in the mother’s fingers can be lifted into the air without fear that it will come unstuck.
Bauer reflex (crawling)
A little person comes into life already able to crawl. It is quite simple to check: lying on his tummy or on his back, the child makes spontaneous crawling movements. And when you put your hand on your feet, the baby will try to push off with your legs from the support that appears. The reflex appears on the 3-4th day of life and fades away only by 4 months.
Support reflex
Being in an upright position and touching a hard surface with its legs, the baby should straighten its legs, and if it tilts slightly, it will try to step over. It turns out that all people subconsciously know how to walk from the moment of birth.
Galant reflex
The reaction of a newborn to holding a finger 1-1.5 cm from the spine is very similar to the fact that the baby is afraid of tickling. Its back begins to bend in the direction along which you ran your finger.
Moro reflex (hug)
When clapping on the bed next to the baby's head, the baby first spreads his arms to the sides, unclenching his fists, and then hugs his body. This is observed up to 4-5 months.
Babinski reflex
When you lightly press on the baby's foot near the II-III toes, the child will bend his toes. And if you run your finger along the outer edge of the foot in the direction from the heel to the toes, then the baby should fan out all his toes on the foot.
Perez reflex
Testing this reflex is the least pleasant of all the physiological reflexes of a newborn, so pediatricians prefer to test it at the very end. The pediatrician, pressing lightly, runs his finger from bottom to top along the spinous processes of the spine. At the same time, the baby arches, raises his head, bends his legs and arms, cries and may even wet himself.
Table of basic congenital reflexes
| Name of reflex, age of manifestation | How to trigger and what reaction is normal |
| Sucking (from the first hours after birth to 3-4 months) | Run along the baby's cheek, insert your index finger into the baby's mouth, or give the baby a breast or bottle - the baby will begin to make sucking movements. |
| Protective (from the first hours after birth to 1.5 months) | Lay the baby on his stomach - the baby will reflexively turn his head to the side. |
| Prehensile (from birth to 3-6 months) | Press something on the baby's palms - the child will wrap his hands around the object or your fingers. |
| Supports (from birth to 1-2 months) | Place the baby vertically so that the baby's legs touch a solid support - the baby will straighten his torso and stand on his full foot. |
| Stepper (from birth to 1-2 months) | Place the baby upright and tilt the child forward slightly - when tilted, the baby will make several automatic stepping movements. |
| Search (from birth to 3-4 months) | Stroke the cheek or corner of the baby's mouth - the child will turn his head in the direction of irritation, lower his lip and move his tongue. If you press on the baby's upper lip, the baby will straighten his head and open his mouth, and when you press on the lower lip, the baby will bend his head and lower his lower jaw. |
| Holding your breath (from birth to 4-5 months) | Place the baby in the water, splash water on the little one's face, or direct a stream of air into the baby's face - the baby will hold his breath for a few seconds and close his eyes. |
| Galanta (from 5-6 days of life to 3-4 months) | Run your hand along the child's back along the spine - the baby will arch his back, and the leg on the side of the reflex call will straighten in the joints. |
| Proboscis (from birth to 2-3 months) | Quickly touch the baby's lips with your finger - the baby will stretch his lips forward. |
| Babinsky (from birth to 1-2 years) | Draw a stroke along the child's sole - the foot will bend on the back side, and the toes will fan out. |
| Robinson (from birth to 3-6 months) | Give the baby thumbs and lift the baby - the baby will tightly clasp his fingers with his palms and hold on. |
| Perez (from birth to 3-4 months) | Run your fingers along the baby's spine (along its spinous processes), moving upward from the coccygeal bone to the cervical region - the baby will begin to scream (the challenge of the reflex is perceived negatively by the baby), raise his head, straighten up and bend his legs and arms. |
| Babkina (from birth to 2-3 months) | Press your thumbs on both baby's palms - the baby will open his mouth and bend his head. |
| Moro (from the first day after birth to 4 months) | Place the baby on his back and hit the surface on both sides of his head, raise the baby's legs together with the pelvis, sharply lower the baby in his arms 20-30 cm down, and then lift him back - the baby will move his arms to the sides and open his fists, after why he will return his hands back as if he was hugging someone. |
| Bauer (from 3-4 days of life to 4 months) | Lay the child on his stomach, and then place your palm on his feet - the baby will begin to crawl spontaneously, pushing off the hand with his legs, but without coordinating his movements (this determines the second name of this reflex - “spontaneous crawling”). |
You can see how to test many important reflexes by watching the following video.
What to do if reflexes are weak?
Some reflexes of newborns do not appear immediately after birth or are manifested to an insufficient extent. There can be many reasons for this: birth injuries, developmental disorders of the child’s nervous system, prematurity, pathologies of the spine (especially the cervical spine), asphyxia
It is important to know that weakening of some reflexes does not always indicate a disease. For example, when the baby is not hungry, when placing the nipple of the mother's breast in his mouth, sucking movements may not occur
In the diagnosis of pathologies of the central nervous system, the presence of spinal reflexes is of great diagnostic importance.
They may weaken or not occur at all in case of serious violations, so mothers and fathers should pay attention to the following points:
- Symmetry of the grasping reflex. If a child squeezes his mother’s finger with only one hand, this may indicate cerebral palsy, paresis, or cerebral hemorrhage.
- The baby extends his arms to the sides (Moro reflex). If abduction of only one arm is observed, this may be a sign of a clavicle fracture or paresis.
- A weakened crawling reflex often indicates a spinal cord injury.
- “Automatic walking” is absent in case of paresis, decreased muscle tone, and cerebral palsy. Such reasons lead to a weakening of the support reflex.
It is important to monitor the position of the newborn's head when turning him on his tummy. The absence or weakening of the protective reflex is considered one of the first symptoms of cerebral palsy
If a mother notices such disturbances in her baby, she should immediately consult a doctor. There is no need to panic: perhaps the parents incorrectly checked for the presence of some unconditioned reflexes.
There is no point in ignoring problems that have arisen and postponing a visit to the pediatrician until later. Remember: only a qualified specialist can assess the condition of the nervous and muscular systems.
An important point is that mothers and fathers know until what age the child retains unconditioned reflexes. If by 5-6 months the extinction of many of them is not observed, you should consult a doctor. Strengthening or the presence of unconditioned reflexes in older age occurs with increased nervous excitability and muscle hypertonicity.
Having learned information about what reflexes a newborn should have, as well as their importance in the development of the child, mothers and fathers will be able to carefully monitor the health of their baby
It is important to remember that often it is by their absence or weakening that pathologies of the nervous, muscular, and skeletal systems can be determined
All that is required from parents is attention, which is an integral part not only in raising, but also in preserving the health of the child.
Formation of new reflexes
Conditioned reflexes begin to form at the end of the first month of life. The child’s motor analyzer and vestibular apparatus begin to work. But such reactions are still quite weak and can easily slow down. This indicates that the cortical structures in a small person are still immature, and excitation in them significantly prevails over inhibition.
By the end of 12 months, the second signaling system is actively developing and its activities are combined with the first. In this case, the first system allows you to analyze and control the reaction to various stimuli coming from outside. Such a system is also present in animals. The second signaling system is formed only in humans when an association of spoken or written words with objects or actions occurs.
Tonic neck reflex
When a child with cerebral palsy turns his head, he can observe an asymmetrical tonic reflex - increased tone of the extensor muscles. It looks like this: in the direction where the child is looking, the arm extends, and at the same time the second arm bends at the elbow. In healthy infants, a subtle asymmetric effect may appear at 3–4 months and quickly disappear. In cerebral palsy, the disease has been studied for several years. This does not allow the child to grow and develop normally: he cannot pick up toys himself, does not focus his gaze on a specific object, and has poor control over his movements. The situation only gets worse with age.
What does a pediatric neurologist examine in newborns?
The first visit to a neurologist includes:
- analysis of the child’s physical development;
- examination for developmental defects and genetic disorders;
- psycho-emotional assessment of the child;
- a detailed survey of parents about neurological problems in family members, how the pregnancy proceeded, about the baby’s behavior, and complaints from parents.
Naturally, a neurologist checks the condition of the intracranial nerves and analyzes all the reflexes inherent in infants, including the Moro reflex.