08/21/2017
Small children not only grow quickly, but also develop by leaps and bounds. Babies discover new movements suddenly for themselves - and very unexpectedly for their parents. And most often this happens when the mother goes to the kitchen to stir the soup, leaving the baby alone on the sofa - because it seems to her that the child still does not know how to do anything and therefore will not crawl far. No matter how it is! Therefore, it is so important to provide a child, even a very small one, with a safe developmental space. This means that if you need to leave, the baby should be either in a crib with sides, or in a playpen, or on the floor, from where he will certainly not fall anywhere. And never leave your child alone on the sofa, on the changing table or in the stroller (the latter - if the baby is already learning to sit down and stand up, that is, after he is about 6 months old.
And yet, in almost every family, it happens that the parents, while caring for the baby, are distracted - the phone rang, the kettle boiled. They left the child on the sofa, and he fell! The first step is to figure out whether you should immediately call an ambulance or whether it’s too early to panic.
Signals when you need to call 03 immediately
- If a small child falls and “passes out” (it must be said that infants almost never lose consciousness even with a severe concussion)
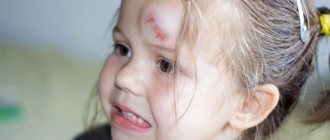
- If you see significant damage (for example, there is an open wound on the head)
- If a child rolls his eyes, he has a seizure
- If he suddenly turns pale, cold sweat breaks out
- If he cries too much, an irritated note can be heard in his voice
- If regurgitation resembles a fountain (vomiting)
- If, some time after the fall, his temperature rises sharply, he becomes very lethargic and drowsy.
- If the fontanel has become convex
All these are signs of a concussion and possible serious consequences of a fall, so you must call an ambulance as quickly as possible, and carry out further treatment in a hospital under the strict supervision of doctors.
Loud crying, taken alone without the other symptoms listed above, is not a criterion that a child’s injury is serious. If the height from which the baby rolled is not higher than the sofa, and there is a carpet on the floor, there is a high chance that the baby was simply very scared - and expresses this by crying.
If a child falls: injuries in children
le> Unfortunately, the baby often ends up on the floor. What should parents do in this case?
Dangerous heights or where a child could fall
A small child is surrounded by care and attention from birth. His loved ones are doing everything possible to ensure that the baby’s health is not in danger. But even the most attentive mother can make a mistake. Sometimes you just need to turn away for a second and the baby is already on the floor.
The fact is that not everyone correctly imagines the capabilities of the baby. Even a newborn child, making chaotic movements with his arms and legs, may well move to the edge and fall, although the likelihood of this is small.
Particularly dangerous places from which a fall can occur for babies under 6 months are the changing table, sofa, and parents' bed. After six months, the baby begins to actively master new movements, learns to sit, crawl, stand on his feet against a support, and then walk.
At this age, he can fall from his crib, from a highchair, from a stroller, etc.?
Most often, when falling, babies hit their heads: up to 1 year of age, the head is the most vulnerable place due to its rather large size and weight in relation to the body. But damage to other parts of the body is also possible. Most often these are bruises, in rare cases - bone fractures or traumatic brain injury (TBI).
If a child hits his head...
Head impacts in babies under 1 year of age are quite common, and they do not necessarily have to fall, because the baby can accidentally hit surrounding objects or furniture while making active movements. In this case, basically everything goes away without consequences: it is not a traumatic brain injury that occurs, but only a bruise. However, when falling from a height, the likelihood of suffering a traumatic brain injury (CHI) increases many times over.
What is TBI?
Traumatic brain injury is mechanical damage to the bones of the skull and soft tissues of the head (brain, its vessels, cranial nerves, meninges).
Traumatic brain injuries include: concussion (mild form of TBI - there are no obvious changes in the structure of the brain, but functional activity may be impaired); brain contusion of varying severity (accompanied by destruction of the brain matter in a certain area, causing severe functional disorders); compression of the brain (severe pathology that occurs against the background of a brain contusion or rupture of a large blood vessel, which leads to the formation of an intracranial hematoma).
In children with typical falls, compression of the brain is extremely rare. To suffer such an injury, a child must fall from a height of at least 2? m or hit a very hard or sharp object.
We assess the situation. Symptoms of traumatic brain injury in a child are not the same as in an adult, which is due to the structural features of the skull and internal structures of the infant’s brain. In some cases, a long asymptomatic course of TBI or, conversely, a violent manifestation of symptoms with minimal trauma is possible. This is due to the flexibility of the skull bones, their mobility relative to each other in the suture area, as well as age-related anatomical and physiological characteristics of the brain. Brain cells in an infant are not yet fully differentiated, i.e. There is no strict division into zones of brain function, which is why the symptoms are most often vague.
When hitting the head, the baby feels pain and redness appears at the site of the impact. In the future, a slight swelling may develop. If nothing else alarms you, there is no need to worry: this is not a traumatic brain injury, but a bruise of the tissues of the head. In this case, you need to give the child a cold compress and calm him down. Cold constricts blood vessels, stopping subcutaneous bleeding, and has an anti-inflammatory and some analgesic effect.
For a compress, a heating pad with ice, a small plastic bottle with cold water, or any cold, non-traumatic object are suitable. It should be wrapped in a diaper or towel, applied to the site of the bruise and held for 10–15 minutes. It is important that the impact of cold is directed strictly at the bruised area - the surrounding tissues should not be affected. If the child does not allow you to hold the compress - he is capricious, dodges - you can moisten a gauze pad, bandage or piece of cloth in cold water and tie it to the damaged area. The bandage should be changed as it warms up within half an hour.
One of the symptoms of a brain injury may be loss of consciousness. But for children this phenomenon is quite rare, and often it does not accompany even severe damage. This is due to the underdevelopment in infants of the cerebellum and the vestibular apparatus as a whole, which are responsible for the coordination of movements. You also have no way of knowing if your baby is experiencing a headache. Thus, the most characteristic signs of traumatic brain injury in an infant are:
- loud screaming as a reaction to pain;
- increased physical activity, general anxiety or, conversely, lethargy and increased drowsiness;
- vomiting, refusal to eat;
- pale skin.
These signs are characteristic of a concussion. For a brain contusion of varying severity (damage to the brain substance itself), the following symptoms are characteristic, in addition to the above (or without them):
- rolling of the eyes, temporary squint or difference in pupil diameter;
- loss of consciousness (this can be assumed if after the fall the baby did not scream immediately, but after one or several minutes).
A child’s consciousness after a fall can be assessed using three signs:
- Opening of the eyes (whether the baby opens his eyes on his own, or to a loud sound, or to a painful stimulus, or does not open at all).
- Motor reaction (here it is important to evaluate the baby’s movements: is there any motor activity at all, does he move his limbs in the same way, is the tone of individual muscles increased).
- Verbal contact (whether the child is walking, smiling, crying, moaning or no voice).
This assessment can be made a few minutes after the fall, when the baby has already come to his senses. Normally, he should move normally, coo (or say syllables) and open his eyes just like he always did.
A dangerous symptom is a temporary external improvement when, after sleep, the child’s external signs of injury that were previously present disappear. But after this, the baby’s condition may deteriorate sharply.
There are also open craniocerebral injuries, when the integrity of the bones of the skull, and possibly the dura mater, is disrupted. In this case, there is a risk of infection of the brain tissue.
Thus, there are many signs of brain injury. Therefore, parents should be wary of any deviation from the baby’s usual behavior. You should consult a doctor in any case if your child falls and hits his head. If everything is limited to a bruise of the soft tissues of the head without other pathological signs, you need to show the baby to a pediatrician and neurologist at the clinic. If symptoms of a brain contusion appear (especially loss of consciousness and lack of reactions to external stimuli - light, sounds), as well as an open head injury, you should immediately call an ambulance.
If the head blow was not accompanied by the appearance of dangerous symptoms (for example, loss of consciousness), the child should be shown to the pediatrician on the same day or, in extreme cases, the day after the injury (you can call a doctor at home or bring the baby to the clinic). If necessary, the pediatrician will refer the baby for consultation to other doctors (neurologist, traumatologist).
Delayed seeking medical help can lead to a worsening of the child’s condition.
Before the doctor arrives
All that the mother can do before the doctor arrives is to calm the baby, put a cold compress on the bruise and provide peace to the baby. If a child has an open head injury, you need to cover the damaged area with a sterile gauze bandage and urgently call an ambulance. If there is an open head injury, cold should not be applied.
When the doctor arrives, he will examine the child and, if necessary, take you and the baby to the hospital for additional tests and treatment.
Diagnosis of TBI
The first step in diagnosis is an examination by a doctor. The doctor evaluates the child’s general condition, his consciousness, the state of reflexes, motor activity, and the integrity of the skull bones. The purpose of further research depends on the preliminary diagnosis after examining the baby and on the capabilities of a particular medical institution. Sometimes just one study is enough to make a diagnosis, and sometimes, if doctors have doubts, they have to do several at once.
If the large fontanel on the top of the baby’s head is not yet overgrown, it is possible to conduct neurosonography in a hospital or clinic - an ultrasound examination of the brain through the large fontanel. X-ray computed tomography (CT) is widely used in the diagnosis of brain pathologies. Currently, CT is the most reliable method for studying the brain.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) does not involve x-rays, but is based on the absorption abilities of magnetic fields. MRI provides higher contrast images of brain tissue than CT. However, CT and MRI are rarely prescribed for infants, since one of the conditions for their implementation is complete immobility of the patient, which is almost impossible to ensure with a small child. These studies for children are possible only under anesthesia if absolutely necessary.
To assess the integrity of the skull bones, craniography (x-ray of the skull) is performed. Ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus of the eye - is an additional research method. It allows you to identify signs of increased intracranial pressure, which is important for diagnosing intracranial hemorrhage or cerebral edema.
Lumbar puncture is a more reliable diagnostic method for suspected intracranial hemorrhage. The cerebrospinal fluid is taken with a needle inserted between the spinous processes of the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae. But during the puncture, the child must be motionless, as there is a risk of damage to brain tissue.
How is TBI treated?
Treatment is prescribed based on examination data and clinical studies. For concussions and bruises of the brain, treatment is usually medication. For a concussion, a child is usually treated at home, and for brain contusions, in a hospital. As a rule, the child is prescribed drugs that have anticonvulsant, antispasmodic, and hypnotic effects. The baby will also be advised to rest for 4-5 days. The word “peace” for a baby should mean the absence of new impressions, limiting the number of people around to mom and dad, maintaining silence in the room where the baby is.
Consequences of TBI
After a concussion, the brain usually recovers within 1-3 months without any long-term consequences. For more serious injuries—brain contusions—the consequences depend on the severity of the injury. They can be different - from dizziness and loss of coordination of movements to increased intracranial pressure and epileptic seizures (convulsions with loss of consciousness).
The result of severe trauma can be psycho-emotional disorders (even dementia) or movement disorders (for example, the inability to make any movements). With open head injuries, there is a risk of infection of the brain tissue (encephalitis) and the development of meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
If the baby didn't hit his head...
The first step is to quickly assess the child’s condition and examine the site of the injury. If you saw the moment of the fall, then finding the place of possible damage will not be difficult. If you were not around, you should, if possible, calm down and carefully examine the baby.
We assess the situation. The site of the injury can be seen by the characteristic redness that appears in the first seconds after the fall. Over the next few minutes, the redness of the skin may increase, as well as the development of swelling, followed by the formation of a hematoma. A hematoma occurs when a large number of subcutaneous blood vessels rupture from an impact, resulting in the accumulation of liquid blood that has a red-burgundy color in the tissues. A small hemorrhage cannot be called a hematoma - it is just a bruise (bruising due to damage to a small number of subcutaneous blood vessels).
When the site of the bruise is discovered, you need to immediately give the baby a cold compress, as described above in the section on TBI.
In a normal course, the hematoma decreases every day, and its color changes. A fresh hematoma is dark red in color, gradually it becomes blue, and then yellow. To speed up the resorption of the hematoma, you can use heparin-containing ointments, which prevent blood clotting and, therefore, have a resolving effect, or make an iodine mesh, which has a similar effect.
Parents should be alert to the sudden appearance during the healing period (in the first 2-3 days after the injury) of redness of the skin over the hematoma, general malaise of the baby, rise in body temperature, increasing pain at the site of the injury (the child in this case will begin to show anxiety, and when touching the place hematoma will react with a sharp loud cry). All this may indicate suppuration. In this case, the baby should be urgently taken to the surgeon. He will open the hematoma so that the purulent contents can flow out and apply a bandage.
If after a fall the hematoma continues to increase in size, you should also urgently consult a surgeon, as this may indicate ongoing bleeding. If the baby remains restless despite a visible bruise, it is better to consult a doctor, since the baby may have a bone fracture. This phenomenon occurs in young children more often than a fracture. You can suspect a crack if swelling appears at the site of the impact, and also if the baby starts crying when you try to move his injured limb.
When examining the site of the impact, it is important to determine whether there is a fracture. Its signs: severe pain at the fracture site; if a limb is broken, it will be very painful for the baby to move it; severe swelling and bruising at the fracture site; change in the shape or length of a broken limb (shortening or lengthening); limited mobility of a limb or, conversely, excessive mobility; crunching sound when moving the injured limb.
If one or more of these signs appears, you should call an ambulance. In this case, the injured area should be immobilized if possible, for example, with a stick or plank tied with any piece of fabric to the broken limb. If the child cannot calm down due to pain, you can give him a painkiller based on PARACETAMOL or IBUPROFEN in accordance with the age of the baby and the dosage indicated in the instructions for the drug. If there is an abrasion at the site of the injury (this is possible when falling on an uneven floor), you need to do the following:
- wash the wound with soap and running cool water;
- treat the damage with hydrogen peroxide;
- treat the edges of the wound with an antiseptic solution (iodine or brilliant green);
- dry the wound with a gauze pad;
- apply a sterile bandage: cover the injury site with a sterile napkin (it can be purchased at a pharmacy - the napkin is sold in a sealed package labeled “sterile”) and secure it with a bandage or adhesive plaster. If sterile dressings are not available, you can use a bactericidal patch.
Treatment of fractures
In the hospital, after an examination, the doctor may order an x-ray, and then, depending on the severity of the injury, measures will be taken: Application of a splint - one-sided plaster in the form of a long strip - consisting of several layers of plaster bandage, which is shaped to the damaged limb and fixed with a bandage (for simple fractures without displacement of bone fragments).
The operation lasts several minutes under general anesthesia, followed by the application of a plaster cast (for displaced fractures and comminuted fractures). During the operation, bone fragments are compared, which is necessary for full restoration of function and the absence of complications after a fracture.
When applying a splint, you and your baby will need to visit a traumatologist for examination once a week - provided that there is no redness under the bandage and there is no loss of sensation in the injured limb. (Parents should be alerted by paleness, as well as coldness of the injured limb relative to other parts of the body).
If surgery is required, you and your baby will have to stay in the hospital for 3-5 days so that the doctors can make sure that everything was successful. Then the baby will be discharged home with a cast, and a traumatologist will monitor him on an outpatient basis.
The cast and splint are removed when the bone is completely fused, which can be verified by taking an x-ray. Depending on the location of the fracture, the duration of this period can range from 2 weeks (for example, with a fracture of the phalanx of the fingers) to 3 months (with damage to the bones of the lower limb and pelvis).
Prevent Injuries
As already mentioned, children fall most often due to the fact that parents underestimate their capabilities. Very small, newly born children also fall - most often due to the fact that mothers leave them on the changing table unattended to run for cream or answer the phone call. Making chaotic movements, the baby is able to move quite well, so in no case should you leave even a newborn child alone where he could fall. In order not to be absent while changing a diaper, changing clothes, etc., prepare everything you need in advance. And if you need to answer the phone or open the door, it is better to take the baby with you or put him in a crib. You should not leave your baby unattended on an adult bed or sofa. Although their height is smaller than, for example, a changing table, for a small child this can be enough to cause serious injury.
It is also necessary to raise the side of the bed in a timely manner when the baby learns to roll over. And when the child starts to get up, it is necessary to lower the bottom of the crib - preferably to the lowest level, so that the baby cannot fall out, leaning over the sides.
To be able to leave your baby alone and not be afraid for his safety, you can purchase a playpen or make the floor in the room as safe as possible (remove wires, put plugs on sockets, remove all small and traumatic objects, put locks on drawers that the baby can reach, secure sharp corners of furniture).
Statistics show that very often babies fall out of high chairs or strollers. Therefore, when placing your baby in a high chair, be sure to fasten him with a five-point seat belt. A baby stroller should also be equipped with such belts, and you should definitely use them, even if the baby is constantly in your field of vision. After all, even if the mother is distracted for just a second, there is a risk that the child will fall. And the consequences of a fall, as we have already seen, can be very serious.
How to get rid of swelling and hematoma
If your baby has a bump or bruise on his forehead, but quickly calms down after crying, the fall most likely did not cause serious harm to the baby. Therefore, the mother’s task is not to grab the phone to call an ambulance, and not to allow swelling to develop at the site of the impact. To do this, apply cold to the site of the “bump” or hematoma. Ice wrapped in a towel should be applied to the sore spot for 15-30 seconds and then removed, allowing the tissues to “rest.” You need to apply ice for 5-10 minutes, this will help reduce swelling and prevent a really impressive “bump” from developing. And of course, it is worth scheduling a visit to your doctor (pediatrician, neurologist, traumatologist). You don’t have to run to him right away tomorrow, but it’s worth coming for an examination in the next few days after the fall and reporting what happened.
How to prevent your child from falling out of bed
Parents cannot provide round-the-clock supervision to their baby, especially at night. To prevent your baby from falling out of bed, make sure your sleeping area is comfortable and safe.
The Siena furniture factory offers modern children's beds made of solid wood that ensure healthy sleep. To prevent your baby from falling, choose furniture with high sides. It is suitable for both preschoolers and teenagers.
Beds from the Siena furniture factory are durable, reliable, compact, and do not take up much space. If there are 2 or 3 children in the family, purchase a bunk bed. Don't be afraid that the baby will fall: strong high sides will protect him during the night's sleep.
The furniture factory's catalog contains beds for every taste, taking into account the design of the room. The product styles are so varied that your little one will be delighted with the gift. Buyers of the Siena furniture factory are offered beds with an orthopedic mattress, made in the shape of a house, with windows, ladder structures for climbing to the upper tier, drawers for bed linen and toys, shelves, and a curved backrest.
The Siena furniture factory takes care of customers by offering high-quality products. To purchase the furniture you like, just call and ask the operator to fill out a request. Payment methods and delivery are discussed individually. Deliveries take place on time without delay. We will bring your baby a reliable and stylish bed that will protect him from unexpected falls.
Injury prevention
And even if, at the time of the fall, the child, as you think, escaped with only a slight fright, the baby should be shown to an osteopath. Because even very minor blows and bruises to the head can lead to a very small, invisible displacement of the skull bones. The baby’s skull bones are mobile, soft and pliable, they absorb shock well. This is why “flying” from the height of a sofa in the vast majority of cases does not lead to serious injuries in children, and this is confirmed by the observations of doctors. But in order to prevent further deformation, which can subsequently lead to microscopic displacement of the bones, it is important that an osteopathic doctor examine the child and help solve the problem. After all, this microtrauma in the future can lead to such serious consequences as deformation of the skull, poor posture, malocclusion, etc.
Children in the first year of life are actively exploring the world; they cannot avoid falls, bruises, and awkward movements. Preventive scheduled examinations by an osteopath are an opportunity to promptly recognize possible bone displacements, which inevitably occur as a child grows and develops, and, using gentle and very effective techniques, solve the problem in a timely manner, balance all body systems and help the baby become healthy and harmonious.
The article is located in the sections: OSTEOPATHY FOR ALL TRAUMATOLOGY AND ORTHOPEDICS
What happens when you fall
Almost every child has fallen from a sofa or other surface after reaching 6 months, when he begins to try to sit up or crawl. Mothers, accustomed to the fact that the baby is completely dependent on them, leave the room for a short time - at this moment the fall occurs.
At this age, babies are not able to maintain balance and fall off the sofa upside down when trying to roll over. The center of gravity in newborns moves to the head, it outweighs the entire body, and the child hits his head.
Don’t panic and run headlong to the doctor, because the child’s body is naturally equipped with mechanisms that protect the baby from all kinds of injuries.
The anatomical features of the cranial bones (they are soft and flexible) ensure easy movement of the fetus along the birth canal. Bone structures remain so pliable for up to a year. When falling, the cranial sutures are displaced, gradually returning to their places.
In addition, the infant fontanel protects the brain from concussions and damage. And the cerebrospinal fluid, located inside the skull, prevents dangerous consequences, as it softens and absorbs shock. The volume of cerebrospinal fluid in newborns is much higher than that in adults.
Therefore, in most cases, when a baby falls from the sofa, nothing bad happens. The child simply hits his forehead and begins to shed tears of fear and pain, which quickly pass. This nuisance worries parents more than it threatens the health of the newborn.
But there are situations when the blow is really serious, and the baby needs urgent help. After all, both a fracture and a concussion can happen. Head injuries pose the greatest danger, since they can be asymptomatic in infants.
Is the height of the fall important?
If a child falls out of bed at 6 months, it is not dangerous.
For children, falls exceeding 40 cm from the floor pose a health risk.
Therefore, if you were present during the fall, estimate its height. The landing itself is also important: the consequences will be different if the child fell from the sofa onto the carpet or onto the tiles.
Alarming symptoms
It’s great if the baby feels good after falling from the sofa or getting hit and quickly forgets about what happened. Parents can relax.
| Physical condition, appearance of the injured area | External warning signs | From the side of the central nervous system | From the gastrointestinal tract | Behavior |
| There is a dent on the skull that was not noticed immediately after the impact. The bruised area hurts and bleeds. | The skin became pale, cyanosis appeared around the eyes, lips, and nose. | The baby cries for a long time and is capricious. | During feeding, an infant often burps, and a one-year-old baby vomits repeatedly. | Disadaptation. |
| The lump on the forehead has increased to a huge size, and swelling is observed. | The eyes are crossed. | Speech is inhibited, babbling is absent. | Food and drink are disgusting. | Psychoses. Wants to cry for any reason, even minor ones. |
| The baby does not turn his head and moves his neck with difficulty. | The pupils have enlarged. | The baby cannot fall asleep, he has begun to sleep poorly. | Increased nervousness. | |
| I feel dizzy and have a headache. | There is blood coming from the nose and ears, and there is discharge of a different kind. | After one year, the child complains of double vision. | Inadequacy. | |
| My back hurts. The spinal cord may be damaged. | The temperature has risen. | Limbs go numb. | ||
| After hitting my temple on the corner, a bruise formed on the side. | Short-term loss of consciousness, maladjustment in space. | |||
| It hurts to move your arms and legs. Check the bones for fractures, take an x-ray. | There is drowsiness. | |||
| Limping. | Lethargy. | |||
| When walking, the one-year-old toddler constantly falls. |
All parents, without exception, must be aware of the potentially dangerous symptoms that can be observed in a child who has fallen head down on the back of the head, or face down.
- After the child has fallen, any disturbance of consciousness is observed.
- After falling from a bed or sofa (changing table, chest of drawers), the adequacy of behavior does not correspond to the situation.
- Any changes in speech.
- The child became excessively sleepy.
- The injury caused a headache that did not go away for more than two hours.
- Convulsive manifestations.
- Vomiting occurs more than twice.
- After a child hits, there is a lack of coordination of movements, orientation in space, and dizziness after more than one hour.
- Weakness in the limbs, the child cannot move a leg or arm.
- After a child hits his head, asymmetry of the pupils is observed.
- Even the slightest disturbance in the functioning of the sensory organs can be a symptom that the injury received is dangerous.
- If a child hits his head and there is any kind of fluid discharge from the ears and nose, including bloody discharge.
- Nose bleed.
- Bruises around the eyes and ears.