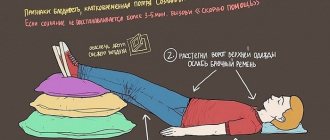
How can your child get a head injury?
The nervous system of children develops gradually.
At first, the child learns to hold his head, roll over, and then begins to better manage sweeping arm movements. At six months the baby begins to sit up, crawls, and a little later unsteadily stands on his legs. Of course, this is a joyful moment for parents when their beloved baby takes his first steps. These steps most often end in a “squat” on the butt, and the baby does not want to take the initiative for several more days, since the first fall made him afraid. When this moment is forgotten, the baby tries again, and everything works out great for him.
But the parents’ joy quickly gives way to fear for their child. After all, the steps turn out to be very uncertain, the baby tries to fall on his side, sit down, or shifts his center of gravity so forward that it seems that he is about to fall and hit his forehead or nose.
Children feel especially insecure when standing on a soft surface. Therefore, people often seek medical help after falling off the couch. In addition, from the moment you take your first steps, you will learn that there are corners in your house, of which there are a huge number. They are very dangerous because they are at the level of your child’s head, and most often children hit their temples on the corner of one of the pieces of furniture.
Even small children pull on themselves all the things that they cannot see well, but which their palm can reach. And these are not always soft plush toys. Kids pull together vases, laptops, lamps, stacks of books and directly “catch” them with their heads, which then form bumps and bruises.
Due to poorly developed orientation in space, poor interaction between parts of their body and surrounding objects, children constantly stumble, cling to surrounding objects, and their legs become entangled, which undoubtedly causes them to fall to the floor.
The baby may fall off the changing table when he learns to roll over onto his tummy.
NEVER leave a baby lying on the changing table unattended, do not turn away from him even “for a second”, because it is at this moment that the baby will roll over on his tummy and fall from a height of a little more than one meter. Considering that the heaviest part of the baby is the head, this is where he hits first!
Alarming symptoms
It’s great if the baby feels good after falling from the sofa or getting hit and quickly forgets about what happened. Parents can relax.
The following signs become a reason to panic and call a doctor (Important! The table can be scrolled left and right):
| Physical condition, appearance of the injured area | External warning signs | From the side of the central nervous system | From the gastrointestinal tract | Behavior |
| There is a dent on the skull that was not noticed immediately after the impact. The bruised area hurts and bleeds. | The skin became pale, cyanosis appeared around the eyes, lips, and nose. | The baby cries for a long time and is capricious. | During feeding, an infant often burps, and a one-year-old baby vomits repeatedly. | Disadaptation. |
| The lump on the forehead has increased to a huge size, and swelling is observed. | The eyes are crossed. | Speech is inhibited, babbling is absent. | Food and drink are disgusting. | Psychoses. Wants to cry for any reason, even minor ones. |
| The baby does not turn his head and moves his neck with difficulty. | The pupils have enlarged. | The baby cannot fall asleep, he has begun to sleep poorly. | Increased nervousness. | |
| I feel dizzy and have a headache. | There is blood coming from the nose and ears, and there is discharge of a different kind. | After one year, the child complains of double vision. | Inadequacy. | |
| My back hurts. The spinal cord may be damaged. | The temperature has risen. | Limbs go numb. | ||
| After hitting my temple on the corner, a bruise formed on the side. | Short-term loss of consciousness, maladjustment in space. | |||
| It hurts to move your arms and legs. Check the bones for fractures, take an x-ray. | There is drowsiness. | |||
| Limping. | Lethargy. | |||
| When walking, the one-year-old toddler constantly falls. |
Important! The cause of falls for newborns is often the inexperience and negligence of young parents. For a baby, ordinary household objects pose a danger: a changing table, a sofa, a wooden cabinet, a cast-iron radiator, a tiled floor, even a low step. You need to monitor a child starting to take independent steps and a helpless baby 24 hours a day.
This is what Dr. Komarovsky thinks about head injuries. Watch the video:
Features of the structure of the child’s skull and brain
- In the first years of life, infants' head size rapidly increases. This expresses the disproportion of growth;
- any slight trauma to the skin can cause serious damage, because the child’s stratum corneum is poorly developed;
- A feature of the blood supply to the head is a richly developed venous network with many anastomoses. About 18 - 20% of the blood emitted by the heart goes directly to the baby's head. These two factors are a risk of massive bleeding in scalp wounds;
- Due to the fragile attachment of the thin aponeurosis to the periosteum, extensive cephalohematomas may appear. In children older than 6 months, the risk is lower;
- The brain part of the child’s skull is smaller than the facial part. Adolescents and adults, on the contrary, have a more extensive facial area;
- A special feature of babies is fontanelles.
They increase the “reserve space” with increasing brain volume for various pathologies, especially if the child hits his temple. It contributes to a longer “clear interval” in case of hemorrhages in the baby. A sharp bulging and/or tension in the fontanel area is a serious sign! You need to go to the clinic urgently!; - The bones that make up the baby's skull are thin, contain few mineral elements, but are rich in water. Due to this feature, linear or depressed fractures are observed, and not comminuted, as in adults;
- diploic veins, devoid of valves, can contribute to the rapid spread of infection from the wound to the cranial cavity;
- the brain grows rapidly until the age of six, then growth slows down;
- the baby’s brain is better supplied with arterial blood, but venous outflow is difficult due to underdevelopment of the veins after the fontanelles close;
- Nerve fibers are unevenly covered with myelin. First, motor (the child hones his skills in walking, coordination of movements, manipulation of hands with objects), only then sensitive. Therefore, the pain is not felt as much;
- The blood-brain barrier is an obstacle between the brain and infectious environmental agents. In children, it is more permeable, so there is a high probability of exposure to toxic and infectious agents on the nervous system;
- at an early age, in response to injury, swelling and edema of the brain often occurs, which can have serious consequences and need to be supervised by a doctor.
Types and symptoms of head injuries
Head injuries due to falls or collisions with a hard surface can be divided into several groups:
- Light damage . They are not particularly dangerous and go away in a couple of days. These are bruises, bumps or small hematomas. In this case, only the epidermal tissue is damaged, small vessels burst. The child usually quickly forgets about the injury and does not experience severe pain.
- Moderate bruises . Open wounds, deep scratches, abrasions, bleeding. The brain and skull bones are not damaged in such bruises. The baby cries for a long time, complains of a headache, short-term clouding of consciousness, and dizziness. After 1–2 hours, the alarming symptoms disappear, skin wounds heal within 1–2 weeks.
- Severe damage . These are concussions, open and closed craniocerebral injuries. The child loses consciousness after a fall, blood flows from the wound, and in serious cases the skull bones are crushed. Such injuries take a long time to heal and are accompanied by unpleasant consequences for children’s health. A concussion does not fully manifest itself immediately, after 1–4 hours or 1–2 days. The baby's coordination of movements is impaired, the skin of the eyelids darkens, and vomiting is observed.
Important! If the baby falls down the stairs or tubing, does not get up, does not cry, call a doctor immediately. There is no need to raise him unconscious. Wait for an ambulance. The cervical spine may be damaged.
What to do if a child falls and hits his forehead?
- Raise the baby, examine the frontal area for open wounds and changes in the shape of the skull.
- By hitting a sharp object, the baby can receive gaping wounds in the forehead and profuse bleeding. In this case, you should call emergency medical care and at the same time apply a pressure bandage or bandage the head with sterile bandages.
- Until medical help arrives, calm down and don’t panic.
Record changes in the child's behavior, the approximate amount of blood loss, tell the doctor if there was vomiting. You should not give any pills on your own. - Did your child hit his forehead on the corner of the tabletop and a “huge” lump came out? Most often, the name “bump” refers to a subcutaneous hematoma, which could appear when the baby hit his forehead hard and damaged a vessel, but the skin remained intact. Venous blood most often comes out and accumulates under the skin. Depending on the size of the hematoma and the child’s well-being, first aid will differ.
If there is a small hematoma and the general condition of the child is not disturbed, cold water can be applied.
This can be meat or dumplings, which are taken out of the freezer and applied to the baby’s skin ONLY through a clean towel or thick cloth for a short time.
Usually about two to three minutes followed by a break of five minutes.
A cold object can cause excessive cooling of the skin, and the child will get frostbite in addition to a hematoma!
You should seek medical help immediately if:
- the hematoma is large, causing anxiety and crying in the child, the baby does not allow him to touch the damaged area;
- After a short cry and the appearance of a lump, the child quickly fell asleep and does not wake up when attempts are made to wake him up.
Do not manipulate the wounded area yourself, do not apply ointment or pierce it, do not give painkillers and solutions.
In the first few hours after a child hits his forehead, he may experience dizziness and double vision. Younger children will rub their eyes and try not to turn their heads.
Try not to disturb the baby during this period. It is advisable to do without playing games on the tablet and watching cartoons. It is necessary to ensure visual rest and apply a cool compress to the child’s forehead.
How to help if your child hits his nose?
- If the blow starts bleeding from the nose, do not tilt the child’s head back. Why? Because it is necessary to know how much blood the baby lost if the bleeding did not stop for a long time in order to provide adequate medical care and avoid adverse consequences.
- Place on a flat surface.
To prevent your baby from being frightened by the sight of blood, you can insert a sterile gauze pad shallowly into the external nasal passage. There is no need to try to insert the gauze swab as deeply as possible in order to remove it later without additional trauma to the mucous membrane. It is advisable not to use cotton wool or cotton pads, since you will have to “tear off” the cotton pad soaked in blood from the wall of the nose, and the cotton fibers can impair the regeneration (restoration) of the mucous membrane. If a child has blood clotting diseases, it is necessary to contact a medical facility. There, medications will help stop the bleeding. - After the blood has stopped flowing and the child is ready for new feats, do not let the baby overexert himself, monitor his body temperature. There is no need to blow out blood clots or rinse your nose; give the blood vessels time to recover. In the first two to three days after the child hits, thermal procedures - bath, sauna, bathhouse - are undesirable.
What should parents do if their child hits the back of their head?
If your child hits the back of their head, don't panic.
The famous pediatrician E. O. Komarosky points out that when a child falls and hits his head, the parents suffer the most, because many falls are not as serious as they may initially seem. Especially if the baby quickly stopped crying, began to play and even smiles at you, there is no lump at the site of the impact, the shape of the skull has not changed, the child did not vomit, and there was no loss of consciousness.
- Assess the child's condition. If, having hit the back of his head, the baby lost consciousness, cannot calm down for a long time, his nose started bleeding, he stopped responding to you, to rattles, or after a short time his body temperature rose, you need to seek medical help.
- Call an ambulance immediately if you notice clear fluid leaking from your nasal passages or ears, as most likely it is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- Parents must provide first aid to their baby. For example, after falling from the sofa, a child could get away with a slight fright and bruises, without contusions.
First of all, apply a cold compress, which you first wrap in a cloth or cotton towel.
For small bleeding wounds, you should not smear them with iodine solution or “green stuff”; you should also not treat the wound itself with alcohol tinctures or vodka. Using unconventional methods, you can apply a chemical burn, and the wound will take longer to heal with the formation of scars.
It is worth treating the wound with hydrogen peroxide, and wipe the area around (if there is skin contamination) with a swab dipped in an aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine.
If vomiting starts, place your baby on his side. This way, the vomit will not enter the bronchi, and the child will not choke. Call an ambulance immediately!
If, a couple of days after your baby hit his head, moaning and shuddering appear in his sleep, his chin or arms are shaking before falling asleep and immediately after, you should see a pediatric neurologist and undergo an examination.
Rule out spinal injury!
If a child hits his head when falling from a sofa, you should not suddenly lift him from the floor, since during the impact not only the head, but also the spinal table, especially in the cervical region, could be damaged. Pay attention to the movements in your arms and legs. With an intact spinal column, without damage to the spinal cord, the baby makes active movements with his arms and legs, shows where it hurts, and his fingers actively clench and unclench.
If, after a fall, the child’s arms or legs do not move, and when he tries to move them, he cries more, it is necessary to seek medical help to exclude fractures.
What could be the consequences if a child hits his head?
Regardless of whether the baby fell out of bed on his back or hit his forehead on the edge of the table, he must be shown to a doctor.
Symptoms of head injuries can be obvious or subtle, and sometimes they are absent altogether. Even unusual activity of a baby may indicate a serious problem that requires professional intervention. Complications of head injuries can occur several days, weeks and even years after the injury.
How dangerous are head impacts in young children?
A head injury in a child under one year of age is usually not dangerous. In this period
The baby’s brain is protected as much as possible by nature. Due to the relative softness of the skull bones, the dynamic sutures between them and the shock-absorbing properties of the cerebrospinal fluid, serious damage is practically excluded. When a newborn is injured, he may not even notice it. Children over six months old after a blow begin to scream and cry a lot, but most often this is not a reaction to pain, but to an unexpected movement in space. If a few minutes after knocking, the child calms down and continues to behave as usual, this is a very good sign.
Although there is no reason to panic in most situations, it is better not to risk it and visit a doctor. He will assess the patient's condition and check his reflexes. Both a month-old baby and an older baby need rest in any case after an injury. You should not put him to bed, but at least for 1-2 hours you need to give up excessive activity, eliminate exposure to bright light and loud sounds on the child’s body. Despite the degree of protection of the brain in the first year of life, everything possible must be done to ensure that the baby has to hit his head as little as possible.
Symptoms of head injury
Newborns are constantly under the supervision of their parents, the level of their activity is very
limited. This allows you to monitor the baby and notice all cases of injury. When an older child falls and hits his head, it may escape the attention of adults. Sometimes children get so carried away that they simply forget to talk about the injury. A bump on the head from a blow is not the only evidence of an accident. There are several points that should alert you and become a prerequisite for a visit to the doctor.
If a child hits their head, this can manifest itself in different ways:
- a hematoma appears - it looks like a bruise or bump, can cause discomfort to a small patient or be practically invisible;
- there are traces of dissection - in some cases it is a small scratch, in others it is a deep and bleeding cut;
- There are no external consequences, but there are changes in the baby’s behavior and condition – poor coordination of movements, mood swings, nausea and vomiting, different reactions of the pupils, drowsiness and much more.
The baby may fall on the carpet and not react to the situation in any way, and the consequences will be serious. It is better not to risk his health and at the first opportunity to visit a doctor who will eliminate any possibility of complications.
Consequences of a bruise
A blow to the floor or other hard surface can result in open and closed wounds. In the first case, there is a violation of the integrity of the skin, and bone damage may occur. Closed injuries are diagnosed when there is no blood on the surface of the affected area. Contrary to popular belief, the latter scenario is not always less dangerous.
The consequences of a bruise are as follows:
- damage to the skin and subcutaneous tissue - this can be a bruise, bump, cut. A bruise of the soft tissues of the head without bleeding usually has no consequences. The presence of an open wound requires immediate treatment to prevent infection;
- concussion is extremely rare in infants due to natural protective mechanisms. The condition has a characteristic clinical picture and requires medical attention;
- Brain contusion is a serious injury that may be accompanied by a short-term loss of consciousness. A child does not necessarily have a headache after a blow. The development of the condition is indicated by the patient’s sallow complexion, darkening of the skin around the eyes, the appearance of blood from the ears or nose, changes in facial expressions, and deterioration in speech;
- Compression of the brain is another dangerous condition that develops against the background of compression inside the skull. Accompanied by profuse and repeated vomiting. Periods of “enlightenment,” when the baby behaves as usual, are followed by moments of loss of consciousness.
The presence of one of the consequences does not exclude the presence of the others. A cut or bump on a child’s head after a fall does not mean that everything went well. If the patient experiences impaired consciousness, problems with coordination, or a fever, it is necessary to urgently call a doctor.
How does a baby get a bump?
When the head is bruised, the vessels located in the soft tissues burst. Blood collects in the thickness of the skin and a hematoma forms. It can be slightly soft or very dense, in different sizes and colors.
The frontal part of the head has the densest capillary network, so the largest and most voluminous cones are formed in this area. At the same time, they are considered the most harmless, because... The frontal bone is the strongest of the components of the skull. Such formations most often resolve on their own, without negative consequences for the body.
You can find out about the causes of a lump in the back of the head here.
Concussion
It is observed after the child has hit his head hard, and the location of the injury does not matter. This is the simplest of all traumatic brain injuries. It is characterized by a short-term loss of consciousness immediately after the impact or some time after it.
Learn more about how to recognize the symptoms of a concussion in this article.
The clinical picture is accompanied by nausea, dizziness, and vomiting. Due to the mobility of the skull bones and shock absorption, concussions in newborns are extremely rare. In this case, a sign of injury is the baby's restless crying and screaming. The baby may refuse food, burp often, and be capricious for no reason.
The brain does not suffer after the blow that led to the concussion. In it, the functioning of a number of cells is only temporarily disrupted, which leads to the listed consequences. After 2-3 days, the patient’s condition returns to normal, but with this injury, bed rest and rest for 7-10 days are still indicated.
What should parents do if your child hits his temple?
- After the baby has hit his temple, it is necessary to assess whether he hears normally. Pay attention to whether he reacts to sharp sounds, whether he hears rattles or whispered speech.
- If you notice strange behavior in a child after a blow, expressed in a sharp emotional response to any irritation (for example, with a sharp sound or bright light, the baby begins to cry, run to another room or hide; a previously sociable child does not understand well the speech addressed to him, requests or performs actions only after a visual image) it is necessary to consult an ENT doctor and take an audiogram.
- If a child hits his head in the temple area on a corner and loses consciousness, seek medical help immediately. You will probably need a neurosonoscopy if your baby is still an infant. Or MRI of the brain if the child is of primary preschool age. It is necessary to exclude fractures of the temporal bone and hemorrhages in the temporal region.
The temporal lobe is involved in processing information coming from the organs of hearing and vision, and is also responsible for understanding speech and emotional reactions.
What happens if brain dysfunction after trauma is not treated?
- Developmental delay in the child.
- Speech difficulties.
- Frequent headaches.
- Dizziness.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Hyperactive behavior at school.
- Difficulty in remembering new information.
What to do if your child hits his head
Head injuries in childhood are almost inevitable, so adults need to know how to react to them. There is no need to panic; you need to act quickly, clearly and in accordance with the specifics of the situation. If there is such a possibility, it is better to immediately call a doctor or an ambulance, which will eliminate the possibility of negative developments.
First aid in the absence of visible damage
First you need to establish what and what part of the skull the baby hit, and assess his general condition. The affected area begins to swell very quickly; cold should be applied to it. This could be a handkerchief soaked in cold water, a bottle of drink from the refrigerator, or frozen food wrapped in a cloth. Keep the compress for 5 minutes.
After a blow, children often begin to have real hysterics. In most cases, first aid for hitting their head comes down to calming the child. A loud cry is not an indicator of severe pain; most often it is the result of fear. The main thing for parents is to remain calm; this will allow them to quickly find out all the circumstances of the accident and begin providing assistance. After the baby has calmed down, you need to limit his activity for 1-2 days. If the baby falls asleep soon after the injury, he should be woken up every three hours and asked simple questions to exclude changes in consciousness due to serious injuries.
You can learn about the treatment of cephalalgia after a blow here.
When to see a doctor after a child falls
If a child hits the back of the head or temple, this requires mandatory consultation with a professional. In the first case, there is a high probability of brain damage, in the second there is a danger of violating the integrity of the skull bones. There is no need to go to the hospital after every accident, but after a severe impact it is better to do so, even if there are no external signs of damage.
Indications for visiting a doctor or calling an ambulance:
- weakness, dizziness, drowsiness;
- the appearance on the surface of the impact is not a bump, but a dent;
- nausea and vomiting;
- prolonged crying, anxiety and severe agitation of the patient;
- pallor, blue lips, heavy breathing;
- enlarged pupils, their different sizes, squint;
- lethargy of the baby, problems with speech;
- bleeding from the nose or ears;
- large hematoma;
- numbness of the limbs;
- even short-term loss of consciousness;
- memory loss, double vision.
Which doctor you see for an injury depends on the type of injury. If this is a cut or a frighteningly large lump, you can visit a surgeon. The specialist will treat the affected area and check the patient for neurological disorders. When it is necessary to exclude the possibility of brain damage, it is better to immediately go to a neurologist.
Drug treatment
Head injuries that result in brain damage require specific therapy. It is strictly forbidden to give your child medications to relieve headaches after a blow. The drugs are selected by the doctor based on the diagnosis. Their action can be aimed at reducing swelling, relieving pain or inflammation, preventing neurological symptoms, and eliminating nausea and vomiting. Parents may only use hydrogen peroxide to disinfect the wound before applying a bandage.
You can find a list of medications for cephalalgia here.
Medicines to get rid of lumps
To speed up the resorption of the lump, you can use traditional methods and pharmaceutical medicines. A good effect is achieved by treating the surface with a mixture of iodine and medical alcohol - the drugs are taken in equal quantities. You can also buy “Troxevasin”, “Rescuer” or “Troxerutin” gels and heparin ointment at the pharmacy.
Motor disorders (paresis or paralysis if hemorrhage occurs after injury)
The consequences of head injuries are completely different, and, unlike adults, deep trauma is not always worse in children than superficial trauma. The consequences will depend on the area of the injury, whether it is combined with other injuries, the age of the baby, how quickly the parents sought medical help and whether they followed the doctor’s instructions, and the state of the child’s body at the time of the injury or blow.
You know that all children are different, and the injuries they receive are also different. Therefore, after hitting your head, you should not give children painkillers, and also give them valerian or motherwort for a sound sleep. This can change the picture of a serious illness and complicate the care of the child.
What are the dangers of head injuries for a child?
With a traumatic brain injury, brain functions are impaired. Without proper and timely treatment, changes in tissues can be irreversible.
Dangerous consequences of head injuries in children:
- skull fracture, hematoma, internal bleeding;
- neurological disorders - epilepsy, coordination problems;
- retardation in physical and mental development, impaired cognitive functions;
- post-traumatic encephalopathy
- paralysis;
- the consequences of head injuries in infancy can appear at the age of 16, when the formation of the frontal lobes ends, which leads to problems with speech and memory.
The most dangerous consequences are stopping breathing and heartbeat. Pathologies often occur during sleep. Therefore, it is important to monitor the child in the first day after the fall, regularly wake him up, and check his reflexes.