When a child’s temperature rises, parents need not only to resort to the use of antipyretic drugs to lower it, but also to look for the root causes of this phenomenon. After all, a child’s body temperature can increase for a variety of reasons. This could be an infectious disease, overheating of the body, teething, etc. Despite the reasons for the increase in temperature, this phenomenon represents a protective reaction of the body to the influence of irritants. A high temperature in a 10-month-old baby may indicate a variety of reasons, but to find out, you will need to go to the hospital. Parents are allowed to give their child antipyretics at high temperatures, but only the attending physician has the right to prescribe drugs to treat the disease.
Temperature norm
The normal body temperature of a baby is in the range from 36 to 37.4 degrees. During the first 10 months she jumps for many reasons. The norm for an adult is considered to be 36.6 degrees. Around 10-12 months it becomes like this in small children.
If a slight increase in the mark on the thermometer is detected in a 10-month-old child, but at the same time he is calm and eats well, perhaps this is the norm at this point in his development. To determine how many degrees is normal for a child, you can monitor the temperature for several days. Measurements must be taken at the same time.
Many factors influence how many degrees the thermometer will show.
- The place where the measurement is made. The temperature in the mouth or rectum will be slightly higher than in the armpit area.
- Type of thermometer. The most accurate is a mercury thermometer. An electronic thermometer can distort data up to several degrees.
- After eating, bathing, or prolonged crying, the mark on the thermometer can rise up to 38 degrees. After sleep, or when the child is cold, a low temperature is observed.
A change in the indicator on the thermometer is a consequence of stress, overheating, a virus, or teething. It may also increase after vaccination. Do not lower the temperature of a child over 3 months below 38.2 degrees. But this is only if there are no contraindications.
Doctors advise giving antipyretic and antihistamines immediately after vaccination. Vaccinations such as BCG and hepatitis B are not accompanied by fever. Vaccinations against polio rarely give a reaction above 38 degrees.
The danger of high fever for children at 10 months
Pediatricians suggest that extreme heat above 39 degrees in the first year of a baby’s life can lead to the development of irreversible consequences. What exact consequences may arise is not specified, because it can be either a mental disorder or chronic diseases of internal organs. If you do not promptly resort to providing assistance to a baby under one year old, then high fever can become a serious problem that will leave an imprint for life.
In addition to the fact that the danger is hidden in extreme heat, the cause of the disease itself, especially of a bacterial nature, can have a negative impact on health. Changes in the brain can only occur if the temperature rises above 41-42 degrees. A normal fever in a child does not pose a danger to his health, but only if the condition does not stabilize.
It is important to know! If your baby has a low-grade fever of up to 38 degrees for a long time, you should see a doctor for diagnosis. In this case, it is possible that the cause of low-grade fever is serious disorders occurring in the internal organs.
Intense heat above 39 degrees is dangerous because there is a strong overload of the heart and vascular system, which can result in a stoppage. The problem is especially pressing if the baby has been diagnosed with congenital heart disease or epilepsy since childhood, which can certainly lead to serious consequences.
Various temperature levels in children
In the case when the child’s body temperature is above 36.6 degrees, parents begin to worry, but this is not always justified.
In the first days after birth, body temperature is about 38 degrees. By the end of the first month it reaches 37 degrees. But the temperature is not always the same number. Adults see that she is constantly jumping.
Over 1 month, body temperature can rise to 38 degrees after vaccination, when the first teeth erupt, due to a lack of fluid, especially in hot weather.
If the number on the thermometer is above 38.2 degrees, this in most cases indicates that pathogenic microbes have entered the body. But even in this case, a decrease in temperature is not required. Suppositories, syrups and other antipyretics can disrupt the process of natural thermoregulation. A high mark on the thermometer is an indicator of the body's fight against infection.
If the increase occurs up to 38.5 degrees, an antipyretic should be used. Various forms of such medicines are produced for children - suppositories, syrups, drops, solutions.
Differences between elevated and high temperatures
Parents should distinguish their children's temperature readings. Words such as high and elevated have a significant difference. What it is, we will find out further.
Elevated temperature and its meanings:
- Low-grade fever ranging from 37 to 38 degrees;
- Febrile, equal to 38-39 degrees.
Heat:
- Pyretic – 39-41 degrees;
- Hyperpyretic - over 41 degrees.
A high body temperature above 39 degrees is dangerous if the baby develops febrile convulsions and fever. If the thermometer readings rise above 39 degrees, and the antipyretic drug does not have the required effect, then you must immediately call an ambulance.
Causes of increased body temperature
The most common causes of fever in infants are the following.
- Overheat. Babies, especially in the first six months of life, can easily become overheated. You should not put a lot of warm clothes on your child or keep them in the open sun for a long time.
- Infection. In this case, other signs appear - cough, runny nose, drowsiness, moodiness, loss of appetite and sleep. It is not difficult for a mother to understand that the child is sick.
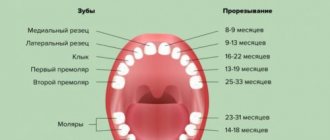
- Teething. During this period, the child constantly scratches his gums with his fingers and pulls all objects into his mouth. The gums become swollen and inflamed.
- Reaction after vaccination. A few hours after vaccination, the temperature rises. The measles, mumps and rubella vaccine causes temperatures to rise to 39 degrees. This is a normal reaction of the body. This level lasts for about three days, in rare cases – up to 5 days. You can bring down the temperature with approved antipyretics. If snot and cough appear on the fourth day after vaccination, we can talk about a bacterial or viral infection.
- Allergy. The temperature remains high as long as the allergen is present. May be accompanied by other symptoms - rash, nasal congestion.
- Stress. After a long cry, overwork, or in the presence of nervous diseases in children of about 10 months, you can observe a rise in the mark on the thermometer.
Body temperature should not be measured every day, as this is stressful for the child. You should use a thermometer in the following cases:
- lethargy, moodiness, anxiety;
- dry mouth;
- temperature fluctuates over several days;
- pulse and breathing became frequent;
- the face turned red;
- if there is chills in the body;
- blurred vision;
- increased sweat production.
In this case, antipyretic suppositories will help. They are harmless and have a quick effect, they are convenient to use.
How to reduce fever in young children
Before doctors arrive, measures should be taken as quickly as possible to bring down the temperature. The following activities are allowed at home:
- drinking plenty of water;
- You can’t wrap your child up too much;
- You should do wet cleaning of the room and ventilate it;
- there should be no bright light, loud or sharp sounds in the room;
- you can make compresses - moisten a sponge with warm water and wipe the child’s body with it (you cannot wipe with alcohol or cold water, as this leads to vascular spasms);
- If you sweat excessively, change your clothes often.
Antipyretic suppositories and syrups must be appropriate for the child’s age. At home, drugs such as Nurofen, Panadol, Ibufen are allowed . You can choose any form of their release - candles, drops, syrups.
The doctor may prescribe Viferon or Genferon suppositories. They have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, and activate the body's protective functions. With their help, you can bring down a high temperature on the third day.
Why does body temperature drop in young children?
The temperature of a baby who is under 10 months old may be slightly low and reach 36 degrees. Even if it reaches 35 degrees, but the child feels satisfactory, there is no reason to worry. If the level drops below 35, you should consult a doctor. Additional examinations will help determine what caused the low temperature.
In rare cases, congenital low temperature is present (always below 36 degrees). The child feels well, so nothing needs to be done.
Low temperature in a child can be caused by various reasons.
- In premature babies, thermoregulation is impaired, so a low body temperature may be observed.
- Less heat is retained during sleep.
- Low temperature is observed with viral diseases.
- Anemia or lack of vitamins in the body leads to weakened immunity.
- A low mark on the thermometer may be a consequence of an overdose of vasoconstrictor nasal drops.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Recent use of antipyretic drugs of various forms (suppositories, drops).
- If the room is cool, then children in the first months of life easily become hypothermic.
What can you do to increase the temperature of a 10-month-old child:
- you need to wrap the child in a warm blanket and give him a warm drink;
- create all the conditions for him to have a good rest and sleep;
- you can do a warming massage;
- taking a vitamin complex.
What is high body temperature?
Elevated body temperature in a child is not an illness at all, but only a symptom of a previous disease. An increase in the norm indicates that the body is beginning to fight the emerging disease. It should be noted here that its increase does not always indicate a disease, for example, teething.
An increase in temperature is a kind of protective reaction of the body that occurs through the influence of various biochemical reactions. When the thermometer readings increase, the immune system fights against the foci of infection that caused the disease.
It is important to know! The temperature rises because the body strives to heal itself, which is normal, and indicates that the child has a strong immune system.
If during illness there is no increase in thermometer readings, but the child becomes pale, dull, weak and inactive, then this indicates serious problems with the immune system. At temperatures up to 38 degrees, the destruction of viruses and infections by the body’s own forces is observed, but if its values exceed the mark of 38-38.5 degrees, then the use of antipyretic drugs cannot be avoided. This temperature indicates that the provoking disease is bacterial in nature, so it is impossible to do without antipyretic and antibiotic drugs.
Parents need to know that elevated body temperature is not a disease at all, but only a sign that the child is developing an illness. The reasons for this phenomenon should be determined by the doctor after examining the baby in the hospital.
It is important to know! If parents notice a deterioration in the child’s condition, then the thermometer readings should be monitored every 15-20 minutes.
When should you seek help?
It is important to consider how many days the high or low number lasts. Doctors' help should be sought when the baby's body temperature, especially under the age of 10 months, is accompanied by other symptoms.
- The disorder occurred in a child less than three months old.
- The appearance of seizures.
- The child's neck becomes tense and difficult to bend forward.
- Severe runny nose, attacks of suffocation, wheezing, wheezing.
- Profuse regurgitation.
- Loose stools with foam and streaks of blood.
- Rare urination, change in urine color.
- The appearance of a rash on the skin.
- Body temperature remains high for more than five days.
- Does not interfere with antipyretics. Suppositories and other medications do not help or last no more than two hours.
- There are chronic diseases of the heart, kidneys or other organs.
- Low body temperature is accompanied by bluish skin, drowsiness, and poor appetite. A low reading on the thermometer in children under 10 months of age can be life-threatening for the child.
It is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of a small child. Features of the structure and functioning of internal organs in infants contribute to the rapid spread of the disease. It is important to recognize the disorder in the early stages in order to prevent serious complications.