What is an allergy test?
- Urgent call to a doctor at home
An allergy test is a common laboratory test that can be used to identify the source of the disease - the allergen, or determine a person’s predisposition to allergies. For this purpose, a specific immunoglobulin test is performed. This analysis can accurately identify allergens that cause an enhanced immune response in the body. To carry it out, blood is taken, which is then mixed with various allergens from contact (household chemicals, detergents), inhalation (pollen, wool, house dust, food for aquarium fish, fungal spores, etc.) and food groups.
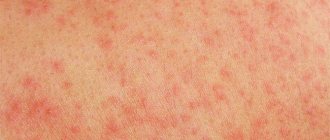
What does a child's allergy look like?
Allergies in a child can manifest themselves in different ways, depending on the cause that causes it and the individual reaction of the body. Common allergy symptoms:
- itching, skin rashes, sometimes swelling;
- nasal congestion, runny nose, frequent sneezing;
- redness of the eyes and watery eyes;
- vomiting, stomach pain or diarrhea.
The most dangerous manifestation of an allergy is swelling of the larynx, which can lead to the child stopping breathing and losing consciousness. Failure to provide timely assistance in such a situation can lead to death.
What is specific immunoglobulin
Specific immunoglobulin, or IgE, is an antibody involved in the development of allergies. They are present in human tissues that come into contact with the external environment - skin, tonsils, adenoids, respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract. Present in the bloodstream in small quantities. When IgE molecules combine with antigens, an immediate hypersensitivity reaction develops. An analysis for immunoglobulins allows you to determine their quantitative content in the blood and, based on the data obtained, draw a conclusion about your predisposition to allergies.
How do you know if children will develop allergies to pets?
Finding out whether children will develop allergies to pets is not easy. The disease begins to develop after contact with the antigen and it may take more than one year before the first symptoms appear. The allergic reaction is caused by a protein that is found on the skin, dander, saliva and urine of animals. In addition, if symptoms that appear on one type of animal are not treated, a cross-reaction may occur and an allergy to other pets may develop.
You can find out about the appearance of cross-allergy by doing molecular allergy diagnostics, which will show which allergens or their components you are sensitive to. By conducting a molecular study, it is possible to predict with a high degree of probability whether a person will develop an allergy to a pet.
If a child did not have allergies until the age of 12-14 years, the risk of developing an allergy to animals is lower than in those children who had allergic manifestations earlier. But it is worth considering that allergies can also develop in adulthood.
Indications for blood tests for allergies
allergy tests if:
– there are clear signs of an allergic reaction that occur seasonally, after eating certain foods or contact with any substances;
– drug treatment of rhinitis, bronchitis (in the chronic stage), conjunctivitis, dermatitis did not bring results;
– the patient has a tendency to allergies due to hereditary predisposition;
– when working in hazardous industries, the patient has constant complaints of cough, rhinitis, conjunctivitis and other symptoms of an allergic reaction;
– it is necessary to determine the state of the immune reaction after the onset of an allergy.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SUGGEST THAT YOUR CHILD HAS ABCM?
Elimination diet
The doctor will first examine your child and ask about any symptoms you may have noticed.
If cow's milk protein allergy (CMAI), also known as cow's milk allergy (CMA), is suspected, your doctor may do certain tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include a blood test, skin prick test, allergy skin test, or an elimination diet followed by a food challenge. It is important not to experiment with a cow's milk-free diet for your baby without the advice and guidance of a doctor. Based on the child's age and the severity of symptoms, the doctor will recommend the most appropriate solution.
The best way for a doctor to confirm or rule out a diagnosis of CM is an elimination diet, which involves eliminating cow's milk proteins from the child's diet, followed by a food challenge in which cow's milk protein is reintroduced. Although BCM is rare in breastfed babies, if you are breastfeeding, your doctor can help you eliminate cow's milk proteins from your diet.
If your baby has an allergic reaction to cow's milk proteins, you will likely notice an improvement very quickly after starting an elimination diet; Most symptoms will disappear within 2-4 weeks and should completely resolve within 6 weeks. If symptoms improve, the doctor will suggest reintroducing cow's milk proteins into the baby's diet in small amounts to see if symptoms appear to confirm the diagnosis. If eliminating cow's milk proteins does not help your baby, then it is unlikely that your baby has CMPA and the doctor will investigate other possible causes for the symptoms observed.
If the diagnosis of ABCM is confirmed, the good news is that with the support of a doctor, AMCM can be managed. The main thing is to contact a doctor as early as possible in order to make a timely and correct diagnosis.
A diagnosis of ABCM should not affect breastfeeding. Mothers are encouraged to continue breastfeeding even when their children have CM. Typically, consultation with a qualified nutritionist is required to completely eliminate all sources of cow's milk protein from the mother's diet .
Find out more about nutrition for ADCM
Study design
As a rule, a blood test to identify allergens consists of three successive stages. First of all, allergy status is diagnosed. It allows you to determine whether the patient has an allergy or not. For this purpose, food, general inhalation, mold tests and an assessment of immunoglobulin E are carried out. If at the first stage at least one positive reaction is detected, then testing with mixtures of allergens is performed. These include food (poultry and meat products, fish, vegetables and cereals, nuts and fruits), as well as inhalation (animal hair and house dust, tree and cereal pollen, mold) groups of substances. If a positive result is established, you will need to take an allergy test again for specific categories.
Is it possible to outgrow an allergy?
It is possible to “outgrow” allergies. By the age of 10, 85% of children no longer have an allergic reaction to milk, egg whites, grains and soy. But often, if a child develops an allergy to peanuts, nuts and fish in early childhood, it persists throughout his life. It is impossible to predict the development of tolerance to allergens. Whether a child will “outgrow” an allergy depends on the type of allergen, the age at which contact with it began, the volume and frequency of the antigen’s influence on the body, and the state of the immune system. Even if symptoms disappear, a predisposition may remain that will require periodic monitoring and examination to avoid the return of symptoms or the occurrence of cross-allergy.
Screening tests
For mixed allergies and other complex cases, a comprehensive analysis is required - a screening method using panels of food and inhalation allergens (from 50 to several hundred items). This is a fast and fairly economical technology that allows not only to compile a list of substances to which the body exhibits an increased response, but also illustrates their combined effects. In some cases, screening tests are performed with a large number of individual allergens. To save costs, a rapid screening with 12 food substances or 12 inhalant substances, or an extended level 1, 2 or 3 test can be performed.
How to cure allergies in a child?
Allergies in a child can be cured after identifying the antigen that causes the hyperreaction. In case of food allergies, it is necessary to change the child’s diet, removing from it all foods that can cause an allergic reaction. At the same time, it is important to choose similar but safe products in order to maintain the nutritional value of the child’s daily menu.
Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor. It may include symptomatic therapy with antihistamines, sprays and ointments. In difficult cases, an allergist may recommend hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs. But in this way, only the symptoms of the disease are eliminated; allergies can only be cured with the help of immunotherapy - this is a long-term treatment that allows you to reduce the body’s sensitivity to allergens.
Timely diagnosis, identification and treatment of allergies can completely get rid of the disease or achieve long-term remission. In this case, the allergy will not affect the child’s quality of life, allowing him to fully grow and develop.
4
2
1
Article rating:
5 out of 5 based on 1 rating
Author: Yatsishena Victoria Anatolyevna
Children's allergist. Highest category. Work experience 21 years.
How to prepare to donate blood
A blood test for allergens is performed during the period of remission on an empty stomach. This is required to ensure that the IgE level is as close to normal as possible. The patient is advised, if possible, to stop taking any medications, including antihistamines. However, such a restriction is introduced only at the request of a doctor. It is not advisable to take allergy tests in acute health conditions (fever, viral infections, gastrointestinal diseases in the acute stage, etc.). Immediately 3-5 days before the test, all highly allergenic foods should be excluded from the diet. Avoid contact with animals whenever possible. You should refrain from smoking 2 hours before the test.
Food allergies in a child - how to prevent them?
Food allergies in a child can be prevented or treated in the early stages of their manifestation. According to statistics, food allergies occur in 4-6% of children. More than 160 foods can cause it, so allergists advise avoiding foods that can trigger an allergic reaction. It is also important to pay attention to the formation of a healthy immune system in the child and to delay contact with possible allergens as much as possible:
- organize proper and varied nutrition;
- do not smoke during pregnancy and in the presence of the child;
- limit the child’s contact with animals;
- use hypoallergenic household items (pillows, blankets, carpets, etc.);
- Ensure cleanliness of the room and regular physical activity.
Also, as a preventive measure for allergies, WHO recommends prolonged breastfeeding for up to 5-6 months and the introduction of the first complementary foods no earlier than 6 months of age. The most powerful food allergens are:
- gluten (found in cereals: rye, wheat and barley);
- fish;
- legumes (peanuts, soybeans);
- lactose (dairy products);
- nuts;
- eggs, etc.
As the child gets older, allergies to certain foods may go away. For example, infants often have allergies to protein and lactose, which disappear in older age. But some allergies don't go away on their own, like peanut allergies.