Causes of pathology
Cystic fibrosis in children is caused by hereditary autosomal recessive type. The reason for the appearance of the CFTR mutation in the hereditary transmission of the gene. The disease affects all organs involved in the production of viscous and thick secretions (sweat, bile, saliva, bronchial secretions, digestive juice). CFTR gene mutations are divided into 5 classes. Depending on the inherited class of mutations, the severity of the manifestations will vary. Classes I, II and III in patients belong to the severe genotype, but IV and V – to the milder genotype. The mutated gene affects the structure and function of the synthesized protein, which leads to the formation of a viscous secretion and disturbances in water and electrolyte balance.
Cystic fibrosis in children has genetic causes, so it is impossible to prevent it if the gene is active in the parents. Statistics say that every 25 people of the Caucasian race are carriers of the mutation gene. If the parents are carriers of the mutated gene, the child has a 25% chance of inheriting it. This indicator includes making a diagnosis. But there is also a 50% chance that a boy or girl will simply be a carrier. In future generations, the damaged gene may manifest itself as active cystic fibrosis.
When to see a doctor
Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis in children is of great importance in terms of survival. Respiratory pathologies appear in infancy or early childhood. Mucus provokes chronic inflammatory processes, which over time leads to damage to the airways and their insufficiency. If a child develops problems of this nature, immediate medical attention and constant monitoring of his health are required. At JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) in the Central District, you can contact a pediatrician, gastroenterologist, and pulmonologist who diagnose and treat this rare hereditary disease. You should immediately consult a doctor in case of meconium intestinal obstruction. This is a kind of constipation, which can later occur in adulthood.
Causes of cystic fibrosis
The CF gene, located on the long arm of chromosome 7, was discovered in 1989. The native protein of the MB-transmembrane regulatory protein (TRMP) gene has not yet been isolated, but its structure and functions have been studied. According to modern concepts, TRBM acts as a “chlorine pump” of epithelial cells of exocrine glands, as well as a regulator of the absorption of sodium ions and the secretion of chloride ions. In CF, dysfunction of the TPBM or its absence leads to increased absorption of sodium ions and decreased secretion of chloride ions. The consequence of this is dehydration (dehydration) of the secretions of all exocrine glands of the body. The secretion becomes thick and sticky, making it difficult to evacuate. Thick secretions (mucus) gradually accumulate and expand the excretory ducts of the exocrine glands with the formation of cavities (cysts). The mucous epithelium becomes dry, the structural components of the tissue atrophy, and fibrosis occurs (normal epithelial tissue is replaced by connective tissue). This leads to secondary changes in the lungs, pancreas, intestines, and urogenital tract. Currently, more than 700 mutations of the CF gene are known. The most common CF gene mutation in children is delF508.
Clinical forms of the disease
Cystic fibrosis forms in children can develop in different ways. There is an international classification of types of disease, but the following are used in clinical practice:
- pulmonary;
- intestinal;
- atypical;
- mixed.
Cystic fibrosis in children manifests itself in different clinical forms depending on the organs in which the disease is localized. In addition to the generally accepted classification positions, there are also the following: pseudo-Bartter syndrome, neonatal hypertrypsinogenemia. Given the large number of forms, the clinical picture may vary. Some of them may combine to create atypical varieties. In the pulmonary form of the disease, the respiratory system is affected and lung function decreases. With intestinal, there is a disruption of the digestive system and insufficient production of pancreatic enzymes. The mixed form is a combination of the first two types, which doubles the manifestation of the overall clinical picture. Atypical cystic fibrosis can be of the cirrhotic and edematous-anemic type.
Classification according to international standards
The World Health Organization and the International Cystic Fibrosis Association have developed a classification that shows typical types of diagnoses. These include:
- chronic pancreatitis;
- disseminated bronchiectasis;
- diffuse panbronchiolitis;
- neonatal hypertrypsinogenemia;
- an atypical type of cystic fibrosis;
- allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis;
- sclerosing cholangitis;
- classic cystic fibrosis with pancreatic insufficiency;
- classic cystic fibrosis with unimpaired pancreatic function.
Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) - symptoms and treatment
Cystic fibrosis is hereditary in nature, so its treatment is mostly symptomatic, it is aimed at restoring the functions of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract and is carried out throughout the patient’s life. It is important for patients with cystic fibrosis to follow a diet, perform a special set of exercises and take medications that prevent the development of infections.
The main goal of treatment for cystic fibrosis is to remove sticky mucus from the airways. To do this, various methods of draining the bronchial tree are used, for example, kinesitherapy - one of the forms of physical therapy that helps cleanse the bronchi from viscous and aggressive mucus.
Kinesiotherapy techniques:
- Deep inhalation and exhalation, allowing mucus to more easily separate from the walls of the bronchi.
- Breathing with resistance from the lips.
- Mobilization - exercises to improve the elasticity of the chest, spine and muscular balance of the body.
Physiotherapy treatment for infants and young children includes both active and passive techniques.
Passive technique:
• the child’s body assumes a certain position for a short time, then changes it;
• accompaniment and stimulation of respiratory movements with the help of hands (contact breathing) - a technique in which the physiotherapist’s hand leads and stimulates respiratory movements;
• manual vibration on exhalation - to support exhalation and help release phlegm, shake the chest with your hand;
• shaking - rhythmic movements performed in one part of the body to cause a reaction in the chest;
• therapeutic body positions - positioning the chest in a state in which the lung tissue stretches and the airways expand.
Active technique:
• influencing breathing, for example through acoustic stimulation - encouraging the child to repeat the loud cries that he makes;
• exercises to develop elasticity of the chest, spine and muscular balance of the body;
• exercises that increase agility, endurance and create pleasure from muscle activity.
Hardware methods play an important role in treatment. “vibration vest” , consisting of an inflatable vest and a pneumatic pulse generator unit, which creates pressure on the chest, has become widespread Such vibrations reproduce the effect of coughing and help clear the bronchi of viscous mucus. Hardware methods are used together with drug therapy [13].
With cystic fibrosis, it is important to follow a diet - food should be high in calories, with a high content of proteins and fats. Food is taken often and in small portions, with additional salt. Food that is difficult to digest is excluded from the diet: coarse fiber, fats from soups, fried foods, chocolate, cakes, pastries. Daily caloric intake should exceed the age norm by 20-40%, mainly due to the increased amount of protein (up to 6 g per 1 kg of body weight per day). Due to impaired pancreatic function, patients do not absorb fats and fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K, so additional intake is necessary.
To facilitate the discharge of sputum, the following drugs are used:
- Ambroxol tablets 30 mg. During the period of remission, the medicine is taken once a day, during an exacerbation of the disease - up to six times.
- Dornase alfa is a genetically engineered version of a natural human enzyme that helps break down purulent sputum. Used with a nebulizer at 2.5 mg once a day.
Bronchodilators are used for inhalation therapy:
- “Berodual” - for one procedure in a nebulizer you need 20 drops of Berodual + 3.0 ml of saline solution. Inhalations are done twice a day in the morning and evening for 7-10 days.
- “Ventolin” - the drug is poured into a nebulizer undiluted, the standard dose is 2.5 ml, no more than four inhalations are allowed per day.
- “Pulmicort” - one procedure requires 1 ml of the drug + 1 ml. saline solution, twice a day in the morning and evening for five days.
It should be borne in mind that in a third of patients, bronchodilators have a positive response, but in the majority, collapse of the airway muscles and a sharp decrease in the volume of exhaled air may occur. In this regard, patients receiving such therapy should be under medical supervision.
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed to all patients with pulmonary symptoms, during exacerbations of the disease or identification of pathogens of respiratory infections to suppress their growth.
Effective combinations of antipseudomonas antibiotics are used for treatment:
Inhalation antibacterial agents: “Bramitob”, “Tobramycin”, “Tobi podhaler”, “Colistin”.
Oral antibiotics: ciprofloxacin, clarithromycin.
Parenteral antibiotics:
- cephalosporins + aminoglycosides;
- antipseudomonal penicillins + aminoglycosides;
- carbapenems + aminoglycosides;
- fluoroquinolones + aminoglycosides;
- cephalosporins + fluoroquinolones;
- antipseudomonal penicillins + fluoroquinolones;
- carbapenems + fluoroquinolones;
- cephalosporins + carbapenems + aminoglycosides [10].
The dose of the administered antibacterial drug should exceed the average therapeutic dose by one and a half times. The course of antibacterial therapy can last up to 3-4 weeks, in case of chronic infection - up to 12 weeks.
To improve digestive function, enzyme preparations are used that contain lipase, protease and amylase, which facilitate the digestion of fats, carbohydrates and proteins, and also promote their better absorption in the small intestine. The selection of doses of pancreatic enzymes is carried out individually based on the clinical manifestations of the disease. The following drugs are used: Pancreatin, Mezim, Creon. Enzyme preparations are prescribed in larger doses than for patients with other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - up to 30 Creon capsules per day.
Treatment for cystic fibrosis is lifelong. The choice of treatment regimen depends on the type of bacteria found in the bronchial secretions of the respiratory tract, as well as on the predominant clinical forms of the disease.
“In recent years, targeted genetic therapy has begun to be used to treat cystic fibrosis, which is aimed at correcting a defect in the most common mutation, F508del [14]. The drug is sold in the United States under the brand name Trikafta. In August 2021, the medicine was approved by the European Commission for use in the EU under the name Kaftrio.” — approx. ed. "Pro-Diseases."
In Russia, original drugs for the treatment of cystic fibrosis are being replaced generics . Generics are similar to original drugs in the composition of the active substance. Many patients complain about their poor quality and side effects. Recently, campaigns have been carried out by patients and parents of cystic fibrosis patients, the goal of which is to return state provision of high-quality foreign medicines.
It is currently difficult to name the side effects of generics, since there are no comparative studies of them with original drugs.
Within the framework of the 44th Federal Law, purchases of medicines are carried out according to the international non-proprietary name. The list of medicines is approved by the government of the Russian Federation. Doctors face liability for prescribing drugs under trade names or purchased by parents and charities. Prescriptions written by a doctor must contain only international names and not trade names. Doctors will be fined for violating this rule.
Although there is one condition: if there are medical indications (allergy, individual intolerance to the generic for health reasons), by decision of the medical commission, the patient can receive the medicine under the trade name. Therefore, the opportunity to obtain an original drug depends on individual intolerance to the generic (which must be proven) and the decision of a medical commission.
Cystic fibrosis is the most common indication for lung transplantation. The main indications for this operation: progressive weight loss, deterioration of pulmonary function, frequent exacerbations, need for oxygen therapy. Contraindications: aspergilloma (tumor-like non-invasive spherical neoplasm, consisting mainly of mycelial cells of a microscopic mold fungus), smoking, psychosocial factors. Diabetes mellitus and treatment with corticosteroids are not an obstacle to transplantation.
Manifestation of characteristic symptoms
Symptoms of cystic fibrosis in infants and older children depend on the type of organs affected. Thick secretion is the main culprit of the processes occurring in the body. When it is in the lung area, blockage of the bronchioles is recorded. This leads to respiratory failure with disruption of normal gas exchange. Then a number of natural negative changes occur. Excessive thick mucus provokes inflammation, the infection continues to develop, reducing the body's defenses. The structure of the bronchial tree gradually changes with the appearance of bronchiectasis. When the pancreas is damaged, the ducts become blocked. It turns out that enzymes necessary for the functioning of organs are released, but they are blocked on the way to the intestines. This pathology occurs most often from the very birth of the child.
Typical symptoms of cystic fibrosis
Signs of cystic fibrosis in children transform depending on age: infancy, preschool, school and adolescence. Clinical manifestations and the rate of their development depend on the inherited genotype of the disease. Cystic fibrosis in infants and its typical symptoms at this age are as follows:
- chronic or recurrent cough and shortness of breath;
- retardation in physical development;
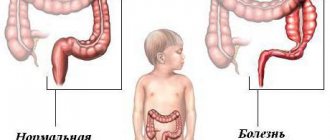
- rectal prolapse and diarrhea;
- neonatal jaundice with a long course;
- oily and foul-smelling stools;
- salty taste of skin, etc.
With age, some symptoms persist and new ones appear. In the preschool period, the following symptoms are observed:
- persistent cough with or without phlegm;
- rectal prolapse;
- retardation in physical development (weight and height);
- chronic diarrhea;
- salt crystals may be visible on the skin;
- chronic shortness of breath;
- deformation of fingers in the form of “drum sticks”;
- low water content in the body (hypotonic dehydration);
- disturbance of mineral metabolism, etc.
At school age, cystic fibrosis in children continues to worsen symptoms. We need constant supportive therapy that can improve the quality of life and reduce the negative manifestations of the disease. Symptoms appear in children with this diagnosis of the following nature:
- chronic sinusitis;
- chronic diarrhea;
- diabetes;
- respiratory manifestations;
- inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- nasal polyps;
- bronchiectasis;
- liver pathologies, etc.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
CF develops as a result of a mutation in the CFTR gene, located on the long arm of chromosome seven. The most common mutation is delF508, a deletion of three nucleotides in exon 10, encoding the amino acid phenylalanine at position 508 of the CFTR protein. In Russia, the frequency of the delF508 mutation is 53%, the second most common is the “Slavic mutation” CFTRdele2.3/21kb, which occurs in 6.4% of the population. The type of inheritance of CF is autosomal recessive.
Changes in DNA structure lead to dysfunction of the CF transmembrane regulator (CFTR). CFTR is a protein that ensures the transport of chlorine ion through the apical part of the epithelial cell membrane. The retention of chlorine anions in the cell increases the absorption of sodium and water cations, “drying up” the mucus produced by the exocrine glands. An increase in the viscosity of excreta leads to clogging of the ducts of the exocrine glands, accumulation of excreta and the formation of cysts. A picture of systemic dysfunction of the exocrine glands develops. Organs are affected if the function of chloride channels in their epithelial cells is impaired. These include: the upper and lower respiratory tract, sweat ducts, excretory ducts of the salivary glands, pancreas, bile ducts, intestines, vas deferens. Due to the blockade of chloride channels, reabsorption of chlorine and sodium ions in the sweat ducts does not occur, which leads to a significant increase in the concentration of these ions in 1 ml of sweat.
Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis in children
Without proper therapy, patients with this diagnosis are doomed. The body is unable to cope with the load created by the thick secretion of the endocrine glands. Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis in children should be early. For this reason, it is included in the mass screening program for newborn children. The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture and tests. JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) in the center of Moscow uses advanced equipment, has its own laboratory and a staff of experienced doctors.
In newborn babies, blood is taken from the heel (Guthrie test) for gene analysis. The results are complemented by a number of other tests. Blood tests are also taken for liver tests, glucose levels, carbon dioxide and oxygen levels to determine the presence of complications in the disease. During diagnosis, collecting an anamnesis is of great importance. If there are risk factors, then an additional analysis is carried out for the presence of digestive enzymes. A sweat test and a genetic test are required to definitively confirm the diagnosis.
Why do a sweat test?
Cystic fibrosis in children can show different symptoms, and a sweat test allows us to examine the clinical picture in more detail. To obtain the material, stimulation is carried out in the forearm area using electrophoresis with pilocarpine. The sweat sample is tested for the amount of chloride (concentration). This test can be performed from a 2-day period, since it shows objective data 48 hours after birth. The difficulty in early diagnosis during this period is the inability to obtain a sufficient amount of sweat for testing. Need >75 mg on filter paper. Before 2 weeks of age, it is not always possible to collect such a volume of material. If the analysis shows positive results, 2 repeat sweat samples will be needed to confirm it. At the age of up to 6 months, the normal chloride level is 29 mmol/l, intermediate - 30-59 mmol/l. Exceeding the figure of 60 mmol/l indicates an abnormal amount of chlorides.
Assessment of pancreas function
Cystic fibrosis in children may show symptoms and signs immediately after birth. Babies initially do not have problems with the functioning of the pancreas. The danger lies in the presence of two “severe” mutations. And the assessment of all factors allows us to determine the level of progression of pancreatic insufficiency. The analysis is based on measurements of fat excretion in feces that are no more than 72 hours old. The concentration of human pancreatic elastase in stool is also monitored.
Additional research methods
Additional methods are used to clarify the state of health depending on the location of the disease and assess the functioning of internal organs. Cystic fibrosis in children exhibits complex symptoms that require correction. Additional research methods make it possible to choose the right path regarding future therapy. They include:
- stool analysis;
- analysis of sputum secreted from the bronchi;
- bronchography and bronchoscopy;
- MRI and radiography;
- spirography.
Symptoms of cystic fibrosis
Symptoms of the respiratory form of cystic fibrosis at an early age include:
- pale skin
- lethargy
- weakness
- low weight gain with normal appetite
- frequent ARVI
- constant paroxysmal, whooping cough with thick mucous-purulent sputum
- repeated prolonged (always bilateral) pneumonia and bronchitis
- dry and moist wheezing, and with bronchial obstruction - dry wheezing.
Treatment of cystic fibrosis in children
Treatment requires complex intensive therapy. This is a team work of doctors from different specialties. Not only pediatricians and endocrinologists take part, but also nutritionists, physiotherapists, pulmonologists, etc. The main goal is to provide maintenance therapy and eliminate acute manifestations of complications. Cystic fibrosis in children may have different clinical recommendations; they depend on the stage of the disease and its form. For each patient, therapy is selected individually. The treatment list includes the following items:
- use of inhaled bronchodilators;
- taking antibiotics;
- taking mucolytics;
- breathing exercises;
- physiotherapy;
- regular physical activity;
- timely immunization, etc.
What is special about the treatment?
The peculiarity of the treatment is the opportunities for a normal life and adaptation. Psychological support, which every patient needs, helps a lot here. As children grow older, they will understand the importance of therapy. With a mild and controlled stage of the disease, many procedures can be performed at home. If there is a fact of pneumothorex, then qualified surgical assistance cannot be avoided. In difficult cases, a lung transplant is indicated. In the intestinal form of the disease, constant intake of enzyme preparations is required for rapid digestion and absorption of food. For the normal functioning of the excretory system, laxatives are indicated. Treatment of cystic fibrosis in children is associated with diet. It should be high-calorie, exceeding needs by 10-15%.
Recovery forecasts
Scientists and pharmacists are constantly working to create new drugs that can normalize the concentration of chlorides in the body and improve lung function. The main goal is to restore CFTR function using corrective medications. At the moment, the hereditary disease cannot be completely cured, but with sufficient medical support it can be controlled. The later the signs of the disease appear, the better the prognosis for the patient. It is difficult to give an accurate prognosis for life expectancy with such a diagnosis. Much depends on the severity of the genotype and the type of its mutation, the rate of occurrence of complications. Treatment of cystic fibrosis in children remains a pressing issue. There are about 3,500 people in Russia with this diagnosis. The average lifespan for uncomplicated stages is 30 years.
How to make an appointment with a doctor
Cystic fibrosis in children is accompanied by medical supervision. If you suspect hereditary factors, the presence of characteristic symptoms and the manifestation of signs, you should seek medical help. JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) provides consulting services to specialists, conducts comprehensive health diagnostics and can offer qualified support for children with severe hereditary diagnoses. The clinic is located in the Central Administrative District and close to the Mayakovskaya metro station, as well as Novoslobodskaya, Chekhovskaya, Belorusskaya, and Tverskaya. Come for routine and preventive examinations at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, building 10. To make an appointment with a pediatrician, you need to call the number.
The clinic employs a staff of doctors of various specialties who help at all stages of treatment of the disease. A special atmosphere of trust creates a comfortable psychological microclimate for young patients. Cystic fibrosis in children has different clinical recommendations for correcting the general condition. A hereditary disease makes changes to the daily routine, constant therapy and procedures are required - these are the main provisions. At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) they work with patients both in inpatient and outpatient settings.
How to confirm the diagnosis?
- Neonatal diagnosis.
- It is performed on newborns in the first month of life. The method is based on determining the level of immunoreactive trypsin (IRT), a pancreatic enzyme, in the blood of a child. In the blood of newborns suffering from cystic fibrosis, its content is almost 5-10 times increased. This analysis is performed if cystic fibrosis is suspected.
- If the doctor suspects cystic fibrosis, he will refer your child for a sweat test, the main test for diagnosing this disease. The test is based on determining the chloride content in sweat fluid. To perform a sweat test, the drug pilocarpine is used - using a weak electric current (electrophoresis), the drug is injected into the skin and stimulates the sweat glands. The collected sweat is weighed, then the concentration of sodium and chlorine ions is determined. For a final conclusion, 2-3 sweat tests are required.
- Tests for pancreatic insufficiency. Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to conduct a coprological study - the feces are examined for fat content. The most accessible and accurate test today is a test for the determination of elastase-1, an enzyme produced by the pancreas.
- Prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Currently, due to the possibility of DNA diagnostics for each individual patient with cystic fibrosis and his parents, prenatal diagnosis of this disease in the fetus is real. Families with a family history of cystic fibrosis who want to have a child are guaranteed the birth of a child without cystic fibrosis in almost 96-100% of cases. To do this, future parents, even during pregnancy planning, need to conduct DNA diagnostics and consult a geneticist. When each pregnancy occurs, you must immediately (no later than 8 weeks of pregnancy) contact a prenatal diagnostic center, where at 8-12 weeks of pregnancy the doctor will conduct a genetic diagnosis of fetal cystic fibrosis. Prenatal diagnosis is essentially the prevention of this disease.