Mechanism of action of the drug
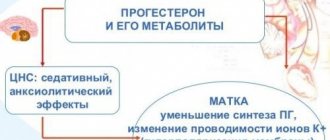
Progesterone, the active substance of Utrozhestan, is identical to the natural hormone produced by the corpus luteum of the ovary. After binding to receptors on the surface of cell membranes of target organs, it penetrates into the cell nucleus and, by activating DNA, accelerates RNA production. The substance causes a transition of the endometrium (the mucous membrane lining the uterine cavity) from the proliferation phase, initiated by the follicular hormone estradiol, into the secretory phase, and after fertilization of the egg has occurred - into a state that is necessary for its normal development. Utrozhestan helps to reduce the contractility and excitability of the muscles of the fallopian tubes and uterus, as well as the formation of a normal endometrium. Activates the development of the end chambers of the mammary gland and induces lactation, provides an increase in fat reserves, stimulating the enzyme protein lipase.
Utrozhestan improves glucose utilization and leads to the accumulation of glycogen in the liver by promoting an increase in the concentration of stimulated and basal insulin. Thanks to the influence of the gestagenic agent, the production of gonadotropic hormones of the pituitary gland increases, azotemia decreases, and nitrogen excretion by the kidneys increases. After administration, progesterone is rapidly absorbed, an increase in its concentration in the blood plasma is noted after 1 hour, and Cmax is achieved after 2-6 hours. When using Utrozhestan 2 times a day at a dose of 100 mg, the average concentration of the substance remains for 24 hours at the level of 9.7 ng/ml.
The vaginal microflora in women consists of many bacteria and fungal organisms. When exposed to negative external or internal factors, their growth increases, which is why various diseases arise, accompanied by pain, heaviness, discharge and itching. Read more in the article: “suppositories for itching in the intimate area.”
Pharmacological properties of the drug Utrozhestan
Pharmacodynamics. The pharmacological properties of the drug are due to progesterone, one of the hormones of the corpus luteum, which promotes the formation of normal secretory endometrium in women. Causes a transition of the uterine mucosa from the proliferation phase to the secretory phase, and after fertilization contributes to its transition to the state necessary for the development of a fertilized egg. Reduces the excitability and contractility of the muscles of the uterus and fallopian tubes. Does not have androgenic activity. It has a blocking effect on the secretion of hypothalamic factors for the release of LH and FSH, inhibits ovulation and the secretion of gonadotropic hormones by the pituitary gland. Pharmacokinetics. Oral administration. An increase in the level of progesterone in the blood plasma is observed from the first hour after oral administration. The maximum concentration of progesterone in the blood plasma is observed 1–3 hours after administration (after 1 hour it averages 4.25 ng/ml, after 2 hours - 11.75 ng/ml, after 4 hours - 8.37 ng/ml , after 6 hours - 2 ng/ml, after 8 hours - 1.64 ng/ml). The main metabolites of progesterone detected in blood plasma are 20α-hydroxy,d4α-pregnanolone and 5α-dihydroprogesterone. The drug is excreted in the urine in the form of glucuronic metabolites, the main of which is 3α,5β-pregnanediol (pregnanediol). These metabolites are identical to the metabolites that are formed during physiological secretion of the corpus luteum. Intravaginally. When administered intravaginally, progesterone is quickly absorbed by the mucous membrane. The maximum concentration in blood plasma is observed 2–6 hours after intravaginal administration and remains for 24 hours at an average level of 9.7 ng/ml after application of 100 mg in the morning and evening. This indicator is identical to the concentration of progesterone, which is noted during the luteal phase. When used in doses above 200 mg/day, the concentration of progesterone is similar to its concentration in the first trimester of pregnancy. The drug is excreted in the urine, mainly in the form of pregnanediol. The metabolites that are detected in urine and blood plasma are similar to the metabolites that appear during the physiological secretion of the corpus luteum.
The role of progesterone during pregnancy
Progesterone belongs to the class of biologically active substances - steroids, the main place of production of which is the corpus luteum of the ovaries. Its daily level in the body depends on the phase of menstruation, the duration of pregnancy, and the use of oral contraceptives. The minimum level of progesterone occurs in the female body at the beginning of the monthly cycle, and the hormone reaches its maximum in the second half, during the release of a full-fledged egg. But now the long-awaited pregnancy has arrived, and progesterone “gets to work”:
- The hormone stops the menstrual cycle, that is, the formation of new eggs, for the entire period of bearing a child.
- Helps the uterus accept (implant) and not reject a fertilized egg in the future.
- Creates conditions for cell division and proper formation of embryonic tissue.
- Influences the emotional and mental state of a woman, preparing her for future motherhood.
- Reduces the activity of the smooth muscles of the uterus to avoid aborted pregnancy.
- Prepares the body for future childbirth by promoting the separation of the pelvic bones and relaxation of muscles and ligaments.
- Activates the growth of the mammary glands, tuning them for the process of lactation.
Throughout pregnancy, progesterone levels continuously rise. If the norm of progesterone during early pregnancy is 12-18.2 nanograms per milliliter, then in the last trimester the normal value will be 132.6-172 nanograms.
Chondroitin and glucosamine are very important substances for musculoskeletal health. That is why drugs containing them are often prescribed to patients with diseases of the joints and spinal column. Read more in the article: “chondroitin and glucosamine: drugs and cheap analogues.”
Why is it prescribed during pregnancy?
Utrozhestan is indicated for women for the correction of diseases caused by inferiority of the corpus luteum. Administration can take place orally or vaginally, and depends on the pathology. Internal administration of Utrozhestan during pregnancy is carried out in the presence of the following obstetric pathologies:
- risk of miscarriage;
- prevention of premature birth.
- Outside of pregnancy, Utrozhestan is prescribed to eliminate the following gynecological pathologies:
- premenstrual disorders;
- infertility due to luteal phase disturbance;
- disturbance of the ovulatory process (anovulation, disovulation);
- gestagen deficiency in menopause;
- mastopathy;
- precimacteric period.
Vaginal use of Utrozhestan is appropriate for:
- inability to swallow capsules orally (toxicosis, diseases of internal organs);
- impossibility of conception due to infertility;
- threat of miscarriage;
- risk of premature onset of labor.
If a woman is confirmed to have a lack of progesterone, Utrozhestan during pregnancy is prescribed in any form, regardless of gestational age. The drug fully compensates for the lack of progesterone without disturbing the woman’s natural hormonal balance. Proper treatment does not cause complications, does not contribute to excess weight gain or worsening pregnancy. But the effectiveness of replacement therapy during gestation depends on the adequacy of the prescribed dose and the general dosage regimen.
When planning a pregnancy
Only a doctor can prescribe a regimen for taking the drug. Here he is guided solely by the clinical picture. The use of the drug has its own characteristics:
- For premenstrual tension syndrome, insufficient luteal phase, fibrocystic mastopathy, dysmenorrhea, premenopause, the drug is taken orally. The daily dose will be 200-300 ml, add to 2 doses. Take the drug in the 2nd phase of the menstrual cycle. The duration of therapy will be 10 days.
- During hormone replacement therapy, Utrozhestan is taken 2 capsules per day. The duration of therapy will be 10-12 days. If menopause has occurred, then 1 capsule per day for 25 days. It is advisable to take it before going to bed, with plenty of water. It is forbidden to drink capsules immediately after meals or immediately before meals.
- If there is a lack of progesterone, use suppositories, 1 suppository once a day. Carry out treatment on days 13-14 of the menstrual cycle. After removal, it changes - 1 suppository 2 times a day (days 15-25 of the cycle). Starting from day 26, the dosage is increased by 1 suppository per day. And so on every week until the maximum result is obtained. The limit is 6 suppositories per day, divided into 3 doses. The duration of therapy can be 2 months.
- In order to maintain the luteal phase during IVF, the drug is used in the form of suppositories. Introduce them intravaginally, 4-6 pieces per day. Start treatment from the day of gonadotropin injection. End of therapy at 20 weeks of pregnancy.
During early pregnancy
Why is the drug prescribed during pregnancy at different stages? During pregnancy, women usually use vaginal administration of the medication. For this, special candles are used. Utrozhestan tablets or capsules are usually not used during pregnancy. More often during pregnancy, expectant mothers are prescribed suppositories. They can be used in the first, second and third trimester.
In the early stages after conception, you can use it as prescribed by your doctor.
Only a specialist can make a decision on prescribing medication based on the woman’s medical examination data. In this case, it is recommended to insert suppositories into the vagina at the same time of day. This method of administering the hormone helps prevent the negative effect of the drug on the digestive system, in particular on the liver. In the first trimester, Utrozhestan is prescribed for the following purposes:
- Prevention of increased uterine tone and elimination of this condition.
- Normalization of the central nervous system.
- Preventing miscarriage and premature birth.
Replenishment of progesterone in the body when there is a lack of it. Utrozhestan does not have side effects on the fetus. This fact is confirmed by numerous medical studies. In extremely rare cases, a child develops a disorder such as an anomaly in the urethra.
Utrozhestan 200 during early pregnancy
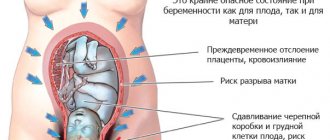
The readiness of the female body for pregnancy and the normal bearing of a child depend, among other factors, on the state of the hormonal system. One of the main hormones regulating this process is progesterone. Progesterone is called the “pregnancy hormone”. It is responsible for the regularity and duration of the menstrual cycle, and in pregnant women, for the normal bearing of the baby. Both a decrease and an increase in progesterone levels are fraught with serious problems. In the first case - miscarriage and spontaneous abortions, and in the second - delayed maturation of the placenta and, as a consequence, various pathologies of the fetus.
The action of Utrozhestan is to compensate for the lack of progesterone.
Utrozhestan capsules are used both as tablets and as vaginal suppositories. In both cases, the highest concentration of the hormone is formed after an hour, and the derivative substances are excreted from the body in the urine. When taken vaginally, the drug does not irritate the gastrointestinal tract and does not cause additional troubles when the tablet is difficult to swallow due to toxicosis.
This is the answer to the question why Utrozhestan suppositories are prescribed during pregnancy, and not capsules for oral administration. Typically, Utrozhestan is taken at a dose of 100 mg twice a day, and 200 mg once a day, at night. The dosage regimen and dosage depend on the method of taking the medicine. Utrozhestan tablets should be taken after meals and with plenty of liquid.
Indications for use of the drug Utrozhestan
Disorders caused by progesterone deficiency. Oral administration: premenstrual syndrome, menstrual irregularities (disovulation, anovulation), fibrocystic mastopathy, premenopausal period, menopause (in combination with estrogen therapy), infertility with luteal insufficiency, prevention of recurrent miscarriage or threatened miscarriage due to luteal insufficiency, threat of premature childbirth Intravaginal use: Reducing the possibility of fertilization in case of primary or secondary infertility with partial or complete luteal insufficiency (disovulation, support of the luteal phase during preparation for in vitro fertilization, egg donation program); prevention of recurrent miscarriage or threatened miscarriage due to luteal insufficiency.
How to enter correctly?
The standard and most effective method of using Utrozhestan capsules during pregnancy is vaginal administration. The doctor will prescribe this medicine at the stage of preparation for conception and during pregnancy in order to create maximum conditions for the fulfillment of the dream of having a healthy baby at term. The woman’s task is to be able to use Utrozhestan capsules correctly, observing the dosage of the drug and equal intervals of time between local use of the medicine. The effectiveness of treatment measures largely depends on this. The undoubted advantages of Utrozhestan when inserted into the vagina are the following factors:
- no negative effect from the passage of the drug through the liver;
- the drug is quickly absorbed;
- most of the active substance enters the vascular system in the area of the reproductive organs;
- no calming or inhibitory effect;
- ensures maximum effect on the inner surface of the uterus;
- the duration of action of the drug reaches 30 hours; the level of progesterone in a woman’s blood when Utrozhestan is applied topically will be stable throughout the day;
- convenience and ease of use.
The doctor will prescribe vaginal use of Utrozhestan during pregnancy against the background of obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus and metabolic disorders. Thanks to this drug and the administration method, there are real chances to carry and give birth to a child against the background of chronic diseases of the internal organs.
Until what week should I take it during pregnancy?
If a woman takes the drug during the 1st and 2nd trimester of pregnancy, then its withdrawal should not be abrupt. For example, if a woman drinks 200 mg of progesterone per day, then for 5 days. the dosage must be reduced by half over the next 5 days. cancel completely. Therefore, it is recommended to start reducing the dose of Utrozhestan at 30 weeks of pregnancy. It will be possible to complete hormone therapy at approximately 31 or 32 weeks. After discontinuation of the hormonal drug, minor bleeding may appear, which is not a pathology; it should completely stop within a few days.
At 35-37 weeks, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination to assess the progress of pregnancy and determine the length of the cervix.
Thus, the dose is reduced gradually and very slowly over 4-6 weeks. In this case, careful monitoring of the pregnant woman’s condition is required: if a decrease in the dosage of the drug leads to the appearance of bloody discharge and nagging pain in the lower abdomen, most likely, you will have to return to the previous dose of Utrozhestan. If no dangerous conditions are observed, drug withdrawal continues according to the scheme, as a result, Utrozhestan is canceled completely or it is replaced with an alternative suitable drug.
Artificial insemination and progesterone supplementation
The situation is different when using assisted reproductive technologies. The IVF procedure is quite expensive and hard on the patient’s body. Therefore, doctors play it safe and prescribe the drug “Utrozhestan” in large doses immediately after embryo transfer. This tactic allows you to prevent miscarriage and the threat of its occurrence.
Typically, the patient is prescribed a daily dose of 600 to 800 mg of progesterone. Take the medicine until about halfway through the term. By the 20-21st week, the pregnancy plan is completed; according to doctors, there can never be too much. Therefore they act like this:
- 15 weeks – 2 tablets of 200 mg in the morning and 2 in the evening;
- 16 weeks – 200 mg (1 tablet) in the morning and 400 in the evening;
- 17 weeks – 200 mg morning and evening;
- 18 weeks – 100 mg in the morning and 200 in the evening;
- 19 weeks – 100 mg morning and evening;
- 20 weeks – 100 mg in the evening;
- 21 weeks - the drug was stopped.
Contraindications for use
Absolute:
- incomplete abortion;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown origin;
- porphyria;
- thrombophlebitis,
- deep vein thrombosis,
- intracranial hemorrhage,
- thromboembolic disorders (stroke, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism) or a history of the listed diseases/conditions;
- suspected or established malignant tumors of the genital organs and mammary glands;
- hypersensitivity to the main or auxiliary components of the drug.
In addition, taking Utrozhestan capsules orally is contraindicated in case of severe liver diseases in history or currently (malignant neoplasms of the liver, hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice, Rotor and Dubin-Johnson syndromes). The drug is prescribed with caution to patients with the following diseases:
- arterial hypertension;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diabetes;
- hyperlipoproteinemia;
- bronchial asthma;
- chronic renal failure;
- mild to moderate liver dysfunction;
- migraine;
- photosensitivity;
- depression;
- epilepsy.
Utrozhestan is not used to protect against unwanted pregnancy. Capsules should not be taken with food, as food increases the bioavailability of progesterone. Patients with a history of depression should be under medical supervision. If severe depression develops, Utrozhestan should be discontinued.
Side effects during pregnancy
Like any other medicine, this drug can cause negative reactions in the body. It is worth noting that most often this occurs when the drug is used independently without a doctor’s prescription. The drug also causes an unexpected reaction in the body when overdosing or reducing the time between doses. The drug "Utrozhestan" may have the following side effects:
- Allergy.
If intolerance to any component of the drug occurs, this manifests itself as a skin rash, itching, and redness of the genitals (with vaginal administration). Nausea and vomiting may also occur. All these symptoms must be treated with appropriate medications. The hormonal medicine should be replaced with one with a similar effect. - Changes in the functioning of the excretory organs.
When used orally, the drug "Utrozhestan" has side effects in the form of increased and diluted stools. Some patients report constipation and bloating. This may be caused by the effect of the drug on smooth muscle. In addition, the drug can cause a diuretic effect on the body. This occurs especially often when using appropriate medications. Most often, treatment for such effects is not required, and therapy is not canceled. - Nervous system reaction.
Side effects of the drug may include headache, weakness and drowsiness. Most often, such symptoms appear within 1-3 hours after administration. Doctors advise in this case to choose an alternative drug. - Bleeding from the genital tract.
Very rarely, taking the drug may be accompanied by spotting and spotting. You should definitely report this side effect to your doctor and change your treatment regimen if necessary.
Features of the drug use
Treatment in recommended doses does not have a contraceptive effect. If treatment is started very early in the menstrual cycle, especially before the 15th day of the cycle, shortening of the cycle or bleeding may occur. In case of uterine bleeding, do not prescribe the drug without specifying its cause, in particular when examining the endometrium. Use with caution in patients with fluid retention (for example, hypertension, diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, patients with epilepsy, migraine, bronchial asthma), with a history of depression, diabetes mellitus, impaired liver function, photosensitivity.
Before prescribing the drug, patients with a family history of neoplasms and patients with recurrent cholestasis or persistent itching during pregnancy, impaired liver function, cardiac or renal failure, fibrocystic mastopathy, epilepsy, asthma, otosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, should be carefully examined. systemic lupus erythematosus. Due to thromboembolic complications and metabolic disorders, the need to stop taking the drug cannot be completely excluded if:
{banner_banstat8}
- visual disturbances such as vision loss, double vision, retinal vascular lesions, proptosis, papilledema
- thromboembolic venous or thrombotic complications, regardless of the site of the lesion;
- severe headache, migraine.
If amenorrhea occurs during treatment, pregnancy, which may be the cause of amenorrhea, should be confirmed or excluded.
Side effects of the drug Utrozhestan
When administered orally, the following side effects are observed:
System | Frequent side effects 1/100; ≤1/10 | Uncommon side effects 1/1000; ≤1/100 |
| Sexual | — changes in the menstrual cycle — Amenorrhea — Bleeding in the middle of the cycle | |
| Nervous | Headache | — Drowsiness — Transient dizziness |
| Hepatobiliary | — Cholestatic jaundice — Itching — Gastrointestinal disorders |
Drowsiness and/or dizziness are observed in case of concomitant hypoestrogenism. Reducing the dose of the drug or increasing the dose of estrogen eliminates these phenomena without reducing the therapeutic effect. If the course of treatment begins at the beginning of the monthly cycle, before the 15th day, a shortening of the cycle or occasional bleeding occurs. In general, changes in menstruation, amenorrhea, or mid-cycle bleeding occur when taking progestins. For intravaginal use: no side effects.
Which is better Utrozhestan or Duphaston?
The question of which drug is better cannot be answered unequivocally. When prescribing both Utrozhestan and Duphaston, the doctor must take into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the purpose of using the medicine. Both drugs do not affect body weight, as they do not lead to fluid retention in the body. This is a very important factor for a woman carrying a child. Medicines do not affect lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, that is, they do not provoke disruptions in metabolic processes.
It is also very important that the drugs do not increase blood pressure. But at the same time, most doctors agree that duphaston is safer during pregnancy, as it has fewer side effects. Unlike urozhestan, it does not cause:
- drowsiness,
- lethargy,
- fatigue,
- tendency to depression.
Duphaston has no toxic effect on the liver and is highly effective in IVF. The drug is considered safe, as confirmed by long-term studies. Utrozhestan is a new hormonal drug and its effect on the fetus has not been sufficiently studied, therefore in some European countries it is not prescribed to women when bearing a child. Although a significant advantage of this product is its release in the form of intravaginal suppositories, which is very important for maintaining pregnancy in the first trimester against the background of possible severe toxicosis.
Features of use
The regimen during pregnancy always depends on the dose of the drug taken. According to the instructions, the drug can be inserted into the vagina or taken orally. The first option turns out to be more preferable for doctors, as it reduces the risk of side effects. Please note that the medication is not prescribed for severe liver failure, the patient’s tendency to thrombophlebitis, or for certain diseases of the nervous system.
The dosage and duration of use are always determined by the doctor individually. The medication can be prescribed to prevent miscarriage (after ovulation) or to treat self-abortion that has begun. Instructions for use recommend using 200-400 milligrams of medication per day. This portion is divided into 2 doses. But gynecologists can prescribe a different dosage.
Advantages of Utrozhestan
With low levels of progesterone in the female body, pregnancy becomes almost impossible. Hormone deficiency can be caused by various reasons: insufficiency of the luteal phase, the presence of diseases or pathologies, unstable emotional state, excessive physical activity and others.
Since the hormone plays a key role in conceiving a baby, it is necessary to increase its level to normal. In such cases, gestagenic drugs are often prescribed; among them, Utrozhestan is especially popular.
It is important to remember that you cannot make a decision on treatment with gestagen on your own; the medicine is prescribed only by the attending physician after an examination and identification of the exact cause of low progesterone levels.
However, according to progressive medicine, these are quite rare phenomena at the planning stage, and doctors often abuse this type of drug, attributing non-existent properties to them. In some cases, HRT is not at all effective; proper nutrition and an active lifestyle will bring much more benefit, for example, with low weight and lack of cholesterol in the blood.
In what cases, after reducing the dose, is it increased again?
The regimen during pregnancy is selected depending on the patient’s condition. First, the gynecologist prescribes an ultrasound examination and a blood test to determine progesterone levels. After receiving the results, the doctor decides whether to start reducing the dose of the drug or wait longer. As you can see, in all situations the dose of medication is reduced gradually. Sharp restriction of the drug or its complete withdrawal can provoke termination of pregnancy.
During dose reduction, it is necessary to carefully monitor the woman's condition. Due to the large flow of patients, the gynecologist is not always able to control the well-being of the expectant mother. Therefore, the responsibility falls entirely on your shoulders. If you suddenly feel worse: pain in the back and lower abdomen begins, brown or pink discharge appears, then you need to return the previously prescribed dose of the medication. A few weeks after normalization of health, the scheme is repeated. During pregnancy at the same time, the patient may be recommended sedatives and sedatives.