Basal temperature, or BT, is the lowest body temperature during rest (rest, sleep). It shows what changes have occurred in a woman’s body during the synthesis of specific hormones. The essence of measuring basal temperature is to establish the onset of ovulation, its timing, and determine the synthesis of progesterone, the main task of which is to prepare the uterus and endometrium for bearing a child.
Some women are skeptical about such measurements, but the basal temperature chart does provide important information about the work and condition of the reproductive system, but only if you take measurements regularly (over 2-3 cycles) and follow all the rules.
Why do you need basal temperature measurements?
They resort to plotting a basal temperature chart in the following cases:
- A woman cannot become pregnant for a year.
- It is necessary to check whether the ovaries produce hormones correctly according to the phases of the cycle.
- A woman has been diagnosed with hormonal disorders.
- You need to find out what day of the cycle ovulation occurs on in order to determine your fertile days. Basal temperature changes dramatically during ovulation.
- A woman suspects inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system (for example, endometritis - inflammation of the surface layer of the endometrium).
- It is necessary to determine whether the woman is pregnant. The method is relevant if there is a delay or your periods are coming, but they are unusual - not the same as they were before.
What should a basal schedule look like when preparing for pregnancy?
Describing how basal temperature changes during the menstrual cycle is useful information, but can be difficult to understand without specific examples. So let's look at some graphs that visually show what measurements you can get.
Normal menstrual cycle
Normal menstrual cycle schedule
During the normal course of the menstrual cycle, you can see two different phases on the graph - in the first, the average level of basal temperature is lower than in the second, and ovulation serves as their boundary. It is not necessary that your schedule is divided into two equal parts of 14 days, as in this example. The duration of the second phase of the cycle for different women can be from 12 to 16 days, and the first can vary within even wider limits. There is nothing unusual in this, just the individual characteristics of the body. However, different cycles of a particular woman should follow the same scenario. After a couple of months of measurements, you will already roughly understand what day of the cycle ovulation should occur.
This graph gives an understanding of what basal temperature is normally observed in preparation for pregnancy. In the second phase it should be 0.3–0.6 °C higher than the average level of the first period. At the same time, a drop in the temperature curve is observed at the end of the cycle, before the onset of menstruation. And, of course, the preovulatory drop followed by a rise is important for the expectant mother.
Anovulatory cycle
Anovulatory cycle chart
In the anovulatory cycle, ovulation does not occur, and hormonal levels change slightly. Throughout the entire cycle, the basal temperature remains almost at the same level - around 36.6 ° C, and the graph does not show pronounced phases and drops that are observed in a normal menstrual cycle.
If your temperature curve looks like this in the first month of measurements, there is no need to panic. Every woman has one anovulatory cycle per year, sometimes more. It’s just that your reproductive system periodically needs rest, and it arranges it for itself during periods during which it is impossible to get pregnant. However, if such a picture is observed for more than two months in a row, you need to consult a doctor - this is no longer a rest, but a possible sign of infertility.
Hormonal problems
Let's look at what a basal temperature graph might look like for various hormonal disorders.
Diagram for corpus luteum deficiency
The corpus luteum forms after ovulation and produces progesterone, which is necessary to prepare the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized egg. If the corpus luteum produces little progesterone, an already begun pregnancy may be terminated.
This condition can be calculated by the slow rise in temperature in the second phase, and for its treatment the doctor will prescribe hormonal drugs.
Schedule for estrogen deficiency
If a high level of progesterone leads to an increase in basal temperature, then an increase in estrogen production leads to a decrease in it. It is thanks to them that the temperature drops before ovulation. With estrogen deficiency, the likelihood of fertilization decreases significantly.
This condition can be identified by an unexpectedly high temperature at the beginning of the cycle, a slow increase in the middle, and a temperature above normal for the second phase. It will not be possible to detect ovulation using such a schedule. In case of estrogen deficiency, hormonal medications are also prescribed.
Pregnancy
Schedule during pregnancy
You determined the day of ovulation using measurements, you have already had that same sex. Keep monitoring - you may soon be able to detect pregnancy even before the test shows two lines!
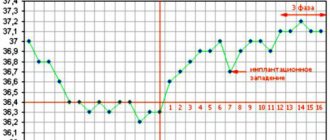
In early pregnancy, basal temperature drops on the day when the egg implants. The characteristic implantation retraction divides the second phase into two, and a third phase appears in your chart, indicating that pregnancy has begun. It is worth remembering possible inaccuracies in measurements and it is better to wait until your doctor confirms this joyful fact. But, most likely, you can already be congratulated - you have begun your journey to becoming the best mother to the best baby in the world!
How does the method work?
The technique allows you to measure indicators taking into account the phase of the cycle.
The menstrual cycle includes two phases - before and after ovulation. In the first phase, BT indicators are lower. Immediately after ovulation there is an increase in the concentration of progesterone in the blood and the temperature rises abruptly. And before menstruation, the basal temperature again becomes lower by 0.3 degrees.
The method of measuring basal temperature has errors. For example, if your body temperature does not increase, this does not always mean that ovulation is not occurring. Despite this, the method is widely used, and the schedule will be useful when visiting a gynecologist, especially if a woman does not become pregnant for a long time.
Question answer
In this article we have collected the most frequently asked questions and answered them. Surely you will find useful information for yourself.
- Basal temperature during pregnancy before delay
One of the most pressing questions is what should be the basal temperature of a woman who is pregnant but has not yet missed her period. As mentioned above, basal temperature rises to 37 - 37.3 degrees in the second half of the menstrual cycle. And it drops to 36 and 9 degrees only two days before the start of menstruation.
In the same case, if the basal temperature does not decrease within 18 days, there is a very high probability that pregnancy has occurred. Moreover, doctors advise in such cases to conduct a pregnancy test even if menstruation has begun. The increase in basal temperature during this period is caused by the effect of the hormone progesterone on the woman’s body.
- Normal basal temperature during pregnancy
As already mentioned, a deviation of basal temperature from normal values may indicate various pathologies. But what is the norm and can this temperature fluctuate? Doctors call the average basal temperature, ranging from 37.1 to 37.3 degrees. But in some cases it can be a little higher - up to 38 degrees. It depends on the individual characteristics of the organism.
- Basal temperature during ectopic pregnancy
There is an opinion that during an ectopic pregnancy, the basal temperature does not increase. However, this is not so - during an ectopic pregnancy, the same hormone progesterone is produced, which leads to an increase in basal temperature. Therefore, an increased basal temperature, alas, is not a guarantee that the pregnancy is uterine. And under no circumstances should you use basal temperature as a diagnostic tool.
- Basal temperature too high
Despite the fact that the average basal temperature ranges from 37.2 to 37.3 degrees, it is permissible to increase it to 38 degrees. But if the body temperature rises even a little higher, this should serve as an alarm. The cause of such an increase can be various inflammatory processes - both local and general.
In any case, if your basal temperature rises, you should not try to independently determine the cause. Firstly, you are unlikely to be able to make a diagnosis on your own, and secondly, any treatment for a pregnant woman should be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. However, do not be alarmed right away - very often the reason is the incorrect measurement of basal temperature.
How to measure basal temperature to determine ovulation?
There are a number of requirements for how to measure basal temperature. Most often they resort to the rectal method (a thermometer is inserted into the rectum).
- Take your temperature at the same time every day. However, it is important that you sleep for at least 6 hours before taking measurements. Measurements are taken while lying down, without getting out of bed, in a calm state. Preference is given to morning time. You can measure BT during the day, but, firstly, it is difficult to get 6 hours of sleep beforehand, and secondly, the results are not always correct.
- To eliminate error, use the same thermometer. You need to hold it for at least five minutes.
- Start measurements from the beginning of the cycle, that is, from the first day of your period. You can collect data at other times, but this is the best option.
- Measure BT for at least three cycles. Only then will the data be informative and reliable.
The received data must be recorded. The most convenient way is to enter them in a special table - it can be easily found on the website and printed. Based on the data in the table, a BT chart is constructed. This is a curve that reflects two phases - follicular and luteal.
If your body temperature has increased, a chronic disease has worsened, or you have recently returned from a long trip, then the measurement results will not be indicative. The same can be said about taking hormonal and sedative drugs. If you drank alcohol or had sex 4 hours before the measurement, the data will also be unreliable.
When and how to measure BT?
Because temperatures vary throughout the day, it is important to take measurements at the same time every day. It is best if it is early in the morning - then these readings are considered the most indicative.
How exactly to do this?
Prepare a thermometer in the evening and place it so that in the morning you can easily pick it up without getting out of bed.
Choose the method you will use throughout the period: you can place the thermometer either in the vagina or rectum.
Decide on time. Small deviations are acceptable, but they should not be more than half an hour.
It is worth measuring the temperature after a full sleep, which ideally should last 8-10 hours. The minimum acceptable value is 5-6 hours.
The time between the procedure and the last sexual intercourse should be more than 12 hours.
It is best to take measurements in a state of complete rest, lying on your back. Experts do not even recommend turning on your side, much less getting out of bed.
You need to hold the thermometer for 3-5 minutes.
Important! It is worth remembering that even a minor cold, as well as taking medications, can affect your performance. Be sure to consider these factors. This will help you avoid wrong conclusions and false hopes.
What basal temperature should be normally and during pregnancy?
Let's study the BT chart using the example of a normal cycle:
- Before menstruation, BT is about 37 ◦C.
- With each day of menstruation, the temperature gradually decreases: by the last critical day it reaches 36.3–36.5 °C.
- The remaining time until the middle of the cycle, the indicators remain at the level of 36–36.6 °C. This is the normal basal temperature.
- On the day of egg maturation and three days after BT it reaches 37.1–37.3 °C. This means that ovulation has occurred.
- In the second phase, the basal temperature is 37–37.5 °C.
- It decreases two days before menstruation. Thus, by the beginning of the next critical days the indicator reaches 36.9–37.0 °C.
During pregnancy, the basal temperature is slightly more than 37 °C. This temperature is comfortable for the fetus. It persists throughout the entire gestation period: the corpus luteum does not leave the ovary and synthesizes progesterone, which is necessary for a favorable pregnancy.
Doctors recommend focusing not on the numbers themselves, but on the difference between both phases - ideally, the difference should not be less than 0.4 °C.
The example considered is an ideal picture. In reality, there is a high probability of various deviations:
- If BT decreases slightly before menstruation, and during menstruation reaches more than 37 °C, endometritis can be suspected.
- High BT in the first phase (follicular) indicates a lack of estrogen.
- Low values in the second phase (luteal) may indicate that there is little corpus luteum. Second-phase insufficiency refers to a decrease in progesterone concentration. In this situation, ovulation still occurs, but in most cases the temperature is below 37 °C.
- If within a couple of days the temperature reaches 37 °C, then decreases; doctors often diagnose adnexitis (inflammation of the uterine tubes).
- If there is a delay and BT remains at 36.8–37.0 °C or higher for 14 days, we can most likely talk about pregnancy. To clarify, you should do a test or donate blood for hCG.
If you are planning to become pregnant, using a BT chart makes it possible to determine ovulation, which significantly increases the likelihood of conception. In addition, the chart will help determine pathology - this is especially important if a woman cannot donate blood for hormones daily. The method also helps in examining couples who are diagnosed with infertility.
When does basal temperature deviate from normal?
If you are keeping a chart and notice that BT has deviated from its normal values, this usually means one of two events:
- or ovulation has occurred;
- or a new life has already arisen in the woman’s body.
In the first case, the chance of getting pregnant increases many times, and it is important for the couple not to miss this moment. Otherwise you will have to wait until next month and try again.
In the second case, the increase in temperature serves as good news: the event that the future parents have been waiting for has finally taken place. A new amazing life awaits them ahead.
A BT schedule in early pregnancy is useful for the expectant mother. If you are already pregnant, and your BT suddenly becomes too high, this is a reason to consult a doctor. Such an abnormality usually signals either infection or inflammation, or an ectopic pregnancy.
When the levels, on the contrary, are below normal, this may indicate that the body has stopped producing progesterone. This means there is a possible risk of miscarriage or frozen pregnancy.
Special conditions for measuring rectal temperature
When measuring basal temperature, it is important to remember that there are many external and internal factors that can affect the data. If we talk about internal situations, these could be:
- colds, infectious and viral diseases, exacerbation of chronic diseases, which are accompanied by an increase in general body temperature;
- problems related to digestion or the rectum, i.e. fissures in the anus, diarrhea, hemorrhoids, etc.;
- inflammatory and purulent processes on the skin - boils, abscesses, wounds;
- exacerbation of some gynecological diseases, such as adnexitis.
- External factors include:
- insufficient sleep before measuring basal temperature - less than five hours;
- sexual contact the night before or in the morning;
- the measurement was taken at an unspecified time;
- affect the indications and intake of alcoholic beverages, medications, psychotropic substances;
- The thermometer readings can also be affected by being on the road for a long time, for example, flying on an airplane or traveling by train.
If all these reasons were present, then this must be noted in the basal temperature measurement chart. In the future, this will help to distinguish natural deviations due to external or internal factors from pathological ones. The schedule also includes those days when there were sexual intercourses without the use of contraception. All these points are very important in the subsequent study of the basal temperature chart and establishing the exact causes of infertility or any pathological process in the female body.
Normal temperature indicators before and after fertilization
If you know what thermometer readings should be at different phases of the cycle, you can easily determine the period of ovulation and select a time favorable for conception. Normal BT values are presented in the table.
| Cycle phase | Cycle days | Predominant hormones | Normal BT values |
| Follicular | 1–12 | Estrogen | 36.2–36.6 °C |
| Ovulation | 13–14 | Estrogen, follicle-stimulating, luteinizing | Decrease to 36.2–36.3 °C Follicle rupture 36.4–36.7 °C After ovulation 37-37.4 °C |
| Luteal | 15–28 | Progesterone | 37.1–37.4 °C |
If fertilization has occurred, the following fluctuations will be visible on the BT measurement graph:
- The day of fertilization is 36.4–36.7 °C, the changes are not yet noticeable, only after 5–7 days, when the fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity, the indicators rise to 37-37.3 °C.
- Introduction of the embryo into the uterine wall - temperature decrease by 0.2-0.4 °C (implantation retraction). 4-5 days after implantation - BT indicators increase above 37 °C.
- For the next one to two weeks, the temperature remains at 37-37.5 °C, but should not fall below.
Based on inflated BT values just before the start of the expected menstrual period, a woman can guess that she is pregnant, even if other early signs of conception (breast swelling, nausea) are absent. After a delay, the fact of conception can be confirmed by a pregnancy test.
Low basal temperature values
As noted above, basal temperature values are a purely individual indicator and there is no strict standard. So, for example, a basal temperature of 36 degrees and a basal temperature of 36.5 degrees is a normal individual phenomenon, provided that the difference between the phases remains at least 0.4 degrees.
If the difference in temperature values is less than 0.4 degrees or the average basal temperature is low, this may indicate a violation.
For example, low temperature readings are observed with the following pathologies:
- corpus luteum deficiency. In the second phase, progesterone begins to be released (another name is the corpus luteum hormone), under the influence of which temperature indicators increase. In case of a deficiency of this hormone, a slow increase in temperature values is observed (sometimes the maximum basal temperature in the second phase is 36.5 degrees) and a failure of the resulting pregnancy is possible. An increase in temperature occurs shortly before menstruation and a decrease in temperature before the onset of menstruation, which is observed in the normal state, is absent. This may be a symptom of hormonal deficiency. In order to make a correct diagnosis, in the second phase of the cycle, a blood test is performed to determine the content of progesterone. If the levels are low, the specialist may prescribe substitutes for this hormone: the medications Duphaston or Utrozhestan. Such medications are taken only after the onset of ovulation. If conception has occurred, a progesterone substitute is taken until 10-12 weeks of pregnancy. The result of abrupt withdrawal of such a drug can be termination of pregnancy. You should also pay attention to the duration of the second phase of the menstrual cycle; if this period does not exceed 10 days, then there is a failure of the second phase. Elevated temperature readings can be a symptom of inflammation of the pelvic organs, the presence of an ovarian cyst. In addition, if a basal temperature of 36.9 is determined after a delay of 2 weeks, then this most likely indicates pregnancy.
- estrogen-progesterone deficiency. With this pathology, in the second phase there is no sharp increase in temperature values. Temperatures increase by no more than 0.3 degrees. This phenomenon is a symptom of hormonal imbalances, which in most cases are the cause of infertility.
- anovulatory cycle. Sometimes in the second phase of the cycle the temperature data does not increase and the maximum basal temperature is 36.7, what does this mean? This phenomenon can occur in the case of an anovulatory cycle, in which conception is impossible because the egg is not mature and is not ready for fertilization. In normal conditions, anovulatory cycles occur a couple of times a year; if they occur more often, it is necessary to discuss this problem with a qualified specialist.
Changes in BT indicators during the cycle
Carrying out basal measurements is one of the cheapest methods for determining ovulatory periods and conception. Throughout the cycle, BT changes in accordance with hormonal changes.
- When menstruation ends, the rectal temperature remains at 36.3-36.6 degrees. It is against the background of such thermodynamic indicators that each cycle the maturation of female germ cells occurs with the active participation of the estrogen hormone, which controls these processes.
- By the onset of ovulation, there is a sharp but insignificant decline, and then a rise in temperature to 37 degrees and even higher. Such a temperature dip is a sign of the release of the egg from the follicle, i.e. ovulation.
- If a female cell merges with sperm, then the basal temperature after conception will remain stably at elevated levels, exceeding 37 degrees.
- If there was no conception, then a few days before menstruation the temperature begins to drop to 36.6 degrees.
Similar changes occur in the female body every cycle.