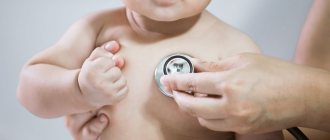
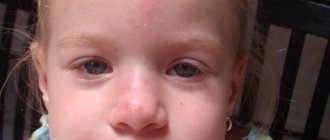
Why does a child's nasolabial triangle turn blue?
Cyanosis is a bluish discoloration of the skin caused by low oxygen levels in the blood. Slight bluish discoloration of the nasolabial triangle is often observed in newborns, and slightly less often in children under 1 year of age.
Possible causes of this condition are divided into physiological and pathological. Physiological ones include:
- hypothermia. If a child is cold, this part of the face darkens. Hypothermia can occur, for example, when swimming if the water temperature is too low;
- strong prolonged scream. When a baby cries for a long time, the concentration of oxygen in his blood decreases;
- excessive stress on the baby during breastfeeding. Sucking milk from the breast is a serious physical activity for the baby, especially for a shortened frenulum of the tongue;
- In some children, the cause of cyanosis lies in thin skin; venous plexuses are visible through it, which lead to this visual effect.
Physiological reasons do not pose a threat to the child’s health.
Parents should not self-diagnose! If the nasolabial triangle is blue, the child should be examined by a pediatrician. He will decide whether there are grounds for an examination by specialized specialists.
Pathological causes include:
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, heart defects: stenosis of the aorta or pulmonary artery, ventricular septal defect;
- lung problems: bronchial asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis, other upper respiratory tract diseases. Sometimes blueness appears as a reaction to inhaling cigarette smoke;
- various neurological pathologies, for example, increased intracranial pressure. In this case, not only blueness of the nasolabial triangle is observed, but also bruises under the eyes, as well as suppression of the sucking reflex - the child sluggishly and reluctantly takes the breast.
A blue nasolabial triangle in a child may be a consequence of a birth injury; it is also observed in children who suffered from hypoxia in the womb. With hypoxia, the likelihood of pathologies of the central nervous system increases significantly.
Blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle
Blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle.
Very often, parents turn to the pediatrician with complaints about blue discoloration around the lips, or, as it would be more correct to say, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. What is this and is it worth worrying about this issue, we will now consider.
The nasolabial triangle is an area on the face limited by the nasolabial folds on the sides, the nose above and the lips below. Cyanosis can be caused by physiological (i.e., occurs in absolutely healthy babies) and pathological (various diseases) conditions of the body.
Physiological conditions.
In the area of the nasolabial triangle, the blood supply is highly developed: both arterial and venous vessels are present. And the skin of infants and young children is very thin and delicate, so the vascular plexuses seem to “shine through” through it and it appears bluish.
Baby crying . Sometimes mothers note that cyanosis appears when crying or prolonged screaming. This is due to the peculiarity of the pulmonary system in newborns. At this time, the level of oxygen in the body decreases (its amount can decrease by up to 92%), and the capillaries expand from tension and are therefore clearly visible through thin skin. In medicine, this phenomenon is called pulmonary cyanosis, and does not pose any threat to health. It disappears when the baby calms down. As the child grows up and lung function improves, this symptom goes away.
Feeding. Sucking at the breast is a big burden for the baby, during which capillaries appear and become visible near the surface of the skin. After feeding, the blueness goes away immediately.
Low air temperature . When your baby is cold, some parts of the body, including the nasolabial triangle, may turn blue. This is due to the imperfect heat exchange system of the child’s body. As soon as the baby warms up, the skin will take on a natural color. The same thing happens while walking. If you notice a blue nasolabial triangle, it’s time to leave the street, because this may be the first sign of hypothermia in a child.
We have reviewed with you the physiological conditions of cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle in children, which are not associated with the manifestation of any diseases. What pathological conditions can lead to the appearance of this symptom?
Pathological conditions.
Respiratory diseases. Respiratory diseases that can lead to cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle include ARVI, pneumonia, bronchial asthma, obstructive or allergic bronchitis, that is, those that lead to impaired air exchange. Of course, along with cyanosis, other symptoms of these diseases should be present (fever, nasal discharge, prolonged dry cough). In this case, you cannot do without consulting a pediatrician, who in turn can refer you to other specialized specialists.
Foreign objects. This is another common cause of cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. Little children are very curious. Their taste buds are best developed, and therefore they experience the whole world through their mouth. Everything that interests them ends up in the mouth - one careless breath and a tiny object ends up in the respiratory tract. The child begins to cough heavily and gasp for air. It is necessary to provide first aid and call an ambulance.
First aid for a foreign body in the respiratory tract : Turn the child face down and tap the back with force, but not excessively. It is better to carry out manipulations over a sofa or armchair so that the baby does not fall on the floor and accidentally slip out of your hands.
Second option. Sit in a chair or chair. Place your baby face down on your left knee. Your left palm should be on his chest and support his neck. With your right hand, make strong pushes with the edge of your palm between the shoulder blades towards the mouth. Additionally, induce vomiting in the child by pressing your fingers on the root of the tongue. Follow all steps until the ambulance arrives.
Neurological pathology. Very often, cyanosis can be observed in children who experienced hypoxia or asphyxia during birth (for example, when entwined with the umbilical cord), and were also born premature. We see a blue nasolabial triangle in children with increased intracranial pressure and immature brain structures. In any case, consultation with a neurologist is necessary.
Congenital heart defects . Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle in a child is one of the first signs of congenital heart disease and heart failure. To clarify the diagnosis and timely treatment, it is necessary to conduct an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart), an ECG and consult a cardiologist.
Problems with the development of the respiratory system. Malformations of the bronchopulmonary system (tracheal stenosis, bronchial hypoplasia, etc.) can also lead to cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. Such conditions require urgent treatment.
Poisoning with drugs or chemicals. Poisoning causes tissue hypoxia, which is manifested by impaired absorption of oxygen by cells, hence cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. Cyanosis will also be observed in children in whose presence their parents smoke, as a consequence of nicotine intoxication.
If the doctor, after examining the baby, did not find any pathologies and recognized cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle as normal, the following measures should be taken so that the blue discoloration disappears as soon as possible.
Be sure to take your child for a walk in the fresh air every day. Long walks will not only strengthen the baby’s body, but also saturate it with oxygen. And if there is no deficiency, then the nasolabial triangle will not turn blue.
Don't let your baby cry for too long. This is harmful not only to the physical health, but also to the emotional comfort of the child. Crying is a form of communication accessible to the baby to the mother. By crying, the child tries to draw her attention to some factors that cause him discomfort (wet diaper, hunger, loneliness and others). Provide him with everything he needs.
Monitor the air temperature in your baby's room. It should not be too hot or cold. Ideally - 21-25 degrees. If your child starts to feel cold, just dress him warmly (in clothes made from natural fabrics so that the skin can breathe).
When you need to see a doctor urgently
Here are some cases in which you should not delay seeking medical advice:
- if cyanosis began to appear after a prolonged cold. Perhaps this is how pneumonia manifests itself in a latent form, and for successful treatment of pneumonia it is very important to start antibiotic therapy as soon as possible;
- if the blueness appears after the child begins to have a strong tremor of the hands and chin, seemingly for no apparent reason. This is an indirect sign that a heart defect is preventing the body from functioning normally.
In the most dangerous cases, cyanosis is caused by mechanical suffocation. It is necessary to ensure that the child is not left alone with small objects that he can swallow. First aid in such a dangerous situation: take the child by the legs, with the head and body hanging down. You can shake the baby a little. A foreign body poses a threat to life, therefore, if you cannot remove it yourself, you should immediately call an ambulance.
The causes of cyanosis are determined by the doctor
Diagnostics
Here is a list of diagnostic tests that need to be carried out to find out the exact cause of the blueness of the nasolabial triangle:
- complete blood count: anemia may be detected
- Ultrasound of the brain. It can be carried out as long as the child’s fontanel is not closed. Using ultrasound, you can diagnose cysts, changes in the ventricles of the brain, and the presence of cerebrospinal fluid;
- cardiogram and ultrasound of the heart - they help identify various heart defects;
- X-ray examination of the chest - necessary to exclude pneumonia;
- bronchoscopy - it is performed to remove a foreign body from the bronchi
- magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Helps to exclude severe pathologies of the central nervous system.
It is important to understand that cyanosis is not an independent disease, but only a sign indicating a problem in the body.
Diagnosis of conditions in which cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle appears in children
It is necessary to diagnose the etiology of the “triangle of death” cyanosis as early as possible.
Diagnosis of the cause of the blueness of the nasolabial triangle is carried out using:
- examination by a neonatologist and/or pediatrician;
- neurologist consultations. It is necessary for prematurity, difficult childbirth and to exclude pathologies of the nervous system;
- X-ray examination of the chest organs. To exclude infectious processes and foreign bodies in the respiratory tract;
- electrocardiogram (ECG) and cardiac ultrasound (ultrasound). These methods allow timely detection of heart pathologies;
- ultrasound examination of the brain (performed with an open fontanel in an infant to exclude pathological changes);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain. Performed in children with a closed fontanel to exclude severe pathologies of the central nervous system;
- bronchoscopy (if foreign bodies enter the respiratory tract).
The task of parents is to timely identify all pathological conditions and seek help (if the slightest changes appear, it is necessary to consult a child with a specialist). It is better to be overly attentive to the baby than to miss a serious pathology that could cost the baby’s life.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures directly depend on what exactly is the cause of the cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle:
- if a heart defect is diagnosed, you need to consult a pediatric cardiologist, perhaps we will talk about the need for surgery;
- in case of pathology of the nervous system, an in-person examination by a neurologist is necessary; he will tell you how to proceed;
- Pneumonia in children is treated in a hospital setting, using antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Regular walks in the fresh air and daily ventilation of the children's room are recommended as preventive measures. Care must be taken to ensure that the child breathes comfortably. If the air in the house is too dry, it is worth purchasing a humidifier; at the same time, this will serve as a good prevention of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections. Smoking should also not be allowed in the house where the child is.
We also recommend reading: alopecia in children
Such a phenomenon as a blue nasolabial triangle in a baby occurs quite often, and in many cases does not pose a danger to the child’s health. However, there are situations when such a symptom manifests itself as a dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, as well as the respiratory system. What is cyanosis and why does it appear?
The essence of treatment of cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle in infants
Do not treat babies yourself with folk or other methods!
Therapy, if necessary, should only be carried out by a doctor. Treatment should be etiological and aimed at eliminating the cause that could cause cyanosis.
For physiological cyanosis, the pediatrician may prescribe:
- carrying out restorative massage and water procedures;
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- limiting stress for the baby.
Perioral cyanosis is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of other diseases.
What it is
Cyanosis is a symptom of oxygen deficiency in the body, which increases the formation of methemoglobin. It is this reduced type of hemoglobin that makes the skin and mucous membranes darker.
Blue discoloration of the epidermis in the area of the nasolabial triangle in infants can be of a pathological and physiological type.
Norm
Basically, this phenomenon is a consequence of increased physical activity. This area also turns blue due to:
- long crying, during which the baby exhales a large amount of air and inhales little, which is why there is a deficiency of oxygen in the blood;
- during feeding. Breastfeeding is a heavy burden for the baby, due to which the superficial vessels dilate and become more noticeable;
- prolonged exposure to altitude leads to a non-pathological decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood;
- hypothermia during swimming or changing clothes causes cyanosis of the area above the upper lip. If, after warming up the infant, the blue discoloration disappears, then this condition is not dangerous.
If the baby’s nasolabial triangle turns blue and does not return to its original appearance in the near future, a blue tint appears on the tongue and fingers, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Cyanosis in children
Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle in an infant is not uncommon and can be observed both in healthy children and in children with diseases of organs and systems (nervous, cardiovascular, respiratory, etc.). In children, the level of oxygen in the blood decreases during strong screaming or crying, but normally it becomes no lower than ninety-two percent. Cyanosis in an infant occurs when the oxygen level drops below this level.
During the newborn period, cyanosis during screaming or crying is the norm, and occurs due to imperfect systems, but as the child grows, the cyanosis disappears. Cyanosis that persists several weeks after birth should be alerted and examined so as not to miss the pathology that causes hypoxia. If cyanosis is associated with extremely thin tissue, this is considered as a variant of the norm.
Sometimes cyanotic nasolabial triangle is observed during infectious diseases such as pneumonia, true croup, etc. In addition to cyanosis, they are accompanied by shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, intoxication, and increased body temperature. If cyanosis and shortness of breath occur instantly - this may be due to foreign objects entering the respiratory tract, parents should urgently call an ambulance.
Pathological conditions that often cause cyanosis in children are congenital heart defects, abnormal development of blood vessels, etc. Therefore, cyanosis in a child should be examined in any case. Carrying out an ultrasound examination of the heart, radiographic methods and an electrocardiogram will help the doctor confirm or exclude the diagnosis and plan further studies. The child should also be examined by a neurologist, because sometimes the cause of cyanosis is underdevelopment of the respiratory system.
Pathology
Pathological cyanosis is divided into 3 groups depending on its development algorithm.
- A permanent type having a central origin. This pathology can occur due to trauma during childbirth, due to increased intracranial pressure, or underdevelopment of certain parts of the brain (respiratory or vasomotor) in infants. In addition to the blue nasolabial triangle, the pathology is also manifested by a sluggish sucking reflex.
- Cyanosis of respiratory nature (pulmonary). Accompanied by additional symptoms, expressed by blueness of the area around the eyes and pale skin. You can also notice during breathing how the baby’s intercostal muscles retract. Blue discoloration of the area above the upper lip in this case is a symptom of the following diseases:
- pneumonia;
- airway aspiration;
- runny nose;
- bronchitis;
- bronchial type asthma;
- inhalation of tobacco smoke or carbon monoxide;
- diaphragmatic hernia.
- Pathology of the cardiovascular type. Appears due to congenital heart defects from the first days of a child’s life. Since this diagnosis cannot always be made immediately after birth, it is necessary to regularly attend routine examinations to prevent the development of dangerous complications.
Possible causes of cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle
The appearance of blue in the “triangle of death” occurs when the oxygen concentration in the blood becomes less than 95%.
The reasons for the appearance of cyanosis in the perioral area in a child can be:
- physiological;
- pathological.
The “deadly triangle” can turn blue in both a healthy newborn and a sick newborn. Therefore, whether a condition is a pathology or not should be determined solely by a doctor!
Does cyanosis occur in healthy babies?
With physiological cyanosis, venous and capillary vessels are visible through the thin skin and appear bluish (cyanotic).
That is, physiological cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle in a baby occurs due to the thin skin on the face (especially of a newborn) and the immature respiratory system.
This type of cyanosis can occur in babies when crying, restlessness, overexcitation, hypothermia, pale and thin skin, prolonged sucking (since this process is a serious burden for the baby and during this period the superficial vessels of the skin may expand, which manifests itself in the form of blue in the area of the “triangle of death”).
Pathological conditions leading to blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle
A blue nasolabial triangle in a baby can be due to the following diseases:
- of cardio-vascular system. These include: heart defects, heart failure, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, etc.;
- respiratory system. These include: bronchial asthma, respiratory allergosis, complicated parainfluenza, pneumonia, bronchitis, obstruction of the respiratory tract by a foreign body, malformations of the pulmonary artery;
- nervous system. These include: increased intracranial pressure, immaturity of brain structures, birth trauma.
Blueness of the perioral area in a baby is only a consequence of diseases of one of these systems.
How to distinguish the norm
To analyze the baby’s health status, parents just need to carefully monitor him. If the nasolabial triangle has acquired a blue tint, pathology can be excluded:
- with normal growth and development of the child;
- in the absence of heart murmurs;
- with normal skin color in the area around the mouth and other parts of the body;
- with active behavior of the baby;
- in the absence of cough or difficulty breathing, when cyanosis appears;
- with a normal pinkish skin tone;
- in the absence of a drowsy and lethargic state.
If at least one of the listed points does not coincide with the actual condition of the baby and the area above the upper lip rapidly turns blue, an urgent consultation with a doctor is required.
What do we have to do
If your baby's area above his upper lip turns blue, you need to look at why it appears. If a symptom occurs during bathing and quickly disappears, it does not pose any danger to the baby’s health. If this skin condition persists, you should:
- Contact your pediatrician as soon as possible. At your appointment, the doctor may prescribe additional tests to make the correct diagnosis and tell you why the upper lip area turns blue. Among the procedures, the doctor may prescribe: an electrocardiogram, an ultrasound examination of the heart muscle, and an x-ray of the chest area. Also, in some cases, it is necessary to visit a neurologist to conduct a complete examination of the child.
- change your lifestyle. It is necessary to maintain optimal temperature and air humidity in the room where the child is. You should go for walks more often, and also soothe the baby when crying. This advice also applies to healthy children, since correct and timely development occurs only in a comfortable environment.
- Do massage. Carrying out a daily massage will stimulate the activity of the nervous system, as well as normalize the functioning of the respiratory system. If a foreign body enters the child's respiratory tract, you should carefully and quickly place the baby stomach down on your lap and lightly hit him on the back. If this method does not work, you should urgently call a doctor to prevent the appearance of blue skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle, as well as suffocation.
Post published by Kitty390 April 21, 2011
2
I’ve been wanting to ask for a long time: the child has pale skin and sometimes blue around the mouth. Is there any reason to worry or is this a feature of it?
Signs of pneumonia in children
19.08.2020
Pneumonia , or pneumonia , is a condition that affects about six in 10 children. It is very important to protect a child from this disease, since not only the health, but also the life of the baby is at risk.
The essence of the disease is that the infection enters the alveoli - bubble-like processes that are located just below the bronchi. The danger is that it is in the alveoli that the process of exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen occurs. And if this process is complicated by inflammation, then the normal functioning of the body while meeting all its needs is impossible.
As a result of the inflammatory process in the alveoli, the child develops oxygen starvation, that is, hypoxia. As a result, the main blow falls on the cardiovascular system - quite often, heart problems are a complication of pneumonia .
If we talk about the causes of pneumonia , then parents should know: the causes of this disease in adults and children are different. Most often, in adults, pneumonia develops independently, but in children, pneumonia is most often the result of some recent infection, for example, influenza or acute respiratory disease.
In the development and occurrence of this disease, an important role is played by immunity and his age: the younger the child’s age, the higher the risk of the disease. In addition, if the child is small, then it is much more difficult to diagnose and treat pneumonia .
Doctors have identified a number of diseases in which the risk of contracting pneumonia increases sufficiently, and the treatment of the disease itself is quite dulled. Among them are malnutrition, rickets, diseases associated with a deficiency of the immune system , anemia, diseases of the central nervous system heart defects .
Although pneumonia occurs due to one cause, doctors distinguish several types of pneumonia . This classification arose because pneumonia can affect different parts of the lungs . So, there are these types of pneumonia :
- focal pneumonia - inflammation of a small area (up to one centimeter in diameter) of the mucous membrane of the lung;
- segmental or polysegmental pneumonia - inflammation of an entire segment or several segments of the lungs ;
- lobar left-sided or right-sided pneumonia - inflammation of the right or left lobe of the lung.
To determine whether a child has pneumonia , you should look closely and listen to his well-being. You should pay attention to:
- breath. Increased breathing and shortness of breath in children can be a sure sign that various inflammatory processes are occurring the lungs
- Body temperature. Elevated body temperature is almost always one of the most important signs of inflammatory processes in the lungs ;
- skin retraction syndrome. It appears when the child breathes, and the texture of the skin between the ribs changes;
- blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle.
Pneumonia is a serious illness, so you should not treat it yourself. That is, if your child has been diagnosed with pneumonia , immediately seek help from a specialist.
You should not use traditional medicine to cure a child’s illness on your own, because there may be no result, and time will be lost. The doctor will prescribe exactly the drugs that are suitable for your child: antipyretics, mucolytics that will help the child get rid of phlegm in the throat .
Based on the general condition of the child, the doctor can draw conclusions: should he undergo inpatient treatment, that is, in a hospital , or should he be treated at home. If the child’s condition is not very bad, then it is quite possible that the mother herself will be able to control his treatment, only from time to time showing the child to a specialist.
Keep an eye on your child, treat him if he gets sick, and let him grow up healthy and loved.
Published in Pulmonology Premium Clinic