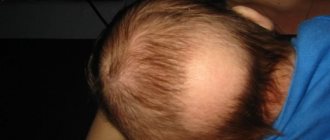
Vitiligo (leukoderma) is a peculiar skin disease characterized by depigmentation, manifested in the form of light spots throughout the body, including the face. They appear due to the lack of melanin production. The disease can develop in people of any age, but the largest percentage affects children and adolescents. Vitiligo in children occurs with certain characteristics.
The disease itself is not contagious or dangerous, but it does bring some discomfort and cosmetic defects. This pathology is characterized by gradual development and a long course.
As the child gets older, the spots increase in size and take on different shapes. If foci of vitiligo are localized in open areas of the body, then under the influence of sunlight, dryness, thickening of the skin in the area of depigmentation, as well as peeling and redness may appear. It is worth noting that sun tanning causes spots to become more noticeable.
Treatment of vitiligo in children with Melagenin Plus lotion
Types of childhood vitiligo
Depending on where the foci of depigmentation are distributed, the following types of disease are distinguished:
Type A (Generalized appearance)
This type is characterized by a long course of the disease. Has the following forms:
- Acrofascial. It is characterized by damage to the distal parts of the limbs.
- Universal. Quite rare in children. Characterized by damage to a large area of skin (more than 80%).
- Mixed. Includes several subspecies; spots are localized over the entire surface of the body, including the head.
- Vulgar. Develops in two or more areas of the body.
Type B (Localized view)
The following forms are distinguished:
- Focal. Vitiligo spots are located only on one side of the body. This type of disease does not progress or spread.
- Zosteriform. It is characterized by a grouping of small lesions in one area of the body.
- Segmental. Depigmentation spreads along the location of large nerves and plexuses.
- Mucous. The spots are localized only on the mucous membranes, as well as on the genitals.
Main reasons
Any of the diseases is collectively called hypopigmentation - discoloration of the skin, nails and hair, which occurs due to a lack of pigment called melanin. One of the most common diseases that is accompanied by the appearance of white spots on the skin of infants is Vitiligo (loss of melanin). The reasons for the origin of this disease are unknown, and the ways of treating it also do not give the desired result. The only thing you can do is try to improve the appearance of your skin in various ways, which we will discuss later.
Pityriasis versicolor
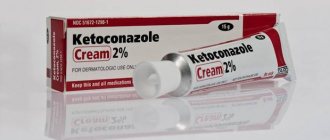
The second most common cause of white spots is fungi, which are found in the body of every person. However, under favorable conditions (moisture and warmth), the number of fungi begins to increase, resulting in red-brown or white spots appearing on the skin. The causes of infection are increased sweating and a warm, humid climate. For treatment, you can use antifungal drugs, for example, Clotrimazole or Terbinafine.
Important! Only a professional dermatologist can make a correct diagnosis, so you should not experiment on your child and his health by self-medicating.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
Symptoms:
- Small white spots exposed to sunlight.
- The skin becomes smooth, but can peel off.
Important! This disease is more common among women with fair skin, the cause of its occurrence is unknown, doctors suggest that it is one of the symptoms of aging.
Pityriasis alba
With this disease, the skin also begins to change its color. Pityriasis alba is most often seen in adolescents and children living in warm climates. The whitish spots become dry and scaly; the causes are still unknown.
Pigmentless nevus
In simple terms, a pigmentless nevus is a birthmark that poses a threat to human life and health, since the development of melanoma is a severe malignant tumor that occurs on the skin.
Other reasons
It is worth noting that white spots may appear on a child’s body due to improper or poorly balanced nutrition. Due to a lack of vitamins and certain pigments, white marks may appear on the human body, which are not dangerous and disappear with the right diet or taking bioactive supplements. In addition, the reasons for the appearance of white spots can be:
- Psoriasis is a chronic non-infectious disease.
- Leukoderma is a disease that can appear after syphilis.
Important! The previously mentioned diseases are extremely rare in infants, but it is necessary and important to know about them, as it concerns health.
Manifestations in children
As for the skin of newborns, white spots on it may appear due to one of these diseases:
- Tumorous sclerosis - white spots, the radius of which reaches 1.5 centimeters. The result of the disease can be more serious pathologies, for example, epilepsy, mental retardation or damage to internal organs.
- Hypomelanosis - may appear after suffering a severe infectious disease; it occurs due to dyschromia of the upper layer of the skin.
Stages of childhood vitiligo
The disease in children has the same stages of development as in adults:
- Initial. First, one small spot appears, which may not increase in size for a long time and is a single spot.
- Progressive. It is characterized by the appearance of a large number of new spots over several weeks and an increase in the size of old ones.
- Repigmentation. This stage is diagnosed if no new foci of the disease have appeared for several months, and existing spots darken, do not grow, and in some places completely disappear.
Parents should know that vitiligo is prone to recurrence. If you manage to completely get rid of the signs of the disease, it may return after some time.
Neurofibromatosis in children
To confirm the diagnosis of neurofibromatosis, the child must have at least 2 of the following signs:
- dark spots
- leiomyomas of the iris
- 2 or more neurofibromas in the form of subcutaneous peas
- heredity
- pathologies in the bones
- freckles under the arms and groin
- optical glioma
To detect tumors and diagnose problems with skeletal bones, two methods are used: MRI and radiography. Children with neurofibromatosis have a larger head circumference than children of the same age without this diagnosis. To diagnose NF2 in children, hearing must be tested. To do this, audiometry is used to check the brain, ear nerves and spinal cord to detect possible tumors.
Studying the child's family history can provide important information. If there is neurofibromatosis of the first or second type, a genetic examination can be performed. But we cannot say that its results are 100% accurate. In some cases, abnormalities can be detected in a newborn baby using chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis.
To make a diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type 1, consultations with the following specialists are needed:
- ophthalmologist
- neurologist
- surgeon
- dermatologist
- oncologist
- geneticist
- neurosurgeon
The doctor may need to see more relatives if there is at least one member of the family with café-au-lait spots, or if there is a family history that indicates that member of the family.
Differential diagnosis
Cafe-au-lait spots are found not only in the disease in question, but in more than a hundred hereditary diseases and syndromes. It is also necessary to distinguish between neurofibromatosis types I and II. In the second type, the tumors are benign, but more aggressive than in the first type.
The absolute diagnostic criterion for NF1 is the presence of bilateral neuromas of the VIII pair of cranial nerves in the patient. In the second type, gliomas, meningiomas, and schwannomas can be detected.
It is necessary to differentiate neurofibromatosis I from Klippel-Trenaunau-Weber syndrome, Proteus syndrome, disseminated lipomatosis, etc.
Differential diagnosis of NF2 in children is carried out with the following diseases:
- schwannomatosis
- nonpolyposis colon cancer
- McCune-Albright syndrome
- LEOPARD syndrome
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
- Noonan syndrome
- "piebald trait"
- Proteus syndrome, etc.
Neurofibromatosis has common features with a disease such as spotted nevus , which is a manifestation of genetic mosaicism. Some researchers consider macular nevus as segmental neurofibromatosis. Children with macular nevus may develop NF1. Nevus occurs in a child from birth or is found in a child until he is 3 years old. With a spotted nevus, the child has light brown spots, against their background there are dark-colored inclusions of small sizes.
Nevus in children is large, but can be small. There are cases of 2-sided lesions. Spotted nevi do not leave the child’s body throughout his life. There is a very small risk of malignant degeneration of the disease. When diagnosing, it is very important to distinguish between macular nevus and neurofibromatosis.
Main symptoms
In general, symptoms of vitiligo in children begin to appear by the age of 9-10 years. At the same time, the clinical manifestations of the disease in infants and older children may be different and develop depending on the general condition of the child. Initially they are small in size, round in shape and pinkish in color. As the child grows, the spots also increase in size, take the form of blots and become milky white.
As a rule, depigmentation does not cause pain. However, too much sun exposure can lead to dryness, irritation and sometimes itching. If a child scratches the spots, it can cause infection of the wounds, as well as their inflammation.
If leukoderma is localized on the scalp, then in these places the hair becomes discolored and turns gray. In this case, the affected areas are less responsive to cold or heat. The disease does not affect the internal organs and systems of the body.
What is Vitiligo?
As mentioned earlier, the most common disease that is accompanied by the appearance of white spots on the skin is Vitiligo. As a result of this disease, spots of various shapes and sizes appear on the skin of adults and children; the cause is the lack of melanin. As a result, the skin is not protected from sun exposure and there is a risk of getting a burn.
Manifestation of Vitiligo:
- On the arms and face, in the elbows and groin.
- Spots appear in separate areas or create groups that merge into a single spot that occupies most of the body.
- The disease does not appear on the feet and palms.
- If spots appear on the head, the hair also loses color.
Causes of the disease:
- Heredity.
- Impaired liver function.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland and endocrine system.
- Incorrect functioning of the pituitary gland.
- Gastrointestinal disease.
- Disease of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Stress and infectious diseases.
- Malfunctions of the immune system.
- Disturbed balance of vitamins and microelements.
Vitiligo is often confused with other diseases, namely:
- Leucoderma.
- Ringworm.
- Pityriasis versicolor.
Important! Only a dermatologist can determine the cause of spots and methods of treating them, so do not delay your visit to the doctor.
Rules of caution:
- You can't sunbathe with a sweaty body.
- It is forbidden to stay in drafts for a long time.
- It is not advisable to use air conditioners and fans.
- You should not stay in air with high humidity levels for a long time.
Important! In general, any violation of the skin is a health problem, however, Vitiligo is not an infectious disease, so it does not pose a danger to others.
Causes of leukoderma in children
It is known that there is a genetic predisposition to vitiligo. The following factors may also influence the development of the pathological process:
- Improper functioning of the immune system. The child's body perceives melanocytes as foreign cells and begins to produce antigens for them.
- Chronic pathologies.
- Aggravated infectious processes.
- Metabolic disorder.
- Lack of vitamins and microelements.
- Chemotherapy.
- The influence of medications.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Chemical burns.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Helminthiasis.
Sometimes the appearance of leukoderma in children is associated with unstable hormonal levels or psychological trauma.
Nature of the problem
In winter, a person pays little attention to the condition of the skin, and the white spots and dots noticed in spring or summer could have been there earlier, but appeared on skin that had darkened from the first tan. Pigmentation disorders could arise due to a decrease in the production of melanin in the body.
Melanin is a coloring pigment that is present in the human body and is responsible for the color of some tissues. The normal state of pigment production depends on many components, including the following indicators:
- the content of nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen and sulfur in the human body (depending on the type of pigment cells, and some other chemical compounds);
- amino acids, the composition of which in the pigment has not yet been sufficiently studied, and only some of them are known;
- normal or pathological state of melanocytes (specific skin cells in which pigmenting dye accumulates);
- functionality of desmosomes (natural bridges connecting melanocytes to keratinocytes and forming functional units);
- the intensity of activity of functional units that ensure the flow of the coloring pigment melanin into the layers subject to color design (this includes not only the hair and iris of the eye, but also the upper layer of the skin);
- the problem may also be in the state of keratinocytes, of which there are about 40 per 1 melanocyte;
- Pigmentation disorders can also occur from disturbances in phagocytosis, which is the natural transition of pigment from the openings of the melanocyte to the surrounding keratinocytes.
Photo: White spots on the leg
White spots can appear on the upper layer of the skin due to any of the listed failures in the process of natural pigmentation, and the knee in this case acts as a convex part of the limb, which is constantly exposed to the sun's rays. Tanning is also the development of pigmentation under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, and disruption of the natural cycle leads to the appearance of white (not colored by pigment) spots.
Melanin synthesis occurs on command, and under the influence of a specific hormone provided by nature, and it is likely that depigmentation occurred under the influence of hormonal imbalance and disruption of the functionality of the endocrine system. This option involves contacting an endocrinologist and restoring normal hormonal levels.
In women, such disruptions are temporary manifestations, especially during the menstrual cycle, during pregnancy or menopause. Disruption of melanocyte production or the natural pigmentation process can occur for several reasons independent of hormone production.
Treatment methods
Basically, the treatment of childhood vitiligo is aimed at restoring metabolism in the child’s body, since most often it is metabolic disorders that become the cause that affects the insufficient production of skin pigment. For treatment to bring positive results, it is advisable to use an integrated approach.
Symptomatic therapy
Its main goal is the maximum restoration of the lost pigment formation function. For this use:
- Local application of corticosteroids.
- Photosensitizing agents that restore normal pigmentation in affected areas of the body.
- In the case of a generalized type of disease, photochemotherapy is used.
- Herbal medicines.
- Ultraviolet treatment (its plus is safe for children over 3 years old)
To make the cosmetic defect less noticeable, skin whitening procedures are performed to reduce the contrast between healthy and depigmented skin.
Drug treatment
The following groups of medications are used for drug therapy:
- Glucocorticoids.
- Antioxidants.
- Immunomodulatory agents.
- Photosensitizing hormonal drugs.
- Multivitamin complex.
Surgery
The main methods of this treatment:
- Autoplasty (affected skin is replaced with healthy skin).
- Transplantation of own or donor melanocytes.
- Transplantation of cultured epidermis.
- Application of tissue genetic engineering.
Such actions are carried out only in extreme cases, since there is a high probability of rejection or suppuration of the transplanted tissue.
It is possible to cure leukoderma, but the final result will primarily be influenced by timely diagnosis of the disease and a well-chosen course of therapy.