About the disease
Herpetic infection is a collective concept that is used to refer to diseases that are provoked by different types of the virus of the same name.
Traditionally, in pediatric practice, pathology caused by type 1 is encountered. This is the so-called labial herpes (rash on the lips). Its peculiarity is its chronic course. It is impossible to completely get rid of the pathogen. With adequate treatment of a child with symptoms of labial herpes, stable remission can be achieved. However, at this time the virus “hides” in the nerve ganglia (ganglia), where it can remain inactive for as long as desired. When favorable conditions arise (primarily decreased appetite), it is activated again. Another common form of herpes infection that can occur in children is varicella (chickenpox). The disease is provoked by the herpes virus type 3. It is important to remember that after successful recovery, the pathogen also goes into a latent form and persists in the nerve ganglia. The risk for the patient may be a reoccurrence of the infection. The type 3 virus, when reactivated, can cause herpes zoster, which is characterized by a more pronounced clinical picture with a deterioration in the child’s well-being and the appearance of rashes along the intercostal nerves.
The specialists of the SM-Doctor clinic have extensive experience in early diagnosis and treatment of all pathologies caused by herpes viruses. Doctors provide the necessary monitoring and quality treatment for children with any form of herpetic infection.
Herpes symptoms
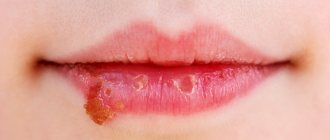
Labial herpes is the simplest and most harmless form of the disease, which occurs most often in children. Apart from discomfort for the baby and parents, in most cases the disease is not accompanied by serious consequences. Typical clinical picture:
- the formation of painful blisters filled with serous fluid in the lip area;
- itching and burning in places where skin elements appear;
- loss of appetite. Breasts may refuse to breastfeed due to pain during feeding;
- general weakness, lethargy, emotional lability;
- increase in body temperature to 37-37.5 ° C (rare).
With adequate treatment, signs of the disease can disappear after 3-4 days.
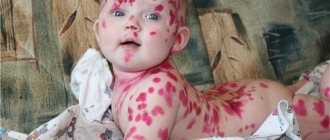
Chicken pox is a typical representative of “childhood infections”. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of rashes with serous contents throughout the body of a small patient. A characteristic feature that allows you to quickly differentiate chickenpox from other infectious pathologies is the obligatory presence of pustules on the scalp and the formation of crusts after removal of the blisters. The disease is also accompanied by a rise in body temperature to 38-39.5 ° C. The severity of the pathology depends on the individual characteristics of the child’s immune system and the aggressiveness of the pathogen.
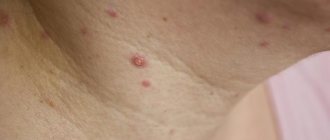
Herpes zoster is accompanied by:
- the occurrence of rashes along the intercostal nerves;
- severe pain in the area where the pustules spread;
- high fever;
- pronounced general intoxication syndrome.
If you detect at least one of these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. SM-Doctor specialists point out that chicken pox and herpes zoster are diseases that require isolation of a small patient in a hospital to monitor his condition and prevent the spread of the pathogen to other family members and the environment.
Herpes zoster in children
23.09.2021
The child's body is very susceptible to infectious diseases in general and herpes infection in particular. It is worth recalling that intrauterine infection of the fetus by the herpes virus can lead to a generalized herpes infection, which is very severe in newborns and can cause deformities, congenital anomalies, blindness and even death.
Local forms, for example, herpes simplex (simplex, type 1) or genital herpes (type 2) are not so severe, although type 2 herpes is of great concern due to its appearance with significant immunodeficiencies. But there is a type of herpes that can cause serious complications in both children and adults. We are talking about a form of infection called herpes zoster. How does it manifest itself, how is it treated, and what can happen if it is not treated ?
Herpes zoster, or herpes zoster, is one of the variants of herpes development. It is characterized by a rash of blisters on the skin, repeating the course of the saphenous nerves , since the virus exhibits an affinity for nervous tissue. These vesicular eruptions classically follow the course of the intercostal nerve. What symptoms do children exhibit with this variant of herpetic infection?
Signs of herpes zoster
Since herpes zoster is an infectious disease, its first symptoms may be fever and malaise. If the immune system is weakened or the rash area is small, then there may be no general symptoms. But local complaints about the place where the vesicular rash appears are always present. These include:
- tingling and burning of the skin
- itching
- the appearance of pain that spreads along the nerve trunks
- the occurrence of skin redness (erythema syndrome) and thickening.
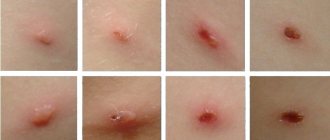
After a period of prodromal (preceding the appearance of the rash) phenomena, the exanthema itself occurs, that is, a typical rash.
It goes through a number of successive stages in its development:
- the spots are replaced by emerging nodules - papules, which are closely spaced and red in color
- subsequently the nodule turns into a vesicle filled with clear liquid; bubbles may merge
- after a few days, the contents of the bubbles become cloudy, their cap becomes flabby, they open, forming erosions
- erosions become covered with crusts, which dry out and fall off, often with hyperpigmentation phenomena.
As a rule, this disease in a child rarely occurs with such a severe complication as postherpetic neuralgia , but, nevertheless, you need to know what it is.
About neuralgia
In some cases, viruses are capable of degenerating nerves in such a way that they begin to generate spontaneous painful and burning impulses that exhaust the patient, lead him to insomnia and are difficult to treat, sometimes throughout his life. Imagine that for most of the day you feel as if you have just been whipped in the ribs by a bunch of nettles. In order to prevent neuralgia from occurring, you need to immediately begin specific treatment at the first suspicion of this viral attack. The earlier it is started, the less likely it is that a child or adult will develop postherpetic neuralgia .
About treatment
As soon as signs of a blistering rash appearing along the course of the nerve, antiviral drugs should be prescribed - Acyclovir, Famciclovir or Ganciclovir. In any case, the side effects from treatment with antiviral drugs will be less than from antibiotics, and they can help in quickly stopping the infection, and most importantly, in the formation of a persistent neurological syndrome.
For example, you can use 200 mg of Acyclovir or Zovirax 5 times a day until the rash stops appearing. It is also recommended to use a cream or ointment with an antiviral effect locally. In this case, an effective antiviral concentration of the drug will be created both in the blood and directly deep in the skin, which allows us to hope for the rapid elimination of rashes. In addition, if necessary, painkillers from the NSAID group and symptomatic drugs (reparants) are used. At the recovery stage, an ultrasound with B vitamins and novocaine.
You should know that treatment of all herpetic infections (not just herpes zoster) does not lead to a radical cure. As a result, the virus is “put to sleep”, and it is again driven into the cells of the nervous system - to where it was in an inactive state, “under the supervision” of the immune system . Therefore, the main task of preventing relapses is constant monitoring of immunity and the use of a vaccine.
Published in Children's Diseases Premium Clinic
Causes of herpes
All variants of herpes infection occur against the background of the activity of the virus of the same name of different types. Since upon initial penetration into the human body the pathogen no longer leaves it, it is important to know the factors that can provoke the activation of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- seasonal colds;
- any conditions that provoke a decrease in immune defense (poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis and others);
- exacerbation of chronic somatic diseases;
- contact with an infected patient.
The virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, so it is extremely difficult to completely prevent a child from encountering pathogenic particles.
Detailed description of the study
According to the World Health Organization, more than half a billion people are infected with herpes simplex virus type 2, and every year an average of 24 million more people are added to this number.
In various countries, the genital herpes virus affects up to 20% of the entire adult population. Moreover, the incidence of genital herpes virus increases as people get older.
Viruses of the Herpesviridae family are constantly present in the human body; their DNA is integrated into the DNA of nerve cells. If the body's immune system is weakened, the virus begins to actively spread in cells.
To date, eight varieties of the herpes virus are known, the most common among them is herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), most often localized on the lips, mouth and facial skin. And herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), which usually causes lesions of the genitals: labia majora and minora, vaginal mucosa, perineal area, inner thighs in women; the head and body of the penis, the scrotum, the inner thighs and the perineal area in men.
Herpes simplex virus type 2 is in most cases transmitted sexually, and transmission of the virus from mother to child during childbirth is also possible.
Most people infected with HSV-2 do not experience any unpleasant symptoms and do not see a doctor. When symptoms appear, patients mainly complain of:
- Itching and burning in the genital area;
- Increased body temperature;
- The appearance of painful blisters with transparent contents (vesicles) on the mucous membranes and in the genital area, which burst and form open wounds.
Characteristic clinical symptoms of HSV-2 in newborns usually appear between the 1st and 3rd weeks of life and include:
- Painful blisters all over the body, mainly on the mucous membranes;
- Skin ulcers;
- Damage to the central nervous system and internal organs.
Herpes simplex virus critically affects the immune system of newborns and is responsible for high morbidity and mortality. Laboratory diagnosis of herpes simplex virus is based on the isolation of the virus in a culture of cells taken from the contents of vesicles (vesicles), followed by identification of the virus. But such research takes a long time - up to 8 days - and is quite labor-intensive to carry out.
Determination of virus-specific antibodies in the patient’s blood serum is used to confirm the primary infection, as well as to establish a diagnosis in patients with asymptomatic disease.
The results of the study are influenced by the form of infection - chronic or recurrent, the reactivity of the body, and the time from the onset of the disease.
In the blood serum of recurrent herpes, high levels of class G antibodies (IgG) are detected. It is important to evaluate the determination of antibodies of this class over time (the study is carried out at intervals of 1 week); if there is a significant increase in the titer of G antibodies, this indicates a recurrent infection (return of clinical manifestations of the disease without re-infection). This study allows us to identify genital herpes, which is asymptomatic or with characteristic clinical symptoms, and is carried out in couples where one of the partners has type 2 HSV, as well as in pregnant women, in order to avoid transmitting the virus to the child during childbirth.
Diagnosis of herpes
"SM-Doctor" is a multidisciplinary clinic specializing in providing high-quality medical services to children of any age. Diagnosis of herpetic infections in our center is carried out according to the standards used in leading clinics in Europe and the world. Our specialists establish a preliminary diagnosis at the stage of the initial examination of the child. Depending on the severity of the clinical picture, the necessary auxiliary diagnostic procedures are selected:
- a set of standard laboratory tests (general blood test, urine test, blood “biochemistry”, etc.);
- specific serological tests (ELISA) to detect antibodies to a specific type of virus in the patient’s blood;
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a highly informative diagnostic method that allows you to detect the presence of a virus in a child’s body with up to 99% accuracy.
"SM-Doctor" is a multidisciplinary center. Thanks to this, if necessary (for example, if complications develop), our patients can be examined by a wide range of specialists in different fields. If the attending physician, in addition to infection, suspects a pathology of internal organs and systems, he refers the sick child for consultation with a cardiorheumatologist, ophthalmologist, neurologist and others. In a short period of time, the child receives a full range of diagnostic services aimed at identifying any abnormalities in the functioning of the body.
Complexes with this research
Male infertility.
Extended examination Analysis of the state of male reproductive health 19,800 RUR Composition Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure 15,030 RUR Composition
Miscarriage Identification of the main causes of miscarriage RUB 29,050 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 10,390 RUR
- Pregnancy planning. Diagnosis of infections RUB 6,010
- IVF planning RUB 9,080
Treatment of herpes
SM-Doctor doctors select treatment for herpetic infection for each child individually.
Our specialists prescribe medications depending on the severity of the clinical picture of the pathology and the presence of concomitant diseases. The following means are traditionally used to combat the virus:
- acyclovir is a specific drug to destroy the pathogen;
- antipyretic medications (paracetamol, ibuprofen) for fever above 38°C;
- auxiliary medications (painkillers, antiallergic and others).
Prevention of herpes
The basic rules that will help reduce the likelihood of infection with viruses of the herpes family are:
- hand washing;
- limiting contact with sick people;
- nasal instillation with saline solutions during the off-season.
There is now a vaccine against chickenpox. Vaccination helps prevent infection and/or development of severe forms of the disease. “SM-Doctor” is a multidisciplinary medical institution that provides effective treatment to children facing various diseases. Herpetic infection in any of its manifestations is not a problem. The main thing is to schedule a consultation with our specialists on time. Contact us!