What affects a child’s height and weight:
- hereditary factors: usually a child inherits growth parameters from one of the parents;
- a well-designed diet: if there is a lack of vitamins and essential substances, height and weight parameters can be seriously reduced; Smoking in childhood, as well as abuse of carbonated drinks and harmful carbohydrates, can retard growth.
- participation in certain sports: for example, height can increase significantly in basketball players, tennis players, volleyball players, and decrease in wrestlers, gymnasts, ballet dancers, weightlifters; Weight loss can occur in long-distance runners.
- health status: in children suffering from chronic pathologies, height and weight parameters are usually far from normal;
- psychological problems: tension between the child and parents, lack of sleep, problematic relationships with peers, etc.
Detailed assessment, recommendations, problems
The issues of harmonious formation of the future of a man and a woman lie entirely on the shoulders of the parents. A teenager's assessment of their appearance is not always objective, and often leads to far-fetched problems and complexes.
This period requires a more attentive and sensitive attitude towards children from adults. It is advisable to control the changing parameters, and discuss the reasons and ways to resolve the situation together with the child.
Short stature or, conversely, too much body length may be predisposing factors transmitted from close relatives. In this case, therapy is not carried out. In the absence of genetic causes, consultation with a doctor is required. You should not draw conclusions on your own and take drastic measures.
In order to minimize the risks of developmental disorders, it is important to adhere to a number of recommendations:
- establish a complete, balanced diet;
- exclude the use of low-carbohydrate, strict, express diets, only restrictions on fatty and high-calorie foods are possible;
- presence of regular physical activity;
- compliance with the prescribed time for sleep and rest;
- alcohol, tobacco, narcotic psychotropic substances are prohibited.
Be sure to read: How many calories are burned when walking and running: calorie burning rate per day without exercise
Weight estimation using body mass index
It is possible to determine the proportionality of development using the body mass index formula. In order to calculate BMI, you need to divide your initial body weight by your height (in m) squared.
For example, a child’s height is 143 cm - that’s 1.43 m, weight - 47 kg.
Let's do the calculation: 47 / (1.43*1.43) =22.9
Table No. 7 BMI assessment
| Coefficient | Correspondence of body weight to height | Recommendations |
| Up to 16.5 | Severe exhaustion | If there is a significant weight deficit, an examination is required. |
| 16,6-18,5 | Minor shortage | Adjust your diet, add a vitamin complex. |
| 18,6-25 | Norm | Maintain the regime. |
| 25-30 | Slightly elevated | Reduce consumption of high-carbohydrate foods, increase daily activity: exercise, walking, slow running. |
| 30-35 | Overweight (first degree obesity) | Corrections as prescribed by a doctor. |
| 35-40 | Second degree obesity | |
| From 40 | Severe obesity (3rd degree) |
Growth Estimate
It is recommended to measure the child's height monthly. When comparing the table value with the data on the measuring ruler, correct interpretation of the results is important.
Table No. 8 Assessment of growth indicators
| Very low | A serious sign of delayed physical development. The child must undergo examination. |
| Short | May indicate a lag. Often found among premature babies. |
| Below the average | A slight shortage, but within normal limits. |
| Average | Norm. Typical for most teenagers. |
| Above average | There may be deviations or a hereditary trait. |
| Very tall | Indicates endocrine disorders. Contact your doctor. |
For an objective perception of the results obtained, one should not rely entirely on the tabular formulations. It is important to take into account hereditary factors, lifestyle, and the characteristics of the puberty period, which play a significant role in the formation of a growing person.
Rating by weight
The table coefficients are approximate and are used as a guide.
Table No. 9 Assessment of body weight indicators
| Great underweight | A clear sign of exhaustion. Therapy under medical supervision is required. |
| Short | Indicates a lag. An examination is recommended. |
| Less than average | A little short of normal. The diet needs to be supplemented with healthy foods and microelements. |
| Average | Norm. An indicator of healthy development. |
| Excess weight | There is a risk of obesity. It is important to adjust your diet and increase physical activity. |
| Very big | A clear sign of obesity. Mandatory contact with a nutritionist. |
Even within normal limits, outwardly the body may appear thin or, on the contrary, plump. This depends on the rate of skeletal formation or the ratio of fat and muscle tissue in the body.
Centile table of height and weight of a child up to one year
| Age | Girls | Boys | ||
| Weight, kg | Height, cm | Weight, kg | Height, kg | |
| Newborns | 3,33 ± 0,44 | 49,50 ± 1,63 | 3,53 ± 0,45 | 50,43 ± 1,89 |
| 1 month | 4,15 ± 0,54 | 53,51 ± 2,13 | 4,32 ± 0,64 | 54,53 ± 2,32 |
| 2 months | 5,01 ± 0,56 | 56,95 ± 2,18 | 5,29 ± 0,76 | 57,71 ± 2,48 |
| 3 months | 6,07 ± 0,58 | 60,25 ± 2,09 | 6,26 ± 0,72 | 61,30 ± 2,41 |
| 4 months | 6,55 ± 0,79 | 62,15 ± 2,49 | 6,87 ± 0,74 | 63,79 ± 2,68 |
| 5 months | 7,38 ± 0,96 | 63,98 ± 2,49 | 7,82 ± 0,80 | 66,92 ± 1,99 |
| 6 months | 7,97 ± 0,92 | 66,60 ± 2,44 | 8,77 ± 0,78 | 67,95 ± 2,21 |
| 7 months | 8,25 ± 0,95 | 67,44 ± 2,64 | 8,92 ± 1,11 | 69,56 ± 2,61 |
| 8 months | 8,35 ± 1,10 | 69,84 ± 2,07 | 9,46 ± 0,98 | 71,17 ± 2,24 |
| 9 months | 9,28 ± 1,01 | 70,69 ± 2,21 | 9,89 ± 1,18 | 72,84 ± 2,71 |
| 10 months | 9,52 ± 1,35 | 72,11 ± 2,86 | 10,35 ± 1,12 | 73,91 ± 2,65 |
| 11 months | 9,80 ± 0,80 | 73,60 ± 2,73 | 10,47 ± 0,98 | 74,90 ± 2,55 |
| 12 months | 10,04 ± 1,16 | 74,78 ± 2,54 | 10,66 ± 1,21 | 75,78 ± 2,79 |
Child at 11 months weight and height
The baby's growth rate has noticeably decreased since birth. He got toned and visually lost weight. This is due to the fact that the baby’s activity has increased. During the eleventh month, the child gained about 200 grams in weight and grew by 1 - 1.5 centimeters . The head circumference increased by 0.5 centimeters, the chest circumference by 0.5 - 1 centimeter.
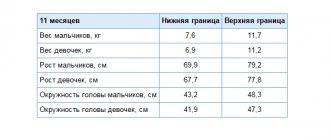
Table of weight, height and volume indicators for boys and girls at 11 months
The table was compiled using WHO data and presents the physical indicators of healthy children at 11 months.
Standards for height and weight of children WHO TABLES VIEW
The average weight at 11 months is 8.7 kilograms for girls, 9.4 kilograms for boys. Height for boys is 74.5 centimeters, for girls 72.8 centimeters.
Centile table of height and weight of a child by year up to the age of 18
| Age | Girls | Boys | ||
| Weight, kg | Height, cm | Weight, kg | Height, kg | |
| 1 year 3 months | 10,52 ± 1,27 | 76,97 ± 3,00 | 11,40 ± 1,30 | 79,45 ± 3,56 |
| 1 year 6 months | 11,40 ± 1,12 | 80,80 ± 2,98 | 11,80 ± 1,18 | 81,73 ± 3,34 |
| 1 year 9 months | 12,27 ± 1,37 | 83,75 ± 3,57 | 12,67 ± 1,41 | 84,51 ± 2,85 |
| 2 years | 12,63 ± 1,76 | 86,13 ± 3,87 | 13,04 ± 1,23 | 88,27 ± 3,70 |
| 2 years 6 months | 13,93 ± 1,60 | 91,20 ± 4,28 | 13,96 ± 1,27 | 81,85 ± 3,78 |
| 3 years | 14,85 ± 1,53 | 97,27 ± 3,78 | 14,95 ± 1,68 | 95,72 ± 3,68 |
| 4 years | 16,02 ± 2,30 | 100,56 ± 5,76 | 17,14 ± 2,18 | 102,44 ± 4,74 |
| 5 years | 18,48 ± 2,44 | 109,00 ± 4,72 | 19,70 ± 3,02 | 110,40 ± 5,14 |
| 6 years | 21,34 ± 3,14 | 115,70 ± 4,32 | 21,9 ± 3,20 | 115,98 ± 5,51 |
| 7 years | 24,66 ± 4,08 | 123,60 ± 5,50 | 24,92 ± 4,44 | 123,88 ± 5,40 |
| 8 years | 27,48 ± 4,92 | 129,00 ± 5,48 | 27,86 ± 4,72 | 129,74 ± 5,70 |
| 9 years | 31,02 ± 5,92 | 136,96 ± 6,10 | 30,60 ± 5,86 | 134,64 ± 6,12 |
| 10 years | 34,32 ± 6,40 | 140,30 ± 6,30 | 33,76 ± 5,26 | 140,33 ± 5,60 |
| 11 years | 37,40 ± 7,06 | 144,58 ± 7,08 | 35,44 ± 6,64 | 143,38 ± 5,72 |
| 12 years | 44,05 ± 7,48 | 152,81 ± 7,01 | 41,25 ± 7,40 | 150,05 ± 6,40 |
| 13 years | 48,70 ± 9,16 | 156,85 ± 6,20 | 45,85 ± 8,26 | 156,65 ± 8,00 |
| 14 years | 51,32 ± 7,30 | 160,86 ± 6,36 | 51,18 ± 7,34 | 162,62 ± 7,34 |
| 15 years | 56,65 ± 9,85 | 161,80 ± 7,40 | 56,50 ± 13,50 | 168,10 ± 9,50 |
| 16 years | 58,00 ± 9,60 | 162,70 ± 7,50 | 62,40 ± 14,10 | 172,60 ± 9,40 |
| 17 years | 58,60 ± 9,40 | 163,10 ± 7,30 | 67,35 ± 12,75 | 176,30 ± 9,70 |
Height and weight tables for children under 10 years old: girls and boys
Important parameters for determining the health of a child’s body are the height and weight of a child under 10 years old, the analysis of which takes into account the following factors:
- gender of the baby;
- weight and height at birth;
- genetic predisposition;
- past diseases - intestinal infections, acute respiratory viral infections, severe dehydration, teething, loss of appetite and others;
- disorders and deviations - congenital pathologies, chromosomal diseases;
- social conditions of education;
- type of nutrition - breast or artificial feeding.
Growth by month
From the moment the baby is born, the doctor weighs and measures him every month. The obtained values are recorded in the baby’s medical record. Their average statistical figures are shown in the table:
Development indicators for girls and boys in the first year of life
Weight by month
There is a separate table showing weight gain for babies up to one year:
Norm and limits of deviation of a child’s weight in the first year of life
Height and weight of a child from one year to 10 years
Very low and high numbers indicate the presence of deviations; those that are above and below the average are considered normal variants.
A table of height and weight for children under 10 years of age is compiled separately for boys and separately for girls and will help you independently determine whether your child’s physical development process needs to be adjusted.
Indicator table for boys
Growth indicators of development of boys under ten years of age
Weight development indicators for boys under ten years of age
The height and weight table for boys aged 10 years shows the proportional ratio for a given time period:
Indicator table for girls
Unlike boys, girls develop much faster. Therefore, it should not be surprising that children of different sexes of the same age may be inferior in performance to each other. The height and weight of girls under 10 years old is presented in this diagram:
Growth indicators of girls under ten years of age
Weight development indicators for girls under ten years of age
Why may there be minor deviations from the table in weight or height?
If you notice insignificant differences from the table values, do not worry. Minor deviations may occur for the following reasons:
- The WHO tables calculate the so-called reference weight and height of a child, that is, they do not take into account many real life factors, including the parameters of a child born prematurely (there are separate tables for such babies).
- The increase in a child’s weight and height over the years is purely individual. In addition, it is necessary to take into account that in the first 12 months development does not occur evenly, but spasmodically. Also keep in mind that in the first months of life, every new food product that you offer your baby always requires adaptation of the body, so during this period the child’s weight may decrease.
Weight and height calculator
The calculator on our page will help you get clear and accessible information about child development. Many mothers are familiar with the situation when a “little one” refuses certain categories of products or simply does not have time to have a full lunch due to a busy schedule. How nutritious is your child's nutrition? Is he getting all the nutrients he needs in the right amounts? We offer a simple and convenient way to find out how you can improve and diversify your children's diet.
Reasons for significant deviations in weight and height from norms
If the child’s height and weight by year significantly from the parameters presented in the table, it is necessary to contact a specialist - a pediatrician or pediatric endocrinologist.
Causes of pathologies of height and weight:
- Late puberty: when a delay in height and weight in a particular child occurs later than in his peers.
- Hereditary factor: stunted growth can be observed from an early age if the child’s family has short relatives.
- The child was born prematurely.
- The baby suffered from intrauterine injuries or received them after birth.
- Genetic abnormalities: usually present with a range of symptoms. Stunted growth, as well as non-standard weight indicators, are precisely such manifestations.
- Chronic pathologies of various systems and organs: heart and blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, bronchi and lungs, anemia.
- Acute lack of vitamins and essential nutrients.
- Use of certain pharmacological drugs.
- Deficiency of growth hormone, which regulates growth dynamics after the child is two years old.
- Thyroid hormone deficiency. It is usually a congenital endocrine pathology and slows down not only the growth, but also the intellectual development of the child.
- Insulin deficiency due to type 1 diabetes.
- Increased production of glucocorticoid hormones due to Cushing's syndrome.
- Vitamin D deficiency, as a result of which the skeletal bones are deformed and symptoms of rickets occur, including growth and weight retardation.
Weight and height standards for teenagers
Each child develops differently. You can independently monitor fluctuations in proportions in adolescents using specially developed and established standards.
Tables of height and weight ratios for adolescents represent average values that describe general boundaries and do not exclude individual aspects:
- the specifics of pregnancy by a woman;
- difficult birth of the mother;
- hereditary factors;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- unfavorable psychological climate in the family.
Normal height and weight for boys
Table No. 1 Growth indicators for boys 12-14 years old (indicated in cm)
| Growth criteria | Age (years) | ||
| 12 | 13 | 14 | |
| Very low | Less than 136 | Up to 141 | Up to 148 |
| Short | 136-140 | 141-145 | 148-152 |
| Below the average | 140-143 | 145-149 | 152-156 |
| Average | 143-154 | 149-160 | 156-167 |
| Above average | 154-159 | 160-166 | 167-172 |
| High | 159-163 | 166-170 | 172-176 |
| Very tall | Above 163 | From 170 | More than 176 |
Table No. 2 Weight indicators for boys 12-14 years old (indicated in kg)
| Weight criteria | Age (years) | ||
| 12 | 13 | 14 | |
| Very low | Less than 28 | Up to 30 | Up to 34 |
| Short | 28-30 | 30-33 | 34-38 |
| Below the average | 30-34 | 33-38 | 38-42 |
| Average | 34-45 | 38-50 | 42-56 |
| Above average | 45-50 | 50-56 | 56-63 |
| High | 50-58 | 56-66 | 63-73 |
| Very tall | More than 58 | More than 66 | More than 73 |
Normal height and weight for girls
Table No. 3 Growth indicators for girls 12-14 years old (indicated in cm)
| Growth criteria | Age (years) | ||
| 12 | 13 | 14 | |
| Very low | Less than 137 | Up to 143 | Up to 147 |
| Short | 137-142 | 143-148 | 147-152 |
| Below the average | 142-145 | 148-151 | 152-155 |
| Average | 145-154 | 151-159 | 155-163 |
| Above average | 154-159 | 159-163 | 163-167 |
| High | 159-163 | 163-168 | 167-171 |
| Very tall | Above 163 | From 168 | More than 171 |
Table No. 4 Weight indicators for girls 12-14 years old (indicated in kg)
| Weight criteria | Age (years) | ||
| 12 | 13 | 14 | |
| Very low | Less than 27 | Up to 32 | Up to 37 |
| Short | 27-31 | 32-38 | 37-43 |
| Below the average | 31-36 | 38-43 | 43-48 |
| Average | 36-45 | 43-52 | 48-58 |
| Above average | 45-51 | 52-59 | 58-64 |
| High | 51-63 | 59-63 | 64-72 |
| Very tall | More than 63 | More than 63 | More than 72 |
Be sure to read: Calorie deficit for weight loss: what is it, how to calculate it correctly, optimal indicators
Height and weight ratio tables for teenage children
The figures offered in the tables are calculated based on average anthropometric values inherent in a particular age.
Table No. 5 Selected ratio of height and weight of boys 12-14 years old
| Period | Optimal performance | |||||
| Flaw | Norm | Excess | ||||
| Height (cm) | Body weight(kg) | Height (cm) | Body weight(kg) | Height (cm) | Body weight(kg) | |
| 12 | 139 | 31 | 159 | 35 | 160 | 52 |
| 13 | 145 | 34 | 165 | 44 | 165 | 58 |
| 14 | 152 | 38 | 168 | 49 | 172 | 64 |
Table No. 6 Selected ratio of height and weight of girls 12-14 years old
| Period | Optimal performance | |||||
| Flaw | Norm | Excess | ||||
| Height (cm) | Body weight(kg) | Height (cm) | Body weight(kg) | Height (cm) | Body weight(kg) | |
| 12 | 141 | 32 | 150 | 40 | 158 | 54 |
| 13 | 147 | 37 | 155 | 47 | 164 | 61 |
| 14 | 151 | 43 | 159 | 53 | 167 | 65 |
During a period of rapid development, inconsistencies in ratios may occur for natural reasons.