- What is a sweet allergy?
- Causes of allergies to sweets
- Who is at risk
- Allergy to sweets: symptoms
- How does a sweet allergy manifest in children?
- What does a sweet allergy look like in pregnant women?
- Diagnosis of allergy to sweets
- Allergy to sweets: how to treat
What is a sweet allergy?
A pathology such as an allergy to sweets occurs in all categories of the population, but mainly occurs in children. The active component that provokes an allergic reaction is sucrose. Once in the gastrointestinal tract, this substance is difficult to digest, stimulating fermentation processes. As a result, food breakdown products and animal proteins enter the blood, triggering the production of immunoglobulin and causing an inflammatory reaction. Sweet intolerance cannot be called an allergy in the classical sense, since it does not imply the body’s sensitivity directly to sucrose. Pathology occurs against the background of incorrect functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and weak local immunity.
Vinikli nutrition - consult a doctor
To make an appointment for a consultation, call or fill out the return form:
(050) 301-99-26 (067) 446-11-79
Damn,
Your request has been successfully sent!
A call center specialist will contact you as soon as possible to clarify all the details.
Sweet allergies are rarely chronic. The pathology is aggravated by periods when consuming sweets in large quantities. With moderate consumption of confectionery products, the disease does not cause discomfort to a person. Pathology develops in childhood, which is due to the instability of the immune and digestive systems. In most cases, an allergy to sweets in children occurs at the age of 1.5-2 years and disappears by 7-8 years, subject to diet (restrictions in the diet of confectionery products). In the future, an exacerbation of childhood illness is possible, but this is usually associated with overeating and poor nutrition.
Treatment
It is impossible to cure a true allergy to sweets. A child with a hereditary disease will have to adhere to the diet for the rest of his life. During acute periods, when the baby could not resist and ate a couple of chocolates or drank soda with sugar syrup, doctors prescribe symptomatic treatment.
Ointments
The following hormonal drugs are allowed for children from 4 months of age:
- "Comfoderm";
- "Advantan".
Apply them in a thin layer once a day; for mild rashes, mix with baby cream. You can smear it on the face for 2-3 days, on the body – up to 7 days. An external medication will quickly relieve redness and itching, but will not relieve internal problems.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky! To restore the water balance of the dermis in case of allergies (dry skin, cracked fingers, ears), lubricate the child’s body after a bath with Bepanten, vitamin F99, emollients Atopic, La-Cri, Locobase.
Tablets, drops for allergies
Restores internal balance in the child’s blood. They reduce the level of histamines and block the allergic response to foreign protein.
Children from 6 months are prescribed drops:
- "Zyrtec", an analogue of "Cetirizine";
- "Fenistil";
- "Zodak".
Children from 3 years of age can take tablet forms of medications:
- "Diazolin";
- "Suprastin".
The dosage and frequency of administration depend on the age and weight of the child.
Cleansing the intestines of allergens and toxins
Infants and kindergarteners need to be cleansed of the storage of dangerous substances in the intestines. Take a course of enterosorbents:
- "Polysorb". 1 tsp. The powder is diluted in a glass of water and should be drunk 20–30 minutes before meals.
- Activated carbon. The dose is calculated according to the following scheme: 1 tablet per 10 kg of baby’s weight. Drink for 4–5 days.
- "Smecta". 2–3 sachets per day.
On a note! Sorbents remove not only toxins from the body, but also calcium. After a cleansing course, it is advisable to replenish the lack of a necessary element by taking a course of vitamins.
Desensitization
This is a new type of therapy that helps children get rid of allergies. Parents should consider an alternative method. This is a drug-induced accustoming of the body to an allergen. The child is given a drug with a low content of dangerous protein, and the dose is gradually increased. The immune system ceases to perceive sucrose as a foreign substance.
The course of treatment is long but effective. The child undergoes procedures from six months to one year. To prescribe treatment, contact an allergist or a special center.
Causes of allergies to sweets
The mechanisms that provoke an allergic reaction lie in the composition of confectionery products. There is a misconception that sweet allergies are caused by sugar, which by its nature is a carbohydrate. Unlike proteins and fats, carbohydrates do not have allergenic properties. Therefore, glucose is relatively safe for the human immune system and cannot be considered the main cause of allergies. Pathological processes are provoked by animal proteins (in particular, albumin) and certain types of fats contained in flour and confectionery products. Also, allergies are often caused by emulsifiers, dyes, flavors and other food additives. Absorbed into the blood along with nutrients, they have a detrimental effect on the immune system.
Biological causes of allergies include hereditary predisposition. About half of food allergies are passed on to children from their parents. Moreover, it is absolutely not necessary that both the father and mother have an allergy to sweets. It is enough for at least one parent to suffer from pathology. There is a possibility of a child inheriting a disease, even if the mother or father had it in childhood. Under such circumstances, sweet allergy in adults is in a chronic stage and is easily transmitted at the genetic level.
Almost any product containing a large amount of glucose can cause an allergic reaction. The following products pose the greatest danger to allergy sufferers:
- chocolate;
- honey;
- caramel;
- sweet baked goods (cakes, pastries, cookies);
- candies;
- condensed milk;
- jam, jam;
- marmalade;
- meringue, marshmallow.
Methods to combat this allergy
How to avoid such a nuisance as a sweet allergy? Quite simple.
- Control the amount of “goodies” you eat. This may seem quite difficult to you, but the less you indulge in chocolate, cakes and other sweets, the less likely you are to develop an allergy.
- Try to moderately diversify the menu. If you eat 20 grams of chocolate, one cake, three waffles and 50 grams of halva, you will be less likely to get an allergy than if you eat two whole chocolate bars.
- Healthy lifestyle. Yes, it will not completely cure your allergies. But it will help reduce the severity of symptoms and overall strengthen the body. Therefore, give up bad habits, do exercises, take time for walks and hardening. And your well-being will improve significantly.
Who is at risk
The risk of development is highest in preschool children. This is explained by the instability of the children's immune system to food irritants. If a child often consumes confectionery products, there is a high probability that he will develop a sweet allergy in the first 2 years of life. Risk factors that provoke pathology also include a woman’s diet during pregnancy. The mother's diet affects the baby's immunity, the development of the fetus's internal organs and systems. The predominance of sweets in a pregnant woman's menu often causes the baby to develop diathesis - an innate tendency to allergic reactions, provoked by abnormalities in intrauterine development.
People with atopic dermatitis are also at risk. This pathology is chronic and represents a hereditary tendency to allergic skin reactions. Irritation occurs due to mechanical impact or ingestion of certain foods. At the same time, an allergy to sweets often accompanies other forms of food allergies. People with this diagnosis often have allergies to citrus fruits, chocolate, and nuts.
The gastrointestinal tract plays an important role in developing the body's resistance to allergens. With various inflammatory and chronic processes in the organs of the digestive system, the risk of developing allergies increases significantly. With slow digestion, food particles begin to rot, and their breakdown products enter the bloodstream in the form of toxins. By poisoning the body, they activate its defense mechanisms. This leads to the active production of histamine, the main provocateur of allergic processes.
Hives from sweets
Urticaria from sweets is the mildest form of an allergic reaction. Although it also brings sufficient discomfort, as it is expressed:
- Rash;
- Blisters;
- Nodules;
- Spots.
It most often appears on the face and neck, but can also appear on any part of the body. Moreover, urticaria is not only a manifestation of allergies, it can also indicate more serious diseases of internal organs and systems.
Therefore, in case of any rash, you should contact the specialists of the Allergomed clinic. For many years, we have been helping people get rid of various allergic reactions, including allergies to sweets.
Allergy to sweets: symptoms
Manifestations of allergies occur within 30-60 minutes after eating sweets. Sometimes the body’s reaction is protracted and develops after 2-3 hours. The severity of symptoms depends on the amount of food eaten and the sensitivity of the immune system to allergens. The most severe reactions occur in children and people with weak immune systems. In this case, one cake eaten is enough to develop an allergy. All existing signs of a sweet allergy are conventionally divided into several categories.
- Gastrointestinal. The victim experiences pain in the abdominal cavity, accompanied by increased gas formation, loose stools, or vomiting. In case of a severe allergic reaction, the temperature may rise.
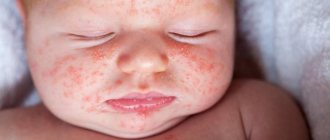
- Skin. Already 20-30 minutes after eating, the first rashes appear on the skin in the form of small red pimples, accompanied by itching. As the allergy progresses, the rash gets worse and the skin begins to peel. Red spots appear on the face and stomach. The hallmark sign of acute food allergies is hives. It manifests itself as numerous blisters that cause itching and burning.
- Respiratory. Symptoms in this category primarily affect the respiratory system. Already in the first minutes after eating, tingling and burning may occur in the oral cavity, which quickly leads to swelling of the laryngeal mucosa. The tumor blocks the airway, causing severe shortness of breath. Later, bronchospasms, runny nose, and dry cough are added to the symptoms described above.
An acute allergy to sweets develops within an hour after consuming an allergenic product and requires urgent hospitalization of the victim. In the absence of medical care, there is a high probability of developing Quincke's edema (giant urticaria). The most dangerous complication of a sweet allergy is anaphylactic shock. It leads to a drop in pressure and loss of consciousness. A patient with anaphylactic shock must be hospitalized immediately, otherwise the condition will be fatal.
What is urticaria?
Hives appear in 10-20% of men and women at least once in their lives. The disease is more common in adults after 30-50 years of age than in children, and about 0.5-5% of the population suffers from a chronic form. Rashes can appear and disappear on different parts of the body, regardless of the type of urticaria. In most cases, men and women experience blistering allergies due to allergens. In children, the most common cause of urticaria is infection (sore throat or acute respiratory viral infection).
Heat, aquagenic, autoimmune, or allergic urticaria in children and adults occurs when high levels of histamine and other chemicals (triggers) are produced in the skin. The production of triggers occurs as a response of the immune system to the action of irritants.
Irritants may include:
- food;
- pollen and plants;
- insect bites;
- chemicals;
- latex;
- dust mites;
- warm;
- ultraviolet or water;
- medicines;
- infections;
- emotional stress.
How does a sweet allergy manifest in children?
Uncontrolled consumption of sweets is the main cause of allergic reactions in childhood. The child’s weak body is not able to digest the huge amount of glucose entering it, which leads to intoxication. Also, the pathology is often provoked by a hereditary tendency to allergic reactions - diathesis. This condition develops in a child in utero and manifests itself in the first years of life. If you follow the diet recommended by the pediatrician, diathesis disappears without a trace by primary school age (6-7 years).
Nutrition plays an important role in the formation of a baby’s immunity. Thus, an allergy to sweets in an infant is directly related to the diet of the nursing mother. If a woman often consumes sweet pastries, candies and other confectionery products, glucose enters the baby's stomach along with breast milk. To avoid the development of allergies in your baby, it is recommended to give up sweets at least in the first two months of feeding. An allergy to sweets in a child who is on a regular diet is also caused by diet. Parents are advised to replace desserts on their child's menu with fresh fruit.
A child's allergy to sweets develops quite quickly; the first signs are noticeable within 20-30 minutes after eating. The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
the appearance of red spots on the hands and face;
- increased body temperature;
- vomit;
- dry paroxysmal cough;
- drowsiness.
Coffee
Despite the excellent invigorating effect of a cup of coffee in the morning, this drink can also cause acne on the face.
Coffee beans contain specific organic acids that increase the level of cortisol, the stress hormone. And cortisol, in turn, activates the sebaceous glands, which leads to their rapid clogging of pores. To keep your skin healthy, it is better to replace coffee drinks with tea, herbal infusions or chicory.
What does a sweet allergy look like in pregnant women?
An allergy to sweets during pregnancy is a fairly common occurrence. The pathology develops against the background of a sharp change in hormonal levels, leading to a decrease in immunity. In addition, pregnant women's metabolic processes are disrupted, which often causes digestive problems. Despite the fact that an allergy to sweets during pregnancy is considered a completely normal condition, it cannot be ignored. When the first signs of illness appear, you should contact an allergist. An allergic reaction is characterized by the following symptoms:
- redness of the skin of the face, especially the cheeks;
- the appearance of a rash on the arms, thighs, abdomen, chest;
- severe itching of the skin;
- swelling of the affected areas.
Is hives a sign of an allergy?
Signs of hives do not always indicate an allergy. In many cases, a single bout of rash is due to an infection or virus and resolves within a few days or weeks. Some people experience repeated attacks of a rash (recurrent urticaria), which occurs as an allergic reaction to various factors:
- foods, most often nuts, chocolate, fish, tomatoes, eggs, fresh berries and milk;
- insect bites;
- medications (for example, hives after antibiotics).
Recurrent bouts of rash usually appear within a few hours of exposure to either factor. Regardless of the cause of the rash and its frequency, you should consult a doctor. Recurrent urticaria can develop from sunlight, cold, pressure, vibration or exercise (physical, contact urticaria).
If the rash is not treated in a timely manner, the acute form can become chronic. For example, chronic induced urticaria may develop with chronic exposure to allergens.
Diagnosis of allergy to sweets
An allergist or an allergist-immunologist examines and treats patients with food allergies. Children's allergies are diagnosed by a pediatrician. Allergists use three main ways to evaluate patients with allergic reactions.
- Blood tests for immunoglobulin. After talking with the patient and clarifying the details of his outpatient card, the doctor sends the patient to the treatment room to collect a venous blood sample. Then the biological material undergoes laboratory analysis for antibody levels. To activate the process of immunoglobulin production, the suspected allergen is introduced into the blood serum. The result of the study is assessed using reagents that can bind to antigen-allergen bonds. Ig blood tests are the safest way to diagnose allergic reactions.
- Skin tests. To create favorable conditions for the development of the allergic process, the allergen is administered to the patient subcutaneously as an injection. Sometimes the irritant substance is applied in liquid form directly to the skin, but this method is less effective. After 2-3 hours, the doctor evaluates the result of the procedure. Skin tests are contraindicated in children under 3 years of age, so a child’s sweet allergy will be diagnosed exclusively through blood tests.
- Provocative tests. This technique is used least often, as it poses a danger to the patient’s health. After provocative tests, the patient remains in a medical facility for about a day under the supervision of doctors. The method is as follows: the patient consumes a certain amount of any sweet product, after which the doctor begins monitoring his condition. If allergy symptoms appear 30-60 minutes after eating, the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed.
The doctor spoke about the causes of allergic reactions to sweets
Many people believe that sweets can cause allergies. At the same time, sugar or, more precisely, its main element - sucrose, present in sweet products, is not an allergen. So why, for example, does an allergic reaction occur after eating chocolate? Allergist-immunologist, candidate of medical sciences Anatoly Bala explained that the reason for this is in individual components of sweetness, and not in sugar.
As a specialist told kp.ru, it is necessary to distinguish true allergies from pseudo-allergic reactions, which can also cause redness, peeling of the skin, burning, sneezing, runny nose, and so on, up to an increase in temperature. But this is not an allergy. The difference between them is the absence of an immunological component: a reaction occurs, but there are no antibodies - specific immunoglobulins of class E (IgE) to any component of the product.
The question is which component and in what quantity is contained in the dessert. If it contains a true allergen, for example, peanuts, nuts, soy, the body's reaction can be strong - up to anaphylactic shock. If there are no true allergens in the sweet product, treatment is not required. But if unpleasant symptoms appear, it is better to consult an allergist, who, using tests, should determine their nature - whether it is a pseudo-allergy or not.
— Sweets are a carbohydrate, not a protein, so they do not cause a true allergy. It is simply necessary to determine the dose of such a product that is safe for humans. If we are talking about food allergies, an elimination diet is prescribed,” says Anatoly Bala.
With such a diet, foods that cause reactions or may cause cross-allergic reactions are excluded. Also, if there are symptoms that require treatment, a specialist may prescribe medications. For severe symptoms, these will be antihistamines or hormonal medications to relieve severe itching, irritation or swelling.
In case of anaphylactic shock, before the ambulance arrives, you can use a syringe pen with adrenaline to eliminate the threat to human life. A simple way to prevent such conditions is to control the amount of goodies you eat. When buying a dessert, you need to find out what is in it. You also need to diversify the sweet menu.
According to the doctor, in a few sittings you can eat a couple of candies, a piece of chocolate, two or three waffles and marshmallows. It is advisable to choose products with a minimum content of allergens and histamine liberators, for example, marshmallows, marshmallows, and marmalade.
It is also necessary to take into account your age, since over the years a person’s level of the enzyme that breaks down histamine gradually decreases: what was safe in youth can cause a rash in old age.
Allergy to sweets: how to treat
Allergy therapy is based on limiting foods containing glucose in the diet. It is recommended to eat sweet fruits, vegetables, cereals, and savory baked goods. It is allowed to add sweeteners (fructose, etc.) to dishes and drinks. Parents need to exercise strict control over the diet of children who have been diagnosed with a sweet allergy. Treatment also involves taking medications to relieve symptoms. For allergies to sweets, patients are prescribed the following medications:
- antihistamines;
- enterosorbents;
- vasoconstrictor nasal sprays;
- hydrocortisone ointments.
Diagnostics or how to correctly identify the problem
Allergy tests can confirm an allergy to sweets. The analysis is carried out in winter, for children after 3 years.
Diagnostics is simple and takes no more than 30 minutes. The procedure looks like this:
- Small scratches are made on the inside of the child’s arm from the wrist to the elbow.
- Low concentrations of allergens are applied to the wounds. The set of substances is determined by the doctor, taking into account parents’ complaints and the results of observations of the baby’s reaction to different products.
- A negative skin reaction at the site of contact with the allergen is a sign of intolerance to the substance. The conclusion is made by the doctor immediately.
In newborns, it is impossible to carry out an instant diagnosis, since the body passes off a minute-by-minute reaction of the body as an allergy.
In other words, irritation from an applied allergen may appear today, but not tomorrow. This is due to the imperfection of the infant's systems.
The doctor makes a conclusion based on the parents’ words and long-term observation of the child’s reactions to food. Most often, mothers are offered the following allergen identification scheme:
- Keep a diary of observations.
- Write down in it every day all the foods that the child and nursing mother consume.
- Pay attention to those days on which the child develops redness on the skin, itching, rash and other allergy symptoms.
- Eliminate harmful foods from the children's diet. Continue observing.