Types of feeding premature babies
Breastfeeding
After premature birth, mother's milk has a special composition that better suits the nutritional needs of premature babies and is suitable for digestion and absorption. Compared to the milk of women who gave birth at term, it contains more protein, especially in the first month of lactation, contains more sodium and fat, and less lactose. This milk is quite easy to digest.
Degrees of prematurity
Babies born before the 37th week of pregnancy, weighing up to 2500 g and height less than 45 - 47 cm are considered premature. Doctors distinguish four degrees of prematurity:
Babies born before 28 weeks are tiny and often weigh less than a kilogram. Externally, they are very different from ordinary newborns: they have thin skin of a red-violet color, and their entire body is covered with hairs (lanugo). Typically, such babies require artificial ventilation and intravenous nutrition. There is no need to be afraid of this: after gaining weight, the child will learn to suck on his own, and special medications will help his respiratory system mature. Expect that the baby will spend several weeks, or even months, in the hospital, but then he will develop without problems at home.
If the baby was born between the 28th and 31st weeks, he will also look like a small alien. But babies from the third group weigh a little more and are sometimes able to drink breast milk or formula through a tube. Some of them know how to cry and grab an adult’s finger, as well as move their arms and legs.
Babies born between 32 and 34 weeks look like miniature full-term babies. Most can breathe on their own, although they sometimes need supplemental oxygen. And some are able to suckle at the breast or bottle from birth.
According to statistics, children from the first group of prematurity (born at 35 - 37 weeks) end up at home the fastest. They have problems with thermoregulation and feeding, but otherwise they very quickly catch up with babies born at term.
Enriching the diets of breastfed premature infants
You can preserve the main advantages of breastfeeding, as well as meet the high nutritional needs of a premature baby, with the help of:
- enrichment of mother's milk with doctor-recommended enhancers - protein-mineral or protein-vitamin-mineral supplements;
- in the absence of breast milk - the introduction of specialized mixtures based on whey proteins, for example, from the Nutrilak line. They are well tolerated by premature babies and are easily digestible
Artificial feeding of premature babies
This is another important way of feeding babies. The main indications for artificial feeding (diluted formula in a bottle) for premature infants are insufficient or complete absence of mother's milk or the child's intolerance to it. In the nutrition of children who were born ahead of schedule, exclusively specialized formulas should be used, the nutritional value of which is higher than standard adapted products.
The abolition of specialized products, as well as the transfer to regular infant formula, should be carried out gradually. Doctors believe that when a baby reaches a body weight of 2500 g or more, it does not serve as a serious contraindication to the further use of formula for premature babies.
When feeding a child in case of insufficient weight gain, such mixtures in a limited volume can be used in combination with classic formulas for full-term babies for several months. The use of infant formula for premature infants in a small volume (1/3–1/4 of the daily volume) can better provide infants born prematurely with nutrients, prevent the development of iron deficiency anemia and osteopenia, and increase the growth rate.
Features of feeding premature babies
Every expectant mother knows the approximate dates when her baby should be born. However, for a number of different reasons, some babies do not wait for the expected date of birth and leave their mother’s tummy a little earlier. If this moment occurs before the 37th week of pregnancy, the baby is considered premature and requires increased attention from specialists, as well as special care from the mother, who should know about the features of caring for such a baby. First of all, parents of a premature baby are puzzled by issues related to feeding. Fortunately, the level of development of pediatric science today, as well as modern food products that take into account the health characteristics of such babies, make it possible to ensure successful nursing of babies born prematurely.
Physiological characteristics of premature babies
The feeding characteristics of premature babies are determined by objective physiological factors, the main one of which is the more or less pronounced immaturity of the digestive system. In particular, in a premature infant:
- small volume of the stomach, which, in combination with a weak muscle layer, causes an increased tendency to regurgitate;
— the intestines of a premature baby also have a weak muscle layer and are easily stretched, increasing the risk of colic;
— salivation, which is necessary for normal digestion, is lower in premature babies than in full-term babies;
— digestive juices are also produced in insufficient quantities, and enzyme activity is reduced, which is why the baby’s immature body does not digest food well, especially fats.
In addition, the proper functioning of the digestive system of a premature baby may be impaired due to pathologies suffered by the baby before birth. In any case, it is obvious that in the first months of the life of a baby born prematurely, what, in what quantity and how often the mother feeds him is of great importance.
Food for a premature baby
Of course, the best food for a premature baby is mother's milk. For a weak baby, it is a real elixir of life, which will provide the baby with all the substances necessary for his growth and development, and will provide him with them in the most accessible form for his weak body.
If for some reason mother’s milk does not sufficiently satisfy the baby’s needs, the doctor may prescribe the use of a special fortifier. This is a drug that is added to breast milk, providing it with additional proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals, thereby meeting the increased nutritional needs of the premature baby. Feeding milk in combination with a fortifier improves the baby's weight gain and accelerates its growth rate, but at the same time allows you to maintain natural feeding, the importance of which for a premature baby cannot be overestimated.
However, it is often mothers of premature babies who have difficulty establishing and maintaining lactation. Often in a situation with premature birth, separation from the child, the baby's sucking reflex impaired due to prematurity, enormous stress and fear for the beloved child, problems with their own health - there are many reasons why mothers of premature babies are forced to give up breastfeeding. In this case, you will need to select an adequate breast milk substitute for feeding.
The fact is that the usual formula is not suitable for premature babies: babies born prematurely grow faster than their full-term peers, which means they need food richer in energy and protein, which is the main building material for cells and tissues. But their ability to absorb essential nutrients, on the contrary, is lower, which should also be taken into account in the composition of the mixture. That is why today almost all major manufacturers of baby food produce special adapted formulas for premature and low birth weight babies, characterized by a high content of protein, a carbohydrate component that facilitates the digestion and absorption of the mixture, as well as essential fats and fatty acids in an easily digestible form. In addition, infant formula for premature infants is enriched with vitamins and microelements in concentrations necessary to meet the increased need of such infants for valuable nutrients. This composition is optimal for premature babies and provides them with the so-called “catch-up growth”.
It is easy to find out special formulas for premature babies: as a rule, the label of such food contains the designation “Pre”, indicating that the composition of the infant formula is optimal for feeding the baby and is characterized by good digestibility and tolerability. However, it is not recommended to choose a formula for a premature baby on your own: a pediatrician should prescribe nutrition for such a baby, taking into account the health status of the particular child: the degree of prematurity, individual nutritional needs, developmental characteristics and even hereditary factors.
There are also subtleties in preparing formula for premature babies: regular boiled or “adult” bottled water may be too “heavy” for the immature digestive system of such a child. Therefore, it is advisable to prepare substitutes for premature babies using special baby water with an optimal balance of microelements and an impeccable bacteriological composition.
How often to feed a premature baby?
The frequency of feeding of babies born prematurely depends on various circumstances, such as birth weight, degree of maturity, and general condition of the body. Most premature babies easily tolerate seven to eight feedings at three-hour intervals. However, with extreme prematurity and a number of pathological conditions, the number of feedings can be increased up to 10 times a day - specific recommendations in this case will be given by the baby’s attending physician.
How much should a premature baby eat?
Often, parents of premature babies fall into a dangerous misconception, believing that the baby should eat more in order to actively gain weight. But it’s just the opposite: the smaller the baby, the less food he needs. After all, the digestive system of premature babies is imperfect, and overfeeding can only harm it.
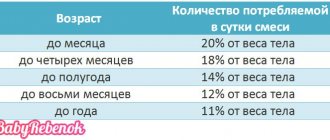
In the first two weeks of life, the daily amount of food for premature babies is calculated using the so-called Rommel formula, according to which the amount of milk or formula for every 100 g of the child’s body weight is 10 ml plus the number of days of the baby’s life. For example, if a child weighs 2200 g on the eighth day after birth, then he needs 396 ml of milk per day (10 + 8 = 18 g for every 100 g of body weight, this is 18x22 = 396 g for a weight of 2200 g). We divide the resulting figure by the recommended number of feedings and get a single serving.
While calculating and measuring the amount of formula is not so difficult, mothers of breastfed babies may doubt whether their child is eating enough. These fears are not unfounded: at first, premature babies may simply not have enough strength to suck the required amount of milk from the breast. Regularly weighing the baby on special baby scales before and after each feeding will help dispel doubts. Modern models will accurately determine the amount of milk consumed down to the gram, and if it is insufficient, the mother will be able to supplement the baby with expressed milk from a bottle.
Of course, feeding a premature baby requires even more responsibility from parents. However, with modern developments in medicine and a wide selection of special food products for premature and low birth weight babies, this task does not seem as difficult as it was even a couple of decades ago. A little effort and attention to your baby’s needs, and very soon he will delight you with regular weight gain, activity and his first smile!
Introduction of complementary feeding to premature babies
Complementary foods can be introduced from 4–5 months of age. The order of introduction of products has its own characteristics. This is due to the fact that some low birth weight children have certain gastrointestinal motility disorders, including after treatment.
Expanding the baby’s diet should begin with the introduction of porridge or vegetable puree. It is better to give preference to industrially produced products. This is due to the fact that their production uses environmentally friendly and proven raw materials, they have a guaranteed composition and proper degree of grinding, and are enriched with minerals and vitamins. Complementary feeding should be introduced with monocomponent products. As for porridges, dairy-free and gluten-free ones (rice, buckwheat, corn) are introduced first. They can be diluted with milk formulas that the baby receives. Porridges should not contain fruit, sugar or other additives. If the doctor has noted that the baby is at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, meat puree can be given as early as 5.5 months (taking into account the good absorption of heme iron from it). Cottage cheese can be given only after 6 months. It is advisable to introduce juices after 8–9 months. Their early introduction can lead to negative consequences: provoke colic, regurgitation, allergic reactions, diarrhea.
Here we are at home!
The baby will be discharged from the hospital as soon as he no longer needs constant medical supervision. Several more conditions must be met: stable weight gain, normal thermoregulation (the baby must maintain temperature without additional heating for 24 to 48 hours), the ability to feed independently (breast milk or formula). And most importantly, you must be able to care for your baby without outside help.
Here are some general tips to help during your first weeks at home.
- Remember the peculiarities of thermoregulation of premature babies. The room should not be too hot or too cold. The optimal temperature is 24 – 26 degrees. The room needs to be ventilated regularly; a humidifier won’t hurt either;
- Try to create soft lighting in your baby’s room and avoid harsh noise, because his nervous system has not yet matured;
- At first, you should not invite guests: for the baby this is additional stress and a potential source of infection;
- When bathing, you need to take into account the degree of prematurity: with moderate prematurity, you can wash the baby in the bath from the 7th to 10th day of life, with deep prematurity - from the 3rd to 4th week. To avoid drying out your baby’s thin skin, use special moisturizers and avoid soap;
- It is better to plan walks with a premature baby a week or two after discharge. If it’s not very cold outside, start with 10–15 minutes, gradually increasing the duration of “exercise” to an hour and a half a day.
Formulas for artificial feeding of premature babies from Nutrilak
The line of formulas for children includes a special product – Nutrilak Premium Pre. This is a specialized milk powder mixture that has a high protein content, a maximum predominance of fat and whey proteins, medium chain triglycerides (MCTs), a reduced lactose content and an increased calorie content. All this can help ensure that the baby catches up with growth compared to feeding with classic formulas.