Until what age should a baby be breastfed?
This question will be correctly divided into two parts: until what age should a baby be fed only breast milk, and until what age should a child be supplemented with milk after the introduction of complementary foods.
Regarding the first point, the World Health Organization (WHO) gives the following advice: exclusive breastfeeding is recommended for up to 6 months of a child’s life. It is undesirable to introduce complementary foods earlier, because the baby’s digestive system is not yet ready for complex foods, or later, because the baby’s body is running out of “innate” reserves of iron and other important substances, and he can only get them with complementary foods.
Regarding the second point, WHO advice sounds like this: it is advisable to continue breastfeeding for up to two years or even longer. We can say that this is more of an emotional than a physiological moment. Breastfeeding forms a close bond between the baby and the mother, and it is better to loosen it gently, gradually and carefully, than to then tear it quickly and to the quick. It is advisable to complete breastfeeding some time before you begin to separate from each other for a long time, for example, you return to work or your child goes to kindergarten.
Causes of improper attachment to the breast
- Using bottle feeding: Before breastfeeding
- With subsequent dietary supplements
- First child
- Missing Traditional Help and Support
Why is breastfeeding better than artificial feeding?
Infant formula has come a long way since its invention. Manufacturers have learned to adjust the fat and protein composition of cow's milk so that it meets the nutritional needs of a human baby, rather than a newborn calf. They began to add balanced complexes of vitamins and minerals to the mixtures and introduce beneficial bacteria. However, human milk still hides many secrets.
For example, only in recent years have researchers understood the role of oligosaccharides in breast milk. Previously, these substances were not paid much attention, but now it has become clear that they play an important role in the formation of the baby’s immunity, and some manufacturers have already begun to add them to formulas.
How many more discoveries are waiting in the wings is known only to the universe. And yet, it is theoretically impossible to create a mixture that will be in no way different from breast milk. It constantly changes - not only as the child grows up, but even during one feeding. Foremilk (the one that comes out in the first minutes) has less calories than hind milk (which comes later), and evening milk contains hormones that calm the baby and promote sound sleep. Breast milk is always different and always meets the needs of the baby. That is why doctors recommend choosing artificial feeding only in cases where breastfeeding is impossible or unsafe for medical reasons.
Here are just some of the benefits of choosing to breastfeed your newborn:
| Our expert |
Karina Petrova
pediatrician
| Despite the fact that manufacturers are trying every year to improve and bring the composition of formula closer to the composition of breast milk, they will never succeed in one thing - to create a product that will provide the same immune protection as mother's milk. Immunoglobulins, antibodies transmitted from mother to child through breast milk, leukocytes, macrophages and many other substances involved in the formation of the child’s immune response cannot be artificially recreated and provided to children today. And nature took care of this thousands of years ago during evolution. In addition, breast milk undergoes qualitative changes constantly, even throughout the day, adapting to the needs of the baby. Undoubtedly, the lines of formulas also differ in age, but their “step” is as much as 6 months (No. 1 - for children 0-6 months, No. 2 - for children 6-12 months, etc.), and calling them equivalent It is still not possible to replace breast milk. |
Dear mothers!
We welcome you to the breastfeeding support group, organized on the initiative of the leadership of the Center for Social and Social Responsibility.
For convenience, you can.
Who are breastfeeding consultants and when might their help be relevant?
A lactation consultant provides psychological support, information and practical assistance in any situation related to breastfeeding, nutrition and lifestyle of a nursing mother, introduction of complementary foods, weaning, etc.
Helps mom make the best decision, taking into account her life circumstances and wishes.
If you need advice on breastfeeding, caring for a newborn, ways to calm restless babies (or restless mothers?). If you just want to speak out, to be listened to, understood, accepted and supported, call the numbers listed below!
How to properly establish breastfeeding after childbirth?
The most important thing is that feeding should begin as quickly as possible. Experts recommend placing a newborn on the mother’s breast in the first hour of life, and there are at least three good reasons for this:
- The birth process was difficult not only for you. Believe me, your little one worked very hard too. He is tired and desperately wants to sleep, but even more desperately wants to eat thick, nutritious colostrum (special milk released from the breast in the first days after childbirth).
- By latching onto his mother’s breast for the first time, the baby gets to know you: he remembers the voice, smell, taste of the closest and most important person in the world. The sooner this acquaintance occurs, the stronger the baby’s emotional connection with his mother will be.
- In the maternity hospital, you are in a unique situation - there are a lot of specialists around you who know how to establish breastfeeding. Try and make mistakes to learn how to cope with them under the supervision of professionals.
Nutrition of a newborn baby
From the moment of birth until approximately 3-5 days after birth, the baby will receive colostrum as food, which in quantity and composition fully corresponds to the baby’s nutritional needs.
During the first days of life, most babies lose up to 10% of their birth weight. This is due to physiological loss of fluid due to changes in environmental conditions and disposal of original feces (meconium).
With the arrival of “mature milk”, children usually regain their birth weight within 5-10 days. However, for some children, 3 days may be enough for this, while others will need 3 weeks.
How to organize feeding a newborn - on demand or by the hour?
What does “feeding on demand” mean? This is a technique that suggests giving the baby the breast every time he asks for it. Moreover, it doesn’t even matter whether the baby really wants to eat or is just excited: breastfeeding on demand becomes a universal answer to any needs - both physical and psychological. Scheduled feeding is a fundamentally different approach, in which the mother must adhere to a strict schedule and not spoil the baby between planned meals.
Experts believe that feeding a baby on demand is more natural. Start with it, and the schedule will establish itself: you will notice that already at 3 months the baby asks to eat at approximately the same time, and at the age of introducing complementary foods, he even develops something like an adult daily routine - breakfast, second breakfast , lunch, afternoon tea and dinner.
Because on-demand feeding rules require the baby to have unlimited access to the mother's breast, some women worry that the baby will overeat. There is no reason to worry, and here's why:
- A newborn has a very small stomach, and milk is digested very quickly. Nature has provided everything to ensure that the baby receives exactly as much food as he needs.
- When feeding a newborn on demand, the baby starts with light food and eats in small sips, so the feeling of fullness comes faster than he has time to eat too much.
- Mother's milk is drink and food at the same time. Foremilk is quite thin and mainly quenches thirst, while thick hindmilk satisfies. If the baby is just thirsty or misses his mother, he will release the nipple from his mouth after a few minutes, but if he is really hungry, the breastfeeding session on demand can drag on for a long time.
- Feeding on demand gives your baby the feeling that food is always available. Thanks to this, he is not inclined to overeat and only satisfies his current needs.
It is logical to assume that formula feeding on demand has the same advantages. But no, this does not work with artificial feeding. Milk from a bottle is drunk faster, and besides, there is no front and back mixture - it all has the same calorie content. Overfeeding with artificial baby milk is one of the main causes of excess weight in babies, so parents have to limit access to food and introduce a feeding schedule. By the way, this is another reason why you should choose breastfeeding over bottle-feeding: it’s simply impossible to watch and listen to a baby burst into tears and ask for a bottle. After all, he doesn’t understand that his mother doesn’t give it to him for his own good.
Common mistakes when breastfeeding
- The baby sucks or “chews” only the nipple.
- The tongue works on the tip of the nipple.
- The lips and gums press on the nipple instead of the areola.
- The lips are sucked inwards.
A baby who sucks only on the nipple does not get enough milk. As a result, he remains hungry and restless, and may even refuse the breast. Improper sucking can lead to engorgement of the mammary glands, cracks and sore nipples.
The mother should know that if the child sucks correctly, his lower lip is turned outward, and muscle movements are clearly visible in the area of their attachment to the jaw bones near the ears, and not in the cheek area. In this case, the load on the surface of the nipple is minimal, since the child grasps with his mouth not only the nipple, but also the areola and the area of the breast located below where the lacteal sinus enters. The baby should extend the breast to the shape of the nipple, which is significantly longer than the nipple itself. The nipple is only a third of the "nipple". Sometimes, at the moment when the baby has just stopped breastfeeding, you can see how the chest stretches out.
In some cases, usually on the 3-4th day, when milk begins to be produced intensively, engorgement of the mammary glands may be observed, the breasts become hard, sometimes painful. A child cannot always take such a breast. In this case, it is recommended to express some of the milk before latching your baby so that the breast becomes softer and he can latch onto it correctly.
If the baby is full, he stops sucking and lets go of the breast. He is either full or ready to suckle on the other breast. It happens that the baby falls asleep as soon as he lets go of the breast.
There is no need to interrupt feeding after a certain period of time or wean the baby. The fact is that some children are lazy suckers, while others are the opposite. Give your child the opportunity to decide when to stop feeding.
What breaks should there be between feedings?
For the previous nine months, the baby lived in a place where there was no day and night, and food was provided around the clock. It is not surprising that he will not immediately get used to the new routine, and at first he will constantly ask for food. It is difficult to say how often you will have to put your newborn to the breast - each baby has its own characteristics and temperament. But count on approximately the following numbers: every one and a half to two hours or 10–15 times a day.
It's tiring, but fortunately not for long. Already in a month and a half, the frequency of feedings decreases to 5–7 times a day, and by six months, many children develop the correct regime: they stop waking up during the night, and all feedings gradually become daytime.
How to improve lactation if something goes wrong?
Even if a woman was taught in the maternity hospital how to feed her baby correctly, and by the time she returned home she was able to establish breastfeeding, from time to time she may have problems with lactation. In such a situation, they talk about a lactation crisis - a temporary decrease in milk production, usually associated with hormonal levels. If this happens, try following these tips:
- Put your baby to your breast more often. In this situation, your baby is the best doctor, and sucking is the most effective stimulator of lactation. Do you feed on demand or by the hour? If the latter, reconsider your views and start giving your baby the breast when he wants it - both day and night.
- Massage your breasts from time to time - stroke and rub them, take a contrast shower. Between feedings, express a little milk: although your hands are not as good as your baby's mouth, this technique also helps stimulate lactation.
- Follow your diet. Eat small portions, but often. Do not forget that during breastfeeding a woman should drink a lot. Warm drinks - water, fruit drinks, green tea and others - increase milk production best.
- It is almost impossible not to get enough sleep for months at a time and not have problems with feeding. Find a way to establish your own sleep schedule - when the baby falls asleep, don’t rush to do household chores, it’s better to rest too.
- Perhaps the problem is not in the chest at all, but in the head - you are experiencing stress, and this does not have the best effect on the functioning of your body. Try to be less nervous (and especially worry about the fact that you have problems with lactation), leave the house more often and do more things that bring you positive emotions. If only you knew how often this simple “life hack” helps improve the feeding of a newborn!
- Pharmacies sell special lactogenic agents - they increase the production of prolactin and, as a result, breast milk. Some plants also have a lactogenic effect, in particular ginger, fenugreek, anise, fennel, cumin, nettle, and seaweed. However, remember that medications and even herbs have contraindications and side effects, so they should only be taken after consulting a doctor.
| Our expert |
Karina Petrova
pediatrician
| Unfortunately, the belief that a nursing mother must follow some kind of special diet remains popular. As a rule, this diet consists entirely of restrictions. As a result, the choice of products remains so meager that it not only often leaves a nursing woman hungry, but also sad, to be honest. WHO experts have long dispelled this myth and urge women to eat a nutritious and varied diet. A nursing mother's diet should include not only buckwheat, turkey, peeled cucumber and a glass of kefir. All types of cereals and meat, vegetables, fruits, fermented milk products, even baked goods and (oh God) a little chocolate - all this is possible and necessary for a nursing woman so that lactation is established as soon as possible, and the emotional background does not suffer. |
How do you know if your baby has enough milk?
Some mothers worry that they don’t have enough milk, and often women who have no problems with lactation at all are subject to such worries. The main criterion in this matter is the dynamics of weight: if the baby’s body weight corresponds to the norms for his age, then everything is in order.
To completely dispel any doubts, talk to your doctor. And don’t put off this conversation: too much worry can actually lead to problems with breastfeeding.
| Our expert |
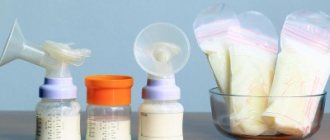
Pumping
Expressing is a procedure for removing milk from the breast, which is carried out for specific indications. Such as:
- Unpleasant or painful sensations in the breasts caused by excess milk, stagnation, mastitis, etc. – You need to empty your breasts effectively.
- It is necessary to increase the amount of milk
- The baby is unable to latch on to the breast or refuses it
- Mother needs to leave and leave breast milk for baby
- The mother is undergoing treatment with drugs that are not compatible with breastfeeding
- The child and mother are separated. Pumping is necessary to maintain lactation.
You can express milk by hand or with a breast pump, but hand expression is usually more effective.
In the absence of the above difficulties, there is no need to express after feedings. This can provoke hyperlactation (excess milk), which forces the mother to pump regularly, since the baby cannot cope with so much milk. This condition takes a lot of time and effort from the mother and increases the risk of milk stagnation and mastitis.
Contact a lactation consultant to find out if pumping is right for you.
Karina Petrova
pediatrician
| The main criterion for sufficient breast milk for a baby is weight gain. In the first month of life, the minimum increase is 140 g per week, in the first half of the year - 125-150 g per week, and at the end of the first year of life - 200-400 g per month. You can also check whether your baby is getting enough breast milk using the wet diaper test. Normally, a child in the first months of life urinates 10-15 times a day. If the number of urinations is less, be sure to contact your pediatrician. |