Every mother eagerly awaits the birth of her baby and hopes to meet him on time. But sometimes this happens earlier, and causes a lot of anxiety for the parents of the little toddler. To dispel your fears, we have prepared an article about the development of premature babies: how they differ from those born on time, what they look like, how they develop during the first year of life.
Which baby is considered premature?
Premature babies are those born before the 37th week of pregnancy and weighing less than 2.5 kg. Depending on the age and weight of the baby, there are 4 degrees of the condition:
| Degree of prematurity | Week of pregnancy | Child's weight | Child's height |
| 1st degree | 35-37 | 2-2.5 kg | 40-47 cm |
| 2nd degree | 33-35 | 1.5-2 kg | 37-40 cm |
| 3rd degree | 31-33 | 1-1.5 kg | 35-37 cm |
| 4th degree | 29-31 | less than 1 kg | less than 35 cm |
You need to know that children born prematurely with a body weight of less than 2.5 kg are called by doctors in the documents:
- low body weight fetus (LBW ) - if the baby was born weighing 1.5-2.5 kg;
- fetus with very low body weight (VLBW) - crumbs 1-1.5 kg;
- Extremely low birth weight (ELBW) fetuses are children weighing less than 1 kg.
A newborn is considered a premature baby who has lived for 7 days.
In addition to weight and gestational age, when assessing the degree of prematurity, neonatologists take into account additional factors that influence the development of the baby:
- the mother has diseases;
- congenital pathologies;
- correspondence of the degree of maturity of the body to the period of pregnancy.
The degree of maturity of the baby is the general condition of the child at the time of birth and compliance with accepted norms of intrauterine development. Doctors evaluate the baby according to 11 main criteria and determine the degree of maturity, which is important in establishing the necessary care and medical procedures.
Also, in the first minutes of a premature baby’s life, doctors check:
- does the baby have basic reflexes and how pronounced are they;
- what is the state of muscle tone;
- level of motor activity;
- Can the baby keep warm on his own?
Taking into account all these factors, a decision is made on the necessary medical support. Prematurity is assessed in the first minutes of a baby’s life. Immediately after birth, doctors suck out mucus from the baby's mouth, and in some cases from the stomach.
In the next moments, it is assessed how much he can breathe on his own, what medical support will be needed in the coming hours. For babies with severe prematurity and weighing less than 1 kg, artificial ventilation of the lungs and the creation of conditions as close as possible to those that were in the mother’s stomach are almost always necessary.
Modern medicine makes it possible to care for children with the tiniest weight (from 500-600 grams). Using various medications, closed and open incubators, neonatologists create optimal conditions for the baby that maximally recreate the sensations of being in the womb.
The birth of a baby ahead of schedule is a complex but solvable issue that requires parents to be attentive and focused. There is no need to panic and give up; along with quality care and supervision from doctors, your baby needs to feel the attention, love and care of mom and dad.
With proper medical care and clear and coordinated actions of parents, babies born prematurely catch up with their peers during the first year of life and are not much different from them.
How to care for a newborn born prematurely
In order for a child born earlier than expected to catch up with his peers faster, parents need to know how to properly care for the baby and what conditions need to be created for him. Improving the functioning of organs and systems of seven-month-old children and the development of their psyche largely depends on parents, especially in the first year of life.
First of all, parents should take care of the microclimate of the room in which the newborn will live. It should be bright and spacious enough. The air temperature in an apartment or house should be in the range from 20 to 25 degrees. The room must be regularly ventilated. Drafts must be avoided.
In addition, new mothers and fathers need to maintain air humidity. Its level should be in the range from 50 to 70%. Too dry air often causes a runny nose. A humidifier, which can be purchased at any hardware store, can make the task easier.
Some children may require additional warming. A heating pad is ideal for these purposes.
Hygienic procedures in the first month of life are not recommended for those babies whose initial weight was less than 2 kilograms. To care for a baby's skin, cotton swabs soaked in warm water are suitable. After completing hygiene procedures, you need to wipe the baby’s skin dry and use baby cream.
Babies weighing more than two kilograms should be bathed every other day in a small bath. The water temperature should be 36-37 degrees. It is best to boil water for hygiene procedures. If desired, you can add chamomile and calendula to the bath. After a few months, it is allowed to use special herbal solutions, which can be purchased at any pharmacy without a doctor's prescription.
You can go for a walk with a baby born prematurely three to four weeks after arriving home. The baby should be dressed according to the weather. In the summer, you do not need to go outside from 11 a.m. to 3 p.m. to avoid overheating. For walks, it is better to choose morning or evening time of day.
You should not walk with a baby whose weight is less than three kilograms, at temperatures below ten degrees. After the baby’s weight reaches this value, you can take walks at minus fifteen degrees. You should not choose crowded places or areas where there are a lot of cars driving around. There is no need for the baby to breathe exhaust fumes. And this will not be beneficial for a nursing mother.
Appearance
A normal pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks.
During this time, the baby turns from a small cell into a full-fledged person who can exist independently from his mother. During this entire period, processes of formation and improvement of all systems necessary for life are ongoing. If birth occurs earlier than the required 38-42 weeks, then the baby does not have time to fully prepare for independent life support outside the mother’s body.
Premature children differ not only from their peers born at term, but also from each other. Different degrees of prematurity have their own characteristics.
Premature baby born at 24-28 weeks:
- Weight less than 1000 g.
- The head is much larger than the chest. The skull has an unusual shape: a high forehead, an elongated nape, large open fontanelles, a very thin neck. The ears are very soft, the cartilage in them is underdeveloped, asymmetry is noticeable, and they are prone to deformation when lying on their side for a long time.
- The legs and arms are very thin, the elbows and knees are sharp.
- The nails do not reach the edges of the fingers, they are very soft.
- The navel is located significantly below the center of the abdomen.
- The genitals are underdeveloped: in girls, the labia majora do not cover the labia minora; in boys, the testicles are not lowered into the scrotum.
- The skin is very thin, wrinkled, flabby. Hyperemia (redness) is very pronounced.
- A network of blood vessels is clearly visible throughout the body; the fat layer is practically absent.
- White fluff is visible on the face, arms, legs, back and stomach.
- Muscle tone is weakly expressed.
- Babies born at 24-26 weeks may not open their eyes in the first few weeks of life.
Premature baby born at 28-32 weeks of gestation
- Outwardly, it is more similar to a normal newborn; the head circumference exceeds the sternum circumference by 2-3 cm.
- On the head there are large open seams and springs of considerable size.
- The ears are soft and easily deformed.
- The navel is located low to the center of the abdomen.
- The genitals are underdeveloped.
- A slight fat layer on the body is noticeable.
- The face, body, arms and legs are covered with white fluff.
- Muscle tone is weak.
Premature baby born at 32-37 weeks
- Body proportions are like those of a normal newborn.
- The skin is pink, there is no fuzz on the face.
- The formed subcutaneous fat layer is noticeable.
- The first curves on the ears are visible.
- Nipples and areola are visible on the body.
- The navel is located closer to the center of the abdomen.
Premature babies are born without completing an important stage of intrauterine development, so they need special care and monitoring of their condition. In most cases, babies have to stay in the maternity hospital in the neonatal department from 7 days to 4 months, depending on the degree of prematurity.
Of course, every mother wants to be home with her baby as soon as possible, but if doctors insist on additional control and stay in a medical facility, you should listen to them.
Features of care
A premature baby requires more attention and precautions when caring. First of all, seven-month-old children, whose development depends largely on their parents and the environment, should grow up in a favorable environment, in love and warmth.
Clothing and related products (caps, socks, etc.) must be made exclusively from natural materials. Fasteners should be in the form of buttons and located on the outside. There should be no tags or labels inside the vests and rompers. They can injure the baby's delicate skin. For premature babies, you need to purchase special clothes, since standard size baby onesies and rompers are too big for them.
Hygiene products deserve special attention. Preference should be given to hypoallergenic compounds, the quality of which is confirmed by certificates. For babies born earlier than expected, it is possible to purchase size zero diapers in baby stores, which are intended for newborns whose weight ranges from one to three kilograms. There are also diapers for children whose birth weight was less than one kilogram.
A massage would be helpful. It will help increase muscle tone, strengthen all ligaments and bones, improve metabolism and the functioning of the digestive system. A child up to one year old can have a massage that includes stroking movements. In any case, before carrying out any manipulations, you must contact a medical institution for the advice of a qualified pediatrician. Some parents provide professional nursing care for their premature baby. A medical professional will not only be able to better assess the development of the baby in the first weeks of life, but also, if anything happens, alert the parents to the occurrence of any problem.
Height and weight in the table
When born, premature babies differ from their timely born peers in weight and height. The shorter the gestational age at which the baby was born, the lower the indicators.
Weight and height of a premature baby at the time of birth, depending on the week of pregnancy
| Week of pregnancy | Weight | Height |
| 24-28 week | 0.85-1.3 kg | less than 35 cm |
| Week 29 | 1.15-1.5 kg | 35-36 cm |
| Week 30 | 1.25-1.7 kg | 35-37 cm |
| 31 weeks | 1.3-1.75 kg | 36-37 cm |
| Week 32 | 1.4-1.95 kg | 36-38 cm |
| Week 33 | 1.55-2.3 kg | 36-39 cm |
| 34 week | 1.8-2.5 kg | 37-40 cm |
| 35-36 week | 1.95-2.5 kg | 40-47 cm |
Babies born before 34 weeks are characterized by severe immaturity of the digestive tract, so their nutrition and rate of weight gain are very different from those of children born before this period.
Children born from 27 to 34 weeks have an immature pulmonary system, so in most cases they breathe with the help of a mechanical ventilation device (ventilator). Such babies are fed through a tube for the next 3-4 months.
The degree of prematurity of the child largely determines the rate at which he gains weight and height in the following months. The immaturity of the nervous, pulmonary, and food systems does not allow the baby to quickly gain the treasured grams in the first months of life. But by 3 months the processes stabilize, and by the age of one year the baby catches up with peers born on time.
Table of weight gain and height of a child during the first year of life, depending on the degree of prematurity
| Age | 4th degree | 3rd degree | 2nd degree | 1st degree | ||||
| Weight gain | Increase in height | Weight gain | Increase in height | Weight gain | Increase in height | Weight gain | Increase in height | |
| 1 month | 180 g | 3.9 cm | 190 g | 3.7 cm | 190 g | 3.8 cm | 300 g | 3.7 cm |
| 2 months | 400 g | 3.5 cm | 650 g | 4 cm | 750 g | 3.9 cm | 300 g | 3.6 cm |
| 3 months | 650 g | 2.5 cm | 650 g | 4.2 cm | 750 g | 3.6 cm | 800 g | 3.6 cm |
| 4 months | 600 g | 3.5 cm | 650 g | 3.7 cm | 750 g | 3.8 cm | 750 g | 3.3 cm |
| 5 months | 650 g | 3.7 cm | 750 g | 3.6 cm | 800 g | 3.3 cm | 800 g | 2.3 cm |
| 6 months | 750 g | 3.7 cm | 800 g | 2.8 cm | 700 g | 2.3 cm | 700 g | 2 cm |
| 7 months | 500 g | 2.5 cm | 950 g | 3 cm | 600 g | 2.3 cm | 700 g | 1.6 cm |
| 8 months | 500 g | 2.5 cm | 600 g | 1.6 cm | 700 g | 1.8 cm | 700 g | 1.5 cm |
| 9 months | 500 g | 1.5 cm | 600 g | 1.6 cm | 700 g | 1.8 cm | 700 g | 1.5 cm |
| 10 months | 450 g | 2.5 cm | 500 g | 1.7 cm | 400 g | 0.8 cm | 400 g | 1.5 cm |
| 11 months | 500 g | 2.2 cm | 300 g | 0.6 cm | 500 g | 0.9 cm | 400 g | 1 cm |
| 12 months | 450 g | 1.7 cm | 350 g | 1.2 cm | 400 g | 1.5 cm | 300 g | 1.2 cm |
| Average indicator in 1 year | 7.08 kg | 68-70 cm | 8.45 kg | 69-72 cm | 8.65 kg | 70-73 cm | 9.45 kg | 71-74 cm |
Average weight of children in the first year of life depending on the degree of prematurity
| Month of life | 4th degree | 3rd degree | 2nd degree | 1st degree |
| Birth weight | 500-1000 g | 1000-1500 g | 1500-2000 g | 2000-2500 g |
| 1 month | 680-1180 g | 1190-1690 g | 1690-2190 g | 2300-2800 g |
| 2 month | 1080-1580 g | 1840-2340 g | 2440-2940 g | 2600-3100 g |
| 3 month | 1680-2260 g | 2590-3090 g | 3190-3690 g | 3400-3900 g |
| 4 month | 2300-900 g | 3340-3840 g | 3940-4440 g | 4150-4650 g |
| 5 months | 2950-3550 g | 4090-590 g | 4740-5240 g | 4950-5400 g |
| 6 months | 3700-4300 g | 4890-5390 g | 5440-5940 g | 5650-6100 g |
| 7 months | 4200-4800 g | 5840-6340 g | 6040-6540 g | 6350-6800 g |
| 8 months | 4700-5300 g | 6440-6940 g | 6740-7240 g | 7050-7500 g |
| 9 months | 5200-5800 g | 7040-7540 g | 7440-7940 g | 7750-8200 g |
| 10 months | 5650-6250 g | 7540-8040 g | 7840-8340 g | 8150-8600 g |
| 11 months | 6150-6750 g | 7840-8340 g | 8340-8840 g | 8550-9000 g |
| 12 months (1 year) | 6600-7200 g | 8190-8690 g | 8740-240 g | 8850-9300 g |
The table of average weight gain and height for premature babies during the first year of life shows approximate figures obtained statistically. Each child is individual and develops at their own speed. It is recommended to focus more on the recommendations of pediatricians and specialists, taking into account the specific situation and the characteristics of the baby.
Why is it better to have a seven-month-old baby than an eight-month-old baby?
There is an opinion that it is better to give birth to a seven-month-old baby than an eight-month-old baby. Why? Let's turn to embryology. 7 months is how many weeks of pregnancy? As already noted, this period lasts from 28 to 32 weeks. The child is actually fully formed and can easily live outside the mother’s womb. However, its organs are not fully developed, the systems do not function to their full potential. Only the stomach and intestines are fully formed. The cerebral cortex is actively developing.
For a long time, doctors argued that the likelihood of successfully nursing a seven-month-old baby is much higher than saving an eight-month-old one. This is actually a myth. At 8 months, the baby’s vital stages of development are behind him, and he is almost ready to be born. The only organ that continues to actively mature is the brain. Experts say that the likelihood of successful nursing of a premature baby depends not even on the period at which he was born, but on his indicators at birth. First of all, it depends on the child’s height and body weight.
Medicine has come so far that doctors are now able to save and deliver babies born at 28-29 weeks of pregnancy. Seven-month-old children, whose development is not complicated by unfavorable factors, with proper care and regular monitoring by medical personnel, after some time are able to catch up with their peers.
When a premature baby is discharged from the hospital
Children born prematurely stay in the hospital much longer than their full-term peers. Depending on the child’s condition, the duration of stay under the supervision of doctors can range from 7-10 days to 6 months. The decision to discharge is made by the doctor, assessing the baby’s condition. In order for the baby to go home, he needs:
- have no developmental difficulties;
- show stable progress in weight gain (over 3-5 days);
- be able to retain body heat;
- breathe independently, eat;
- weigh more than 2.3 kg.
Another important parameter for the discharge of a premature baby is the parents’ ability to care for the baby and the ability to provide him with all the necessary conditions.
What does a baby born prematurely look like?
A baby born prematurely differs in appearance from full-term babies. Premature babies are characterized by:
- large head (up to 1/3 of body length);
- the frontal part is larger than the facial part and makes up 2/3 of the total size of the head;
- tiny short arms and legs;
- the navel is located lower than in full-term babies;
- undeveloped genitals (a huge genital gap in girls, testicles that do not descend into the scrotum in boys);
- lack of subcutaneous fat (blood vessels are visible through the skin);
- soft ear cartilage (the pinna curls and sticks together);
- small undeveloped marigolds;
- the skin is wrinkled, red;
- tummy is convex, spread out:
- the neck is short;
- displaced large fontanel;
- possible areas without skin on the small fontanelle;
- weakness, lethargy.
After a week or two, very premature babies develop bulging eyes. You shouldn’t be afraid of these signs: with proper care, they will gradually disappear when the baby begins to catch up with its peers.
Child development
One of the most exciting issues among parents of premature babies is the development of the baby in the first year of life. Babies born prematurely are in most cases very weak; mothers and fathers worry whether their child will be able to catch up with their peers in basic indicators.
According to statistics, almost all such children during the first half of life show results below their peers, but starting from 6 months they quickly catch up and in some cases overtake children born on time. But the development of the nervous system still proceeds differently: in such children it is often unstable, which is why hyperactivity appears.
1 month
In the first month of life, most babies born prematurely are under constant supervision of neonatologists. Babies with severe prematurity will be in the hospital for 3-4 months. Depending on the degree of prematurity, they can be placed in a closed or open incubator.
The primary task of doctors during this period is to stabilize the child’s condition and allow all systems of his body to develop to the required parameters.
Children who cannot retain heat are placed in a closed incubator, are on mechanical ventilation and need special therapy and medications to accelerate the maturation of body systems. After the baby’s condition has stabilized, he is transferred to an open incubator.
Children who can breathe on their own, have acquired all the necessary reflexes and have learned to eat, are transferred to a special department where they are observed until discharge.
In the 1st month of life, premature babies do not gain weight well. This is associated primarily with insufficient intrauterine development and an underdeveloped sucking reflex. To increase the amount of food entering the baby’s body, in most cases feeding is carried out through a special tube.
The recommended diet for these babies is breast milk. Mommy needs to try to maintain the opportunity to breastfeed by constantly pumping and stimulating lactation.
In the first month of life, it is important for a newborn to be in a room with constant temperature and humidity, and to avoid contact with a large number of people. Those around you should strive to create conditions of maximum sterility.
During this period, the child is in an unprotected position, his body tries to achieve normal levels as quickly as possible and cannot effectively resist infections.
Acclimatization, incomplete development of body systems, makes a premature baby very weak in the first month of life: he sleeps almost all the time, is little active, and muscle tone is reduced (hypotonicity). All a baby can do at this age is sleep and swallow food. At this moment, contact with the mother, a feeling of her care and love, is vitally important for the child.
Prematurity is not a death sentence. Modern medicine works wonders in caring for babies born with a weight of 500 g or more. If you find yourself in such a situation, then try to find the strength to be close to the baby, give him your love and attention, he will feel your support.
2 months
In the second month of life, babies with 1-2 degrees of prematurity are sent home, while those with 3-4 degrees remain under the supervision of doctors.
During this period, the sucking reflex is still poorly developed, and the baby must be fed with expressed milk from a bottle with a nipple, which must first be sterilized.
In the 2nd month of life, pediatricians recommend introducing the first exercises to children who have been sent home: lying on their stomach.
During this period, very rapid fatigue of the toddler is still observed, but an increase in muscle tone is already noticeable.
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity:
In the 2nd month of life, they learn to concentrate their gaze on an object, begin to study their surroundings, but are still very weak and get tired quickly. From about 1.5 months, motor activity increases and muscle tone increases.
A characteristic feature of premature babies is that the hand is clenched into a fist; the thumb is very difficult to move to the side. During this period, the pediatrician may recommend working out the fingers with a special massage to stimulate the grasping reflex.
By the age of 2 months, babies try to hold their head up, but it is still very difficult, and the baby gets tired quickly.
Babies 3-4 degrees of prematurity
They remain under constant medical supervision and are usually discharged home after complete stabilization of all body systems and with a weight of more than 2.3 kg.
In the second month of life, close contact with the mother is very important for very premature babies. Even if it seems that the baby is not responding to you, then you need to understand that he is simply still very weak.
3 months
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity
In the third month of life, a premature baby becomes more active, shows interest in food, and gains weight and height faster. Pediatricians do not recommend leaving a baby at this age to sleep on his stomach; it is better to lay him on his back and turn his head to the right or left.
Children learn to focus their gaze on surrounding objects and try to gradually raise and hold their heads. By this age, the baby's weight should double.
The grasping reflex appears; the child can hold a small object in his hand.
Children with 3-4 degrees of prematurity
The ability to concentrate your gaze on an object appears. Muscle tone gradually increases, and the baby becomes more active.
By 3 months, the first attempts to raise and hold the head appear.
Healthy babies who have reached a weight of 2.3-2.5 kg are discharged from the hospital home.
At this age, the pediatrician may recommend visiting a special massage therapist to stimulate muscle development.
4 months
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity
Neuropsychic processes are gradually activated, the baby tries to communicate and makes new sounds.
I am getting better at grasping and shaking the toy, but I still feel a strong tone in my hands. After consulting with a pediatrician, it is worth finding a specially trained massage therapist who would help relieve excess tension and stimulate the development of body muscles.
At the 4th month, daily walks in the fresh air become important for a newborn, but you should carefully monitor the baby’s clothes, dress him according to the weather, and avoid hypothermia and overheating.
Closer to 5 months, babies of 1-2 degrees of prematurity delight their parents with their first conscious smile.
Children with 3-4 degrees of prematurity
The baby has grown stronger and is actively examining the surrounding objects. Now he manages to independently hold his head and rotate it in search of the source of the sound. Almost all healthy premature babies reach a weight of 2300-2900 g at the 4th month, are able to eat on their own, and go home.
5 months
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity
By 5 months, premature babies with grade 1-2 practically catch up with their peers.
They shake rattles with pleasure, examine their surroundings with interest, and happily make contact with adults. The perception of sounds increases, the baby quickly turns its head in the direction of the sound, trying to find its source. A pleasant innovation is the child’s reaction to his mother. When she enters the room and begins to talk to the little one, he noticeably perks up, begins to smile and babble.
By 5.5 months, babies are trying to roll over from their back to their stomach.
Children with 3-4 degrees of prematurity
New sounds and a desire to play with rattles appear. It becomes easier to hold small objects, and the baby begins to consciously smile.
6 months
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity
The weight of a child with 1-2 degrees of prematurity triples by 6 months. Having mastered the technique of turning from back to stomach, the little one moves on to studying the reverse movement. Differences in physical development with peers born at term are practically erased.
After consultation with a pediatrician, assessment of health and physical skills, children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity begin to be introduced to complementary foods. Products for the first complementary feeding should be discussed with your doctor in order to choose the best option.
Neuropsychic development proceeds at a rapid pace. Children show increased interest in communicating with adults and playing games.
Children with 3-4 degrees of prematurity
The baby's favorite pastime is shaking the rattle, holding it tightly in the handle. Auditory perception is enhanced, and the little one really wants to understand where various sounds are coming from, he quickly moves his head in order to catch where the knocking, noise, and conversation is coming from.
Learn to turn from back to stomach.
7 months
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity
An active and sociable baby is trying to master the ability to crawl. Outwardly, he is no different from his full-term peers. Autonomy in play increases, and the desire to eat on one’s own appears. Babies born at 34-38 weeks acquire their first teeth and learn to sit.
Children with 3-4 degrees of prematurity
The ability to toss and turn from back to stomach is mastered, the desire to learn to crawl appears, but motor skills are still not enough.
In the absence of contraindications and sufficient weight, after consultation with a pediatrician, complementary feeding may be introduced.
8 months
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity
The baby learns to sit and play independently in this position. It is still difficult to hold your back; the muscles that support the spine are still weak, so the back arches.
The number of movements increases all the time, the baby seeks contact with adults. Now you can notice that the little one understands the speech addressed to him. If you speak in simple sentences and ask to point to an object familiar to the baby, he will gladly point his finger at it.
Attempts to master crawling are gradually becoming more successful. Most babies can already move themselves across the floor on their bellies. The most active ones get on all fours and swing in this position in different directions.
Children with 3-4 degrees of prematurity
The ability to move your body on your belly appears. Muscle strength is not enough to do this over a long distance, so the baby gets tired quickly and can fall asleep right during the game.
Children with 3 degrees of prematurity try to sit; this is not yet available for babies with 4 degrees of prematurity.
9 months
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity
Differences with peers born at full term have practically disappeared. The little ones sit confidently, crawl on all fours, and actively show their desire to communicate.
Some children begin to stand up on their own and try to move along the wall.
Now the baby sleeps less, begins to speak the first syllables, and every day increases his knowledge about the world around him.
Children with 3-4 degrees of prematurity
The skill of sitting has been fully mastered.
Teeth begin to appear.
The amount of sleep decreases, but still accounts for most of the day.
10 months
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity
By 10 months, premature babies confidently stand on support and crawl.
If you call the baby by name, he will turn and smile. The back muscles have become stronger, and now the little one sits straight, holding his back straight. Play activities become varied, the baby is very interested in household objects.
Children with 3-4 degrees of prematurity
There are attempts to stand at the support, to take the first steps along the railing.
Syllables are actively manifested in speech. When talking with a baby, you can notice that he understands well what they are talking about. If you ask your baby to show you where an object he knows is located, he will happily point his finger at it.
11 months
Children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity
At the 11th month of life, children with 1-2 degrees of prematurity do not differ from their peers physically. Actively crawling and trying to take their first steps, they study the surrounding objects with interest. Toys that make sounds, inertia and wind-up toys are of increased interest. In response to addressed speech, you can hear more and more different syllables and simple words.
Children with 3-4 degrees of prematurity
Babies with 3-4 degrees of prematurity stand confidently against the wall and try to move along the support.
Interest in adult food appears.
12 months
By 12 months, all healthy premature babies, with proper care and attention from their parents, catch up with their peers in physical development. By the age of one year, most of them try to walk, talk, and actively study various playing techniques.
Table of appearance of basic skills depending on the degree of prematurity
| Skill | 4th degree of prematurity, weight up to 1000 g | 3 degree of prematurity, weight from 1000 g to 1.5 kg | 2nd degree of prematurity, weight 1.5-2 kg | 1st degree of prematurity, weight 2-2.5 kg |
| Fixing your gaze on an object | 2-3 months | 2-2.5 months | 1.5-2 months | 1-1.5 months |
| Independent head support | 3-4 months | 3-4 months | 2 months | 1.5-2 months |
| Turn from back to stomach | 6.5-7.5 months | 6-7 months | 5-6 months | 5-5.5 months |
| Turn from stomach to back | 7.5-8.5 months | 7-8 months | 6-7 months | 6-7 months |
| Sits independently | 9-12 months | 8-10 months | 7-8 months | 6-7 months |
| Stands alone | 11-12 months | 11-12 months | 9-10 months | 9 months |
| Walks independently | 14-15 months | 14-15 months | 11-13 months | 11-12 months |
| Pronunciation of words | 12-14 months | 12 months | 11-12 months | 11-12 months |
Child at home
Of course, when discharging the child home, the doctor will give the mother all the necessary recommendations for further care for him. Within the framework of this article, we will limit ourselves to only the most general considerations.
- You will have to maintain a certain temperature at home - in the child’s room it should be about 22-23°C. Although your baby's thermoregulation is usually working by the time he's discharged, he still has to spend a lot of his own energy warming his body, so you need to make sure he's comfortable, otherwise all the calories extracted from hard-earned food will go toward maintaining body temperature rather than keeping him warm. weight gain. But don’t forget - a child can also be overheated, which is no less dangerous.
- Sterilize the bottles and nipples you use to feed your baby. Try to ensure that, at least at first, the child does not have contact with all the relatives and friends who are eager to visit you - his resistance to infection is weak, and he has no reason to get sick at all.
- Feed your baby often, don't worry if he stays at the breast for a long time - premature babies suckle less actively, and they need to be given time to get enough. If you see that the baby is tired, stop feeding, give him a little rest, and supplement with expressed milk. Be sure to consult with your doctor whether, in addition to your breast milk, your baby needs to receive a special formula containing all the substances and multivitamins he needs. There are supplements that dissolve in breast milk and reduce the risk of vitamin deficiency in a premature baby.
- Complementary feeding can only be started with the permission of a doctor. Typically, complementary feeding is introduced when the child weighs 6-7 kg and eats about 1000 ml of breast milk or formula per day, but if necessary, complementary feeding is prescribed earlier.
- Do not be alarmed if your child does not begin to rapidly gain weight from the very first days. The child usually even loses weight in the first two weeks, but, as a rule, begins to gain weight from the third or fourth week. On average, the weight gain per week of a premature baby is initially 100-200 g. In the third or fourth month, it will double its weight (a full-term baby doubles its weight in the fifth month), and triples it in the sixth (a full-term baby only at the end of the first year).
- You should not torment yourself with a feeling of guilt due to the fact that the child was born prematurely and, therefore, be excessively careful and spoil the baby too much. A premature baby is truly an unusual creature and requires special treatment. It is best to consult with a good child psychologist, a methodologist who has the skills of a variety of educational games and techniques. They are the ones who will allow you to create the most favorable environment for the harmonious development of a child and compensate for all the difficulties that your tiny son or daughter had to face as soon as they came into this world. Medical practice shows that with proper care and a properly selected course of rehabilitation, even very premature children catch up with their peers in basic psychophysical parameters by 1.5-3 years.
Features of feeding children born prematurely
Depending on the degree of prematurity of the child, that is, the week of pregnancy in which the baby was born, different complementary feeding options can be used:
- breastfeeding from the first days of life (1st degree of prematurity, presence of a sucking reflex);
- bottle feeding (2nd degree of prematurity, feeding with expressed breast milk);
- feeding through a special tube (3-4 degrees of prematurity).
The option of feeding a child is determined by a doctor in the first hours of the baby’s life and is based on the general condition of the child, his ability to feed independently, and the maturity of the main body systems.
Breast milk is considered the preferred product for feeding premature babies. If possible, breastfeeding should be maintained for as long as possible.
While in the maternity hospital, feeding of premature babies is monitored by doctors, and if necessary, adjustments are made to the amount of food offered. Upon discharge from the hospital, doctors give their nutritional recommendations, and the process comes under the control of the parents.
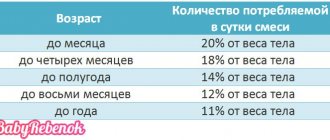
The required amount of milk per day is calculated based on the child’s weight and age.
| Child's age | Daily food intake |
| 10 days - 2 months | ⅕ of body weight |
| 2-4 months | ⅙ body weight |
| 4-6 months | 1/7 body weight |
| 6-8 months | ⅛ body weight |
| 8-12 months | 1/9 body weight |
Offering your baby the exact amount of food per feeding is quite difficult, especially when breastfeeding.
- When breastfeeding, you need to focus on the child's behavior: he will not eat more than he should.
- When artificial feeding, it is recommended to pour formula or milk in an amount exceeding the norm by 10-15 ml, taking into account that the baby will not drink everything.
Feeding a premature baby is an important factor in the baby's development. It is recommended to develop a nutritional and complementary feeding plan together with a pediatrician, taking into account the characteristics of a particular baby.
Advice for parents of a premature baby
- Your child is still a little different from everyone else, but over time and with your help, he will be able to catch up with his peers in his development.
- Fight for breastfeeding, it is very important for such babies
- Particular attention is paid to nutrition; such children eat more slowly and usually in smaller portions, but somewhat more often than full-term children. The interval between feedings should not exceed 4 hours.
- Premature babies are easily susceptible to infections, so you should carefully monitor the cleanliness of the room and limit the number of people who want to visit the baby at first.
- At first, doctors do not recommend putting such weakened babies to sleep on their tummy; it is better to place the child on his back.
- When swimming, the water temperature should be at least 37°C
- In the room where the premature baby is located, the temperature should be about 23-25°C. — Sterilization of bottles and nipples is mandatory for such children; try to follow this rule, especially in the first months of the baby’s life.
- Premature babies benefit greatly from a special massage that can be performed by an experienced specialist. After consultation, parents can perform simple massage techniques on their own.
- Complementary foods and vaccinations are prescribed strictly on the doctor’s recommendation, after assessing the baby’s condition.
- Be sure to follow all the doctor’s recommendations; if necessary, immediately call a doctor at home or an ambulance.
Vaccination
Children born prematurely are not subject to vaccination as scheduled. For each specific premature baby, the vaccination schedule is calculated by the pediatrician based on the characteristics of its development and weight gained.
Before vaccination, the doctor must measure weight and height, check blood tests and assess the general health of the little one. For the administration of each individual vaccine, requirements have been developed for the minimum weight of the child to be immunized.
First year of development in months
The third stage of nursing - follow-up observation
Relative normalization of the basic vital functions of the body does not always, unfortunately, mean that the premature baby has finally caught up with his peers in psychophysical development. Nowadays, follow-up observation rooms for children born with extremely low body weight are being opened in many Russian cities. Catamnesis in medicine is information about a patient collected after the end of the initial observation (in this case, after discharge from the intensive care unit or nursing premature babies). Of course, in the follow-up rooms, not only children are monitored, but also systematic correction of the deviations identified in them is carried out. Methods for such correction are a topic for another discussion.
Possible health problems in premature newborns
When born prematurely, the baby’s organs and systems do not have time to fully develop. Therefore, such children often have health problems.
Respiratory disorders
There is no surfactant in the lungs, so the baby cannot take its first breath. With a weight of less than 1 kg, the child does not breathe on his own. He is connected to a ventilator. Congenital pneumonia often occurs in premature babies. Their breathing stops for a long time (apnea).
Blood changes
The breakdown of hemoglobin that occurs after childbirth leads to jaundice in premature babies; it lasts longer. When a baby is born early, anemia occurs.
Gastrointestinal pathologies
The most dangerous pathology is necrotizing enterocolitis. Inflammation and subsequent death of part of the intestine occurs.
Nervous system problems
Sometimes premature newborns experience bleeding in the brain. The consequences of the disease are different. Due to oxygen starvation, cerebral palsy, dementia, and developmental delay occur.
Cardiovascular system disorders
The main pathology is unstable blood pressure.