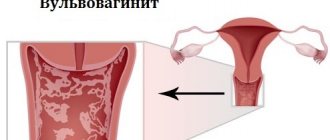
In gynecology, vulvitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of a woman’s external genitalia.
The inflammatory process covers the labia, clitoris, external urethral opening, anal area and surrounding tissues (pubis, inner thighs, etc.). At first glance, such a pathology should bypass children of the younger age group and affect only adult women of reproductive age. However, statistics show that acute vulvitis in girls of childhood and adolescence is the most common reason for visiting a pediatric gynecologist. In some cases, doctors even diagnose vulvitis in newborn girls.
To notice and provide medical assistance in time for the development of vulvitis is the most important task of responsible parents . Advanced acute vulvitis in a child can involve the vaginal mucous membranes in the inflammatory process, which leads to aggravation of the little patient’s condition and provokes the development of vulvovaginitis. In addition, the acute process gradually turns into a chronic form, which inevitably affects the sexual, reproductive and menstrual function of an adult representative of the fair sex. This inflammation is dangerous due to the formation of synechiae (adhesions) of the labia minora, erosion of the cervix and uterine body, as well as the addition of cystitis and urethritis.
Why are diaper rash dangerous?
Even a minor diaper rash caused by a baby's diaper can cause a lot of trouble and trouble. The baby begins to be capricious, sleep poorly, and lose weight. If you continue to ignore unpleasant symptoms, inflammation will occupy large areas and deep layers of the epidermis. Advanced stages are no longer just redness on the butt or groin, but deep, weeping wounds, debilitating and quite painful.
At the same time, the baby’s body temperature rises, internal organs malfunction, and indigestion begins. Against an inflammatory background, the immune system weakens and secondary infections occur.
Important! If you do not start treatment right away, then cracks, weeping wounds, ulcers, and ulcers appear on the baby’s body. The spread of pathogenic microflora is extremely dangerous for a fragile child’s body. Therefore, you should respond immediately.
Causes of vulvitis in girls
The high incidence of inflammation of the mucous membranes of the genital organs in girls is associated primarily with the physiological characteristics of newborns and children of a younger age group. At birth, the reproductive tract and membranes of the genital organs are sterile. Only after a week, opportunistic microorganisms master this nutrient medium, forming a prototype of normal female microflora. However, unlike the genitals of an adult woman, the child’s vagina does not have a sufficient number of microorganisms, which explains the inferiority of the protective reaction. The fact is that it is the vaginal microflora that provides the acidic environment of the genital membranes. A high level of acidic components causes the death of dangerous pathogenic flora, effectively protecting a woman from infectious and viral pathogens.
Thus, initially the girl’s genitals are defenseless against aggressive bacterial factors. Only by adolescence, the pH environment of the mucous membranes transforms from neutral (pH 7.0) to moderately acidic (pH 4.0-4.5).
The second important provoking factor of childhood vulvitis in girls is the imperfection of the child’s immune system, namely the deficiency of immunoglobulins, phagocytes and components of the compliment system. It is important to monitor the state of the child’s immunity, because hypovitaminosis, taking antibacterial drugs and the presence of endocrine disorders in the girl, such as diabetes, are considered risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing inflammation.
The immediate cause of vulvitis in a child is infection. The following bacterial pathogens are considered the most dangerous in this regard:
- Nonspecific infections . This group of pathogens is also called opportunistic pathogens, since they normally live on the patient’s mucous membranes and are part of the healthy, complete microflora of the genital organs. This group includes all opportunistic aerobic and anaerobic flora and yeast fungi. To activate them, favorable conditions are necessary, in the form of weakened immunity. The situation is aggravated by failure to maintain personal hygiene, ignorance of the correct washing technique, wearing synthetic underwear, injury to the genitals, etc.
- Specific infections . This includes pathogens that are not normally present in the microflora of the vagina and external genitalia of a child - chlamydia, ureaplasma, gonorrhea, herpes virus, gonococci, mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc. Infection of children most often occurs through household means due to poor hygiene and the entry of strangers objects in the vagina (insects, toys, sand, etc.). In adolescents, infection can be caused by sexual relations and masturbation. Vulvitis in newborn girls can occur due to infection during contact with the contaminated birth canal of the mother.
- Fungal pathogens . Mycotic vulvitis develops as a response to the death of microflora in response to antibiotics and hypovitaminosis. This form of vulvitis in infants can be a consequence of diaper dermatitis.
- Helminthic infestations . Pinworms and other helminths usually affect children who have frequent contact with animals. This cause is often classified as a nonspecific form of pathology.
- Allergy . A rare form of the disease is atopic or allergic vulvitis, which manifests itself as a hypersensitivity reaction to an allergen. Both food products (citrus fruits, sweets, nuts, etc.) and local hygiene products (soap, balms contained in diapers, sanitary pads) can act as an irritant.
- Anatomical disorders of the structure of the genital organs . If a child has developmental abnormalities of the external genitalia, the risk of inflammation increases sharply. This is especially true in cases where the girl has incorrect localization of the external urethral opening, a gaping genital fissure, the external labia are too open, and the mucous membrane is excessively thinned.
Prevention of diaper rash in newborns
In order for the treatment of diaper rash in a baby to be successful, you need to follow the recommendations of specialists.
Several rules will help prevent the development of problems with infant skin:
- strict adherence to hygiene;
- regular air baths;
- washing children's underwear with proven, hypoallergenic products;
- introduction of the first complementary foods according to generally accepted standards;
- Diet compliance by a nursing mother.
A specialist tells young parents how to get rid of diaper rash in young children. They can use various medications and cosmetics that can quickly correct the situation and return the integument of the child’s body to a healthy appearance.
Types of vulvitis in children
Depending on the timing and severity of the pathology, three forms of the disease are distinguished:
- acute vulvitis in girls - symptoms persist for up to 1 month;
- subacute vulvitis - duration is up to 3 months;
- chronic vulvitis - all inflammatory conditions whose symptoms persist for more than 3 months.
Chronic and subacute vulvitis in girls of preschool age, caused by nonspecific pathogens, are considered common.
Symptoms of vulvitis in girls
The first signs of the development of the inflammatory process are severe itching and burning in the groin area. Upon visual inspection of the affected area, parents also note external symptoms of vulvitis in the child in the form of severe redness and swelling of the labia and clitoris. Often inflammation also affects surrounding tissues. Also, upon examination, small ulcerations and erosions may be revealed, which indicate a severe course of the pathology and require immediate consultation with a doctor.
As the disease develops, children in the first years of life experience anxiety, frequent crying, and sleep disturbances. In older children, this condition is easier to diagnose. For example, vulvitis in a three-year-old girl will manifest itself in the fact that the child constantly touches the genitals, rubs the inflamed tissue and complains of pain during urination. Excessive rubbing and scratching of thin, inflamed mucous membranes can lead to injury, which the child’s parents should prevent.
Another characteristic sign of the development of an inflammatory reaction of the external genitalia is the appearance of unusual discharge from the child’s vagina, which gynecologists call leucorrhoea. These discharges cannot be confused with the norm. In most cases, there is profuse, watery leucorrhoea that is colorless and has an unpleasant odor. Discharge when infected with E. coli is considered one of the important diagnostic signs, as it has a greenish tint and emits a very strong fecal or putrid odor. At the same time, candidal forms of pathology are accompanied by white, curdled leucorrhoea, which resembles the classic manifestation of thrush.
The general condition of a child who has developed vulvitis or vulvovaginitis is often weakened; the girl may have a fever and sleep disturbances. Children often complain of pain in the lower abdomen and show increased excitability and irritability. If the disease is the result of helminthiasis, the child may refuse to eat.
Types of diaper rash
If you discover diaper rash on your child’s bottom or in another part of the body (for example, between the legs), you need to immediately begin treating it. However, you should understand exactly what type of inflammation it is and what could cause it.
In babies under one year old, the following types of inflammatory dermatological reaction occur:
- Diaper dermatitis is a rash of varying intensity in the area where a diaper is worn, where contact with urine and stool can occur: the groin, buttocks, scrotum in a boy, labia in a girl, around the anus, lower abdomen. At the same time, other parts of the body remain untouched by the rash.
- Allergy ring , a photo of which can be seen on the Internet. It is observed in the anus and buttocks. The rash is bright red, small, caused by a change in diet or exposure to a food allergen to the baby.
- Intertrigo . It occurs exclusively in the area of skin folds: neck, armpits, elbow and knee bends, on the hips, in the groin. The provoking factor is mechanical rubbing and excess moisture.
- Seborrheic eczema . It looks like a large red spot in the lower abdomen or on the genitals. Has clear outlines. Gradually it becomes swollen and rough.
- Candidiasis . The rash appears anywhere. It is characterized by large size, redness and a whitish tint in the center.
- Impetigo . This is diaper rash in the child’s groin, as well as in the buttocks, which is complicated by infection with staphylococci. The rashes look like small pustules that tend to merge with each other. During the pathological process, they burst, leaving weeping wounds. After drying, dry crusts of a golden brown hue appear.
Diaper dermatitis
Allergy ring
Intertrigo
Seborrheic eczema
Candidiasis
Impetigo