February 26, 2019
Averyanova Sveta
The first months of a child’s life are a very important and responsible period for mom and dad. Any deviation from the norm is a cause for concern for parents. An umbilical hernia in newborns often causes distress. In such situations, a completely reasonable question arises: “What to do?” The main thing is not to panic!
According to statistics, it occurs in 20% of full-term and 30% of premature babies. Girls are 2.5 times more likely to suffer from this pathology than boys. Having a hernia can be scary for parents. However, in most cases it responds well to conservative treatment.
What it is
An umbilical hernia (hernia umbilicalis) is the protrusion of internal organs through defects in the abdominal wall in the navel area. In newborns, it occurs due to disturbances in the process of closure of the umbilical ring during the healing of the umbilical wound.
Like any hernia, it has three components:
- hernial orifice;
- hernial sac;
- hernial contents.
In this case, a wide or deformed umbilical ring serves as a way for the abdominal organs to exit. The omentum or intestines protrude through it, ending up directly under the skin, being wrapped in peritoneum and transverse fascia.
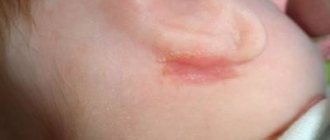
Here's what it looks like in the photo in reality:
An umbilical hernia in newborns develops more often in the first two months of a baby’s life, being a congenital pathology. However, the disease can manifest itself at a later date (up to a year).
Diagnosing the disease at any age is not difficult, although for parents a hernia looks scary. As a rule, examination is enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes ultrasound, general clinical tests and other studies may be needed to promptly identify complications of this disease.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of umbilical hernia in newborns and children of the first years of life does not cause difficulties. During palpation of the abdomen, an enlarged umbilical ring will be identified. You can notice the area of divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles and the hernial protrusion by lifting the head and torso of the newborn.
If there are indications for surgical treatment of an umbilical hernia in a newborn, a number of instrumental studies are performed:
- herniography (x-ray examination of the hernial sac with the introduction of a contrast agent into it);
- radiography of the gastrointestinal tract using barium sulfate;
- plain radiography of the abdominal cavity;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs.
Omphalocele is diagnosed at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus
In most cases, fetal umbilical hernias are diagnosed at the stage of intrauterine development of the child during a routine ultrasound examination.
Causes
An umbilical hernia in infants appears due to the anatomical features of this area. The fact is that the lower part of the umbilical ring is denser than the upper, since it is formed during the obliteration of blood vessels, being replaced by strong connecting structures.
On top, almost the entire space of the umbilical cord is occupied by adipose tissue, which during the formation of the scar becomes its weak point. Failure of connective and muscle fibers in the peri-umbilical zone leads to disruption of the formation of a normal tight closure of the umbilical ring.
For reference! Often, weakness of certain anatomical structures is inherited. Therefore, if mom or dad had an umbilical hernia in childhood, there is a very high probability of developing the same pathology in their descendants.
Embryogenesis also plays an important role. It has been proven that alcohol abuse, smoking, taking certain medications and substances, and infectious diseases during pregnancy lead to underdevelopment of connective and muscle tissue in the unborn child.
The presence of a defect in the area of the umbilical ring does not always manifest itself as a hernia. With a small size of the hernial orifice, the pathology can proceed secretly and independently for a long time, disappearing without treatment by 2–3 years. But this rarely happens.
Usually even small hernias make themselves known. Parents can see a protrusion on the anterior abdominal wall, emanating from the umbilical area. This happens when intra-abdominal pressure increases.
Factors that provoke the release of formation are the following:
- severe, prolonged, annoying crying or coughing;
- indigestion (flatulence, colic, constipation);
- throwing a small child up;
- early adoption of a vertical position (the baby began to sit and walk early).
Parents can eliminate or prevent all of the above reasons. If your child constantly cries a lot, you should take him to the pediatrician. If a persistent cough occurs, the baby should be given special drops or syrup. Digestive problems are solved by the nursing mother following a diet if the baby drinks breast milk, and by selecting formula for bottle-fed children.
Well-known doctors, in particular Dr. Komarovsky, have already said many times that there is no need to rush to put a child on his feet. The child must sit down and stand up on his own. However, even in physically underdeveloped children who lead a sedentary lifestyle, the chance of a hernia increases.
Important! Until the baby is 9 months old, you need to trust nature. Everything will happen naturally. First, the child will crawl and sit, and only then will stand on his own legs and take his first steps. During this time, the muscles of his tummy will become stronger and will be able to easily withstand the increase in internal pressure.
Infants with a lack of vitamin D (rickets) and diseases characterized by damage to the connective tissue and muscles of the whole body will have an increased risk of developing an umbilical hernia.
This also applies to babies born before 37 weeks, since all their systems and organs are not fully formed. Parents of such children need to be especially vigilant.
Until now, on the Internet you can find a version that an umbilical hernia in newborns occurs due to improper cutting of the umbilical cord in the maternity hospital. This opinion is wrong. The technique of cutting and tying the umbilical cord cannot in any way affect the anatomical features of the umbilical ring. A hernia can appear regardless of
the type of navel in children .
Causes and risk factors
Very often, among the main reasons why a child develops a hernia, parents cite incorrect cutting of the umbilical cord in the maternity hospital, due to which an overly wide umbilical ring was formed, followed by a hernia. However, this is not the case at all, because the causes of pathology are completely different.
The human abdominal wall consists of several layers:
- skin;
- muscles;
- peritoneum;
- subcutaneous fat;
- dense aponeurosis.
Since the main load-bearing layers are muscles and aponeurosis, it will depend on their strength and development whether a problem will arise or not. If there is a weak spot in these layers, then the elastic peritoneum will begin to protrude through the hernial orifice, and when the hernial sac increases in size and extends under the skin, such a protrusion can be both felt and seen.
In addition to the anatomical predisposition to the disease in the form of weakness of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, connective tissues or umbilical ring, the impact of increased intra-abdominal pressure also plays a huge role.
As already mentioned, there are several types of hernias. First, let's look at what affects the appearance of a congenital hernia.
- The most common reason in this case is simple heredity or a genetic factor, which consists in the hereditary weakness of the connective tissue of the umbilical ring, that is, if you or your husband had a hernia, then it will most likely make itself felt in the baby too.
- Premature pregnancy - a baby born prematurely will have little weight, and its connective tissue is still completely immature, so umbilical hernia very often occurs in babies born prematurely, as well as in low-weight babies with a body weight below critical (less three kilograms).
- Also, the cause may be dysplasia or other disorders that cause underdevelopment of children's organs and connective tissues during pregnancy.
- A hernia can occur if the internal organs are located in a non-standard manner, plus if the functioning of the child’s abdominal organs is severely weakened.
Risk factors that influence the subsequent appearance of pathology include an unfavorable course of pregnancy:
- if during pregnancy the mother suffered from inflammatory, somatic or severe infectious diseases;
- led an unhealthy lifestyle - ate poorly, drank alcohol, smoked;
- has been adversely affected by chemicals or toxins;
- lived in an ecologically unhealthy environment;
- took various medications or other medications that are undesirable or prohibited for use during pregnancy;
- if the pregnant woman herself suffers from any diseases, defects or pathologies.
All these factors have a strong negative impact on the child growing in the woman’s belly, provoking a delay in its development and the risk of various disorders, including anatomical muscle weakness, undeveloped connective tissue, and improper formation of the structure of the umbilical ring.
However, this is not all, because a hernia can also become acquired, that is, it can occur in a completely strong, full-term and healthy child. Why? Let's get a look. Here are the reasons that can lead to this result.
- Since the muscles of the umbilical ring in a newborn baby are still weak, even minor factors that can cause an additional decrease in their tone will contribute to the formation and development of a hernia.
These include the most common diseases - rickets and malnutrition. They create very favorable conditions for the development of pathology.
- The umbilical ring may close a little slowly, as a result of which, with accompanying provoking factors, a hernia will also begin to form.
- It is possible that the baby’s hernia did not appear immediately after birth, but if there is an anatomical predisposition, it will definitely make itself felt a little later.
- Very often, a hernia appears due to partial closure of the umbilical ring area by the abdominal fascia, and also because the abdominal fascia is not as dense as it should be.
If, in addition to all this, the muscles of the child’s abdominal wall are constantly tense, and intra-abdominal pressure increases due to intestinal colic, increased gas formation, constipation or other disorders of the digestive tract, whooping cough or dysentery, diseases of the respiratory system and nervous system with the syndrome of increased nervous excitability, frequent prolonged crying and screaming of the baby, the umbilical ring will heal even more slowly and worse, which provides favorable conditions for the development of a hernia.
In this video, a pediatrician talks about the causes of an umbilical hernia and shares tips on treatment methods.
After birth, a number of changes occur in the child’s body that adapt it to extrauterine life. In particular, after the umbilical cord remnant falls off, the walls of the umbilical ring close and its gradual obliteration (overgrowth) with scar tissue occurs. The lower part of the umbilical ring closes better, as it has a muscular membrane.
There is no muscle layer in the upper part, and therefore it closes much worse, which creates the preconditions for the formation of a hernia. Additional closure of the umbilical ring is largely facilitated by the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. However, in newborn children their tone is still weak, so any, and even more significant, increase in intra-abdominal pressure (straining, crying, coughing, sneezing) leads to the release of the peritoneum, omentum, and intestinal loops through the dilated umbilical ring into the peri-umbilical space. Over time, this mechanism leads to the formation of an umbilical hernia in newborns and children in the first years of life.
Crying and coughing in a newborn can provoke the development of an umbilical hernia due to weak tone of the abdominal wall muscles
When coughing and straining, the abdominal organs penetrate through the umbilical ring into the peri-umbilical tissue and gradually stretch it more and more.
Acquired (postnatal) umbilical hernias begin to form during the newborn period, but clinically they usually begin to appear somewhat later (from 2-3 months).
In addition to postnatal umbilical hernias, congenital (embryonic) hernias also occur in newborns. Another name for this type of hernia is omphalocele. They represent an anomaly in the development of the anterior abdominal wall, the consequence of which is the prolapse of internal organs into the umbilical cord. The disease occurs with a frequency of 1 case in 3000-4000 births.
Omphalocele or embryonic umbilical hernia is an anomaly of the anterior abdominal wall.
Negative factors affecting the body of a pregnant woman can provoke the formation of an embryonic umbilical hernia in the fetus:
- viral diseases (flu, hepatitis, measles);
- pathologies of pregnancy (disorders of placental circulation, severe gestosis, anemia, cardiovascular disorders);
- smoking, including passive smoking;
- drinking alcohol;
- ionizing radiation;
- taking medications that have a teratogenic effect;
- living in an area with poor environmental conditions.
The formation of an embryonic hernia is associated with genetic disorders, since this deviation is a component of such genetically determined diseases as Edwards and Patau syndromes, as well as the OEIS complex [O - omphalocele, E - ectopia of the bladder (i.e. its location outside, not inside the abdominal cavity), I – fusion of the anus, S – spinal defects].
Symptoms
The main symptom is the presence of a formation in the navel area. Depending on the size, it may look like a small bump or a voluminous bulge. In most cases, the diameter of such a ball will be 2–3 cm.
A pathological tubercle will appear in situations where intra-abdominal pressure increases (crying, constipation, etc.).
d.) and disappear at rest, on an empty stomach and during sleep.
The characteristics of education are as follows:
- a bulge from 5 mm to 5–6 cm or more, round or oval, less often - irregular in shape, which protrudes from the navel;
- soft to the touch;
- painless;
- the skin in the navel area is not changed;
- under the formation a wide umbilical ring can be felt, which is a hernial orifice;
- with a large lump, the skin becomes stretched and thinner, as a result of which intestinal peristalsis can be observed;
- easy to put inside with a characteristic squelching sound;
- comes back when intra-abdominal pressure increases.
Many parents are interested in questions: does an umbilical hernia hurt, is the child’s anxiety and digestive problems related to it, what are the risks of strangulation, and what will happen to it in the future.
Doctors assure that if the course is uncomplicated, this pathology does not cause inconvenience to the baby. An exception may be the situation when the hernia sticks out. Then the child will be able to touch her with his hands, showing interest in her and the associated anxiety.
You can hear the phrase from grandmothers: “ The child cried a lot and often started screaming, so he screamed for a hernia .” This statement is incorrect, as is the fact that this disease causes intestinal colic and flatulence. More often, unpleasant symptoms are associated with improper feeding of the child. As a rule, the baby's intestines adapt over time and signs of intestinal discomfort go away.
A protrusion on the anterior abdominal wall is a cosmetic defect, and many mothers and fathers try in every possible way to get rid of it. However, it should be understood that excessive efforts and the use of some traditional methods can lead to complications.
The occurrence and symptoms of umbilical hernia in newborns
There is no need to panic that your child has an umbilical hernia, as this is quite natural. Every parent should understand what a hernia is and what its etiology is. On the tummy in its central part there is an umbilical ring, which consists entirely of ligaments.
Due to this ring, the baby receives:
- Vitamins;
- Minerals;
- Oxygen.
As soon as the child is born, the umbilical cord and necessarily its vessels are ligated. Over time, part of the navel falls off, and the ring begins to tighten and scar with the help of connective tissue.
If this process does not occur, then partial removal of the omentum or intestinal loop into the cavity of the umbilical ring is possible.
The same problems can occur in a pregnant woman, as the umbilical ring gradually weakens as the belly enlarges. A hernia can occur during an improperly performed caesarean section and even during normal labor. After birth, every child has a weak umbilical ring, and therefore all infants may have primary signs of this problem, however, by the age of 1 month, the pathology disappears in some, while in others it remains and requires treatment, but only competently.
What is the danger of the disease
Like any other, an umbilical hernia can lead to emergency surgery. This situation, according to doctors, happens extremely rarely, but every parent must know what a strangulated hernia looks like and be able to recognize its signs.
How to determine infringement - the following symptoms will tell you, even at the initial stage of the process:
- the hernia looks tense, full, motionlessly fixed in the umbilical ring, the skin over it is thinned, its color is changed;
- upon palpation, the compaction is sharply painful and inactive;
- the child will scream from severe abdominal pain, he may twist during a painful attack;
- severe dyspeptic disorders appeared (vomiting, bloating due to non-excretion of gases, etc.);
- body temperature has increased, there are signs of intoxication.
Important! In the event of a strangulated hernia, it is impossible to try to force the contents of the hernial sac into the abdominal cavity, since these actions will only aggravate the situation.
Any delay with such a clinical picture can become a tragedy. Indeed, when strangulated, the intestinal loops located in the hernial sac are clamped by the umbilical ring, and the required amount of blood stops flowing to them. The processes of tissue necrosis begin. Feces contribute to the rapid development of the inflammatory process. Perforation of the hernia is possible.
Tissue necrosis occurs rapidly. The extent of the surgical intervention performed and the prognosis depend on how soon a sick child is taken to the hospital. All dead tissue (parts of organs) will have to be cut out. If the operation is not performed in time, gangrene will begin.
To prevent an emergency, parents need to closely monitor the hernia. If it gradually increases in size, periodically does not straighten well, its release is accompanied by anxiety in the child, you should not wait for the disease to develop, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Alarming symptoms are constant constipation and failure to pass gas, the appearance of mucus and blood in the stool, systematic nausea and abdominal pain.
With improper care and non-compliance with hygiene measures, a hernia can be complicated by the development of an infectious process. Large formations often lead to chronic constipation (even coprostasis) and inflammatory bowel diseases.
How to determine an umbilical hernia and its pinching in a baby?
Abdominal pain in a child with an umbilical hernia is a sign of problems! When pinched, part of the trapped organ is not supplied with blood! And if the situation is not corrected in time, this part may become dead.
We offer introductory symptoms to identify a pinched umbilical hernia:
- Sometimes the intestines become trapped in an umbilical hernia. This is called a strangulated hernia. When this happens, the baby usually experiences a lot of pain and the lump may be hard and red . Urgent medical examination is necessary to repair the hernia in time to prevent possible damage to the intestines.
- If the child does not experience a painful reaction when touching the arch, the arched bursa can be lightly pressed on the abdomen. If the newborn does not show signs of pain, does not cry or grimace, then everything is fine.
- A sign of possible problems, even in the future, will be pain in the child's abdomen, especially after active movements. For example, you did morning exercises for your child, and he starts crying a lot. This is confirmation that you need to see a specialist.
- Sometimes additional ultrasound examination may be required. It serves to monitor the progress of an umbilical hernia. Especially if the bulge is relatively large and may contain loops of intestine, ultrasound is necessary for further examination.
Pinching!
Visit your doctor in the following cases:
- The bulge becomes painful
- Vomiting and/or diarrhea occurs when the bulge is present
- The belly is getting bigger
- Body temperature rises
- The bulge becomes more swollen, discolored, or bluish-red
- The bulge no longer hides back into the abdominal cavity
An umbilical hernia is usually harmless to the baby. Basically, it disappears on its own within the first 3 years of life. And in very rare cases, there is a danger that the intestines will get into it and pinching will occur. In adults, the percentage of this danger is much higher.
If an umbilical hernia does not go away on its own by age three, it should be surgically repaired before preschool age. The operation is usually performed from the age of 5, but much depends on the situation. If surgery is not performed in time, the risk of pinching increases. In girls, an existing umbilical hernia can create problems with later pregnancy.
Treatment at home
Small umbilical hernias (up to 3 cm) go away on their own when the child reaches three years of age. Doctors say that no active action is required to cure them. However, with large formations, for the purpose of prevention and to reassure parents, pediatricians give recommendations for conservative treatment.
It must be comprehensive, systematic and long-term. The plan of therapeutic measures is selected by the doctor. If the baby’s family members agree to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, the treatment process begins.
Popular methods of dealing with umbilical hernia include:
Bandage (belt, corset)
The special bandage BG-101D and other children's models are used in combination and with the progression of pathology. You should not purchase the product yourself; it should be chosen by a doctor. The doctor explains to parents how to use the bandage correctly.
The bandage belt allows you to securely fix the hernial sac inside the abdominal cavity, equalizing internal and external pressure. It performs the following functions:
- prevents internal organs from coming out;
- has a weak compression effect in the umbilical area;
- is a kind of corset for the muscles of the abdominal wall;
- prevents hernia strangulation.
The device is used as an independent method of treatment, and in the pre- and postoperative period. Externally, the product looks like a wide belt with fastenings. It is made of hypoallergenic material.
However, if the baby experiences an allergic reaction when using it, the treatment is canceled.
You should not wear a bandage in case of complicated hernias or in the presence of skin diseases at the site of fixation.
The doctor decides how long to wear the bandage belt. The doctor must also correct the umbilical hernia before using the device for the first time. Parents can then do this. The scheme for putting on the bandage is as follows:
- put the baby on his tummy for a few minutes to let the gas go away;
- carefully examine the baby’s skin on the back and stomach, assess the condition of the hernia - the skin everywhere should be clean and dry;
- lay the belt on a hard surface;
- place the child on it with its back down;
- carefully straighten the hernial contents and fasten the belt, making sure that the belt is located exactly in the navel area (one parent can help the other by holding the baby);
- wear the device no more than 12–16 hours a day, removing it at night.
As a rule, after two months of wearing a bandage, small hernias successfully regress. This treatment method is optimal and safe in most cases.
Patch
You can buy an umbilical hernia patch at a regular pharmacy. The contraindications for it are the same as for the bandage. The doctor must direct the hernial contents into the abdominal cavity before the first gluing. He trains parents.
The patch can then be removed at home. However, if the sealing is done incorrectly, the risk of complications is very high, so it is still recommended to entrust the replacement procedure to a specialist.
In Soviet times, an ordinary adhesive plaster was used, which often caused unwanted local reactions.
Nowadays modern hypoallergenic products have appeared.
The most popular is the Porofix patch, which is made of waterproof material, which allows you to bathe your child without removing it. The navel must be sealed for 10 days, then replaced. The duration of the course is determined by the doctor. If any skin manifestations appear in the area where the product is applied, it must be immediately removed and treatment discontinued.
Taping
Kinesio taping has gained particular popularity recently. It is used to treat many diseases of the musculoskeletal system. However, pediatricians recommend refraining from gluing tapes to infants.
Scientific studies have not been conducted to confirm the safety and effectiveness of this method. Applying tapes to the umbilical area is dangerous.
Massage
Massage, like gymnastics, is, in principle, recommended for all infants. However, you need to massage a child with an umbilical hernia correctly, otherwise the effect may be negative. In order not to harm the baby, it is enough for the mother to learn how to perform simple actions by watching how a specialist does it.
First, perform circular stroking movements on the tummy (strictly clockwise, along the loops of the large intestine), then counter stroking, then pinching around the navel.
The massage is combined with placing the baby on his tummy and turning him on his side. This allows you to strengthen not only the rectus muscles, but also the oblique muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. Typically, massage procedures are done in the evening, after bathing, when the baby is as relaxed as possible.
Strengthening poses (laying on the stomach)
This is the simplest and most obvious way to strengthen your abdominal muscles. Each time before feeding the baby should be placed on the tummy. It should lie there for 10–15 minutes. Naturally, the hernial contents should be in the abdominal cavity.
Exercise therapy (gymnastics)
Young children should perform physical therapy under the supervision of professionals. An anti-hernia set of exercises is aimed at strengthening and improving blood circulation in the anterior abdominal wall. This includes:
- encouragement of turning over and twisting legs in the air;
- squatting with adult support;
- exercise on a fitball, etc.
The older the child, the more varied the activities will be. Exercise therapy is carried out only in fixing devices (bandage, regular plaster).
Copper nickel
Since ancient times, people have had a method of attaching a five-ruble coin to the navel (sometimes they use a ruble or a kopeck). Modern medicine has proven that this ancient method of treatment with copper is not only useless, but also dangerous. By resorting to such “treatment”, parents expose their baby to a huge risk of developing navel omphalitis (inflammation of the navel) and other serious consequences. Therefore, no manipulations with placing a nickel on the navel should be done.
Surgical department "SM-Clinic"
We employ some of the best surgeons and other pediatric specialists in the city. We will promptly diagnose an umbilical hernia in your baby, give the necessary recommendations or correct the defect surgically. Our clinic is equipped with advanced equipment and has a convenient hospital where children feel comfortable and pleasant.
Call us to make an appointment or ask any questions.
Sources:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29083740 Troullioud Lucas AG, Jaafar S, Mendez MD. Pediatric Umbilical Hernia // StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019-. 2019 Jul 5.
- M.A. Zvorygina, A.F. Khafizova, S.N. Styazhkina. Hernia of the anterior abdominal wall // Questions of science and education, 2021, pp. 62-66.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15329986 Fassiadis N, Theodorides A, South LM. Novel technique of small umbilical hernia repair in children // Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2004 Jul;86(4):305-6.
Grebenyuk Mikhail Viktorovich Clinic
Author of the article
Grebenyuk Mikhail Viktorovich
Specialty: surgeon
Experience: 18 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Is surgery necessary?
According to the observations of pediatric surgeons, small umbilical hernias are prone to self-healing. In three-year-old children, the tissues of the umbilical ring gradually become stronger, losing their elasticity, and the defect closes. However, if the disease does not go away by the age of 5, then there is no chance of self-healing. In this case, surgical tactics involve planned surgical treatment.
The optimal age for umbilical hernia surgery is 5–7 years. At this age, the baby's tissues are pliable and quickly recover, forming a healthy umbilical ring. Adolescents may experience certain difficulties during surgery.
Emergency operations are carried out strictly according to indications. Surgeons will agree to operate on huge hernias that are prone to complications only after the baby reaches 6 months. The decision to undergo surgery is always made based on the doctor's opinion.
How common is this disease?
Hernia occurs in 20 percent of newborns. Especially often in boys. In the case of prematurity, this phenomenon is observed even more often, in 35 percent of babies.
As a rule, a hernia is detected already in the first month of life. In most children, the umbilical hernia goes away by six months, and in the rest - by about 5 years, while the umbilical ring gradually decreases and closes.
There are cases when the hernia does not go away even by the age of five. Then the doctors, in order to avoid further complications, suggest that the parents undergo surgery for the child.
Massage and gymnastics are effective means of eliminating an umbilical hernia. Your pediatrician should familiarize you with their techniques.
How is the operation performed?
Planned hernia repair is performed in a hospital under general anesthesia. The operation lasts 20–30 minutes. The surgeon reduces the hernial contents and sutures the hernial orifice; special meshes are not used in children.
There are several types of operations, which mainly differ in access, but their essence is the same. Previously, they used the same technique as in adults, according to Dyakonov - Mayo - Sapezhko. The Lexer method or the Spitz operation are possible. In the latter case, the postoperative suture will have a semi-oval shape.
Lexer method
Mayo method
Sapezhko method
Also, laparoscopy is now increasingly being performed, lasers and new minimally invasive, highly effective techniques are being used. The scar after such interventions is almost invisible (even if the hernia was large), and the patient can be discharged from the hospital earlier. However, such operations are performed for a fee.
Surgery for weak umbilical ring
Surgery is possible and can be performed at completely different ages.
Among the indications for its implementation, one can note the presence:
- Severe enlargement of the hernia, but in children older than 1 year;
- Pinching;
- Maintaining diagnosis until age 5 years.
The main goal of surgery will be to eliminate the defect in the form of weakness of the umbilical ring. The operation is called hernioplasty. During the operation, the hernial sac is excised, the hernial orifice is sutured and strengthened, as well as the internal organs are returned to the abdominal cavity to their rightful location. The operation lasts no more than half an hour, and if there are no complications in the condition, the baby can be sent home.
Postoperative period
After the baby wakes up from anesthesia, but not earlier than 12 hours after the operation, he can be given water. The liquid should be drunk in small sips.
A day later, when intestinal motility appears, the child can be offered broth (or light soup), jelly, kefir, compote and baked apple. On days 2–3, the menu is expanded by adding porridge, fruit puree and yogurt. Over the next 24 hours, the baby is gradually fed his usual foods.
From the first day, if the child actively moves and sits up, a postoperative bandage should be worn on the stomach. The baby should not leave the bed for the first 24 hours.
In the next two days, a gentle hospital regime is observed, that is, jumping, sudden movements, etc. are excluded. The bandage is used for at least 2-3 weeks. You can walk and move freely at home in it.
After 3-4 weeks, the recovery will be over, and the child will be able to begin living as usual. However, in the future it is better to refrain from excessive physical activity, in particular from physical education. No special rehabilitation is required after standard hernia repair in children.
Can the situation return to normal without treatment?
In some children, the deviation in the development of the umbilical ring from the norm is less than seven millimeters, while the protrusion is very small or completely invisible. In this case, the doctor diagnoses “enlarged umbilical ring.” Sometimes it goes away on its own - this is what the children's parents hoped for when medicine was not yet developed.
But today there are ways to solve the problem with guarantee, and you should not neglect them:
- The child should be seen regularly by a doctor.
- Rupfix umbilical plates will allow you to fix problem muscles and painlessly, gradually return them to their normal position. Due to the lack of allergenic properties, the plates can be worn for a very long time.
- Therapeutic massage is prescribed, which can be performed both in clinical and at home conditions.
- Special gymnastic exercises for newborns, regularly placing the baby on his stomach on a hard surface are additional measures to get rid of hypotonicity of the umbilical ring.
- With an integrated approach, you can count on quickly getting rid of the problem. Wearing Arilis umbilical plates will play a key role as they will provide positive effects continuously.
The Arilis company has proven itself well among parents. According to many reviews, you can see significant improvements in just ten to twenty days. Rupfix plates do not cause discomfort, do not cause allergies, yet they adhere very well and significantly surpass any medical bandages in their characteristics. Thanks to the use of such plates, it is possible to significantly speed up the process of getting rid of the so-called umbilical hernia in a newborn.
Traditional methods of treatment
In addition to the above-mentioned copper nickel, young parents can hear the following advice from the older generation:
- to gnaw with teeth;
- give the child a rhubarb decoction;
- smear the umbilical area with butter and propolis at night;
- tie fern leaves;
- apply compresses with whey;
- wipe with cotton wool soaked in diluted vinegar;
- other methods (spells, homeopathy, etc.).
There are websites of so-called healers on the Internet, where they describe in detail how, in their opinion, an umbilical hernia in newborns should be treated. They provide photos of cured patients. Sometimes parents, not trusting doctors who say that the hernia will go away on its own, turn to charlatans. The cost of their services is high, but the effect is zero.
It should be understood that folk imagination is limitless, and these methods have no scientific basis, so they should be avoided. Often, due to such dubious procedures, when they talk, put a nickel and use other dubious methods, the newborn ends up in the hospital.
Important! Trust your child's health only to professionals. Any treatment method must be approved by a doctor.
Exercises for an umbilical hernia in a child and symptoms
There is a special set of exercises against umbilical hernia. But only a doctor can prescribe it, after examining the child. Symptoms of a problem such as an umbilical hernia can occur in the first month of life. If the navel sticks out forward and this can be seen with the naked eye. There are those babies who have such a navel due to anatomical features and the name of this pathology is the cutaneous navel. In order not to confuse this physiology with the true problem, you need to familiarize yourself with the symptoms of the disease.
A hernia in a newborn requires treatment when it manifests itself:
- A protrusion that has a round shape and is located in the area of the umbilical ring, which can be easily pushed inward, and the diameter of such a protrusion is about 1-10 cm;
- Pathologies that can be noticeable as soon as the baby tenses his abdominal muscles, for example, when crying or coughing;
- Severe anxiety and weather sensitivity;
- Severe flatulence for no reason, which can actually cause severe irritability.
If, against the background of a protruding navel, bloating, pain, as well as general weakness, lethargy and drowsiness often occur. In special cases, the child may suffer from nausea, vomiting, and nervous tension.
It is important to remember that there is such a diagnosis as coprostasis, which is a complication of an umbilical hernia.
In general, if the problem is treated correctly and in a timely manner, the problem can be eliminated without consequences. Treatment should only be carried out by a doctor.
Weakness of the umbilical ring can be eliminated by placing it on the tummy. The method is not complicated and does not require much effort. According to the recommendation of pediatricians, laying out should be done half an hour before meals on a hard surface. In this position, the child begins to move all parts of his body, which significantly increases the pressure inside the abdomen and also allows gases to be eliminated from the intestines. Systematic implementation of this exercise helps strengthen the muscles in the abdominal wall.
Prevention
Parents often ask doctors why this pathology occurs and how to prevent it. Prevention should begin with pregnancy planning. The expectant mother is obliged to prevent any negative impact on the fetus during pregnancy.
If a child has already been born with an umbilical hernia, the main task of the parents is to prevent the progression of the disease. To do this you should:
- exclude situations where the baby is forced to cry for a long time and hysterically;
- get rid of digestive problems (eliminate constipation, remove gases, follow a diet for a nursing mother, etc.);
- do not throw the baby up, do not sit him down, do not put him on his feet prematurely;
- prevent and promptly treat diseases the main symptom of which is cough;
- do not overuse swaddling that is too tight;
- prevent rickets (take vitamin D;
- from 2 weeks of age, gradually begin to strengthen the abdominal muscles (massage, swimming, special poses and exercises).
Here's what Dr. Komarovsky recommends regarding umbilical hernia:
To avoid complications, you should carry out hygiene procedures daily and promptly detect the slightest changes in the navel area. Any information should be obtained from your doctor.
What causes umbilical hernia in newborns (video)
With the right approach, it is much easier to eliminate the disease, but it is better to prevent it by simply taking preventive measures. Every pediatrician can talk about them, but they are not difficult to perform and do not require professional training. It is worth noting that if a hernia is left untreated, the consequences can be serious and quite dire. In particular, the baby’s life is at risk, and it is not uncommon that, due to pinching, the child does not have time to be taken to the intensive care unit for medical intervention. Monitor your child's condition more carefully and he will remain healthy for a long time.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Can a hernia go away without surgery?
Yes, as a rule, an umbilical hernia in newborns heals on its own by the age of 3 years.
Can a hernia appear a year after birth?
An umbilical hernia in newborns usually manifests itself in the first two months of life, but in isolated cases it can also appear in a one-year-old child.
Can a hernia burst?
An umbilical hernia in a newborn cannot burst on its own. Its perforation is possible due to tissue necrosis or trauma.
Causes of umbilical hernia in newborns
The reasons for a small umbilical hernia in children can be very different. But this is mainly due to the fact that the navel has weak tissue. Especially often, a hernia can be a consequence of the presence of factors that provoke the formation of such a pathology.
These include:
- Prematurity;
- Lightweight;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Frequent coughing, constipation, or crying;
- Weakness of muscle tone, which is characteristic of rickets;
- Gender, since in girls umbilical hernia occurs much more often.
A big misconception is that parents believe that the cause of an umbilical hernia is an improperly tied navel during childbirth. In fact, this is a myth and nothing more, since this action cannot in any way affect the moment.