Unstable functioning of the lymphatic system in childhood is caused by a still fragile, unformed immune system. When the lymph nodes in children become enlarged (more often this manifestation is noticed behind the ears or on the neck, under the jaw), this may indicate the development of serious diseases in the body. But most parents prefer to warm up the lymph node behind the child’s ear rather than seek qualified help. Such behavior towards your child is irresponsible! At the first symptoms of enlarged lymph nodes, you should consult a doctor, and below we will look at why.
Why does the child's lymph node behind the ear become inflamed?
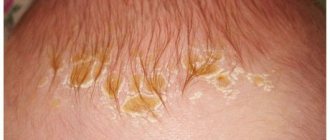
If the lymph nodes behind the child’s ears become hard and convex, resembling a lump in appearance and to the touch, it means that the inflammatory process has been going on for a long time
Lymph nodes perform several functions in our body. The most important of them is filtering. In this way, the body is protected from the invasion of various pathogenic agents. Accordingly, any changes in the lymph nodes (their enlargement, thickening, redness) indicate the onset of pathological processes in the body. Let's consider what to do if a child has an inflamed lymph node behind the ear, how it manifests itself and why.
Symptoms of inflammation
An inflammatory process in the lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) or enlargement of the lymph nodes without inflammation (lymphadenopathy), which occurs against the background of a disease, is accompanied, first of all, by the symptoms of this disease. That is why the appearance of an enlarged node behind the ear in children can be difficult to notice immediately. But there are special signs of the inflammatory process, and they are represented by the following deviations from the norm:
- the lymph node is enlarged so much that it is visually noticeable;
- palpation can either cause pain or not be felt at all;
- the child complains of headache, chills or fever, the temperature rises;
- Children’s mood may deteriorate, they become capricious, sleep poorly, lethargic and refuse to eat;
- in some cases, the skin over the tubercle turns red;
- the condition of the hair deteriorates (it becomes brittle, dandruff appears).
In rare cases, lymphadenitis and lymphadenopathy may be asymptomatic. This is a very bad sign! A complete examination of the child’s body is required immediately.
If the lump behind the ear is hard to the touch and hurts even without palpation, this is a symptom that the infection has been developing for a long time, and the inflammatory process is at an advanced stage. If your child complains of pain in the ear or under the jaw, he should be examined independently: in some cases, this may be a manifestation of pathology in the lymph node.
Possible reasons
Any type of sore throat and acute respiratory viral infection can cause inflammation of the lymph nodes behind the ear in a child
Lymph nodes are distributed throughout the body and appear depending on the organs or structures in which pathological processes occur. Behind the ears are the cervical and postauricular lymph nodes. They can respond to changes in the nasopharynx, ears and mouth, brain, skin, soft and hard tissues.
In a healthy state, the lymph node cannot be palpated, is invisible visually, is not fused to the skin and does not cause any discomfort.
If we talk about lymphadenitis (inflammation) and lymphadenopathy (increase in size), then these conditions can occur as a result of various factors. There are the following possible causes of enlarged lymph nodes behind the ear in a child:
- acute or chronic form of pharyngitis, tonsillitis or laryngitis;
- sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis;
- caries, stomatitis or periodontal disease at an advanced stage;
- inflammatory processes in the ears (otitis media, etc.);
- furunculosis;
- wounds or ulcers in the mouth that do not heal well and are a source of infection;
- damage to the oral mucosa by a fungal infection;
- any type of sore throat;
- meningitis;
- infectious viral diseases, for example, rubella, measles, chickenpox, influenza, etc.;
- some allergic reactions;
- cold;
- benign or malignant neoplasms.
Most often, the cause of an enlarged lymph node behind the ear in a child is a cold, flu, or one of the diseases of the ENT organs. If the lump becomes inflamed on only one side, this indicates the localization of the pathological process.
Inflamed lymph nodes behind the ear of a child: clinical picture
The clinical picture of inflammation of the lymph nodes is quite pronounced and parents, as a rule, quickly notice the problem. It should be noted that the pathology appears suddenly and with proper treatment goes away without a trace within 14 days. If lymphadenitis becomes chronic, treatment may take 1 month. Obvious symptoms of the disease include:
Doctors call enlarged lymph nodes in a child lymphadenitis (we recommend reading:). Among the common symptoms of lymphadenitis, experts include fever and changes in the behavior of young patients. Kids become lethargic, they eat poorly, get tired quickly, and get irritated. When pus forms in the place where the lymph node is inflamed, the clinical picture of the disease worsens. If the lymph node feels hard to the touch, like a lump, then the problem arose a long time ago. Hair loss and large amounts of dandruff indicate a fungal infection that needs to be treated immediately.
Diagnostics
First of all, the child will need to be examined by an otolaryngologist, then undergo a series of examinations and undergo some tests
If your child has swelling under the ear, you should contact your pediatrician for an initial examination. The doctor collects anamnesis, examines the child, feels the inflamed lymph nodes and those adjacent to them. If only one “bump” has increased, and its diameter has changed slightly, there is no redness or pain, and the child’s general condition is satisfactory, then the doctor may not prescribe medication or physiotherapeutic treatment. But this is only possible if it is known that the baby has only had a cold or flu. Then further diagnosis is pointless - lymphadenopathy is a residual manifestation of the disease.
If other of the symptoms listed above are present, the pediatrician will refer the child for examination to a specialist: an ENT doctor, an allergist, a dentist, an immunologist or an oncologist.
A number of laboratory tests will also be prescribed:
- general blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine.
If the lymph node is particularly painful, and the swelling and redness are severe, then additional clinical tests will be required to establish the root cause and make a diagnosis:
- biopsy (for purulent lymphadenitis);
- MRI or CT;
- Ultrasound;
- radiography.
Timely and complete diagnosis is very important when a child has inflammation of the lymph node. It should be understood that not only the future health, but also the life of the baby depends on this.
In paid clinics, an appointment with a pediatrician costs an average of 1,000 rubles, and a general blood test costs about 500 rubles. Admission and diagnostics in public hospitals are free of charge.
Causes of the inflammatory process in the parotid lymph node
There are about six hundred lymph nodes in the human body. Each of them is a rounded formation 0.5-50 mm. In most cases they form groups. Lymph from there is sent to regional nodes.
The parotid lymph nodes are located along the posterior auricular vein. When a person is healthy, they are soft and cannot be felt. But when a focus of inflammation appears, they become larger, denser, and are easy to palpate. Most often, this is how lymph nodes react to a disease of a nearby organ. First of all, it is provoked by inflammation of the ear, a boil in the external auditory canal, congestion in the ear, and neuritis of the auditory nerve. Secondly, the area of inflammation is the mouth and throat: caries, periostitis, sore throat, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat, salivary glands and tonsils. In some cases, the cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes behind the ear is ARVI with rhinitis, mumps and rubella. In the case when the lymph node has enlarged due to the action of one of the listed factors, but does not hurt or fester, doctors diagnose “local lymphadenopathy” - this is the reaction of the lymph system to an infection in a certain disease.
When there is excessive inflammation of the lymph node, swelling and pain, the diagnosis is “lymphadenitis”. And this is inflammation of the lymph node itself, the cause of which is its damage by infected cells from other foci. In this case, there may be a significant increase in body temperature and suppuration in the lymph node area.
The system of human lymph nodes in the neck and head (including behind the ear)
Treatment Options
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate the root cause that led to the enlargement of the lymph node behind the ear. Since such manifestations are secondary, they disappear immediately after proper treatment. Depending on the form of lymphadenitis, different treatments may be required. The atmosphere in the home, the baby’s activity, sleep patterns and diet also play an important role in the child’s recovery. Therefore, it is necessary to take into account many factors.
Restoring the normal shape and condition of the lymph node may take several weeks. Parents should be patient and not palpate the “bump” three times a day.
Medications
For ear infections, topical treatment in the form of drops is used
Drug treatment of inflammation of the lymph nodes under the ear in a child is the basis of general therapy. The course and intensity of therapy depend on the type of infectious pathogen, diagnosis and individual characteristics of the patient.
So, to eliminate lymphadenitis, drugs from the following groups can be used:
- antibiotics;
- antiviral;
- antifungal.
For ear infections, topical treatment in the form of drops is used. Allergic reactions are eliminated with age-appropriate antihistamines. For frequent and prolonged colds and acute respiratory viral infections, immunomodulatory and vitamin preparations are used: they stimulate a speedy recovery and strengthen the immune system.
Other treatments
A course of physiotherapeutic procedures can be prescribed by a doctor only if he is sure that there is no suppuration in the lump. As a rule, such procedures are represented by UHF and compresses based on dry heat.
Under no circumstances should you engage in self-treatment and warm up the node! Only a doctor can determine the presence of pus in a node. If you apply warm compresses to a purulent lymph node, this will only worsen the situation - the infection will develop faster.
The presence of an abscess requires minor surgical intervention. The pus must be removed and the tissue cleaned. If the exudate does not find an outflow path, the capsule will constantly increase and then simply burst. As a result, infected pus will affect healthy organs and enter the bloodstream.
The operation is simple, the child’s body quickly recovers after such interventions. To consolidate the result after surgery, drug therapy (antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs) is prescribed.
ethnoscience
Various herbal preparations in the form of decoctions or infusions can be used as traditional medicine. Both externally and internally, any prescriptions should be used only after consultation with a pediatrician! Remember that the child’s health is the responsibility of his parents. The lymphatic system is a very important and sensitive structure, and therefore you should trust only the recommendations of a specialist.
- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
Lymphadenopathy is an increase in size, as well as a change in the shape of one or an entire group of lymph nodes of various origins, without signs of inflammation.
A person has about 600 lymph nodes. Normal sizes are up to 1 cm. The cervical, axillary, inguinal, and intra-abdominal lymph nodes are more often enlarged. Playing a protective role, lymph nodes are among the first to stand in the way of the spread of infections and other foreign antigens (allergens, tumor cells, etc.).
Until a child reaches 12 years of age, the lymphatic system is considered immature, although its formation begins in the early prenatal period. This explains the high incidence of lymphadenopathy among pediatric patients.
Among the causes of enlarged lymph nodes, infectious diseases occupy first place, then systemic diseases of connective tissue, and blood diseases.
Fortunately, lymphadenopathy of a specific tumor nature in children makes up no more than 10% of the total morbidity. A malignant form of the tumor process, which predominates in childhood, is lymphosarcoma. Rarely, enlarged lymph nodes in children occur with severe allergic reactions and helminthic infestations. You need to know that the use of a long course of certain antibiotics and antifungal drugs can provoke the development of a generalized form of lymphadenopathy, the signs of which gradually disappear after discontinuation of the drugs.
Infectious causes of enlarged lymph nodes are varied - these are:
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- fungi;
- parasites.
Infectious diseases that most often occur with enlarged lymph nodes:
- viral (Epstein Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, other herpetic viruses, measles, rubella, viral hepatitis, HIV);
- parasitic (toxoplasmosis, etc.);
- chlamydial infection;
- mycoplasma infection;
- fungal diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria, tick-borne borreliosis, listeriosis, yersiniosis, etc.);
- mycobacterial (tuberculosis).
If an infectious cause of enlarged lymph nodes is suspected, an epidemiological history is important:
- contact with domestic animals (for example, cats);
- eating undercooked meat, raw water;
- going out into nature;
- swimming in ponds;
- visiting exotic countries.
If lymph nodes are enlarged, you should contact the following specialists:
- infectious disease specialist;
- hematologist;
- surgeon;
- oncologist (if necessary).
Services and prices
Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with an infectious disease specialist
1,800 rub.
Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with an infectious disease specialist
1,700 rub.
Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatric surgeon
1,800 rub.
Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatric surgeon
1,700 rub.
Ultrasound examination of lymph nodes
1,300 rub.
Isaev Andrey Aleksandrovich Head of Department, pediatric surgeon Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 43 years
Make an appointment
A child has an inflamed lymph node behind the ear: what to do?
Lymph nodes are peripheral parts of the branched human lymphatic system.
They are arranged in groups, connected by vessels. There are especially many of them around vital organs. If a child has an inflamed lymph node behind the ear, it should be shown to a doctor immediately
The main function of the lymphatic system is to maintain homeostasis in the body. It is a barrier that prevents any foreign agents from entering the body - bacteria, viruses, foreign proteins, toxins.
Why does the lymph node behind the ear become inflamed?
Normally, lymph nodes are not visible and cannot be detected by touch. If a local or widespread inflammatory process begins in the body, the lymph nodes may enlarge and lymphadenitis develops.
With lymphadenitis, not only an enlargement of the lymph node is observed, but also redness, swelling and an increase in the temperature of the skin above it. Often not only the lymph node itself hurts, but also the skin around it.
Lymphadenitis is:
- local or regional;
- one-sided or two-sided;
- generalized.
The most common causes of lymphadenitis:
- infection of the body - bacterial, viral, fungal diseases;
- immune and autoimmune diseases;
- oncological processes.
What to do if a child has postauricular lymphadenitis
Behind-the-ear and parotid lymphadenitis are a common pathology in childhood. They occur when:
- airborne infections - ARVI, influenza;
- inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs - tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis;
- inflammation of the oral cavity - stomatitis, caries, pulpitis;
- infectious lesions of the upper respiratory tract - tracheitis, bronchitis.
Depending on the infection that caused lymphadenitis, the processes may be:
- nonspecific, caused by streptococcus, staphylococcus, E. coli;
- specific, provoked by tuberculosis, tularemia, syphilis.
In addition, lymphadenitis can be acute or chronic. In acute processes, soft and mobile lymph nodes are usually palpated. If the process is chronic, the lymph nodes are denser as a result of the proliferation of connective tissue.
If a child has an inflamed lymph node behind the ear, it must be urgently shown to a pediatrician. After examination and routine clinical examination, the doctor will give the necessary advice and prescribe treatment.
.
Treatment of inflammation behind the ear in a child is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor.
In complex cases, when the cause of lymphadenitis remains unclear or the process occurs with complications, the pediatrician will prescribe additional examinations, advise which doctor to contact and give a referral for consultation. This could be a surgeon, ENT doctor, phthisiatrician, dentist, infectious disease specialist. If, after a collegial examination and examination, it remains unclear why the lymph node is inflamed, the patient is referred for hospitalization.
Diagnosis
As was said, the lymph nodes behind the ear and in the neck tend to enlarge in the case of any acute respiratory viral infection of the upper respiratory tract, as well as inflammation of the organs of the ear, nose and throat. This explains the importance of medical history data (details of the disease, previous diagnoses, etc.).
Lymph nodes may not enlarge very much - reaching the size of a pea. And there are also such as walnuts. But in all cases, when making a diagnosis, it is necessary to carefully examine the lymph node and palpate it to determine not only the size, but also the degree of pain. It is also necessary to examine the lymph nodes in the back of the head and neck. In addition, the glands located nearby are subject to examination: salivary, tonsils, lacrimal, thyroid. In some cases of inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes, data from a patient interview and examination by a doctor are sufficient to make a diagnosis and determine treatment methods.
In such cases, therapy for the underlying disease that caused the lymphadenopathy ensures normalization of the size of the lymph node. But if the antibacterial agents prescribed by the doctor did not give the desired effect, and the inflammatory process behind the ear did not stop, the node increased to 3-4 centimeters, hardened, the inflammation spread to the tissues in the immediate vicinity of it, a general blood test is necessary. The degree of damage is determined by the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the level of leukocytes.
When the results of a blood test are unsatisfactory, the treating physician will order an x-ray, ultrasound, or computed tomography. This is important because inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes can be a manifestation of lymphoma (primary malignant tumor) or metastases to the nodes. Therefore, the doctor may refer you for additional consultation to oncologists and prescribe a biopsy.
Medical tactics for lymphadenitis
The question of what and how to treat lymphadenitis depends on the form of the disease and the presence of complications, the causes of the pathology.
After the viral infection is cured, it is possible that the painless lymph node will remain enlarged for some time. But this condition does not require special treatment; after some time, the signs of lymphadenitis will go away on their own.
For serous nonspecific lymphadenitis, the following is often used:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- antihistamines;
- vitamin therapy.
After the inflammation disappears, physiotherapeutic treatment is prescribed.
If the lymph node is enlarged as a result of the tuberculosis process or tularemia, the underlying disease is treated. Surgical treatment is indicated only if inflammation transforms into a purulent process or becomes necrotic in nature.
Health care
The choice of treatment method is made by the doctor in accordance with the established diagnosis.
Prescription of medications
The standard course of anti-inflammatory therapy includes taking the following drugs:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics (Azithromycin, Vancomycin, Amoxicillin).
- Antipyretics (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Paracetamol) in tablets, as well as in the form of injections, powders and suppositories for emergency reduction of high fever.
- Painkillers (analgesics):
- ointments (Nurofen, Dolobene, Indovazin);
- injections (“Promedol”, “Dexalgin”, “Butorphanol”);
- tablets (“Tramadol”, “Diclofenac”, “Bral”).
Surgical intervention
Severe furunculosis and sialadenitis, pathologies caused by neoplasms, require radical treatment methods. The opening of the boil or salivary gland is performed under local anesthesia, followed by the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Cancer patients are observed and, if necessary, operated on in specialized medical institutions (oncological dispensaries), where they periodically undergo courses of radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Causes of the disease in children
Lymph nodes are part of the immune system of the human body. Therefore, their inflammation indicates the presence of health problems. Most often, in response to the activity of a bacterial or viral infection, a disease called lymphadenitis develops - an inflammatory lesion of the lymph nodes. It is provoked by infectious diseases; in rare cases, malignant neoplasms become the cause.
Enlarged lymph nodes behind the ear in children indicate the occurrence of diseases of the organs located in the immediate vicinity of the node. These include hearing pathologies:
- eustacheitis;
- otitis;
- furunculosis of the external auditory canal;
- sinusitis;
- inflammation of the auditory nerve.
Causes
The appearance of a “bump” behind the ear indicates that the child has enlarged one or more lymph nodes. The sizes of such formations can be very different.
In a newborn baby, the “bump” can be quite large
It is important to note that pathologies of the lymph nodes can appear at very different ages. In normal condition, the lymph nodes are of normal size and are tightly connected to the surrounding skin.
They do not hurt and do not bring any discomfort to the baby.
The color of the behind-the-ear lymph nodes usually does not differ from healthy skin. They have a pale pink color.
Various causative factors can lead to the development of this pathological condition:
- Chronic otitis media or sinusitis can lead to the spread of the inflammatory process to nearby postauricular lymph nodes. This situation develops especially often when the baby has just had some kind of cold or ARVI.
- Inflammation of the behind-the-ear lymph nodes also occurs in children with sore teeth. Periostitis or caries contributes to the spread of inflammation to the area of the lymph nodes, which are located in close proximity. Quite often, this process occurs only on one side, where the diseased teeth are located.
- Even an ordinary runny nose, which occurs in a prolonged form, can lead to inflammation of the lymph nodes. Particularly dangerous in this case is the appearance of nasal discharge due to various bacterial infections.
- The most dangerous microbes are staphylococci and streptococci. In this situation, inflamed lymph nodes will persist in the sick baby as long as there is a high concentration of pathogenic microbes in the body.
- A “bump behind the ear” can form on a child’s head due to a bruise. Such formations appear most often in young children. At this age, children begin to actively explore the world around them. This symptom manifests itself especially often in infants. This pathological condition can develop as a result of the child frequently falling when trying to walk, as well as when the baby begins to try to stand on his feet.
- If a child hits his head on an object, various injuries may appear on his frontal bone. This situation can also manifest itself in a child with the appearance of a “bump” both on the face and behind the ear. The size of the formation in some cases can even reach 4-5 cm.
- Immunodeficiency conditions, congenital or acquired, are also manifested by various pathologies of the lymph nodes. Thus, intrauterine HIV infection can lead to the appearance of bilateral inflammation. In this case, the lymph nodes reach the size of a walnut. They are usually very firm in density and painless.
- Tuberculosis infection, which occurs with a decrease in immunity, is also manifested by an increase in various groups of lymph nodes. The appearance of a small “bump” at the back on both sides is one of the characteristic symptoms of tuberculosis in children. The course of this disease is also quite severe. A sick child looks very exhausted and lethargic.
- The use of certain medications can also contribute to the development of enlarged lymph nodes in a child. Thus, taking allopurinol, some types of beta blockers, captopril, cephalosporins and other types of antibiotics, gold preparations, antimalarials and sulfonamides leads to the appearance of a “bump” behind the ear in a sick baby. In this case, the process is most often two-way.
- The appearance of a “bump” behind the ear in a child can be a manifestation of very dangerous pathologies. This is how various neoplasms of the hematopoietic organs and even some malignant pathologies can manifest themselves. Lymphosarcoma or lymphogranulomatosis are common diseases that lead to the fact that the cervical lymph nodes of a sick child increase significantly in size.
Signs of inflammation of the lymph nodes
Inflammation of the lymph node behind the ear is a sign of the disease, so the symptoms accompanying its enlargement depend on the primary source.
The development of pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature reaching 38 °C;
- the occurrence of painful sensations when palpating the nodes, pain can radiate to the jaw and ears;
- there is redness in the area of skin near the ear;
- the occurrence of edema in the area of the inflammatory focus;
- loss of appetite, drowsiness, lethargy, increased irritability and moodiness;
- skin rashes, including purulent ones;
- fungal infections are accompanied by peeling of the epidermis, itching, hair loss;
- intense headaches.
Lymphadenitis has a sudden onset; timely and competent treatment contributes to the patient’s recovery after 14 days. The condition of the lymph nodes is normalizing. For chronic pathology, therapy can last about 30 days.
If the parotid lymph node is affected by a purulent process, intense, shooting, pulsating and almost incessant pain is noted. Such symptoms are a reason to provide medical assistance. Any inflammatory process that occurs in the head area poses a threat to the child’s life and therefore must be treated immediately. Delay in treatment of a purulent disease threatens sepsis.
Tactics for treating lymph nodes behind the ear
If the lymph node near the hearing organ is enlarged due to colds, otitis, flu, it is necessary to treat the primary infectious focus directly. As a result, the nodular formation returns to its normal state.
In the event of an inflammatory process due to infectious diseases, the doctor prescribes the use of antiviral, restorative, and, if necessary, antipyretic drugs. Quite often the inflammation goes away on its own.
For the treatment of acute pathologies and bacterial infections, broad-spectrum antibiotics are indicated. If the cause of the pathology is a disease of allergic origin, antihistamines are used. Analgesics and anesthetics can reduce the severity of pain. Additionally, a course of vitamins is prescribed to boost immunity.
If the lymph node is inflamed due to otitis, the attending physician prescribes special drops and antibacterial agents for the child. For a milder stage of the disease (otitis externa), the use of these medications and physical therapy is sufficient.
The formation of purulent lymphadenitis, complicated by a necrotic process, requires immediate surgical intervention, in particular opening of purulent formations. In the postoperative period, anti-inflammatory and detoxification therapy is carried out. But in such a situation, drug treatment is not enough. A child needs quality home care. The treating specialist will explain the rules for treating a sick child in order to avoid worsening his condition.
Antibiotics for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the armpits
But the list of medicinal substances of natural or semi-synthetic origin that suppress the growth of living cells (most often prokaryotic or protozoan) is quite extensive.
So what antibiotics should you take for swollen lymph nodes? Only a specialist can answer this question, and only after a systematic examination of the patient’s body. In the case of diagnosing a pathology of a specific nature, the source of the disease is usually microorganisms such as tuberculosis, syphilis, actinomycosis, gonorrhea, anthrax, plague, tularemia. Inflammation of the lymph nodes of a nonspecific nature includes sources such as staphylococci, pyogenic gram-negative bacteria, and streptococci.
Based on the above, it is not worth making an independent diagnosis and prescribing a drug. This should be done by a qualified specialist, only then can we talk about truly effective treatment and a favorable prognosis for the future.
Therapy for lymphadenitis is carried out mainly in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of a doctor, who, in the case of the formation of phlegmon - purulent inflammation of fatty tissue - may prescribe surgical intervention to open the abscess and establish drainage.
But in order to determine the causative agent of the disease, the necessary research should be carried out, which takes quite a lot of time (bacteriological culture is carried out for at least a week). You can’t wait that long for results; the inflammatory process continues to progress. Therefore, the attending physician prescribes powerful antibiotics for inflammation of the lymph nodes with a wide spectrum of action.
Mostly, the doctor prescribes already proven drugs, for example, opicilin, ceftriaxone, lificillin, flemoxin, eurocillin, bactipene, ceftazidime, amoxicillin, oracillin, ampicillin, isticillin, amoxiclav, campicillin and many others.
But you shouldn’t hope that after taking a couple of tablets the inflammatory process will stop and the problem will be solved. With the right approach to therapy, the duration of the treatment course is usually about two weeks. After this period, the patient’s condition usually stabilizes sharply, the lymph node returns to normal, and the person returns to normal.
The entire human body is penetrated by the lymphatic system, which is a barrier and filter that allows you to cleanse the body of pathogenic flora that penetrates it. If an invasion occurs and a bacterium or virus enters the body, it is initially inhibited and accumulates in the lymph nodes, where it is eliminated by white blood cells.
But if the infection turns out to be more persistent, then the white cells have to become more active. This process leads to the development of inflammation affecting the lymphatic system. Well, since the lymph node has a blocking function, it is it that takes on the main load. It is this clinical picture that leads to inflammation of the lymph node. Sometimes this may affect the neck or groin area more, but often the inflammatory process affects the lymph node in the armpit.
If the lymph node is inflamed in the armpit, this indicates that nearby organs need to be examined for infection. It is necessary to take the body’s “signal” quite seriously - it may indicate a fairly deep damage to the body. After making a diagnosis, the doctor describes a comprehensive treatment for the established pathology.
But you won’t be able to bypass antibiotics for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the armpits. They are included in almost any treatment protocol. The list of drugs in this pharmacological group is quite extensive, but the antibiotics prescribed are not targeted, but strong, with a wide spectrum of damage. Since the inflammatory process must be stopped, and there is not always time to wait for the pathogen to be identified.
If during therapy a pathogenic flora has been identified, then the attending physician can adjust the treatment by replacing the previous antibiotic with a more effective, targeted one. This drug will work aimed at the identified pathogen that has the greatest sensitivity to it.
Patient care
If a child has a lymph node pain behind the ear, the pediatrician will advise parents to carefully care for the sick baby. Following some rules will speed up the patient’s recovery process and significantly improve his well-being:
- heating of the nodular formation is prohibited, the procedure provokes the spread of infection, which contributes to the deterioration of the condition;
- for this purpose, massaging the affected area and applying compresses are also canceled;
- to strengthen the body’s defenses, it is recommended to take a course of multivitamins;
- it is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of the ears and oral cavity - the main centers of infection;
- you need to dress the child depending on the weather conditions, so as not to cause severe sweating or hypothermia;
- To form the protective properties of the body, a child needs a balanced diet rich in beneficial microelements.
To monitor the condition of the lymphatic system, children are recommended to have their blood tested twice a year. If inflammation of the node is detected, the specialist will develop an individual treatment regimen.
When lymphatic formation increases, the use of traditional medicine is contraindicated, since the cause of this anomaly can be quite serious. The best solution in such a situation would be to consult a pediatrician in order to avoid serious complications and speed up the recovery process.